Halting seasonal drought in Barind through efficient water resource management [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Barendra elakay Khara proshaman
approaches_6143 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Establishing National Land Use and Land Degradation Profile toward Mainstreaming SLM Practices in Sector Policies (ENALULDEP/SLM)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Department of Environment (DoE) - บังกลาเทศ1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
08/04/2020
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Introduction of sustainable water usage to prevent impacts of seasonal droughts in Barind region, Bangladesh
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Barind is a drought-affected area of Bangladesh. It covers about 7,770 sq. km, that is 41% of the North Western part of Bangladesh, spreading over 16 districts of Rajshahi and Rangpur Division. It is one of the driest areas in Bangladesh with comparatively high temperatures - though cooler in the wet season from mid-June to October. Rainfall in the area varies from about 1500 mm to 2000 mm per annum. Temperature ranges from 4 degree Celsius to 44 degree Celsius. The area is at a comparatively higher elevation than the adjoining floodplains. There are two main terrace levels - one at 40m and the other between 19.8 and 22.9 m above mean sea level. The total cultivable area of Barind is about 583,000 ha, of which 34% is loamy, 10% is sandy, and 49% is clay: the remaining 7% is of other composition.
In the 1980s, the area was predominantly single cropped, and yields were poor and subject to seasonal drought, from late February to early May (up to the onset of pre-monsoon). No crops could be grown during the "rabi" season (November to May). The impacts of drought were severe and affected food insecurity and livelihoods. To address the situation, the Bangladesh Agricultural Development Corporation (BADC) under the Ministry of Agriculture (MoA) initiated two projects. One in 1985: The Barind Integrated Area Development Project and subsequently in 1992, the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) as a separate institutional entity. Both the projects focused on a new approach to water extraction, distribution and management practices at institutional level. Deep tubewells were installed and maintained by BMDA, rather than privately (which is often practiced in other parts of the country).
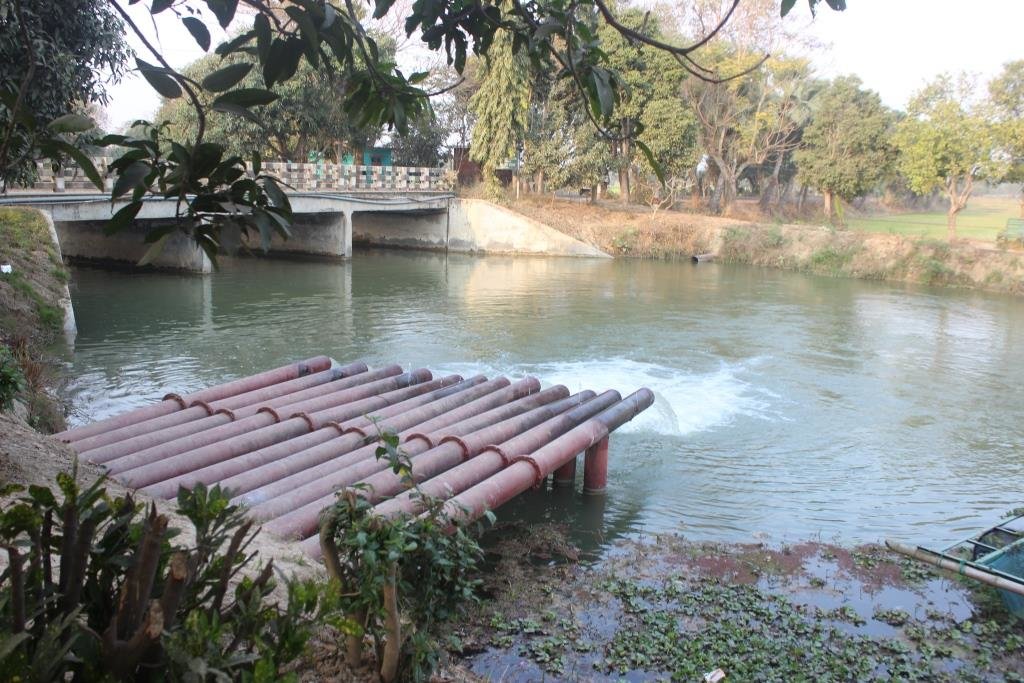
Deep tubewells (DTWs) were installed to abstract water from 15-20 meters, and water was initially distributed through open channels. Later, these were fitted with smart card–operated electric/solar pumps to develop a drought-resilient irrigation system Both projects have helped the Barind region reduce poverty and achieve self-sufficiency in rice. Without supplementary irrigation, there would be crop failure.
Since it was established, BMDA has focused on halting seasonal drought in Barind, and increased cropping intensity by providing irrigation through 15,800 DTWs in different districts. That reduced the cost of irrigation water for one bigha (0.1ha) from about $40 to <$20. On the other hand initiation of smart cards and buried pipelines for water distribution increased the efficiency of water use and facilitated revenue collection by the BMDA. However abstraction of groundwater (GW) for irrigation triggered another issue - drawdown of GW in the area, which even led to abandoning shallow tubewells (STW) used for drinking water.
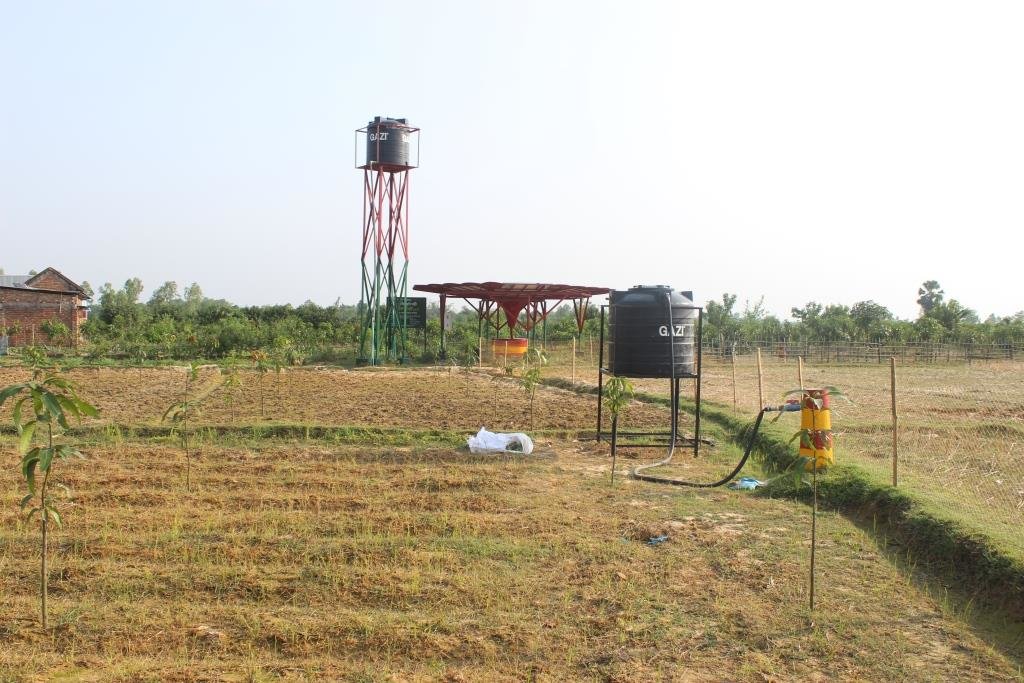
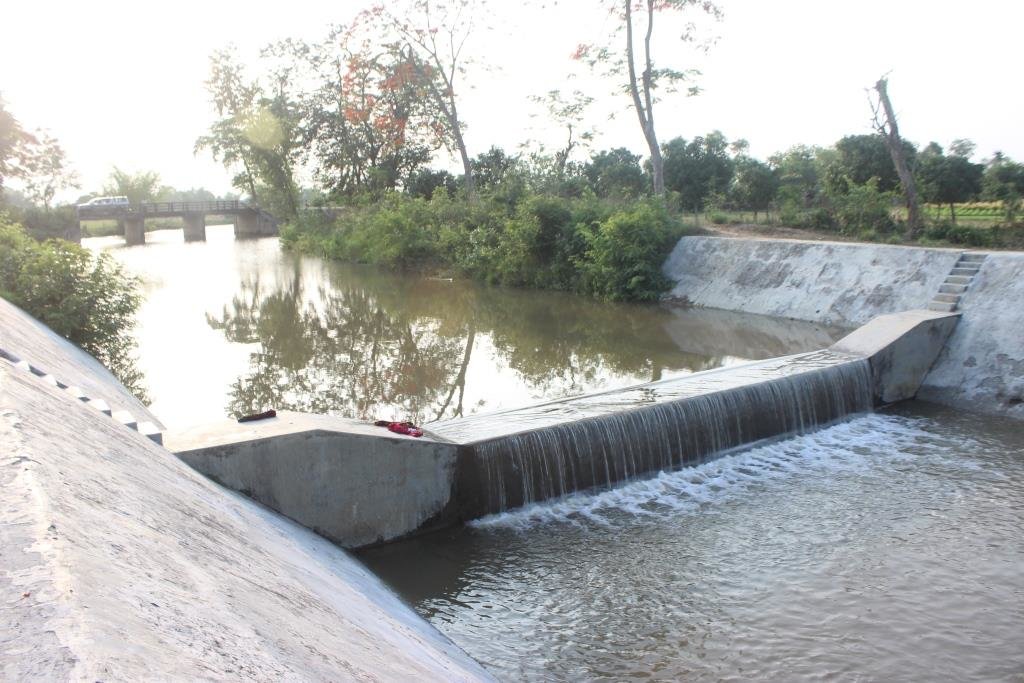
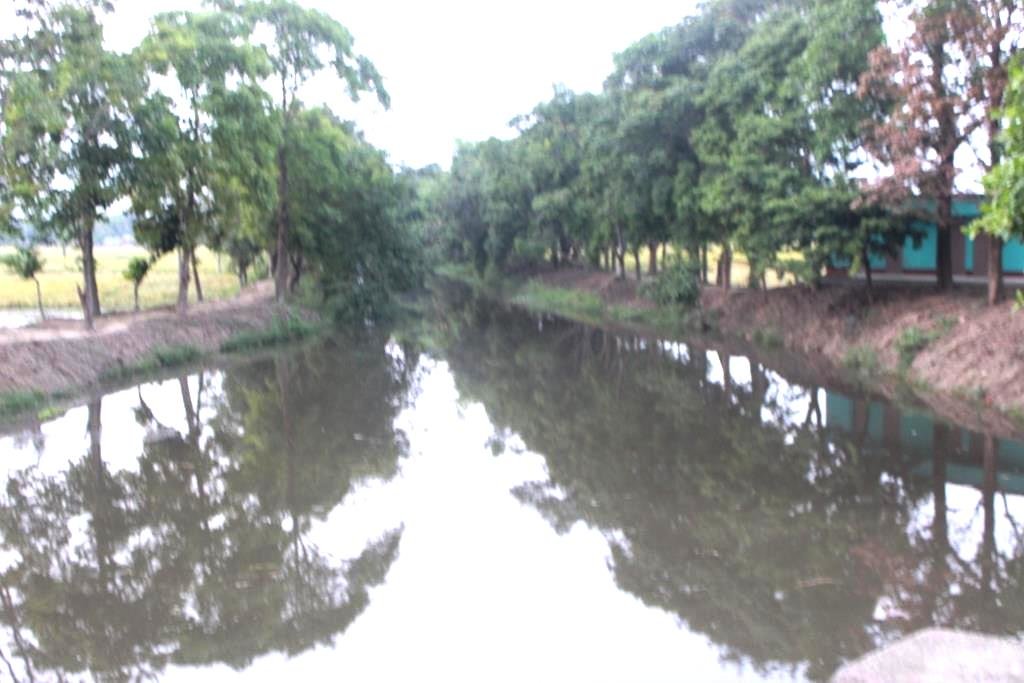
In 2004 BMDA initiated another project, to lift surface water from the Padma river to ponds/canals/rivers in the main land after re-excavation. These sources are used as reservoirs and at the same time contribute to GW recharge generally. At the same time, usage of solar power instead of electricity is another means of reducing the cost of pumping water.
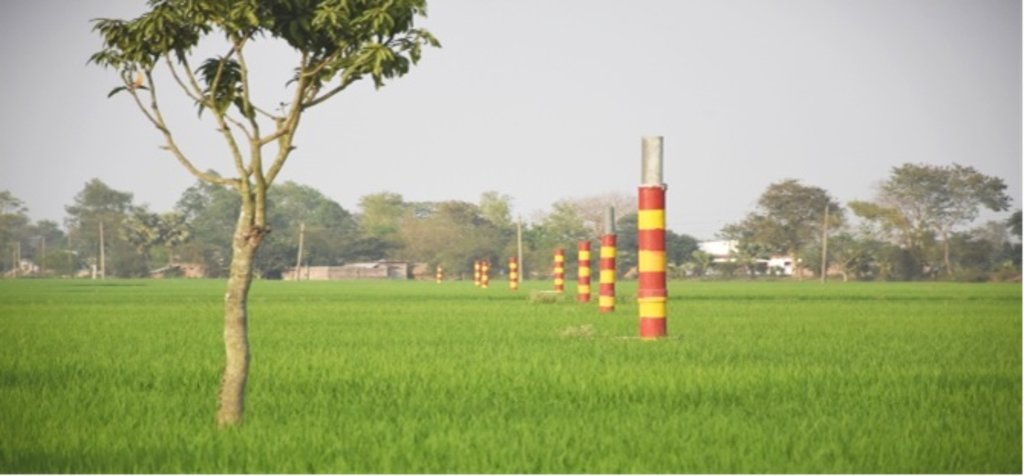
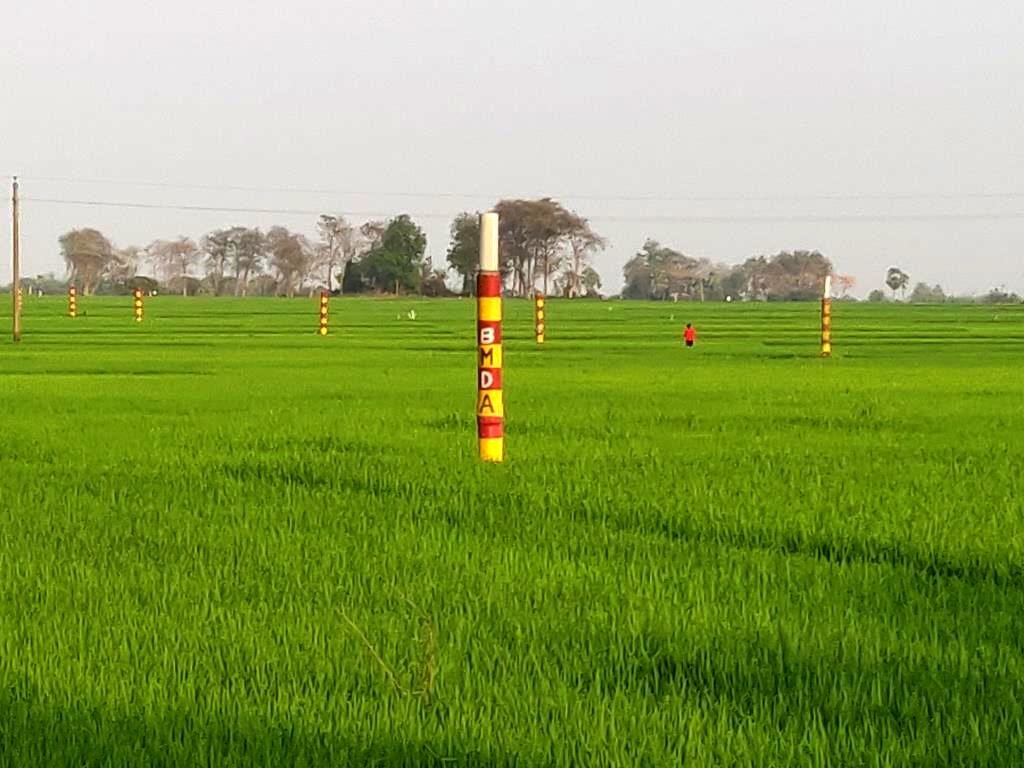
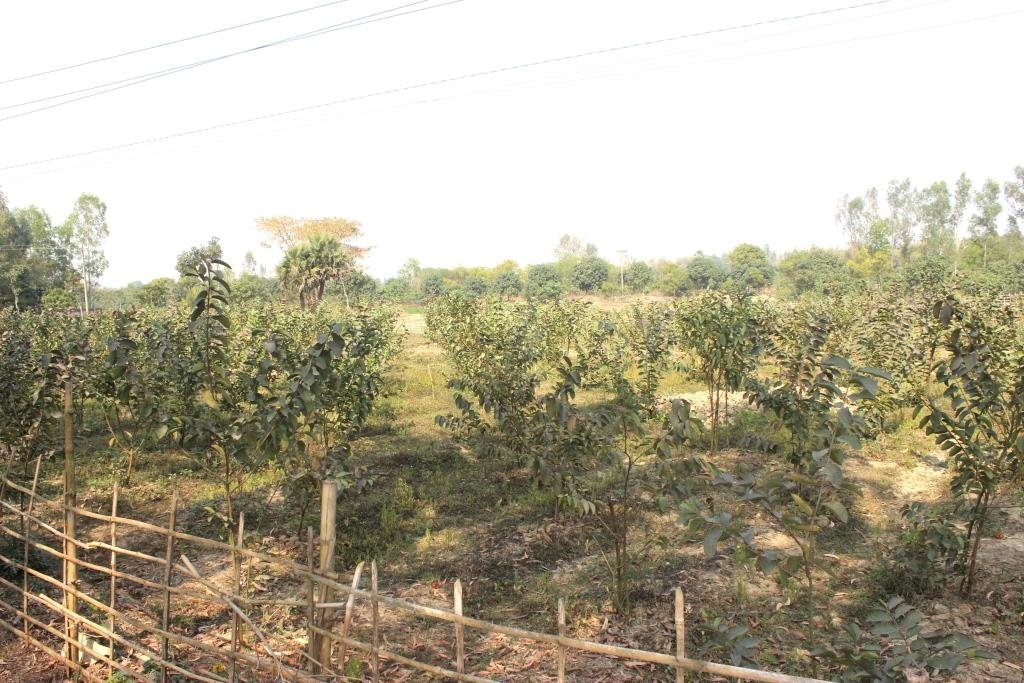
BMDA again installed 490 dugwells where STW or DTW could not be constructed. These dug wells are used for safe drinking water and small-scale irrigation. These measures have meant that, at present, the area avoids seasonal drought in most of the locations. Potatoes, "boro" and transplanted "aman" occupy more than 50% of the cultivable land. In addition, provision of safe drinking water and improved communications have boosted the local economy. The approach embraces various technologies including (1) tapping river water (from the Ganges, Mahananda and Tangan rivers0; (2) storing water in creeks or ponds; (3) distribution to farm land through subsurface irrigation pipes (buried pipelines); (4) use of low lift pumps (LLP) with solar energy support ; (5) prepaid water metering - usage of smart cards; (6) conversion of derelict water bodies to become effective water reservoirs ; (7) dug wells with solar power for water abstraction; (8) orchard plantations where both surface or groundwater are limited; (9) plantations of trees and horticultural crops along road and channels to change the land cover; (10) usage of compost to improve soil health. All of these contribute to land degradation neutrality (LDN) in one way or another.
Finally BMDA's approach is to boost productivity in the drought affected Barind through its projects, and encouraged communities to adopt diversified land use: previously much land remained fallow during most of the year outside the monsoon. Institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) and many NGOs promote a variety of seasonal, annual and perennial crops in the area, the use of balanced fertilizer, plantation of high density fruit crops. The impact of the BMDA approach has greatly changed the drought-affected Barind.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
ข้อสังเกตทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับรูปภาพ:
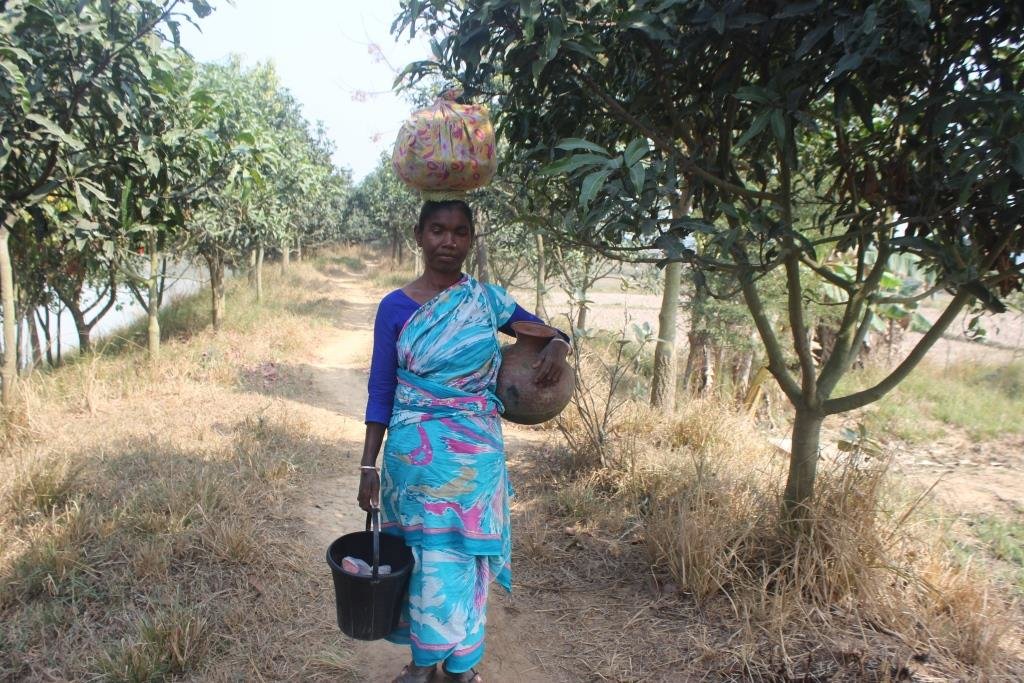
All these pictures demonstrate the usage of surface water for irrigation and livelihoods in Barind.
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Rajshahi
ความคิดเห็น:
Barind which was the driest area of Bangladesh, has now changed its landscape to green.
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
1992
ความคิดเห็น:
Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) is continuing with more development projects to provide irrigation facilities with more options. Cropping intensity has increased, and most of the single cropped land has been transformed to double and triple cropped land.
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
To provide irrigation water for cropping in dry season.
To increase cropping intensity in drought affected areas of Barind.
To manage land use or land cover in Barind.
To mobilize community on rational usage of soil and water resources.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เอื้ออำนวย
Increased livelihood options and access to education, marketing, health services.
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เอื้ออำนวย
Increased access to financial institution.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เอื้ออำนวย
All technical support provided by BMDA.
การร่วมมือหรือการทำงานประสานกันของผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติ
- เอื้ออำนวย
BMDA supports all action in related to irrigation, maintenance, water supply etc.
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
Lands owned by land users
นโยบาย
- เอื้ออำนวย
Land users are in the line of BMDA policies.
การกำกับดูแลที่ดิน (การตัดสินใจ การนำเอาไปปฏิบัติใช้ และการบังคับใช้)
- เอื้ออำนวย
Traditional approach.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เอื้ออำนวย
Community has access to technical support.
ตลาด (จัดซื้อปัจจัยนำเข้า ขายผลิตภัณฑ์) และราคา
- เอื้ออำนวย
All inputs are available in the area.
ปริมาณงานที่ทำได้ กำลังคนที่มีให้
- เอื้ออำนวย
Available, people are getting work now.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Men and women are involved in the process
Growing crops as of their choice, for example: rice, fruits, vegetables or orchard trees.
- องค์กรที่ขึ้นอยู่กับชุมชน
Farmers have societies,
Influenced in choice of crops, etc.
- องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน
Several NGO s are functional in the area.
Most of them are supporting credit and marketing facilities
- รัฐบาลระดับท้องถิ่น
Local institutions involved in the process
Capacity building, advisory services on fertilizer usage, crop selection etc.
ถ้ามีผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียหลายคนที่เกี่ยวข้องให้ระบุหน่วยงานตัวแทน:
BMDA is working as lead agency
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ไม่ลงมือ | Farmers are using irrigation water for their crops supplied by BMDA and they pay revenue |
| การวางแผน | ไม่ลงมือ | Farmer nor the community are involved in the planning process |
| การดำเนินการ | ไม่ลงมือ | Land users allow to set buried pipelines under their fields. |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ไม่ลงมือ | Land users are not involved in the M&E but they participate in the events organized. |
| ไม่มี | Land users only choose their crops to be grown |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
Barind Multipurpose Development Authoroty (BMDA) is the symbol of development in Barind area also of the Tista fldooplain and the Old Himalayan piedmont plain.
ผู้เขียน:
ShoaibJU
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
ระบุว่าการตัดสินใจตั้งอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ:
- การประเมินความรู้ SLM ที่ได้ทำการบันทึกไว้เป็นอย่างดี (การใช้ข้อมูลในการตัดสินใจ)
- สิ่งที่ค้นพบจากงานวิจัย
- ประสบการณ์และความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว (ไม่ได้ลงบันทึกไว้)
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง ให้ระบุ เพศ อายุ สถานภาพ ชาติพันธุ์ เป็นต้น:
BMDA has trained staff to care for the system by and large. There are both male and female staff.
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- กำลังดำเนินการ
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
หัวข้อที่พูด:
Buried pipeline maitenance, good seed production, marketing etc.
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
BMDA has field offices at each upazila to look after the system
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
- ภูมิภาค
อธิบายถึงสถาบัน บทบาทและความรับผิดชอบ สมาชิก เป็นต้น:
BMDA has it headquarters at Rajshai city and sub-offices at all "upazila" to where the pipeline extended.
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
- อุปกรณ์
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
BMDA monitors groundwater levels regularly, and also the pipelines and other operational activities.
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ แสดงว่าการจัดเตรียมเอกสารนี้มุ่งหวังที่จะเอาไปใช้สำหรับการติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลใช่หรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
During the documentation of the SLM best practices of the Banrind area intensive conversations, meetings and workshops were organized with all officials of headquarter and filed offices.
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
All infrastructural establishment cost were born by BMDA
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- ไม่มี
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| หิน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| ถนน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Installation and maintenance cost borne by BMDA, but farmers have to pay for water through smart cards (Pre-paid).
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ทำให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นมีอำนาจขึ้น ปรับปรุงการเข้าร่วมของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Farmers are using irrigation water for their crops
ช่วยในการตัดสินใจโดยดูจากหลักฐาน ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
As of now buried pipe lines for irrigation water supply are being adopting in many areas of the country.
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Usage of water rationally: BMDA installs control meters for each of the land user.
ปรับปรุงความร่วมมือกันและการดำเนิน งานของ SLM ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The approach had changed the Barind ecosystem at large.
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Land users enable to use irrigation water for growing crops of their choice
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ ให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Other local institutions in Barind area are involved in the system.
ทำให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นมีอำนาจขึ้น ปรับปรุงการเข้าร่วมของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Adoption of the irrigation system at all areas of the Barind.
ช่วยบรรเทาความขัดแย้งหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Stakeholders are enable to use water as they like.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The area was resource poor before the 1990s. Now livelihoods of the community improved largely.
ปรับปรุงความทัดเทียมกันด้านเพศและให้อำนาจแก่ผู้หญิงและเด็กผู้หญิงหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Man and women are engaged themselves in their land and crops.
ส่งเสริมให้เยาวชนหรือบุตรหลานของผู้ใช้ที่ดินให้เข้าร่วมใน SLM:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Interventions with new crops, specially high value fruits etc in the area.
ปรับปรุงประเด็นของการถือครองที่ดินหรือสิทธิในการใช้ ซึ่งขัดขวางการนำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Land tenure system is traditional, where large areas are sublet or leased to the individuals or groups by the land owners.
นำไปสู่ความมั่นคงด้านอาหารหรือปรับปรุงโภชนาการให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The area produces a large amount of cereals, potatoes, vegetables, fruits etc.
ปรับปรุงการเข้าถึงตลาดหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Fruits and paddy rice have good markets.
นำไปสู่การเข้าถึงเรื่องน้ำและสุขาภิบาลได้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Safe drinking water where tubewells do not function, and sanitation also developed as the system.
นำไปสู่การใช้ที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืนหรือแหล่งพลังงานหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Using solar power to abstract dug well water greatly facilitates the community.
ปรับปรุงความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการปรับตัวให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงของสภาพภูมิอากาศหรือสภาพที่รุนแรงและภัยพิบัติหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Vegetative cover in the Barind has changed the ecosystem at large.
นำไปสู่โอกาสในการจ้างงาน รายได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Local people are having work everywhere of the Barind.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
Cropping intensity increased
- กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
Low cost of irrigation water contributes to benefits for the land users.
- การเสื่อมของที่ดินลดลง
Halts or reduces seasonal drought
- ความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติลดลง
Less climate extremes, no crop loss due to drought. Temperature relatively cooler than before.
- กฎและระเบียบ (ค่าปรับ) หรือการบังคับใช้
No social unrest
- เกียรติภูมิ แรงกดดันทางสังคม ความเชื่อมแน่นทางสังคม
Livehood improved greatly.
- จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
Local people are now aware of the environment. They grow trees around their homesteads, preserve water in their ponds etc.
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
Buried pipeline irrigation has changed the Barind area greatly.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| More crops could be grown throughout the year, |
| Crop diversity is possible, annual, perenial or seasonal |
| Secure crop production |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Minimum loss of irrigation water |
| Surface (river) water usage minimize stress on ground water usage |
| Improved ground water recharge |
| Safe drinking water where tubewell is not available. |
| Usage of solar power for lifting water from dug well or for lifting water to buried pipeline |
| Introduction of water meters reduces misuse of irrigation water |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The system could be implemented at single farmer level | Developing community approach with the support of the government |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Very high pressure on land and soil resources | Lower water consumptive crops could be introduced |
| Severe soil nutrient depletion may develop | Use of manure/ compost or organic matter or crop rotation to enrich soil |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Intensive field visit with responsible officers (5) from BMDA and interview with beneficiaries (30) .
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Especially the farmers (5) who used to grow very high density fruits crops and of solar powered dugwell (3)
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
10 officers from different institutions, like BMDA, DAE, University of Rajshahi, SRDI, NGO, Fishries etc.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Few official docments of design and plan of pipelines, dugwell etc.
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Baring Multipupose Development Authority
URL:
http://www.bmda.gov.bd/site/page/2ea693ba-ac10-4ada-b304-111d72a72105/-#
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Pro-Poor Groundwater Development
URL:
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/33246/Pro-Poor-Groundwater-Development-The-Case-of-the-Barind-Experiment-in-Bangladesh.pdf?sequence=5
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล