Mulching [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Paul Kahiga
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Mulching
technologies_1318 - เคนยา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenia
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenia
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
P.O.Box, 62000-00200, Nairobi, Juja, Kenia
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Wamuongo Jane
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Karanja Andrew
+254 729 054547
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
เคนยา
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - เคนยาชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
09/02/2011
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Mulching is done by covering the soil surface between crop rows, around trees (mostly fruit and orchard) or vegetables with cut grass, crop residues, straw or other plant material in order to retain soil moisture, prevent or suppress weed growth and enhance soil structure.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
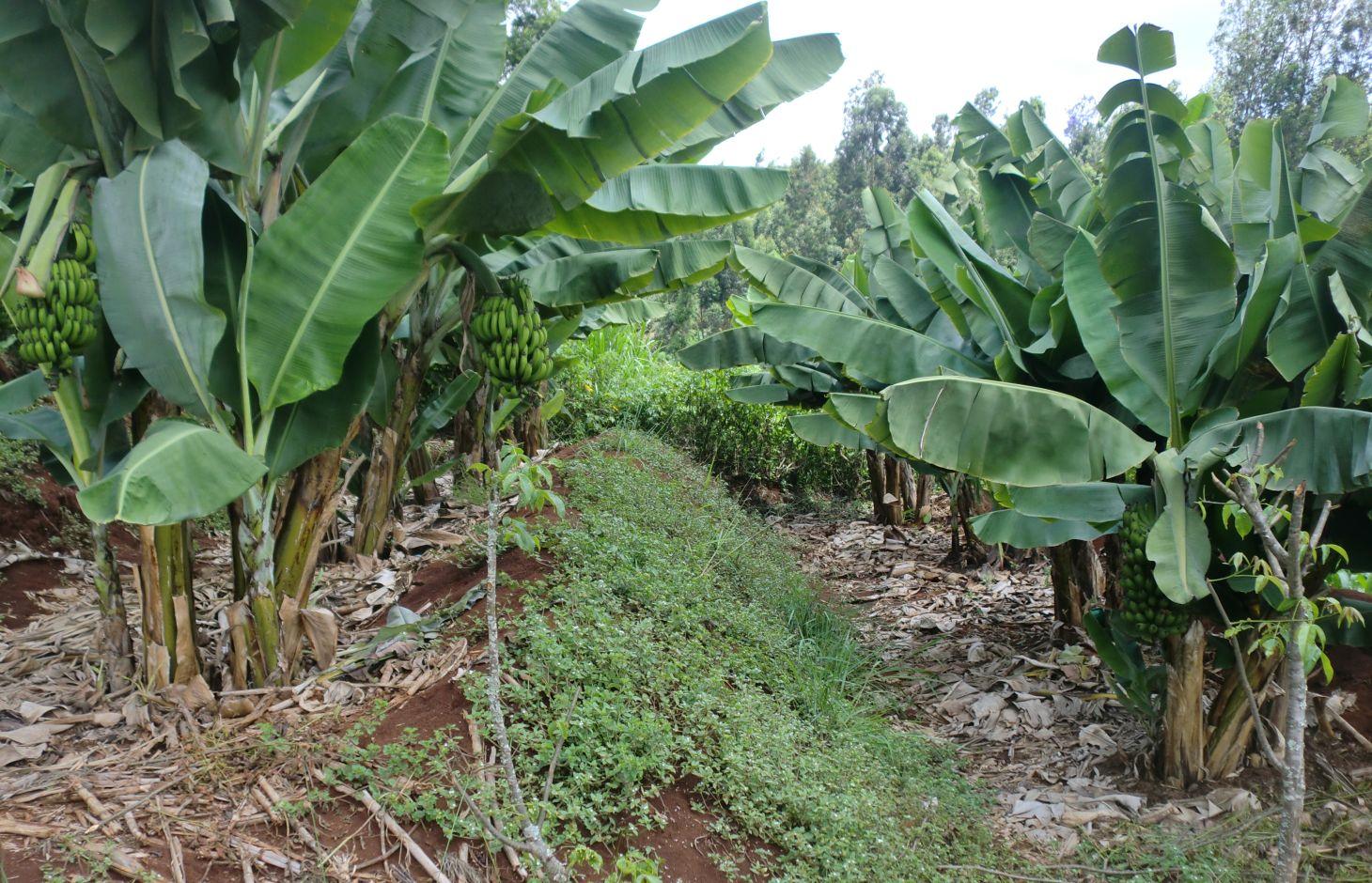
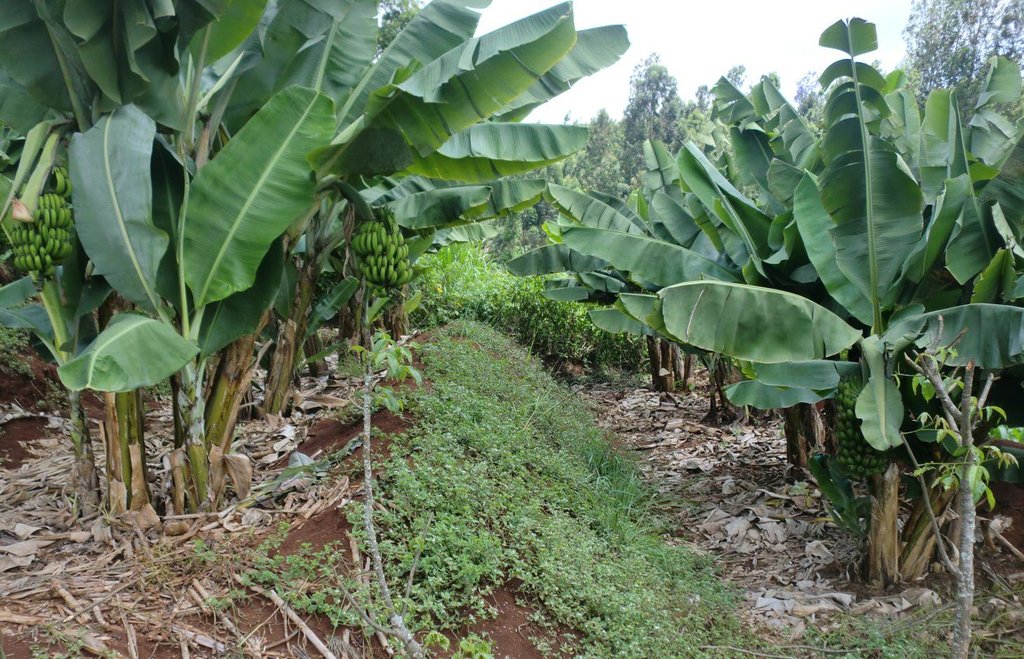
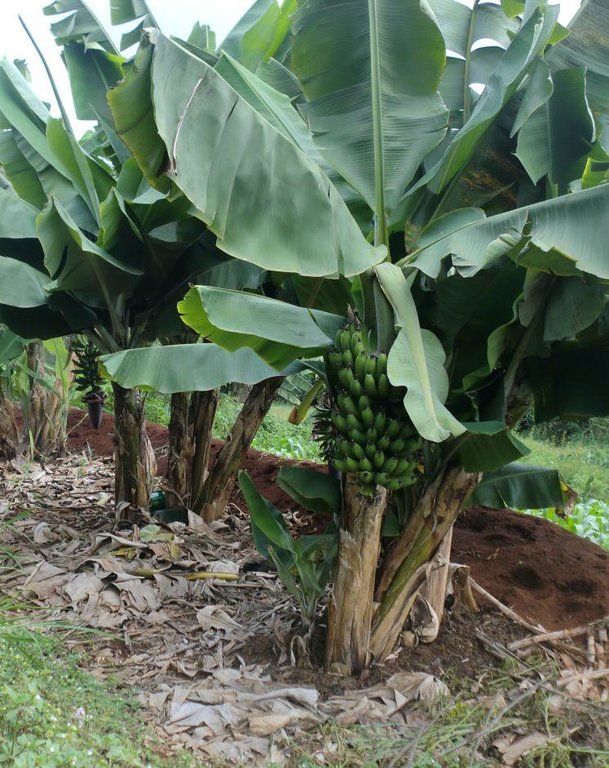
A layer of crop residues, cut grass, straw or other plant material is spread on the soil surface between crop rows or around the vegetables or orchard trees in order to retain the soil moisture by limiting evaporation, prevents weed growth and enhances soil structure. Farmers in the Upper Tana Catchment mostly uses crop residues as mulch especially after the harvesting season. Banana leaves in Embu county are used as mulch on banana plants.
Purpose of the Technology: Mulching is mostly used in the Upper Tana Catchment to retain soil moisture by limiting evaporation, it also prevents weed growth and enhances soil structure. It is commonly used in areas that are mostly affected by drought and weed infestation. In Embu District, mulch on banana plantations is supplemented with farm yard manure as shown in the photographs above. The most readily available source of mulching materials is banana leaves themselves even though other type of mulch materials are also in use. Some farmers use the these leaves both as mulch and as livestock feeds during the drought seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The mulch layer is rougher than the surface of the soil and thus inhibits runoff. The layer of plant material protects the soil from splash erosion and limits the formation of soil crust. It is worth to note that the choice of mulch depends on locally available materials. In alley-cropping systems, hedgerow biomass is often used as mulch. Another strategy is to leave crop residues, such as maize stalks on the ground after harvesting. Mulch can be spread on a seedbed or around planting holes. Large pieces of crop residues should be cut into smaller pieces before spreading on the soil's surface. There are many advantages of using mulch which include, increase of soil moisture, reduction of excessive evaporation from the soil surface, suppression of weeds which further reduces labour cost of weeding. Mulching reduces high fluctuations in soil temperature, which means improved conditions for microorganisms in the soil. It also increases soil organic matter and thereby improves soil structure. Mulch protects the soil against splash erosion and runoff. The disadvantages of mulch includes the following; unavailability of suitable materials for mulch, some seeds of mulch might germinate and become weed problem. If crop residues are used as mulch it might mean a loss of animal fodder. Especially in the drier parts of Mbeere district, dry mulch has been reported as fire hazard. Sometimes it is difficult to spread mulch on steep slopes and it can also be a possible habitat for pests and diseases.
Natural / human environment: Areas with limited rainfall usually respond very well to mulching. Mulching is not applicable in wet conditions however, the soils should have good drainage.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Eastern Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Embu North District
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop: Coffee
Major food crop: Bananas, maize and vegetables
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, weed infestation and excessive evaporation in the farm lands
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low soil fertility and excessive evaporation of soil moisture
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180, Longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most of the farmers use mulch from their crop residuals
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The technical drawing on the left shows banana trees planted on benches. Fodder grass that is used to feed livestock is planted to stabilize the slopes. FYM is first spread at the base and latter covered with mulch made from the banana leaves.
Location: Embu North. Eastern Province
Date: 06/09/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: Banana leaves
Quantity/ density: 2
Remarks: mulch is spread on the surface surrounding the banana trees
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farmyard Manure
Quantity/ density: 1
Remarks: Farm yard manure is first applied around the banana tree then the mulch is spread over
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Kshs.
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
100.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
400.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Apply banana leaves and FYM | จัดการพืช |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Lifespan of the leaves: 1 year
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 70.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting the banana leaves and applying FYM | จัดการพืช | one in every six months |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cutting the banana leaves and applying FYM | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 19.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Pangas to cut the leaves, shovels and wheels barrows to carry the FYM
number of mulched banana plants
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour and availability of mulch determines the cost of the technology
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: no
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Few farmers have shops/kiosks that they use to supplement their income other than farming
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It has contributed to soil erosion control through improved ground cover, reduction of splash by rain drops. Improved soil fertility and moisture content of the top soil and increase of yield.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Rats and squeals can hide in the mulch before decomposition
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Addition of FYM before the mulch enhances retaining of moisture
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After decomposition, the rich organic matter and nutrients remains in the soil for long time.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Crop materials for mulch are available on site i.e banana leaves |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Mulch in banana plantations is generally easy to be established and to maintain. |
| Mulch in banana plantations reduces rain drop's splashing energy thus reduces loss of top soil which could occur due to splash of the rain drops. |
| After sometime, the mulch materials eventually rots and becomes manure thus improving soil organic matter |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Habours termites and pests before complete decomposition. | Use of biodegradable insecticides incase of infestation of termites and other pests. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| In absence of other supplemental materials, mulch in banana plantations requires regular replacement due to continuous decomposition. | supplementing of the banana leaves with other crop residues. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล