Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
"Tipid Saka"
technologies_1021 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
Jasper Manalo
jasper.o.manalo@monsanto.com
Monsanto Philippines
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Edicer Ocampo Jr
6349 536 4455
edicer@lycos.com
FSSRI, http://www.uplb.edu.ph/research/research-centers
ฟิลิปปินส์
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los (Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los) - ฟิลิปปินส์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Monsanto Philippines Inc. - ฟิลิปปินส์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
04/09/2001
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Conservation Tillage Technology (Zero Tillage) or "Tipid Saka" - A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Brief Description about Conservation Tillage Technology
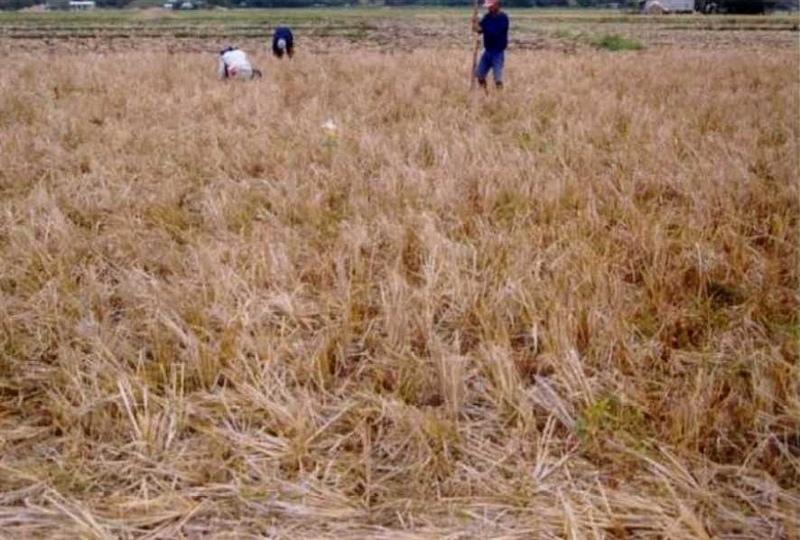
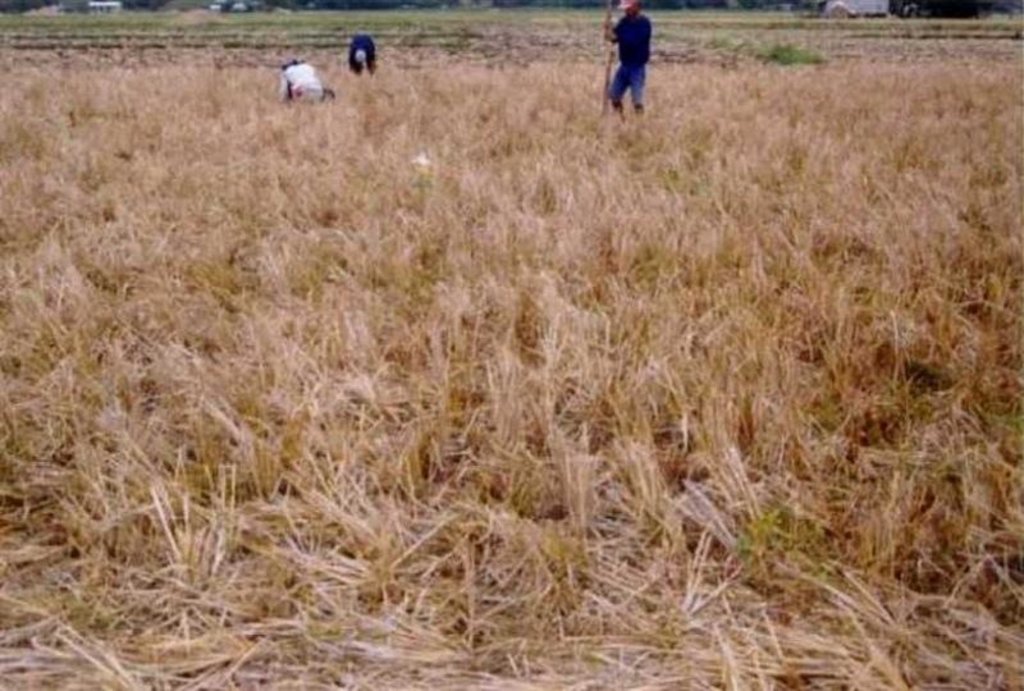
Conservation tillage is the practice of planting seeds through the stubble of last season’s crop, rather than plowing and disking the field. The stubble protects topsoil against loss to wind and rain and reduces chemical run-off to streams. By not plowing, farmers also conserve soil moisture, which can reduce irrigation demands. Farmers can save fuel by reducing the number of farm machinery passes across their fields. In simple terms, Conservation Tillage can be said to lie along a continuum of two other techniques:
Minimum Tillage - mouldboard plowing is replaced by light tillage with tined implements, with or without a low toxicity non-residual herbicide to eliminate both perennial and annual weeds. 30% or more of the soil surface is kept covered by soil residues until final seedbed preparation. Conventional planting equipment can normally be used. Zero Tillage - planting is normally conducted without any preparatory tillage, or seedbed preparation. Normally, this technique requires specialized machinery for planting which can displace residues from the previous crop. A low toxicity non-residual herbicide application is recommended where growing weeds are present. There are numerous potential advantages of conservation tillage:
Farming Benefits
For farmers the primary benefits of CT, achieved with any loss of yields, include:
- More sustainable farming due to dramatic reductions in soil erosion caused by water or wind
- More efficient conservation and utilization of water under dryland conditions
- Improved energy efficiency as a result of reduced fuel requirements associated with fewer field operations
- Greater crop and farm profitability through reduced direct and indirect costs for chemicals, fuel and labor.
Environmental Benefits
At the same time, CT offers a number of significant benefits to the environment, these include:
- Greater biodiversity than with standard cultivation practices where the surface has no crop residues
- Reduces the build-up of soil sediments in reservoirs, drainage, ditches, etc. caused by soil erosion
- Less pollution of drinking water sources caused by run-off of soil, fertilizers and pesticides
- Reduced CO2 emissions due to increased soil organic matter level
Furthermore, crops grown without tillage use water more efficiently, the water-holding capacity of the soil increases, and water losses from runoff and evaporation are reduced. For crops grown without irrigation in drought-prone soils, this more efficient water use can translate into higher yields. In addition, soil organic matter and populations of beneficial insects are maintained, soil and nutrients are less likely to be lost from the field and less time and labor is required to prepare the field for planting. In general, the greatest advantages of reduced tillage are realized on soils prone to erosion and drought. Also achieved are greater water-stability of surface soil aggregates, higher microbial activity and earthworm populations and higher total carbon. Soil loss is less from sprinkler irrigation than in the plow treatment.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Laguna
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
San Jose, Abra de Ilog, Sta. Cruz, Sablayan
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
"Tipid Saka" is being practiced by farmers in the sites of San Jose, Mindoro Occidental since the dry season cropping (1999-2000) with the entry of UPLB Corn project and Monsanto Philippines, Inc.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Although the technology has long been practiced by farmers particularly in the upland areas, zero tillage practices for corn production after rice was introduced in the SWC sites of Mindoro Occidental by the UPLB Corn project through the "Tipid Saka technology of Mosanto Philippines, Inc.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major cash crop: rice, corn
major food crop: rice, vegetables
other: fruits, tobacco
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Continuous salinization due to intrusion of salt water and soil fertility decline. Loss of topsoil by water erosion seriously affects soil productivity, degrades water quality and causes costly sedimentation problems.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain and increase crop yield.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Generally, first crop of rice is planted in early part of June nad harvest in mid October. Followed by green corn and/or vegetables in November and harvested in February. Yellow corn is planted in December and harvested in March to April.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated is common but less used than rainfed
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- cost reduction
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 m2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Ha: aridification
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
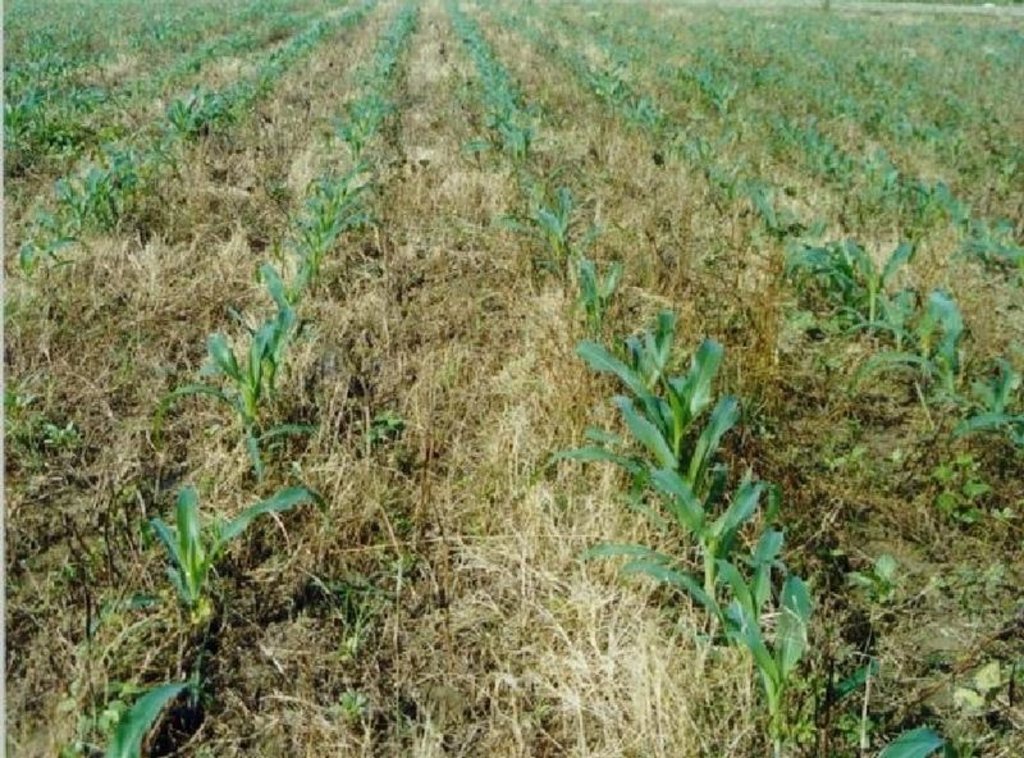
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residues, rice stubbles
Remarks: crop residues serve as mulching materials once killed by POWER herbicide
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: application of POWER herbicide 7-10 days after irrigation
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.00
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour vouluntarily and paid | ha | 1.0 | 147.6 | 147.6 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | post harvest | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seed | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | BIO-N | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | man person days | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | marketing: transportation | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | marketing: packaging | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 541.2 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st side dressing, Release of trichogramma | จัดการพืช | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 2. | 2nd side dressing, Off-barring and hilling-up | จัดการพืช | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 3. | Detasseling | จัดการพืช | late vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 4. | Spray POWER herbicide, Planting | จัดการพืช | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Retouch application of POWER herbicide, Replanting | จัดการพืช | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: plow, harrow, hand tractor
Per hectare of land
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Land cultivation- zero tillage offset the costs incurred during land preparation. Labor costs for hand tractor and carabao-drawn plows are substituted by costs of spraying POWER herbicide which is significantly less expensive
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
450.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landfroms: Area has generally flat topography located along wide plains.
Slopes: Small isoloated areas have slope of 0-2%
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture is medium andtextural analysis of samples show that the soils are silt loam.
Soil feritlity is low and the areas have high potential soil salinity problem.
The soil water storage has a capcity of 53.66% to 77.53% .
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 15% of the land.
5% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, plumbing, business, offer of labor services to neighbors
Market orientation of production system: mixed (subsistence and commercia (Corn)l: Sold to feed millers, surplus is kept for next cropping.
Level of mechanisation: Rich farmers can afford to rent trators but Carabao-drawn plow is still dominant among averaged income farmers.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
2-5 ha also common but lowest ranked
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
input constraints
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10
หลังจาก SLM:
2
การอัดแน่นของดิน
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil fertility
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
300 households
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
300 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Multinational company such as Monsanto Philippines, Inc. Continuously disseminate the technology through promotion of POWER herbicide
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| Increase soil water storage |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Labios, R.V. Et al. 200-2002," Conservation Tillage Practices in Corn Production After Rice: A Case in San Jose, Mindoro Occidenta"l. Pamhplet published by UPLB, DA-BAR, and National Corn RDE Network. P33
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Labios, R.V., Robles, A.Y., Javier, P.A., Garcia, M.U., Gonzales, P.G., Luis, E.M., Labios, J.D., Medina, C.M., Valencia, G.Z., Tamisin, L.L., Ocampo, E.P. Jr., Miciano, D.M. 1999. Annual Report. Enhancing Adaptation and Utilization of Location Sp
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Manalo, J.O. 2000. Tipid Saka Technology. Monsanto Philippines, Inc. 7th Floor Ayala Life FGU Center, Madrigal Business Park, Alabang, Muntinlupa City.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล