Reduced livestock numbers [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Christian Wirz
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1343 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Sahdullo
Karsang 1
ทาจิกิสถาน
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
20/08/2008
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
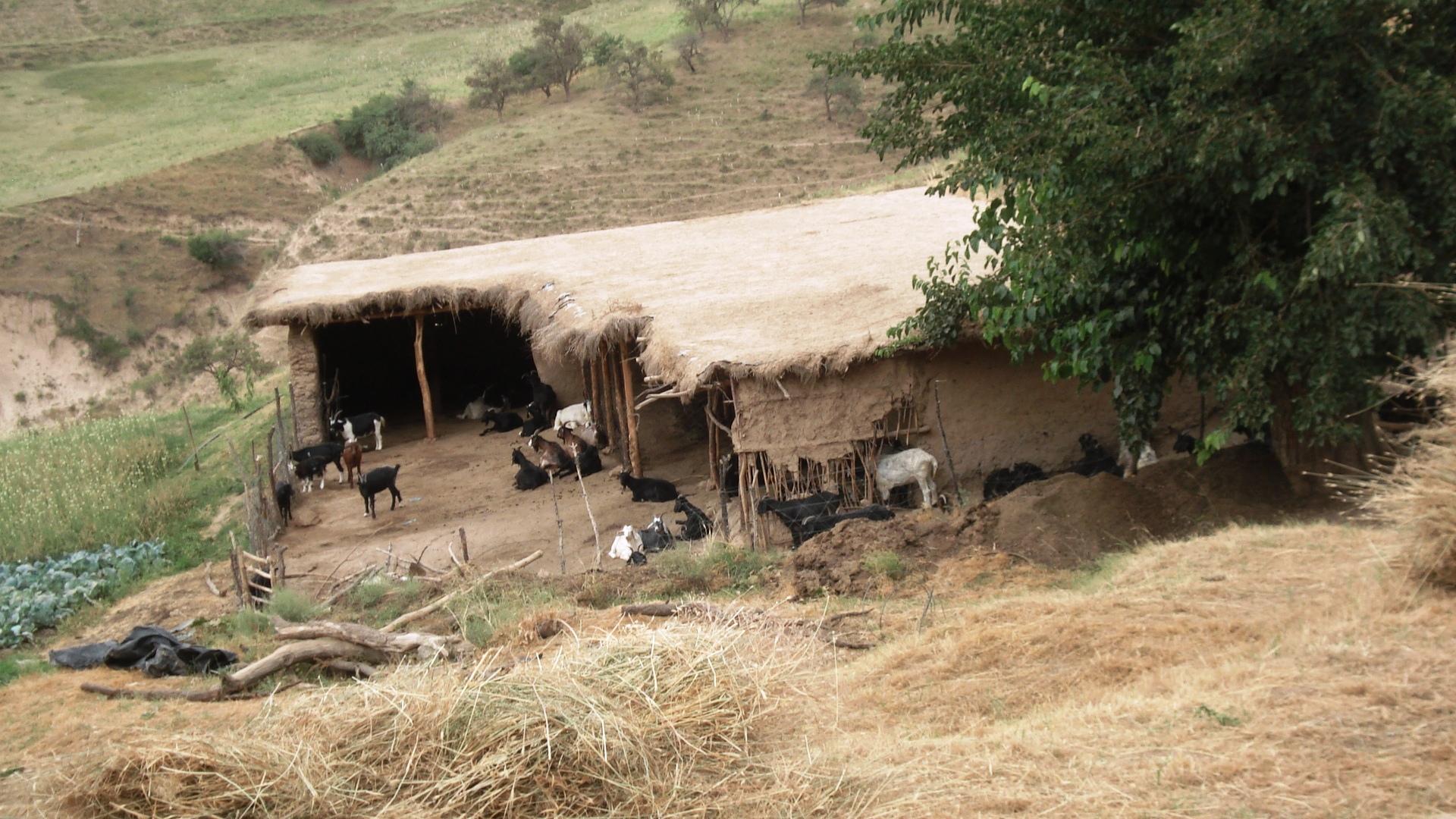
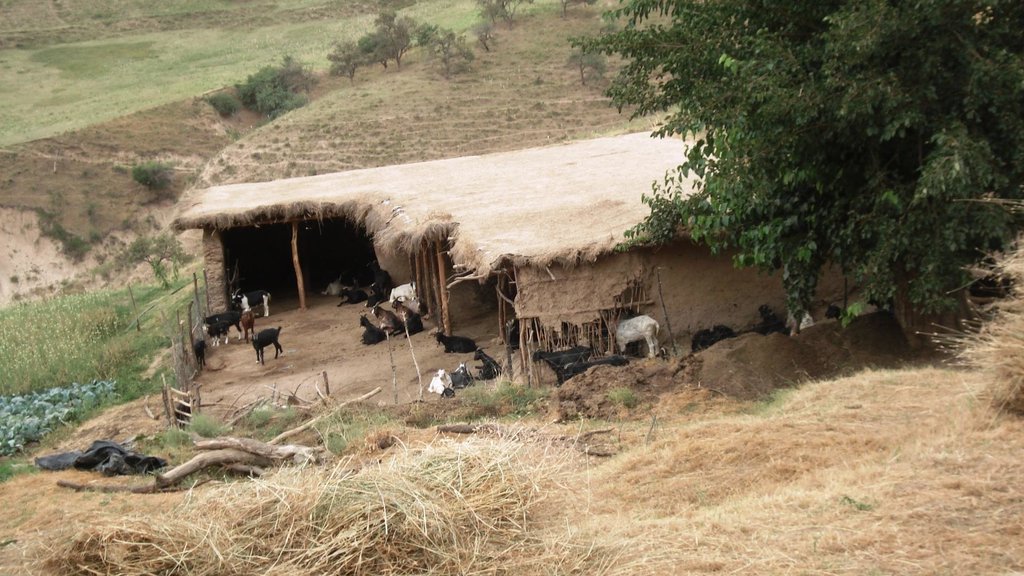
The grasslands are used as pastures by a reduced number of livestock belonging to an individual land user.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
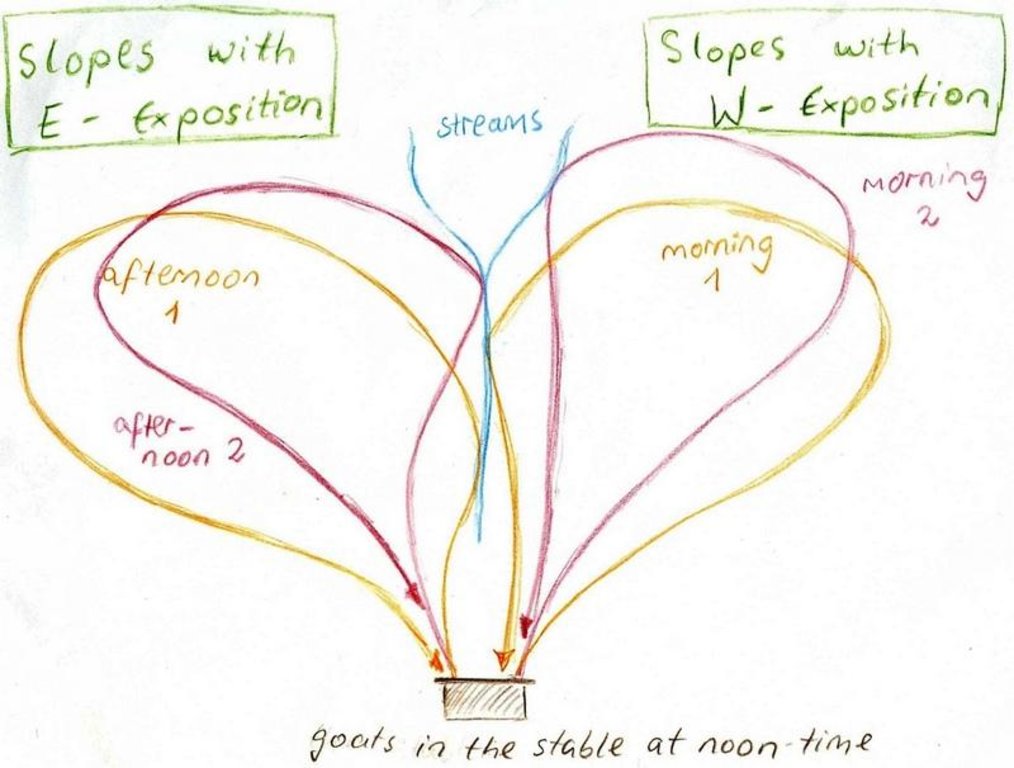
The around 50 goats are brought to the pastures early in the morning and will be brought back to their stable from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. After this, they will be accompanied to the pastures again. In the morning the west-exposed and in the afternoon the east-exposed pastures are visited. The same rotational scheme is applied over the whole year, which means that the same pastures are visited daily. The pastures are exclusively used by the land user fror more than the half of the year (from autumn to spring). In summer the pastures are also used by the village herd of the nearby village (Karsang). Herding is mostly the task of the land user's sons but sometimes he will accompany the animals by himself. Cows are let out on the pastures in the morning and come back in the evening by themselves.
Purpose of the Technology: The reason for west-facing grazing in the morning and east-facing in the evening is that grass is moist at these times of day. This is also why at noontime animals are not on the pastures. The animals are led slowly by the herder as to not tire them, to make them fatter and to avoid damages on vegetation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: No special pasture maintenance activities are undertaken.
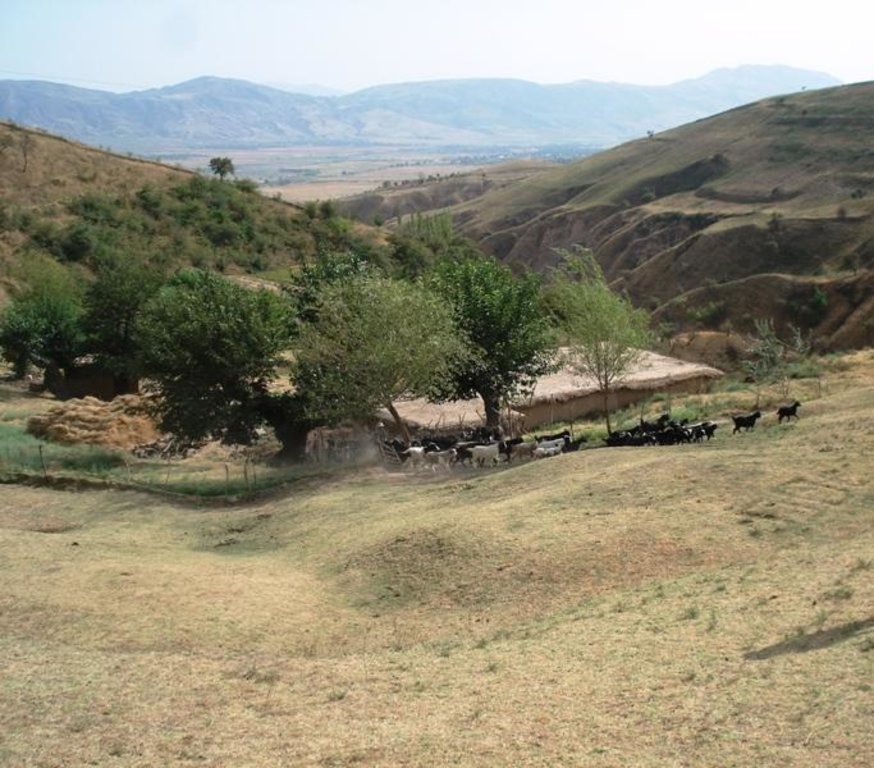
Natural / human environment: The area is around one hour away from the village which actually controls the pastures (communal pastures). In addition snow lies longer in spring than further down. This means that the village herd only comes here from late spring to late summer, which decreases the pressure on the pastures. Together with the situation in a small depression that protects from high radiation in summer this contributes to the generally better pasture quality (greener, more grasses) compared with the village pastures in proximity to the villages. An important factor contributing to the generally good conservation state are the reduced livestock numbers. They are only reduced because the land user is close to these more distant pastures and the village is quite far away.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Region of Republican Subordination
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The land user has rented land for the establishment of a self-sufficient agropastoral system after independence (early 1990ies). A part of the area was used as cropland when there was still a village (in the middle of the 20th century) whereas other parts of the land were also used as pastures.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Goats, cows
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Especially in the places where animals pass regularly and where they stay for longer times physical degradation of soils (compaction, crusting) together with the degradation of vegetation (cover and biomass) are major problems. In addition, low fertility is also a problem for vegetation growth.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water erosion problems associated with wood chopping. And trees wood be very important for climate regulation.
Ranching: Goats, cows
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Nov
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.5 m2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Big herds passing daily), other human induced causes (specify) (Inappropriate soils used for grazing), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional (Incapacity of government to implement soil conservation.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Daily rotation on pastures of the village Karsang.
Location: Above Naobad. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user developed his own rotational scheme.)
Technical knowledge required for herders (sons and grandsons of land user): low (They just need to apply the scheme.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Reduced livestock numbers
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Somoni
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
3.42
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying livestock | ด้วยการจัดการ | Reduced livestock numbers |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อื่น ๆ | Buying livestock | Goats | 50.0 | 87.7 | 4385.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4385.0 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herding | ด้วยการจัดการ | Daily |
| 2. | Giving salt to livestock | ด้วยการจัดการ | Twice per week |
| 3. | Fodder for livestock | ด้วยการจัดการ | In winter |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Herding daily | days | 365.0 | |||
| อื่น ๆ | Salt for animals | for one year | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Fooder for livestock | winter | 1.0 | |||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 12.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The only effective costs mentioned by the land user is salt for animals. Other inputs - be it labour or winter forage - does not have to be paid, respectively bought.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour input is decisive: As long as work is done by family members costs are restricted on alimentation. If external labour is hired, wages have to be added.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Mainly medium, but also low
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: Mostly no groundwater, since very hilly.
Water quality (untreated): Good source water, since no diarrhae after drinking it.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Many medical plants
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are implied in housework, whereas men are working as herders, because of traditions.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: The land user only depends on the rented land, cultivated together with his two sons and their families.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The household has much more grazing land than average village households.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Pastures are in theory used by village communities, but enforcement of rotational grazing in remote ares is difficult. These pastures are therefore something between communal and open access pastures. The water is used by the land user without any restrictions.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
His animals yield higher prices on the market than average livestock.
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The productive success of the land user lets him appear richer than the rest of the village.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Having a big herd on a big pasture area is a guarantee for better self-sufficiency.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Especially in the establishment phase there was jealousy about the success, especially in fruit-production.
Livelihood and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Especially biomass is reduced by daily grazing.
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Especially the proportion of grasses is higher compared with other village pastures
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
On the long term benefits of animal husbandry might be slightly reduced due to damages on vegetation (and soils) by the own and by the animals of the village herd.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The only land user with this form of management known is the one interviewsd
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: This form of management combines an exceptional personal spirit of innovation and financial means to lease land as to establish a self-sufficient system in the hills. It is also necessary to have a truck and / or car to transport goods to the market and to stay in touch with the rest of the family in the village, since it is too small to offer space to all the household members.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Self-sufficiency is the main success for him. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It requires high labour inputs and motivation, which for the land user are necessary to have success in the post-USSR setting. |
| The animals yield a higher price because they are fatter than the other animals. |
| The geographic location is clearly an advantage, because the land user is far away from the negative impact of village herds. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
At the same time quite positive for soil and water conservation and productive in terms of meat and sold livestock. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land user could rent (parts of the) pastures the interest of planting trees as a measure of rehabilitation would increase. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Trees cannot recover because of constant grazing. | Only if the land user is sure that investments will profit him, that is if land tenure is clarified, will he invest into active conservation measures. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Especially at the crossing-points of the land user's herd with the village herd degradation phenomena (trampling paths) are visible. | By an agreement between the village (land commitee) and the land user the land use could be reglemented clearer. |
| This form of land use is difficult to maintain for young people who want to participate in social life. And it is not sustainable because it does not permit allvillagers to practice such forms of herding that require much land. | The land user should be able to rent a part of the pastures (smaller than the actually grazed 50 ha) where he would be need to conserve soils and vegetation (for instance. by tree-planting or more sophisticated rotation. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล