Terracing in Watershed [อัฟกานิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Aqila Haidery
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kordak dar Abriza
technologies_1732 - อัฟกานิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Fuleki Blanka
Helvetas
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Resilient Watershed Management Plan [ทาจิกิสถาน]
The participatory watershed management plan (WMP) is an interdisciplinary approach at community level to raise awareness on the watershed management concept and improve understanding of the watershed approach in planning and management of natural resource.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Askarsho Zevarshoev
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
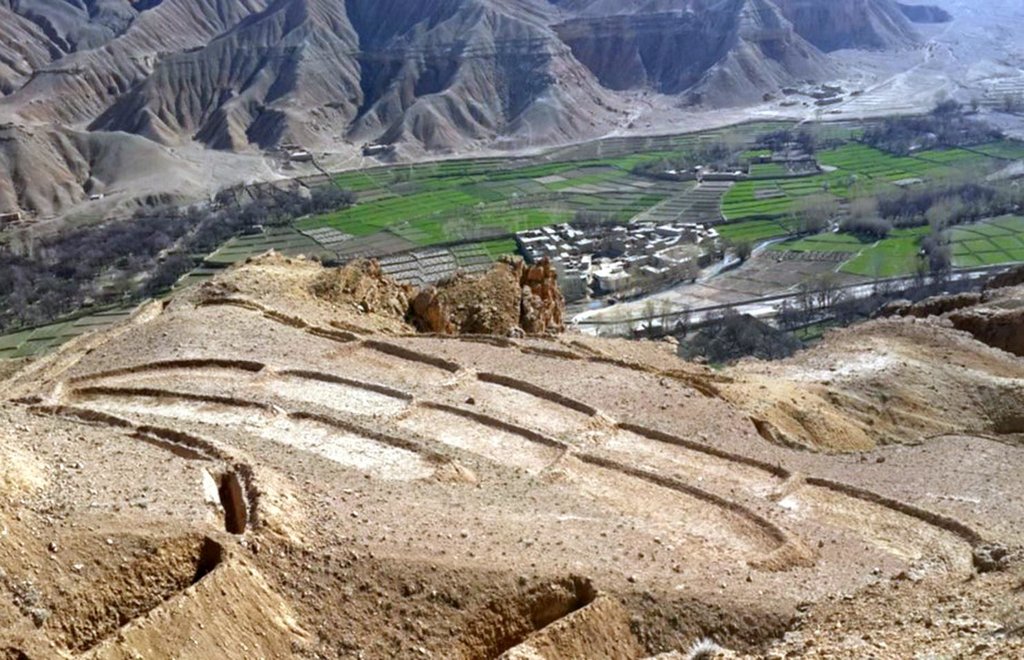
Reshaping unproductive land into a series of levelled, gently-sloping platforms creates conditions suitable for cultivation and prevents accelerated erosion.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The terracing in watershed fact-sheet is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation which is funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
Due to the enduring conflict and to the breakdown of common-pool resources management in upper catchments areas over the past decades, most pastures in Afghanistan are degraded.
Uncontrolled grazing of animals tilling grazing land to grow cereal crops are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in the upper catchments. One of the negative consequences is repeated flash floods each year causing loss and damage of agriculture lands, gardens, road, canal, infrastructure, houses and even lives. To decrease the severity of flash floods and extend vegetation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation in Saighan district has established watershed activities.
Purpose of the Technology: Terrace construction was identified as an effective measure in degraded watershed areas to:
•control runoff and decrease flash flood;
•increase water infiltration;
•create the opportunity for income from cultivation of valuable crops in the terraces.
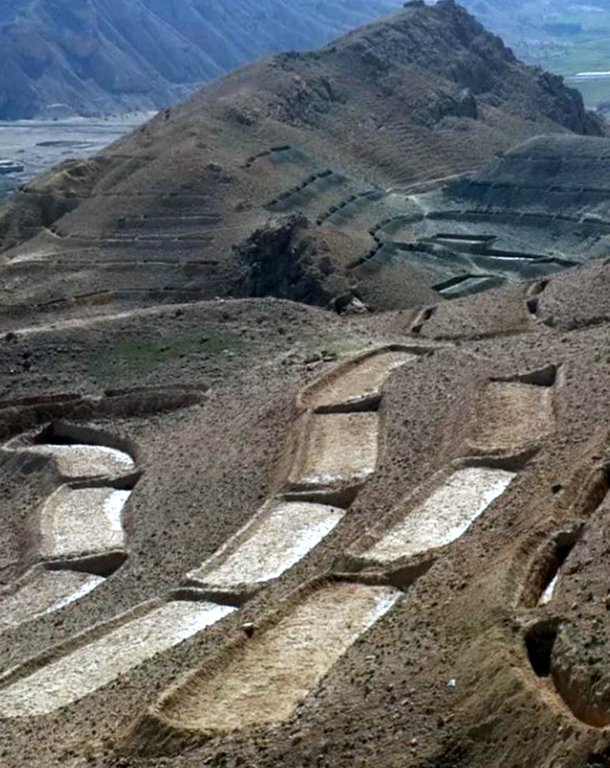
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Having selected the watersheds and established watershed committees, watershed master plans were prepared and various structural and agronomical measures identified and estimated for each unit of land. Community laborers, trained by HELVETAS technical staff, constructed the terraces under supervision of watershed committee members. 600 terraces, each measuring 10 m x 3.6 m were constructed on seven hectares of land. To ensure maintenance, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation facilitated the creation of community saving systems and invested 10% of the project budget for maintenance of each watershed. It improved the capacity of watershed members, so after ending project support the community watershed committee would be able to manage maintenance of watershed measures.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan province is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The soil texture is clay, sandy loam and clay loam with moderate type of soil fertility, naked area of upper catchments causes that most of Saighan villages face to water scarcity during May to September and can’t grow valuable crops.The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple crops (wheat) and fodder crops.Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity during May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
The average annual income from one hectare in the area of having enough irrigation water is 250000 AFN (3676 USD) and in the area which has no enough irrigation water is 67500 AFN (992 USD).
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อัฟกานิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Bamyan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Saighan
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Since 2010
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: March to July

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Harvest of shrubs and over grazing for over 20 years resulted in the lost vegetation cover. Top soil erosion is severe and gullies are visible.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Due to the lack of alternatives for fuel and lack of opportunities for income during decades war, people were compelled to use the natural resources in the upper catchment areas.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: March to July
Livestock density: 10-25 LU /km2
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- Extensive grazing

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Shrub cutting), overgrazing (Over grazing and no management), droughts (3 years drought), population pressure, war and conflicts (3 decades of civil war)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
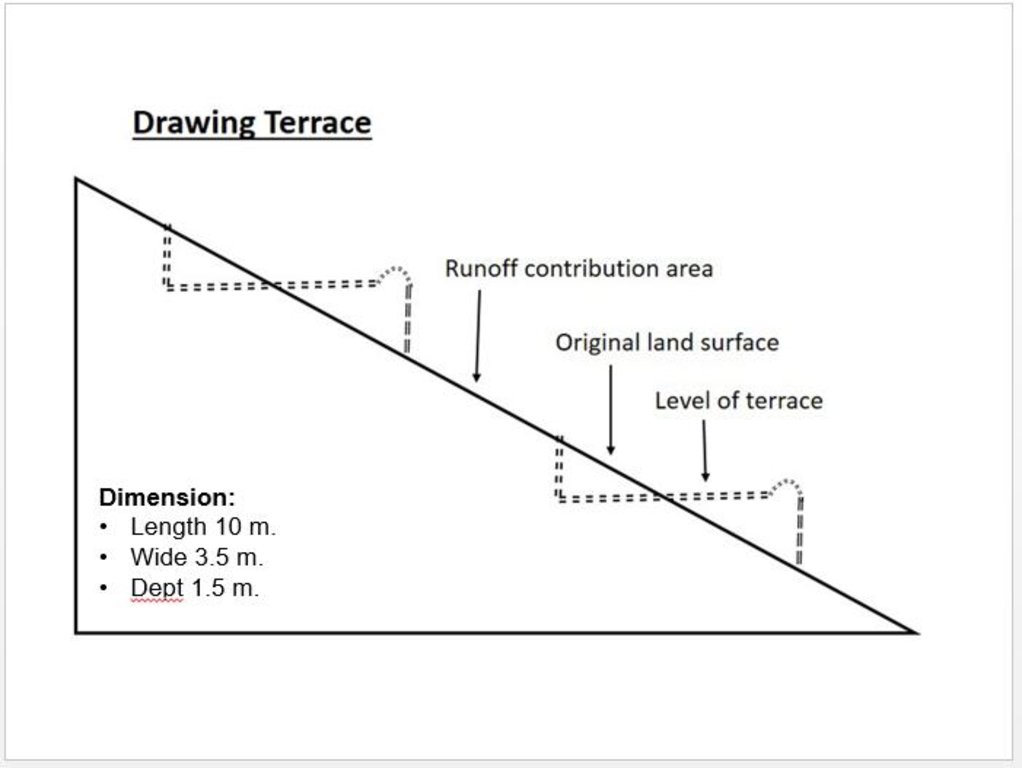
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical drawing of a terrace built in the watershed for the mean of vegetation.
Almost all the terraces constructed on the hill sides has 10 m length, 3.5 m width and 1.5 m depth.
Location: Saighan. Bamyan
Date: 19/04/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (In order to design well)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.8
Spacing between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Construction material (earth): Excuvation of soil and leveling
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 36m3
Catchment area: 36m2
ผู้เขียน:
Shabir Shahem, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, Afghanistan
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.88
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labor cost for the construction of the terraces | 1 month |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labor cost for the construction of the terraces | persons/day | 1200.0 | 5.88 | 7056.0 | 10.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 7056.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 7056.0 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing of few terraces after heavy rain falls | 3 times a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Repairing of few terraces | persons/day | 6.0 | 5.833333 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 35.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 35.0 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labor cost is the determinate factors which was affecting the costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The culture doesn't allowed women to work as labor for construction works
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
10% of the land users are rich (Households who have land and livestock).
35% of the land users are average wealthy (Households who have land only).
45% of the land users are poor (Howseholds who have less or not land).
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60
หลังจาก SLM:
80
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Technology reduce flood and lower lands doesnt effect by floods
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20
หลังจาก SLM:
25
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increasing under ground water by applying technology
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
50
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cultivation of cash crop in the terraces (farm income from uplands)
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology has effective role on reducing flash flood and as well through cultivation of valuable crops the community get more income from watershed area
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
100
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Leveled terraces infilter the water
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
50
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Technology let the water infilteration more
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
50
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Control runoff
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The annual rainfall should be considered according to the slope of the area while designing terrace.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The establishment cost of this technology seems to be high but once they are built they need very less maintenance cost with lots of benefits in the other hand.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
444 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
444 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Construction of terraces in the watershed requires lots of investment costs.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Good measure that is easy to be applied by the people. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conducting training and workshops for capacity building of the community members. |
|
The application of this technology results to the control of runoff and reduction of the flash flood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative measures should be considered. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
A good technology for the better control of runoff and keeping the moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cultivation and sustainable maintenance of the plants in the terraces. |
|
Preparing and providing a good and proper place for cultivation and plantation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plantation of the local plants which has more resistance and are adaptable to the natural environment of Saighan district. |
|
Getting more income through cultivation of valuable crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protection of cultivated seed from grazing animals |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Requires high investment and financial cost. | People should as well have contribution in the cost by providing the labor work. |
| In case the technical measures are not considered and applied properly it may increase infiltration and subsequently increases the soil moisture which may trigger landslide on slopes during rainfalls | High level of the technical staff and knowledge to be considered and as well the area should be studied and observed deeply. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Resilient Watershed Management Plan [ทาจิกิสถาน]
The participatory watershed management plan (WMP) is an interdisciplinary approach at community level to raise awareness on the watershed management concept and improve understanding of the watershed approach in planning and management of natural resource.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Askarsho Zevarshoev
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล