Enhancement of existing SLM technologies into demonstration sites [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Habib Kamolidinov
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
ADB, GEF, GITEC, DMC. Rural Development Project
approaches_2634 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
GITEC/ADB/DMC Rural Development Project Land Management Institute - ทาจิกิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
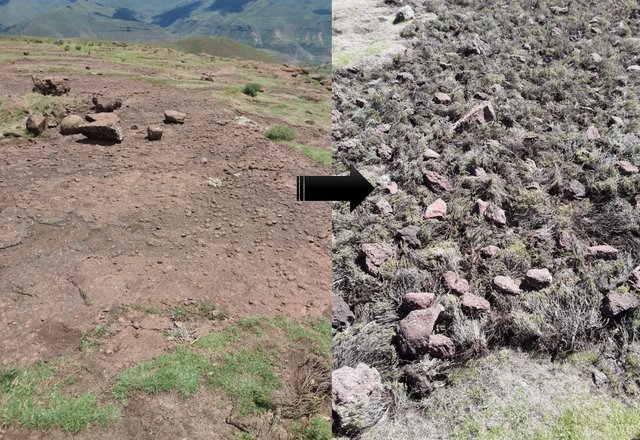

Brush Layering [เลโซโท]
The technology requires removal of invaders as resources for layering. The technology enhances accumulation of silt and moisture storage in dry-lands due to increased organic matter content in the soil from the brush.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Matoka Moshoeshoe
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
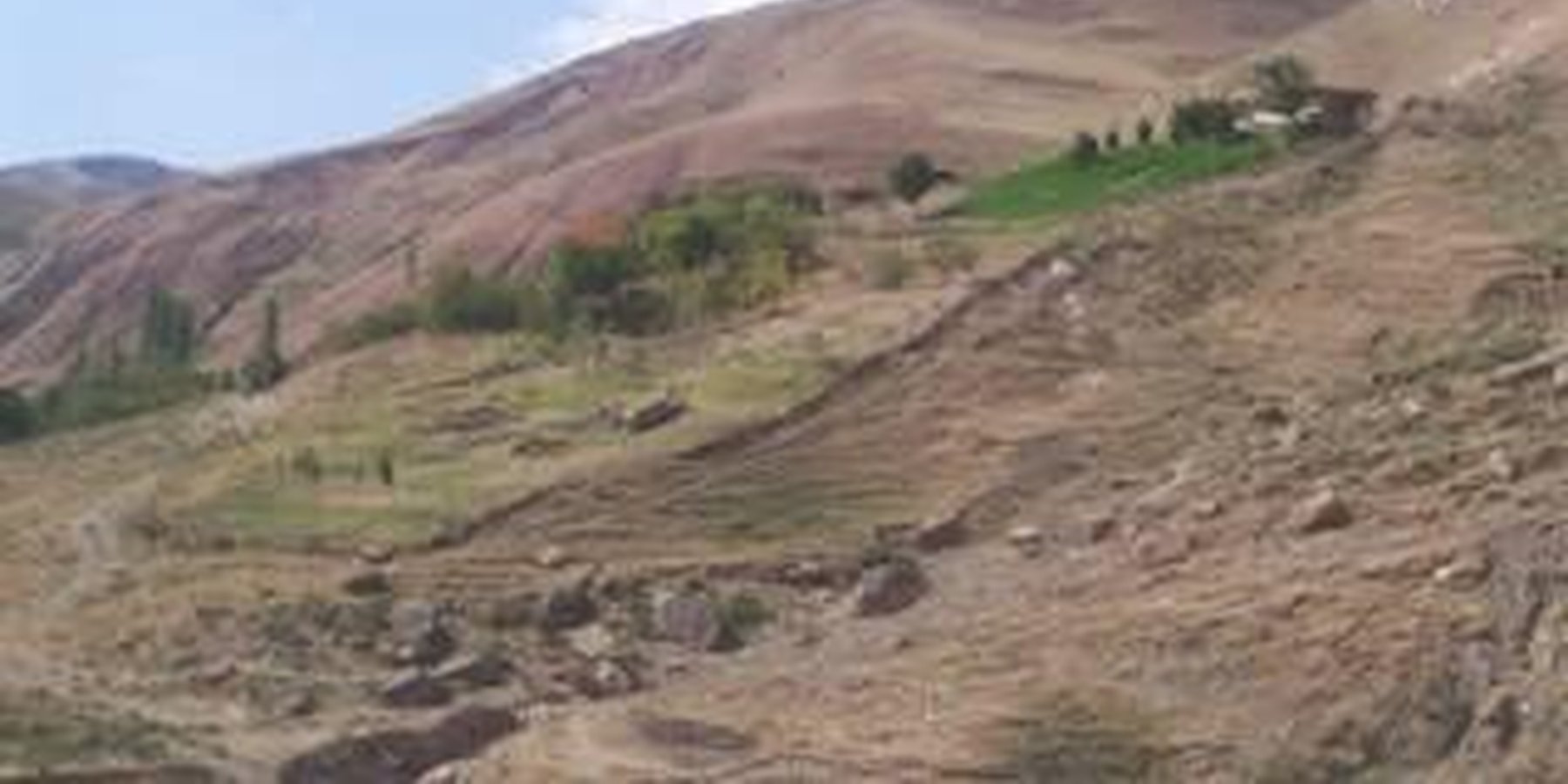
Enhancement of existing self developed SLM technologies into demonstration sites.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: The farmer clearly stated that his prime, initial aim in taking over this “ruined and abandoned land” was to improve and better assure the quality of his family’s lifestyle, through enhanced and assured food and fodder production. He also recognised the potential for future profit, through sale of his excess produce to market. Currently, the family has almost no need to buy food (and fodder) from nearby markets, apart from flour (for bread making). This is a large cost saving factor. In hindsight, the farmer sees that he has dramatically improved land quality within the enclosure through mitigating erosion and increasing year-round vegetation cover
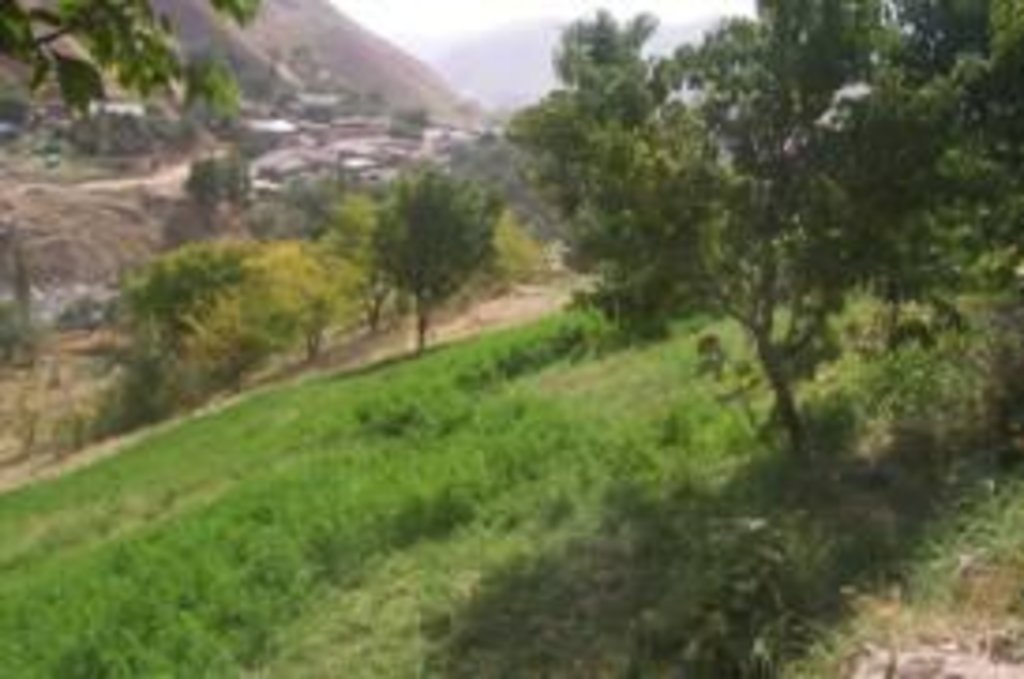
Methods: The success of the enclosure is the result of using several methods. The fence construction was critical to keep out both domestic animals (cattle, goats and sheep) and wild ones, (pigs and wolves) from what was to become a vegetation rich “island” amoungst the bare and degraded hillslopes. Stone clearing (by hand) of the whole area inside the enclosure greatly improved land quality due to enhanced soil depth and subsequent vegetative growth. Tree planting (apple, cherry, apricot, pear) was critical to provide family food. Lucerne planting provided food for the farmer’s animals (1 cow, 10 goats) that provide milk and meat. A small area of land near the homestead (approx. 20 x 20 metres) was levelled into several small terraces for vegetable production (potatoes, garlic, onion, peppers, tomatoes). Irrigation is conducted within the upper part of the enclosure; water being provided by a 20mm polythene pipe that brings water from 1.5 km away where there is a permanent spring.
Stages of implementation: The family (Enomali) first occupied this land in 1984. The first task was tree planting – the first orchard trees – on 0.1 ha of the current enclosure. This was fenced, then after nine family members left (to work in Dushanbe) he expanded the fence to the current 0.2 ha and continued to plant trees. Stone removal continued through the 1990s and even to today. The lucerne and vegetable gardens were initiated in the 1990s and continue to be enriched. The fodder, trees and vegetable production is an ongoing task, as is feeding the animals with the home-grown fodder. He continues to plant orchard trees every year and currently has more than 100. He gained a “certificate” of ownership” in 2008.
Role of stakeholders: All of the work within the enclosure has been conducted by family members. The main two are the husband and wife, though in the early stone clearing and fence construction days his 1st cousin assisted. His son and daughter in law have also assisted (though the son now works in Dushanbe) – even the young grandchildren help.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
RRP
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Varzob, Luchob
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
1984
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2014
ความคิดเห็น:
The small area was all that the family could manage, as there was an initial large workload, clearing stones and fence building, etc
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- Local initiative enhanced by programme activity
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused on SLM only
The prime, initial aim in taking over this “ruined and abandoned land” was to improve and better assure the quality of his family’s lifestyle through enhanced and assured food and fodder production. He also recognised the potential for future profit, through sale of his excess produce to market. Now, he wants to expand the area within the enclosure to 1 ha with extra fencing and supplementary irrigation supply from another spring.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main problem to be addressed was reducing poverty, to help achieve a better and more sustainable lifestyle by producing better quality food and fodder.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เป็นอุปสรรค
This family were one of the first in this region to take over this area of “ruined” land and begin improvements. However, the farmer did not see this as arduous, rather he welcomed the chance to work hard and provide for his family
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Family working together to improve land
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The farmer could improve his SLM but would need financial assistance
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
He has now gained a certificate of ownership that ensures ownership until his death. The government still owns the land and he pays $5 US a year in tax (total).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Application for land entitlement certificate
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: There was no compelling need for the farmer to get a “entitlement certificate” but he did so anyway.
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Not applicable. The water (irrigation) is “free” and there are no current disputes over his use of the spring water
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The family provided their own solutions to any problems since the project began in 1984
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
ปริมาณงานที่ทำได้ กำลังคนที่มีให้
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The family have worked consistently for 26 years, slowly but have created better land and vegetation conditions
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Only the land users (family)
The men focused on the heavier labour tasks of fence building and stone removal. The women focus on the garden, and fruit production and bee keeping.
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | The extended family, when available |
| การวางแผน | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Principally the husband and wife – Mr Enomali and wife |
| การดำเนินการ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | The family |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Mr Enomali and his wife are continuously evaluating the production quantities and quality from their labours |
| Research | ไม่มี | Not applicable |
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพียงผู้เดียว ( ริเริ่มด้วยตัวเอง)
การอธิบาย:
The family has chosen and implemented all methods within the enclosure with no external assistance of any type.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). The family has chosen and implemented all methods within the enclosure with no external assistance of any type.
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ไม่
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: The family, generally, take note of the effect of their practices in terms of production
economic / production aspects were None monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- < 2,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (The Emomali family): 100.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
all labour was family-provided
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
There is a dramatic visible difference in both the degree of erosion and vegetative land cover between the enclosure and the surrounding land (see picture in 1.3.3). Also, the production quantity and quality of food and fodder from this enclosure has continued to increase.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
After the fall of the Soviet Union, many in Tajikistan experienced poverty, particularly food shortages. This farmer foresaw this and commenced his enclosure enrichment work. In this way he ensured
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The farmer says that several of his neighbours have been doing similar interventions to his – fencing, stone removal, planting orchards etc. What he has done is very visible from the main road through the valley, and many people have observed the results of his efforts over the years
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
His family eat well, plentiful and very fresh/organic produce from their own household plot
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
- จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
The farmer never had external “support” in the first place, so his approach continues to improve, with no support.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| As above, as these words were transcribed during the farmer interview, on site |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Though not an initial objective, the farmer now recognises that he has dramatically improved land quality and vegetation cover within the enclosure, further assuring continued increased production through improved soil conditions (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By continuing to do what he has been doing for 20+ years already. ) |
| The farmer has achieved what he wanted; assured quantity and quality of food/fodder production to assure his family’s livelihood. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: He wants to increase his enclosure area by 5 times. To do this he will require fencing and pipe for irrigation.) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| As above, as these were the sentiments of the farmer during on site interview |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The farmer does not have sufficient financial means to purchase the additional fencing and irrigation pipe he requires to extend the current enclosure area to 1 ha size | Involvement of local banks |
| The total lack of institutional support. This has not necessarily negatively impacted on the farmer – but rather has led to a reduced uptake of his (excellent) practices elsewhere, both locally and nationally. | Immediate visits of local agronomic staff (governmental) to record the modalities of what has been achieved at this site, to help ensure the wider implementation for improved land quality and vegetative cover, at a more national level. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
There is no relevant documentation
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Brush Layering [เลโซโท]
The technology requires removal of invaders as resources for layering. The technology enhances accumulation of silt and moisture storage in dry-lands due to increased organic matter content in the soil from the brush.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Matoka Moshoeshoe
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล