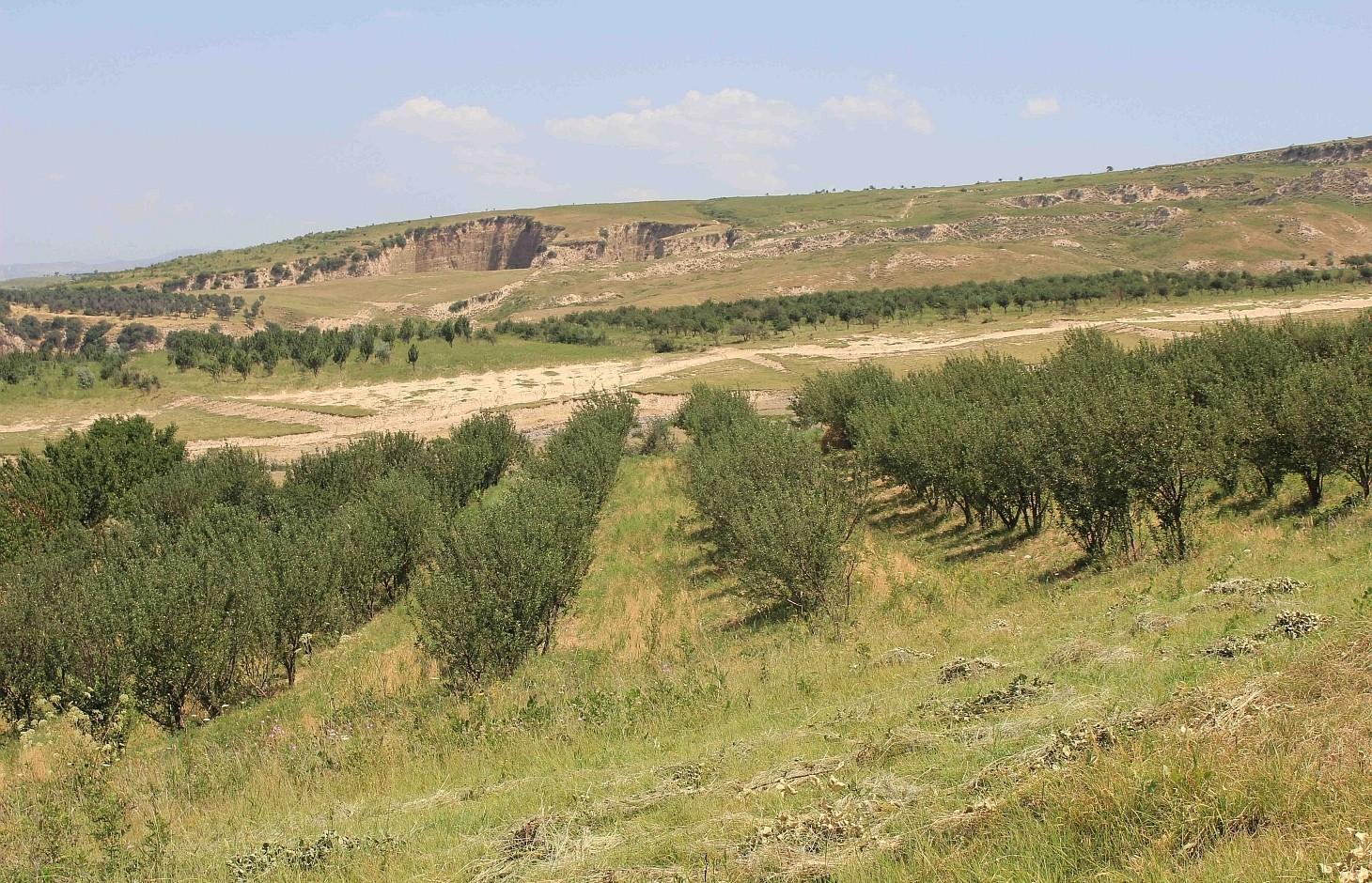
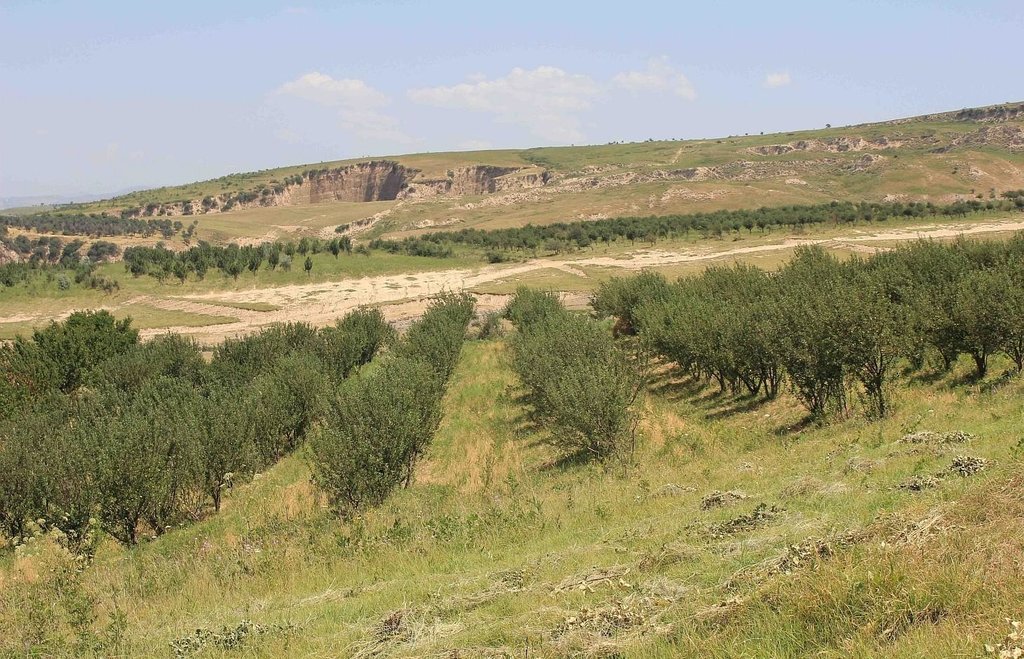
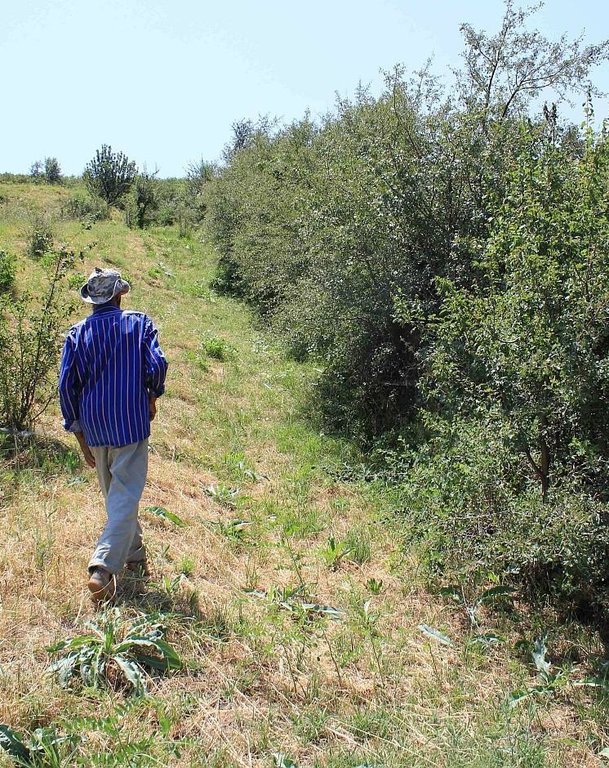
Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Malgorzata Conder
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano
Bog
technologies_1128 - ทาจิกิสถาน
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 28 ธันวาคม 2016 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 31 พฤษภาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 2 มิถุนายน 2017 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 4 สิงหาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
09/07/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Orchard based agroforestry established on the hill slopes of Muminabad
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Between 1993 and 94 an individual farmer initiated an orchard by planting a mix of fruit trees, such as apricots, walnuts, cherries, almonds and mostly apple trees in the rainfed hill zones of Muminabad District.
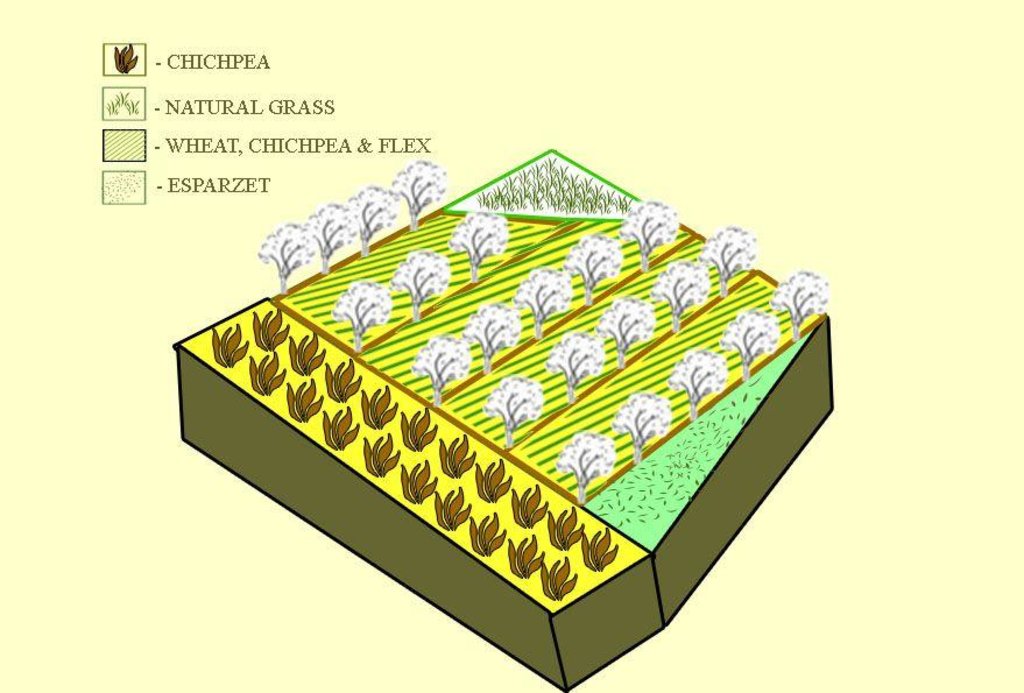
In the first couple of years 416 newly planted seedlings were watered manually: water was brought by trucks near to the plot and distributed to the seedlings with buckets. The orchard was established on the existing grazing land and therefore the seedlings had to be secured with a fence from livestock grazing nearby. First hard wire was used for fencing. Simultaneously, hawthorns (Dulona in Tajik) were planted along the fence in order to provide even stronger protection and establish a live fence for the future. Now, the fruit trees are fully-grown and fruits can be harvested every year. The farmer prunes trees annually, which is the key for fruit production. The farmer pointed out that in rainfed areas soils contain less nutrients and usually big trees do not produce high yield. Furthermore, pruned tree branches are used as firewood. The farmer also applies the pesticides B52 and B58, three times a year in the months of April, May and June. The total area of the plot is 1.03 hectares, whereof 0.60 hectares are orchard; Esparcet is covering roughly 0.30 hectares, 0.07 hectare is for haymaking and the rest of the 0.06 hectares is used for growing chickpea and wheat. There is also a road for machinery to pass and to turn around when plowing the land.
Purpose of the Technology: Shortly after the fall of the Soviet Union, the government officials distributed land to the villagers. The farmer always had a big interest to establish a small orchard and he obtained little more than a hectare of land. It is his project for retirement. He and his family worked hard throughout the establishment phase. They experimented by planting a variety of vegetables including melons and watermelons. The wild animals ate many of the vegetables and melons, what resulted in the farmer's idea of intercropping Esparcet.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: According to the farmer, the first two years were very labor intensive and crucial to establish the orchard. He also had to face a challenge posed by the community, as overnight people from the nearby villages stole roughly 100 of his newly planted seedlings. This is one of the reasons why the farmer had to plant hawthorn in order to establish a live fence. In summary: The establishment phase included planting of young seedlings; manually watering for the first two years; plowing in between the tree rows by machinery; building a fence around the plot and planting/sowing hawthorns. Maintenance activities consist of the following activities: planting new seedlings; pruning of existing trees; grafting new sorts of trees, plowing by tractor in between the tree rows annually; chickpea and wheat cultivation; application of chemical pesticides three times a year. For cutting wheat, the farmer gets support from his son and friends. Every day, he goes to his orchard, which is located at a distance of more than 1.5km from his house. When this technology was documented he was about to build a small clay hut in his orchard.
It should be noted that the terrace structure was not implemented at once, but over the years tilling in between the tree rows along the contour lines formed terrace shaped rows.
The structure of terraces has been built over the years by tilling in between tree rows along the contour lines.
Natural / human environment: Muminabad is situated in the southwest of Tajikistan (Khatlon Province) and its hills are covered by loessial soil. Winter temperatures are low and the amount of precipitation is high. Summers are very hot and dry. The growing season lasts from March/ April to September/ October.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muminabad
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion by water, heavy rainfalls, absence of vegetative cover on the hill slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water, extensive grazing, gully erosion.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/oct
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 m2.
1.03 ha in total, whereof 0.6 ha is orchard
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Extensive grazing led to a reduction of soil cover, which is the major source of erosion), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Removal of trees left the soil unprotected against precipitation and extreme weather events), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees were cut as firewood for fuel consumption), overgrazing, land tenure (Land abandonment after Soviet collapse), governance / institutional (Lacking istitutional support)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More extreme rainfall events), floods (As a result of extreme events there are more floods in the region)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The fenced plot is mainly used for the orchard intercropped with chickpea, flax and wheat. Esparcet and grass for haymaking covers only a small part of the plot. The part on the left handside is also used to turn the tractor when ploughing, which is why this part is affected by soil erosion and rills. The whole property is fenced by hawthorns (dulona). The orchard has a terrace-like structure due to annual plowing by tractor.
Location: Sarmaydon 2. Muminabad
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 416
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, apricot, pear, cherry
Other species: intercropped with chickpea and wheat
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Somoni
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
4.83
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
12.40
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging a deep barrier for protection around the plot with a bulldozer, 1 day | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once (1993) |
| 2. | Plowing in between the rows by tractor, labor, petrol and rent for one day | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once (1993) |
| 3. | Planting fruit trees, 3 days by 3 persons (3-5 Somoni per seedling, 3 Som/ seedling planting) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once (1993) |
| 4. | Watering young seedlings for the first couple of years by truck (60 TJS per truck) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | one day a week/ 50 times a year |
| 5. | Construction of fence with hard wire and haw thorn (approx. 320m) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once |
| 6. | Buying and replanting of 100 stolen fruit seedlings | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | 1.0 | 2777.6 | 2777.6 | 100.0 | |
| แรงงาน | machine hours | 1.0 | 136.7 | 136.7 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | petrol | l | 1.0 | 22.8 | 22.8 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | hard wire and pillars | m | 1.0 | 465.8 | 465.8 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seedlings | pc | 1.0 | 320.5 | 320.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3723.4 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor ploughing, labor, petrol and rent, 1-2 hours, 2 persons | ด้วยวิธีพืช | spring, once a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around trees, 5-6 days, 3-4 persons | ด้วยวิธีพืช | spring, once a year |
| 3. | Pruning of the approx. 400 fruit trees (3 TJS per tree) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every year |
| 4. | Bringing water from village and watering (40 liters a day,20l on each donkey, 3 h for walking and watering) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every day |
| 5. | Applying pesticides, 1 person, 7 days (5 hours per day) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Three times a year: April, May, June |
| 6. | Sowing wheat and chickpea (1 person, 2 hours) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | spring, once a year |
| 7. | Cutting wheat and chickpea (2 persons, 4 hours) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | autumn, once |
| 8. | Harvesting fruit trees (3.6 TJS per fruit tree) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | autumn, once a year |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 4493.5 | 4493.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | petrol | l | 1.0 | 38.0 | 38.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | pesticides | l | 1.0 | 77.5 | 77.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seeds | pc | 1.0 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4625.5 | |||||
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The technology was established during the Soviet Union and most of the expenses were calculated on the price basis of that time. If technology is priced by current prices, the total sum would be very high and no farmer would be able to afford. Thus, current prices were not identified. Nowadays, machinery cost, buying hard wire for fencing and buying seedlings would be the most costly factors.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After 6 years income is very comparable to the establishment cost
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
98% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Cost of the technology is very expensive, which discourages farmers to implement orchards based agroforestry.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Grafting trees especially apple and pear trees on native hawthorns is an affordable and sustainable way of creating orchards in semi-arid areas with rainfed agriculture. Hawthorn is a plant adjusted to dry areas with strong and deep roots, which endures the hot summer months. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tree nursery workshops and educational programmes about local species through seed associations |
|
Intercropping wheat, chickpea, flax and Esparcet in between the tree rows gives an extra economic incentive and also improves land productivity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge raising, inspection of those good practices by other farmers |
| Haymaking with natural grass and Esparcet provide the farmer with an opportunity to produce hay for the winter months for his livestock, so that he does not need to purchase it from the market at high costs. |
| The farmer practices pruning on a regular basis to keep the trees in good shape for better fruit production, but also to have sufficient fire wood for the winter months. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Compared to other plots with orchards there is almost no soil erosion which is mainly due to good land management practices, e.g. the slow building up of terraces. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustain the practice of contour ploughing |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It is expensive to establish such orchards nowadays, because of the high cost for purchasing seedlings and hiring other machinery. | See comment below |
| Growing new seedlings and grafting trees is a cheaper way of establishing a new orchard, but it is not commonly practiced among the farmers in the region. | There should be a tree nursery workshop in order to raise awareness among the young generation of farmers. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Since the orchard is located in a rainfed area, hot summer months make the technology vulnerable to drought. To some extent the technology is tolerant to dryer summers, but maybe not for prolonged droughts (e.g. two successive drought). |
The farmer has suggested that grafting fruit trees on native hawthorn (dulona) trees has potential for farmers when establishing orchards in rainfed areas. In extreme events (extremely dry years), the farmer brings water for supplementary irrigation from his house by donkey. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล