Ficus Natalensis Agroforestry System [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wilson Bamwerinde
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Okusimba emituba n'ebimera
technologies_1153 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Lubega Emmanuel
Rakai district
ยูกันดา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
05/12/2013
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Community development appraoch [ยูกันดา]
The approach involves the community and other development partners identifying opportunities, challenges and appropriate solutions through collective action.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wilson Bamwerinde
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Ficus natalensis based agroforestry system protects crops on windy hill slopes facing Lake Victoria and reduce runoff towards the meandering Kagera River Valley.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
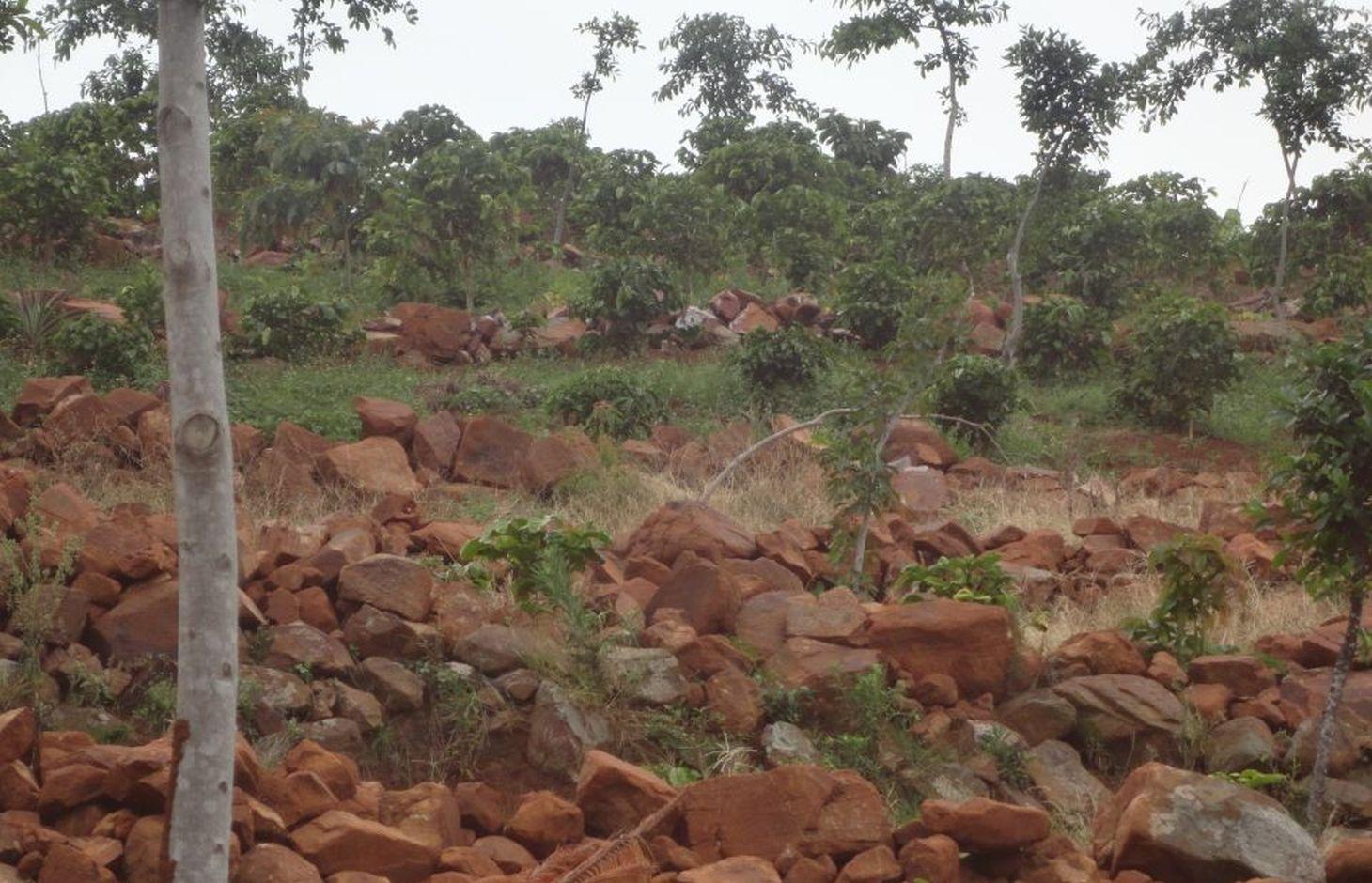
คำอธิบาย:
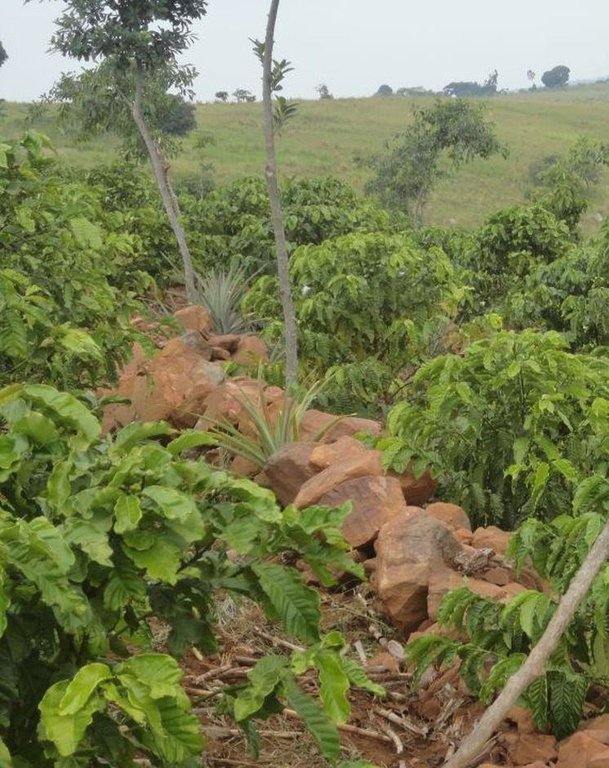
Ficus natalensis is traditionally scattered in crop fields as a land management practice in central and south-western Uganda. The improved technology designed through community participation involves planting lines of Ficus natalensis along the contour at an interval that enables the tree to provide shade to young crops without depriving them of sunshine. When planted together with coffee trees or in banana plantations, the tall Ficus tree forms the top storey that protects the crop from the hot sun.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Ficus based agroforestry is to protect the soil from erosion. Within 3 to 5 years the Ficus tree forms a deep root system that stabilizes the soil. In addition, it drops leaves which quickly decay to provide both soil cover and manure thereby increasing the fertility of the soil. The trees provide firewood, fodder for livestock and bark cloth which can be used domestically or sold to supplement household income. They also act as wind breaks.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Ficus Natalensis is propagated using cuttings from young branches which are planted vertically 6 m apart along a contour. Propagation material is readily available and cheap, making the technology inexpensive to establish. Any annual or perennial crop can be inter-cropped with Ficus spp. provided the tree canopy is managed well. The tree is quite robust and can attain heights of over 20m, with a very extensive canopy if left to grow. Pruning raises its canopy to the desired height above the ground. In its early stages, fencing is required to protect the tree from damage by livestock. Within 12 to 18 months, however, the tree is established enough to withstand browsing. Only simple tools like hoes and garden forks for digging holes/pits are essential for establishment of the technology. The implementation of the technology on steep slopes (> 50%) is not possible without other supportive SLM interventions, in Rakai these include construction of stone lines and mulch application.
Natural / human environment: The pruned branches of Ficus natalensis are used as fuel wood when dry. Therefore scarcity of fuel wood may lead to over-harvesting of branches and destroying the canopy. Nonetheless, the tree regenerates quickly with the coming of the rains. Ficus tree can live for a hundred years.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Uganda
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Rakai District (Kijonjo Parish)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.96681 31.69066; -0.96706 31.69111; -0.96717 31.69033; -0.96757 31.69038; -0.96774 31.69073
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Agroforestry is a traditional practice but was reintroduced in a better structured, systematic form by organizations like VI-Agroforestry and Kagera TAMP.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop tree and shrub cropping: Coffee
Major food crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Banana
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize and beans

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Major cash crop: Coffee
Major food crop: Bananas
Major other crop: Ficus Spp.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe deforestation as trees were cut down for firewood, charcoal, timber and for agricultural use;
Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Prolonged dry weather, destructive rainstorms and declining soil fertility
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Agro-forestry is used in combination with banana and coffee growing.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to December
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 m2.
The technology is becoming dominant in Kijonjo parish and other parts of Rakai district especially due to climatic changes that have led to shorter rainy seasons. However, farmers also recognize its potential for soil conservation.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A6: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: mulching (supp.
Specification of other structural measures: stone lines (supp.
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of conservation measures), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Over cultivation), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting trees for timber and opening up more agricultural land), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Cutting trees for fuel wood and charcoal), poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep and very steep slopes)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
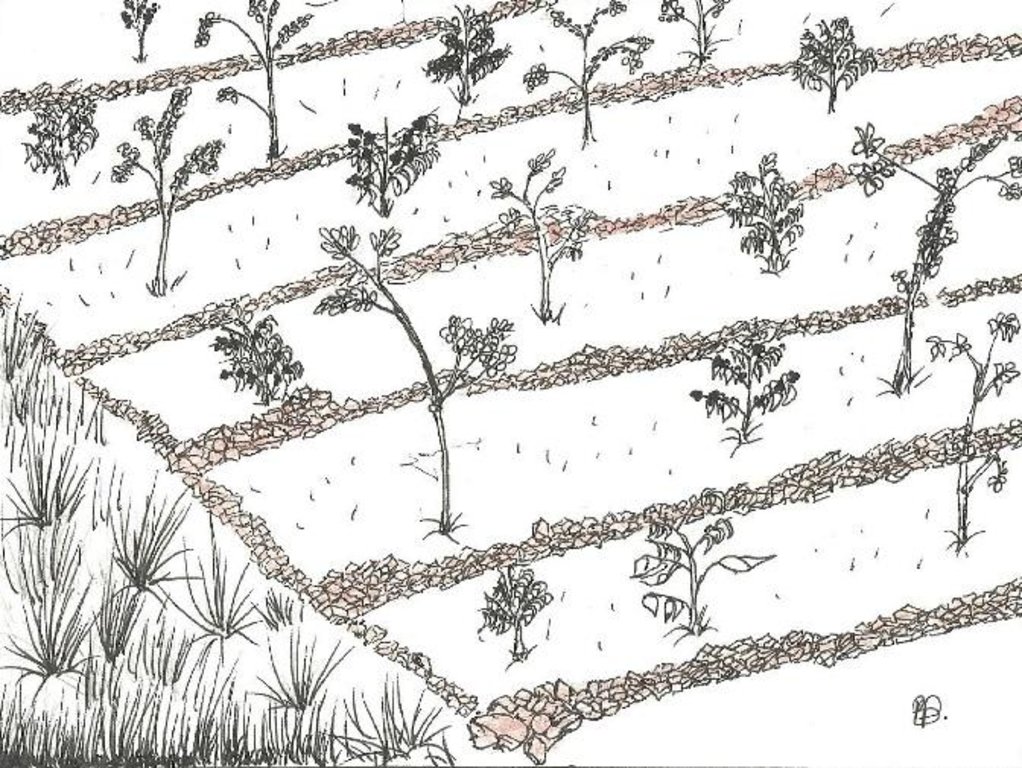
A diagram showing Ficus spp. trees planted to provide shade to coffee trees.
Location: Kijonjo B. village. Rakai
Date: 2013-12-05
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge of which trees will do well with the crops to be cultivated)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Land user dedication and a little guidance is enough for the implementation of the technology.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 20m
Trees/ shrubs species: Ficus natalensis (also serves as perennial fodder), planted in the field using stem cuttings
Perennial crops species: Robusta coffee planted using seedlings bought from specialized nurseries
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35%
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Ushs
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
2500.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sourcing planting materials | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Beginning of rains |
| 2. | Making pits | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Beginning of rains |
| 3. | Planting cuttings | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Wet season |
| 4. | Spot weeding | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Wet season |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Sourcing planting materials | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Making pits | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting cuttings | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Spot weeding | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 2 panga | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | 2 hoes | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Cuttings (500 stern cuttings) | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 122.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Spot weeding | ด้วยวิธีพืช | twice a year |
| 2. | Pruning | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Wet season |
| 3. | Removing and processing the bark into bark cloth | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Once in 2 years |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Spot weeding | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Pruning | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Removing and processing the bark into bark cloth | ha | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | 1 panga | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | 1 hoe | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 38.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: The technology only requires simple tools like hoes and pangas.
The costs were calculated for wind breaks and optimum canopy after establishment. Calculations were done in December 2013, considering activities of the previous (September-November) wet season.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The most important factor affecting cost is labor to transport the bulky stem cuttings to the site. However, Ficus Natalensis is easy to establish and is durable (over 100 years) depending on management. It is extremely hardy and when it grows to 50cm to 100cm stem diameter it can be used for timber or to make dugout canoes. Establishment costs are easily recovered.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The area receives two rainy seasons (March-May & September-December)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. The area lies at the equator.
The area has a dry and a wet season, but other factors influencing its weather include proximity to Lake Victoria and the Kagera River.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l (1269-1310m a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, while technology is good for all kind of slope, the description given here is for a steep slope) and hilly (ranked 2)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1) and very shallow (ranked 2). The technology has also adopted to moderate to deep soils to support root development of trees.
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, 70% of the soil in the area is sandy) and medium (ranked 2, 20% of the soil is loamy)
Soil fertility: Medium
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (the organic matter is medium but has improved with agroforestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (soils are manly sandy)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (soils are predominantly sandy)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: 5-50 m (The technology does best in soils with ground table of 5-50m to enable root developement)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, there is no surface water in dry season) and medium (ranked 2, some, in the wet season)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, from unprotected source in swamps)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
While the surrounding valleys below are swampy and very rich in biodiversity, only a fraction remains at the slopes due to destruction of habitats.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
21% of the land users are rich and own 57% of the land (Business men.).
63% of the land users are average wealthy and own 34% of the land (Teachers).
16% of the land users are poor and own 9% of the land (orphans and widows.).
Off-farm income specification: There is a difference in income levels between those who have implemented the technology and those who have not.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (only manual labour is used-casual labourers)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, most produce is for home consumption only surplus is sold) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Ranked 1: 0.5-1 ha. For most average income families.
Ranked 2: <0.5-1ha. For the poor.
Ranekd 3: 1-2 ha. For the rich households.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most land users have access to untittled land and have open access to water.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
100
หลังจาก SLM:
400
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
coffee and bananas
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
For wood fuel (firewood & charcoal). there was almost nothing before.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
conservation of moisture, improved soil fertility
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Agricultural land on which Ficus is planted
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
respondents reported increses in income but not documented.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Realization of the benefits has led many farmers to need more help therefore raising the cost of labour
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
incresed agricultural produce.
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
backcloth is used for cultural functions .eg. burying the dead.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology has improved availability of both food and fuel wood. Some products from trees used in agroforestry such as backcloth (Embugo - Luganda) are sold, diversifying household income.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
dried tree leaves add humus and organic matter in the soil.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
various tree species are used for agroforestry.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Prevention of predisposition towards landslides
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
windbreaks reduced wind velocity.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Risk of lightening strikes
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs for both establishment and maintenance are a small fraction of the benefits accruing from the technology.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
8
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
8 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There is spontaneous adoption of the technology as it builds on traditional farming practices in the area.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: High demand for shade-grown coffee and bananas in addition to the highly valued bark cloth used in art and crafts has increased farmer appreciation.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Ficus is used to provide backcloth that is sold for the making of Art and crafts and for cultural functions. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Management to accelerate healing of the bark within a shorter period should be investigated |
|
Trees shield crops from dangerous storms /rains and intense sunshine. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage the spread of the canopy |
|
Ficus is good and attractive to birds and insects How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provision of material support in form of seedlings, farm tools for accelerated multiplication |
|
Ficus natalensis leaves are cut and fed to livestock like goats. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage indeginous trees and growing fodder crops such as calliandra and nappier grass |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Demand for wood fuel is high How can they be sustained / enhanced? Local bye laws should be enacted to control deforestation and encourage tree growing |
|
It improves soil fertility-Ficus natalensis sheds leaves once every year, adding to soil humus. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More guidance should be given to the farmers for sustained spontaneous adoption of the technology |
|
It checks the speed of wind thereby protecting crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other agricultural, ecological and social benefits could be explored in this scenic area facing the Kagera River where it enters Lake Victoria |
|
Stakes made from the Ficus branches can be used to grow climbing plants eg. passion fruits, yams as well as climbing beans How can they be sustained / enhanced? More tree planting should be encouraged |
|
Prevents soil erosion by checking raindrop splash, speed and amount of surface runoff and stabilizes the soil. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Because the ficus tree takes time to establish, other technologies such as trenches and grass strips could be used to reinforce it |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The trees can hinder crops from light if canopy is dense | Prune periodically to enable other crops access to light |
| Some trees can fall especially during heavy and stormy rains, damaging plants and animals. | cutting excessive branches to reduce the load borne by trees. |
| Trees can attract lightening ,which destroys plants and animals. | Avoid putting animals under tall trees. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Some tree species especially with short roots , compete with crops for nutrients. | Planting tree species with deep roots to avoid competition for nutrients. |
| It is a home for weaver birds and caterpillars. | Use scarecrows and biological control. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Community development appraoch [ยูกันดา]
The approach involves the community and other development partners identifying opportunities, challenges and appropriate solutions through collective action.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wilson Bamwerinde
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล