Bush Control and Biomass Utilisation [นามิเบีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Johannes Laufs
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bush Control and Biomass Utilisation
approaches_2809 - นามิเบีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
01/06/2015
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Public and private stakeholders in Namibia cooperate in the implementation of a national Bush Control and Biomass Utilisation programme. The programme consists of the three components (1) Creation of an enabling framework, (2) Advisory Services and (3) Value Chain Development.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
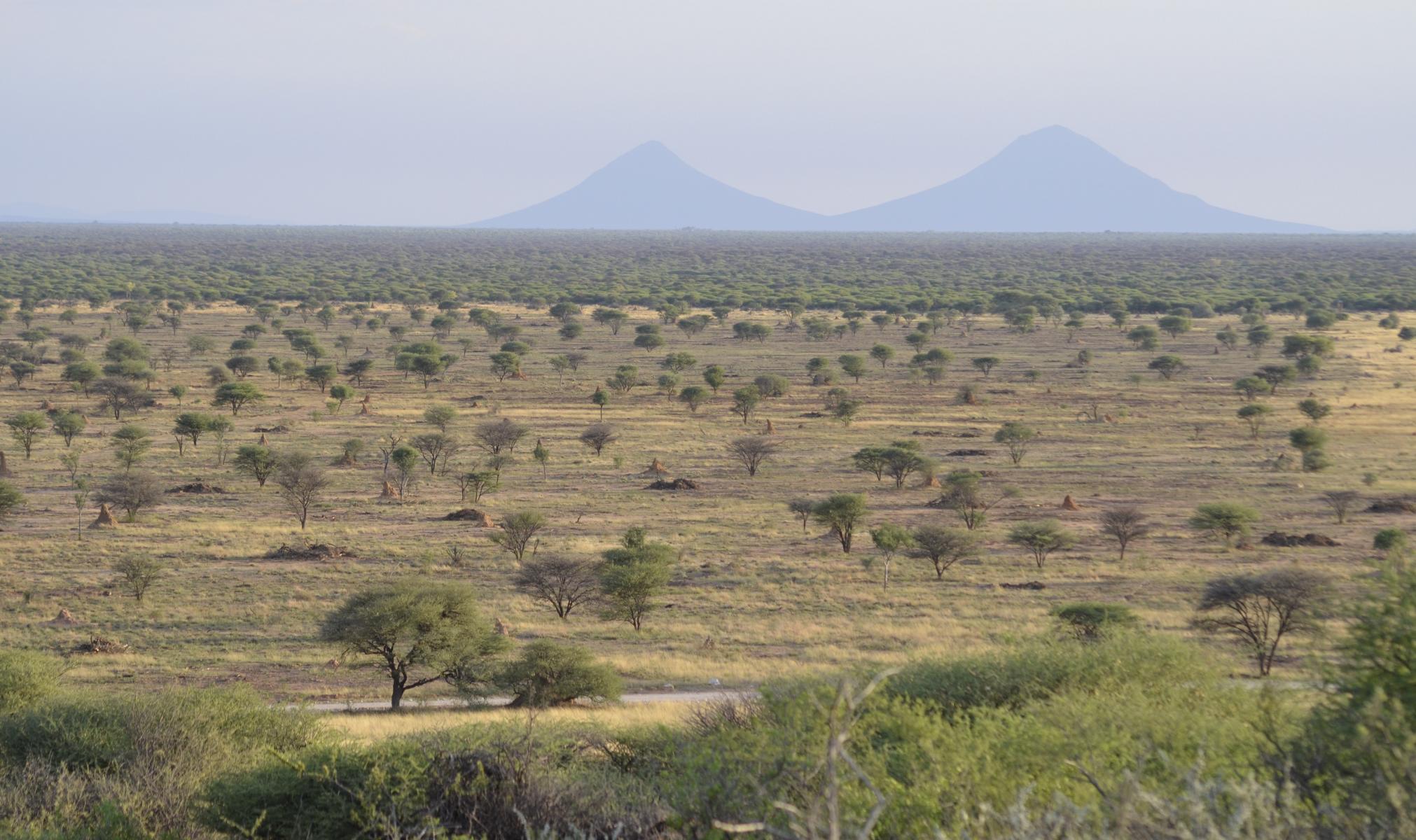
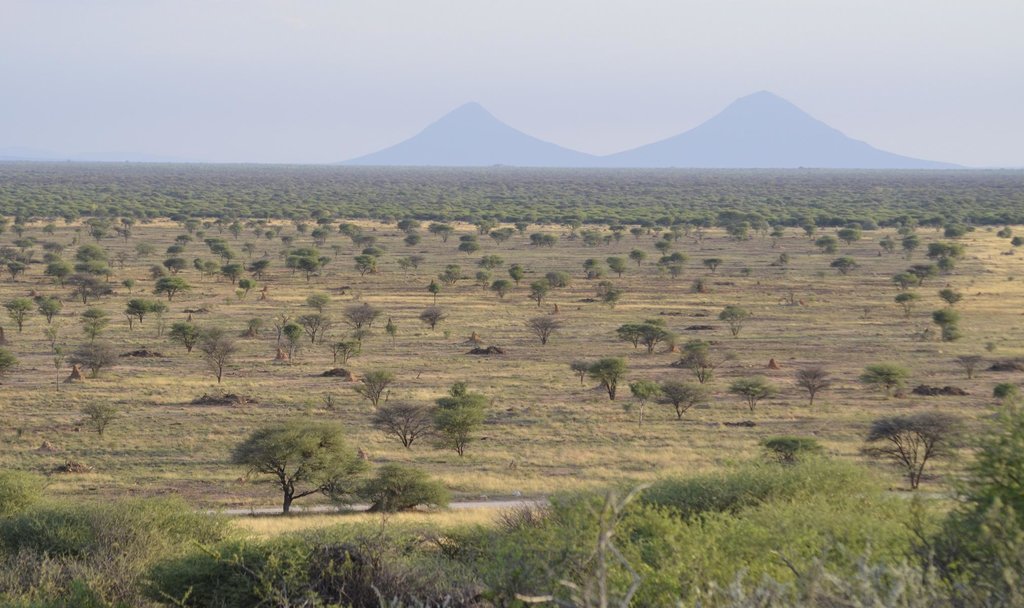
Public and private stakeholders in Namibia cooperate in the implementation of a national Bush Control and Biomass Utilisation programme. It is a response to the immense challenge of bush encroachment in the country.
Namibia is affected by bush encroachment on a massive scale. The phenomenon currently affects some 45 million hectares of farmland in 9 of the country’s 14 regions. Bush encroachment has lowered the livestock capacity of rangeland by up to two thirds. It further results in severely reduced biodiversity and limits the recharge of groundwater.
Various factors contribute to the accelerating rate of bush encroachment in Namibia. A primary cause of bush encroachment of savannas is overgrazing by livestock. When overgrazed, the grass layer loses its competitive advantage and its ability to utilise nutrients and water efficiently. Higher infiltration of water and nutrients into the sub-soil results, which in turn benefits bush and tree species, allowing them to dominate.
Another important theory is the state-and-transition model, which states that savanna ecosystems are event-driven, where rainfall and its variability impact on vegetation growth and its composition. This model implies that bush encroachment is not a permanent phenomenon and that a savanna can be changed to its grass-dominated state by favourable management or environmental conditions. Woody plants establish themselves after dry periods followed by a few wet years, and then maintain themselves by utilising most of the water. Rather than a gradual annual increase in numbers, the general rule is that woody plants establish in large numbers during certain years and at varying intervals.
Other factors contributing to bush encroachment are the reduction in the frequency of wildfires as well as the absence of browsers (e.g. through fencing of farms and replacing the natural composition of wildlife by cattle or smallstock).
Bush encroachment is accompanied by a change in the dominant grasses: perennial grasses are often lost, being replaced by annual species often of inferior quality for livestock. Annual grasses are generally less productive than perennial grasses. Thus, animal production on an annual grass sward is very precarious and less sustainable.
Despite the negative impacts, the encroacher bush has developed into a huge biomass resource, estimated at about 200 to 300 million tonnes. Measures used to combat bush encroachment create positive opportunities for the Namibian economy, such as the use of the resource for electricity generation and value chain development in other sectors. Bush harvesting therefore offers the potential to increase agricultural productivity, economic growth, employment and energy security, without competing with food production.
In line with the national development plans, the approach aims to strengthen the restoration of productive rangeland in Namibia. It identifies value chain opportunities to trigger large-scale bush thinning activities. Its focus is closely aligned to the National Industrial Policy of 2012 and the Growth at Home Strategy, which promote domestic value addition for local resources. The project will foster institutional development in the biomass sector and provide support to improve the legal and regulatory framework for large-scale bush control.
The programme consists of the following three components:
(1) Creation of an enabling framework: harmonisation of sector policies and improvement of relevant regulations; strengthening of institutional capacities.
(2) Advisory Services: strengthening of existing farmer outreach services and knowledge dissemination to farmers, businesses and public sector decision makers.
(3) Value Chain Development: identification and piloting of relevant value chains for encroacher bush as a trigger for bush control.
The programme is implemented in collaboration of various public and private sector stakeholders. Its coordination is ensured through a cross-sector steering committee, which includes the line ministries of the following sectors: national planning, agriculture, environment, energy, industrialisation.
Key outputs of the programme include:
Enabling Environment:
- Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
- Introduction of Harvesting Authorisations Guidelines
- Development of dedicated financial products (loan subsidy schemes).
Institutions:
- Introduction of the De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS)
- Introduction of the Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG).
Knowledge:
- Compilation of baseline data on bush encroachment and bush control
- Technical know how on technologies
- Compilation of relevant regulations and environmental principles.
Value Chain Development:
- Piloting of various value chains, including modernised charcoal production, bush based animal feed and household cooking fuel.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
นามิเบีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Bush control is applied across Namibia on many privately owned farms. Activities are most concentrated in the regions of Khomas, Omaheke, Otjozondjupa and Oshikoto.
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Pointers indicate hotspots (e.g. urban centres) around which activities are concentrated. It is not possible to depict each site where bush control is implemented due to the high number of individual activities and because no GIS based mapping has been conducted.
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2014
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอนให้ประมาณวันที่ที่ริเริ่มใช้แนวทางนี้ :
น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (เร็วๆนี้)
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2021
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
Develop, test and upscale the implementation of bush control technologies in Namibia.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เอื้ออำนวย
Strong awareness of the need to implement bush control across all stakeholder groups.
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of cooperation and information exchange.
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Limited variety of dedicated/customised financial products available; cost of finance high.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of cross-sector coordination and limited funding sources for sector representative bodies (e.g. associations).
การร่วมมือหรือการทำงานประสานกันของผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of interaction and knowledge sharing.
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
Clear land tenure in commercial areas and suitable concepts in communal areas (e.g. conservancies and community forests).
นโยบาย
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of policy harmonisation across sectors; need to resolve conflicting mandates of relevant authorities (e.g. industrialisation vs. resource protection).
การกำกับดูแลที่ดิน (การตัดสินใจ การนำเอาไปปฏิบัติใช้ และการบังคับใช้)
- เอื้ออำนวย
Clear governance and management in commercial areas
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Unclear decision making processes for income generating projects in communal areas.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of bush control know how among land owners
ตลาด (จัดซื้อปัจจัยนำเข้า ขายผลิตภัณฑ์) และราคา
- เอื้ออำนวย
High national and international demand for woody products
ปริมาณงานที่ทำได้ กำลังคนที่มีให้
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Low level of skills among workers
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Commercial farmers, communal farmers
Implementation of bush control and/or availing land for bush control and biomass utilisation activities
- องค์กรที่ขึ้นอยู่กับชุมชน
conservancies, community forests
Implementation of bush control and/or availing land for bush control and biomass utilisation activities
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
Farmer outreach services and independent experts
Dissemination of information and skills development
- นักวิจัย
Namibia University of Science (NUST), University of Namibia (UNAM)
Complementary research projects
- ภาคเอกชน
Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
Representation of corporates involved in bush harvesting and biomass value addition.
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
National Planning Commission (NPC)
Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Forestry (MAWF)
Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET)
Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME)
Ministry of Industrialisation and SME Development (MITSMED)
Policy and strategy development; sector steering; law enforcement, monitoring and evaluation.
- องค์การระหว่างประเทศ
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammmenarbeit (GIZ)
Implementation of bilateral cooperation project
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | High awareness and mobilisation within the farming community |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Good participation in public workshops and conferences |
| การดำเนินการ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Implementation of bush control by individual farmers |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ไม่ลงมือ | Very limited monitoring and evaluation through individual land owners |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
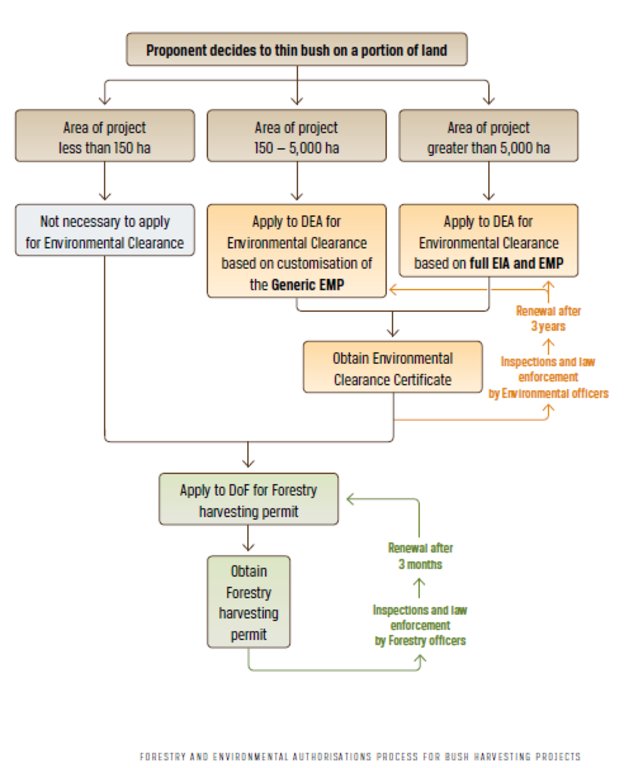
Legal and regulatory framework for large scale bush control: the flow chart explains the three levels of categories for the Environmental Clearance process. The categories are as follows:
- Small bush harvesting operations covering less than 150 ha: no environmental clearance required
- Medium bush harvesting operations covering between 150 and 5 000 ha: environmental clearance based on a generic Environmental Management Plan (EMP) is needed
- Large bush harvesting operations of more than 5 000 ha, Environmental Clearance based on Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Environmental Management Plan (EMP)
Abbreviations:
DEA - Directorate of Environmental Affairs, Ministry of Environment and Tourism
DoF - Directorate of Forestry, Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Forestry
EIA - Environmental Impact Assessment
EMP - Environmental Management Plan
ha - hectares
ผู้เขียน:
Southern African Institute for Environmental Assessment (2016)
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดในฐานะที่เป็นส่วนรวมของแนวทาง
ระบุว่าการตัดสินใจตั้งอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ:
- การประเมินความรู้ SLM ที่ได้ทำการบันทึกไว้เป็นอย่างดี (การใช้ข้อมูลในการตัดสินใจ)
- สิ่งที่ค้นพบจากงานวิจัย
- ประสบการณ์และความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว (ไม่ได้ลงบันทึกไว้)
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- กำลังดำเนินการ
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
- จัดการประชุมสู่สาธารณชน
หัวข้อที่พูด:
- Environmental and forestry policy and policy emplementation (training for government officials from regional offices)
- Implementation of bush control and biomass processing (training for farmers and SMEs)
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Advisory services through the De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS, www.dasnamibia.org)
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ประเทศ
อธิบายถึงสถาบัน บทบาทและความรับผิดชอบ สมาชิก เป็นต้น:
Launch of
- De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS)
- Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
Re-organisation of
- Namibia Charcoal Association (NCA)
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- ด้านการเงิน
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
- อุปกรณ์
- Institutional Development
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
Three sector institutions have been supported in order to achieve increased coordination of efforts. The Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG) is a non-profit association, representing the interest of bush harvesting and processing companies. The De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS) is a national platform for the dissemination of knowledge on the topics of bush encroachment, bush control and biomass utilisation.
The Namibia Charcoal Association (NCA) represents the already well established charcoal production sector. Through a re-organisation process, the association has been strengthended and turned into a fully functioning sector representation.
Thre three organisations are planned to merge in the near future in order to achieve a better alignment of their mandates and synergies of activities.
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
National Bush Information System
- Scope of bush encroachment
- Scope of bush control activities
- Success rate of bush control methodologies, incl. secondary impacts (employment)
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ แสดงว่าการจัดเตรียมเอกสารนี้มุ่งหวังที่จะเอาไปใช้สำหรับการติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลใช่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เศรษฐศาสตร์หรือการตลาด
- นิเวศวิทยา
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Collaboration with scientific institutions and networks on:
- Identification and development of suitable technology
- Correlation with ecosystem services, e.g. grounwater recharge and biodiversity
- Identification of market for bush based products
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- > 1,000,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Pooling of resources between national government, international donors and private sector
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- ไม่มี
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุเงื่อนไข (อัตราดอกเบี้ย การชำระคืน):
Commercial loans with grace period of up to 3 years and interest rate of 7-8%
ระบุผู้ให้เครดิต:
Commercial banks: First National Bank (FNB), Agribank
Development Bank of Namibia (DBN)
Environmental Investment Fund (EIF)
ระบุผู้รับเครดิต:
- Individual households/farmers
- Service providers/business
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Development of authorisations guidelines and review of regulations with regard to Environmental Management Plans (EMPs) and Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs).
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ทำให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นมีอำนาจขึ้น ปรับปรุงการเข้าร่วมของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Increased dissemination of information and exchange between land users on experiences with technologies; stakeholder representation through associations and participation in high level national conferences.
ช่วยในการตัดสินใจโดยดูจากหลักฐาน ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Various publications to capture best practices in bush control and biomass utilisation, including farmers manuals.
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Development of various guidelines
ปรับปรุงความร่วมมือกันและการดำเนิน งานของ SLM ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Improvement of cross-sector collaboration through steering committee
ระดมกำลังหรือปรับปรุงการเข้าถึงแหล่ง เงินทุนสำหรับการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Involvement of financial institutions with the aim to develop customised financial products.
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Various publications to capture best practices in bush control and biomass utilisation, including farmers manuals.
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ ให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Increase awareness of the opportunity of the biomass resource among public sector stakeholders as well as within the business community.
ทำให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นมีอำนาจขึ้น ปรับปรุงการเข้าร่วมของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Through introduction of steering committee, working groups as well as through the strengthening of sector representative bodies/associations.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Employment creation in bush control and biomass utilisation, e.g. in charcoal production
ปรับปรุงความทัดเทียมกันด้านเพศและให้อำนาจแก่ผู้หญิงและเด็กผู้หญิงหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Promotion of dedicated employment opportunities for women, e.g. in charcoal packaging
นำไปสู่การเข้าถึงเรื่องน้ำและสุขาภิบาลได้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Improved groundwater recharge in bush controlled areas. Research is ongoing and first results indicate a significantly improved infiltration of rainwater into the groundwater. The reduced number of bushes leads to reduced evapotranspiration.
นำไปสู่การใช้ที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืนหรือแหล่งพลังงานหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
First biomass energy projects launched (industrial heating) and in preparation (national grid electricity production).
นำไปสู่โอกาสในการจ้างงาน รายได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Employment in bush harvesting and processing, especially in charcoal production.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
Need for bush control in order to increase carrying capacity of land.
- การเสื่อมของที่ดินลดลง
Rehabilitation of land through bush thinning.
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
Land users have the capacity to implement bush control, either with own means (mainly manual and semi-mechanised bush harvesting) or through the involvement of service providers (mainly fully mechanised bush harvesting for the supply of large-scale off-takers).
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Financial viability of bush control through the introduction of value chains (as compared to mere removal of the biomass) |
| Improved access to information and know how |
| Improved advocacy/ communication with government authorities |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Mindshift among public and decision makers from focus on the challenge (bush encroachment) to the opportunities (value addition). |
| Cross-sector cooperation through steering committee |
| Involvement of private sector as driving force for implementation |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Limited direct (financial) support | Introdution of incentive schemes |
| Limited opportunities in remote areas, i.e. when distance to biomass off-takers is too large | Further development of on-farm solutions (e.g. bush-to-feed) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Complex programme steering requirements, due to multi-sector relevance. The national programme for Bush control and Biomass Utilisation is currently anchored in the Directorate of Forestry (DoF) of the Ministry of Agriculture. This adequately accounts for the fact that the bush resource is part of the national forestry/biomass resource and its utilisation must be regulated as such. However, this anchoring does not allow for an effective promotion of biomass utilisation (e.g. SME promotion, industrialisation concepts, development of logistics hubs) and innovative end-uses (e.g. development of biomass power plants). For this purpose other line ministries, such as Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME) as well as Ministry of Industrialisation and SME Development (MITSMED) are part of the programme's steering committee. | Establishment of national coordinating body to formalise the current steering committee |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Baseline Assessment for De-bushing Programme in Namibia (2014)
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS) Namibia, Resource Section
URL:
www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
URL:
www.n-big.org
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล