Water-conservation technology at cultivation of the cotton in south. K [คาซัคสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
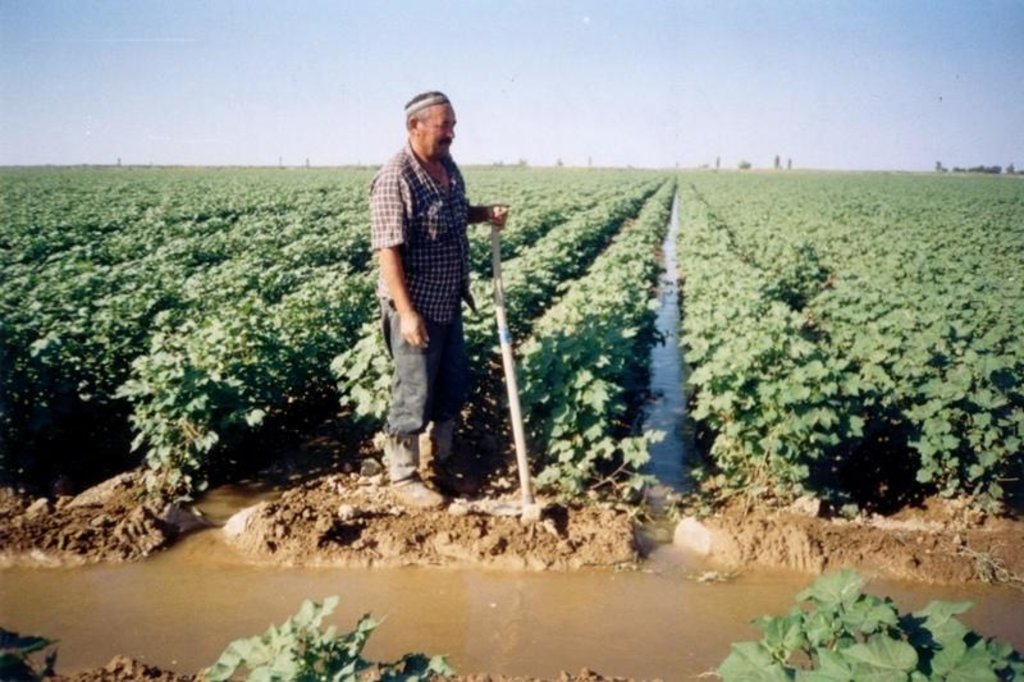
Watering through furrow
technologies_1091 - คาซัคสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Vyshepolsky Frank
คาซัคสถาน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Khe Tatyana
kniv@nursat.kz
Taraz city
คาซัคสถาน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mukhamedzhanov Khamit
Scientific Production Center for Water management
12 Koigeldy str
คาซัคสถาน
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan (MoA) - เอริเทรีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
30/09/2003
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The technology of watering through furrow reduces the settlement (recommended) sizes of irrigating norms up to 30% keeps soil fertility
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
It is applied for watering on furrow at ploughed cultures.
It is intended for decrease in irrigating norms and preservation of fertility of soils.
The technology of watering through furrow
-Does not result in change of zone system of agriculture
-Provides pass of soil-cultivating technique on dry furrow therefore are reduced the rates of soil condensation
-Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration shed from the irrigated grounds evaporation
-Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms (recommended) up to 30%
-Reduces loading to drainage system up to 30%
-Slows down the rates of development of erosive processes and keeps soil fertility
-Raises productivity of cultivated cultures at deficiency of water
-Improves ecological conditions due to reduction of drainage shed of water for limits of irrigated files
-Does not demand additional expenses for its introduction
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
คาซัคสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Southern Kazakhstan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Basin of Syrdarya
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Caused (provocative) waterings for reception of shoots at drying up of soil in a zone of an arrangement of seeds.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- Reduce amount of irrigation water
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major cash crop: Cotton

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water resources management. Reduction of technological losses of irrigating water at its transportation from water-fence up to fields of an irrigation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Technologies of the water-conservation, reduction of norms of entering of mineral fertilizers, increase in soil fertility. Normalization of water-submission on cultures and soil-meliorative conditions.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), breaking compacted topsoil, pits, deep tillage / double digging
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: phospho-gypsum
Remarks: 4t/hec
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: tillage through grooves
Pits
Remarks: breaking compacted soil
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: by cultivator
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.50
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 650.0 | 650.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Polyethylene film | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 745.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage | จัดการพืช | between / weekly |
| 2. | entering of phospho-gypsum | จัดการพืช | watering / once a year in the autumn |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
ถ้าเป็นไปได้ให้แจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนการบำรุงรักษาตารางข้างล่างดังต่อไปนี้ ให้ชี้ระบุลงไปถึงปัจจัยการผลิตและค่าใช้จ่ายต่อปัจจัยการผลิต ถ้าคุณไม่สามารถแจกแจงรายละเอียดต้นทุนได้ ให้ทำการประมาณค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดในการบำรุงรักษา:
3.0
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Tillage and appliyng phospho-gypsum | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Polyethylene film | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 125.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
For arrangement of 1 ha width of furrow makes 100 meters, quantity of furrow makes 50
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Arrangement of furrows its cutting and reinforcing of the bottom of furrow
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
235.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Growing pirriod 4-5 months
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Valley of the Syrdarya river . Foothill plains of a ridge of the Karatau
Slopes on average: Flat for valley landforms for foothill plains
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium (Alluvial gray soils) - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium for alluvial meadow soils and poor for light gray soils
Soil water storage capacity is low for alluvial meadow soils and very low for light gray soils
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are rich and own 50% of the land.
19% of the land users are average wealthy and own 39% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 1% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Due to pasturable live stock and cultivation of gourds
Market orientation of production system:Mixed for grain-crops, grasses and commercial orientation for cotton
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for ploughing, chasing and harvesting and mechanised for tillage interrow cultivation
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
expenses on water
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil fertility
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The area of flooding at the end of a field is reduced 3-4 times
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Dump of drainage waters is reduced up to 2 times
norms of entering of mineral fertilizers
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to decrease of washing out nutrients
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
850 households in an area of 40km2 (10-50 persons per km2)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
850 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The existing system of water-subdivision does not provide for water consume on demand of farmers within the limits of allocated limit but establishes sequence of watering. At present water-subdivision the farmers who watering on furrows an create, additional stocks of a moisture and so the watering technology through furrows has not received universal application
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Improves working conditions of labours and work of soil-cultivating technics |
| Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms |
| Raises productivity of agriculture at deficiency of wate |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration, evaporations, shed from fields of on irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Till progressive method od an irrigation drop, rain |
| Reduces intensity of soil condensation and development of denitrify processes |
| Reduces loading to drainage system and rates of pollution of water sources |
| Prevents degradation of the irrigated soils |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Increase in expenses for interrow processing | Application of soil cultivating technics |
| Increase in quantity of watering | Reinforcing furrows by pipes |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Reduction of the interwatering period | By increase in volume of use of subsoil waters to subirrigation |
| Increase in interrow processing | Regime of subsoil water management |
| Increase in cost the current expenses at watering and interrow processing | Increase in productivity of cultivated cultures |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Reports: Technology of an irrigation on the farm site in zone of Arys-Turkestan channal. 2000-2002 year.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
SPC for Water management
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Recommendations on stabilization of agriculture in a zone of Arys-Turkestan channal
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล