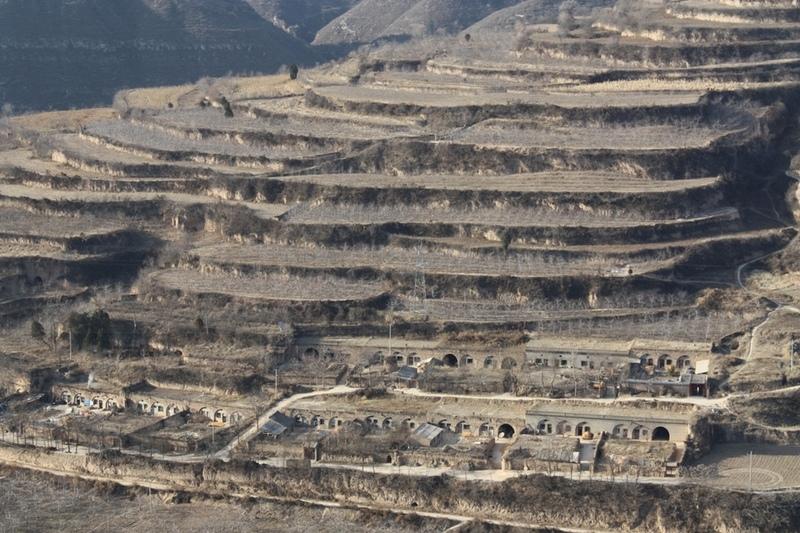
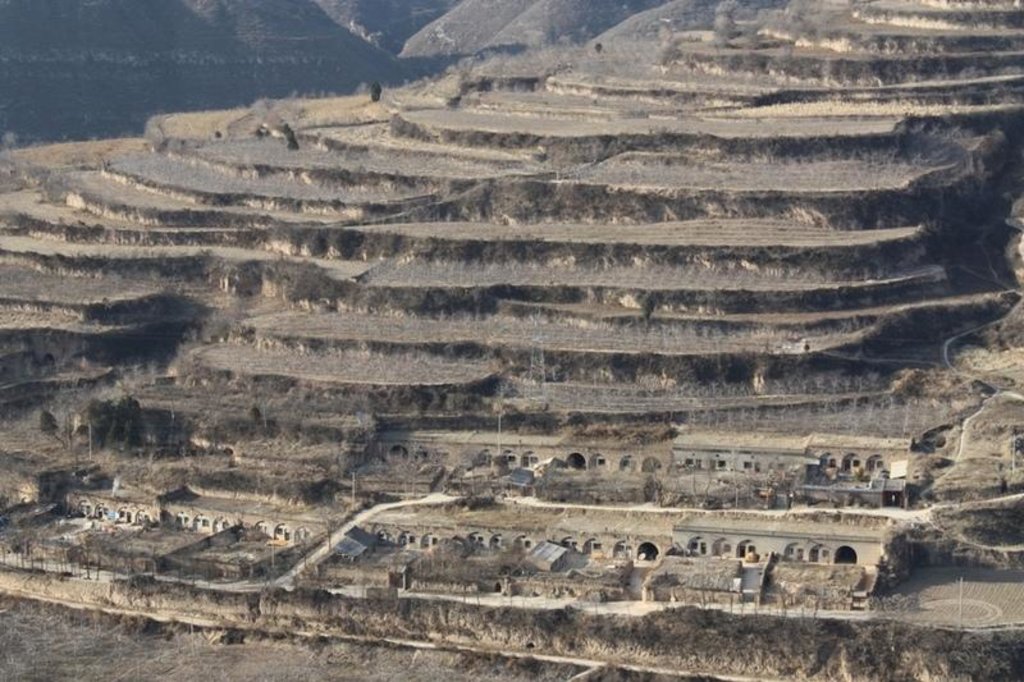
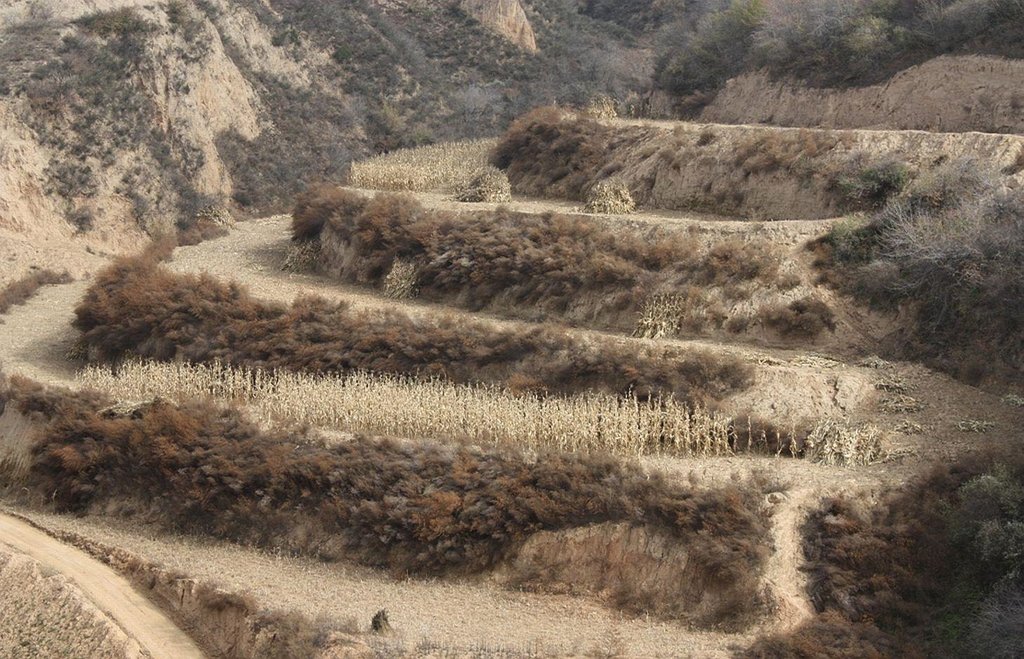
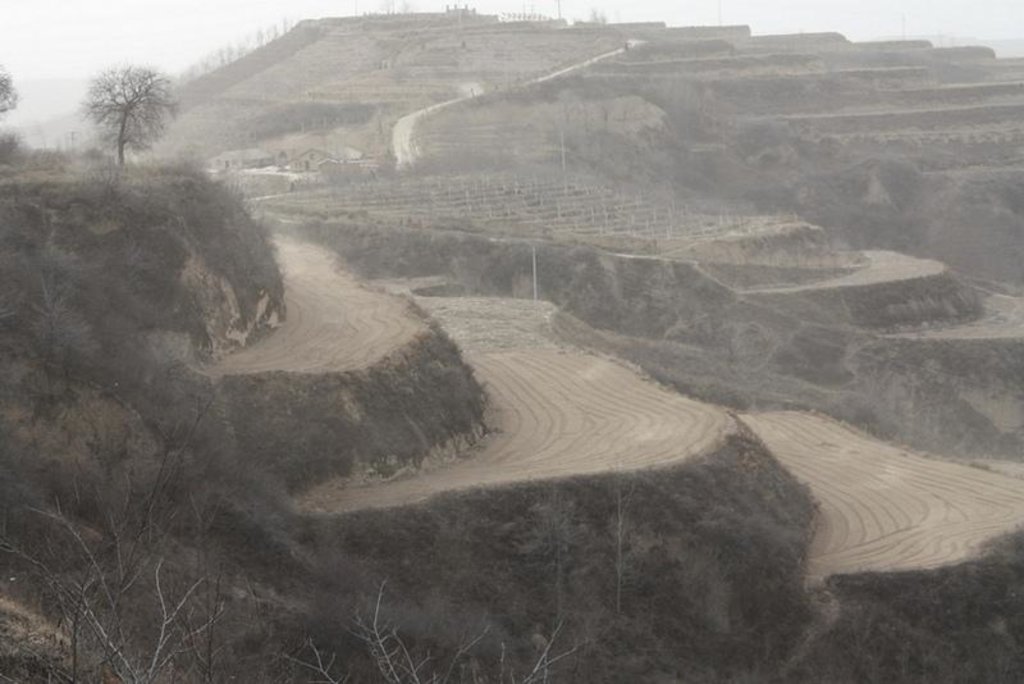
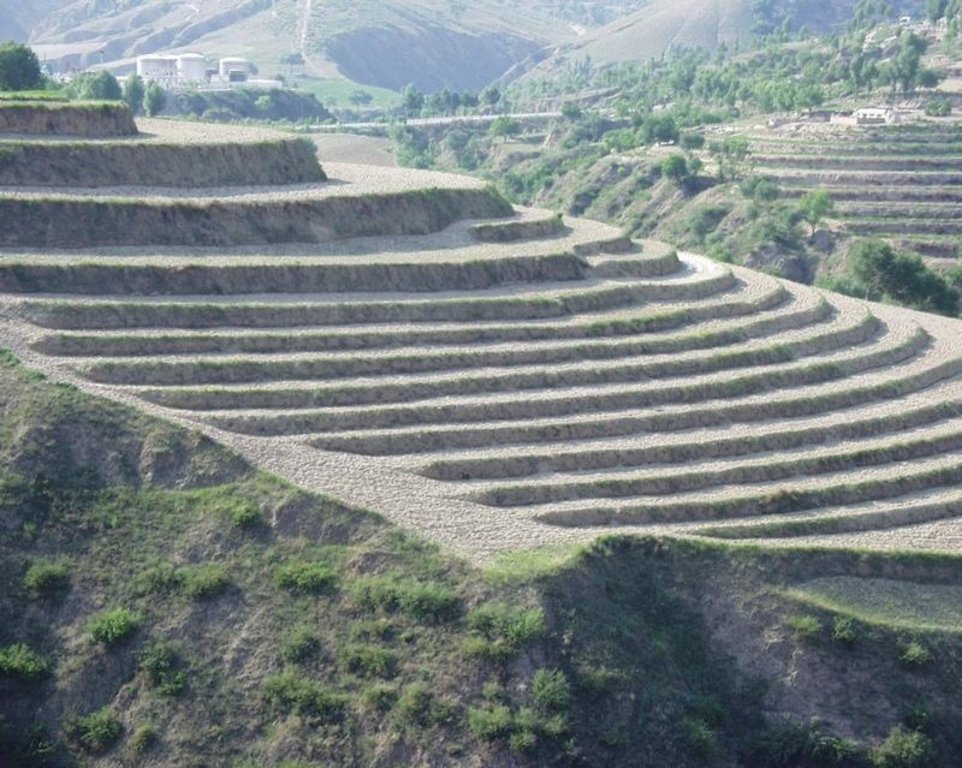
Bench terraces on loess soil [จีน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Fei WANG
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
土坎梯田,梯地
technologies_1445 - จีน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
20/01/2009
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
A Terrace is a structural SLM practice with a raised flat platform built on the slope to reduce soil loss and runoff on the slope, increase the rainfall infiltration and yield.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
A terrace is a leveled section of a hilly cultivated area, designed as a method of soil conservation to slow or prevent the rapid surface runoff and erosion of topsoil. Often such land is formed into multiple terraces, giving a stepped appearance.
Purpose of the Technology: To change the landform for better agricultural condition of operation of tillage and harvasting, reduction of soil erosion and water loss and finally for higher production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The building of a terrace in the loess plateau takes long because loess is very soft and deep and the severe soil erosion and shortage of water in agriculture hinders the process, as well. Previously, terraces were constructed by hand. These terraces weres narrow and damaged by the great storms. Now, the machinery is used to build wide terrace with high bank size in the loess plateau. The establishment of terrace needs a lot of money but it is a long-term investment. The maintenance of terrace is considerable economic because the major efforts are the annually improvment of terrace bunds .
Natural / human environment: The soil erosion is very severe because of the cohesionless loess soil and very intensive rainfall storms in the summer and autumn that would destroy the land surface into broken hilly area. Terrace is a kind of measure to resolve it combining with crops. The human activities here is very intensive because they must plant on the slopes that would make the soil erosion greater.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
จีน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Shaanxi Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Yanhe River Basin
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The terrace in this site has been formed since 1994 with machinery. The land is quite wide and large enough for agriculture in the hilly loess region,
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Main cash crops: Beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
Main food crops: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crops: vegetable
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water losses are alarming in this region. The loose loess, steep slopes, and intensive storms in the summer and autumn, accelerates this process. Aditionally, the lack of rainfall negatively impacts agriculture and vegatation. Sediment deposition could increase the river bed and diminish capacity of reservoirs. On one hand side floods occur frequently because of fast and large runoff and on other hand side sedimentation in rivers reduce their water carring capacity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The low yield of crops and the low income from land is more important for the local people. It is necessary to improve the agricultural conditions. The land, especially the tableland and gentle slope land could be convert into terrace.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The composation of agriculture is very simple here.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 253.3 m2.
The total area with different measures is till to 2000. Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is seriously broken by cutting gullies induced by water erosion. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (The natural vegetation in this region is grass on theslope and trees on the gully and alluvial land. After the destroy of natural, the soil loss increases greatly.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (About 70% of annual rainfall is in the summer and autumn. The storm is very intensive.), population pressure (The population density account for 71 capita per square km.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (The rainfall varies greatly in different year and different seasons. The drought happened frenquently.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
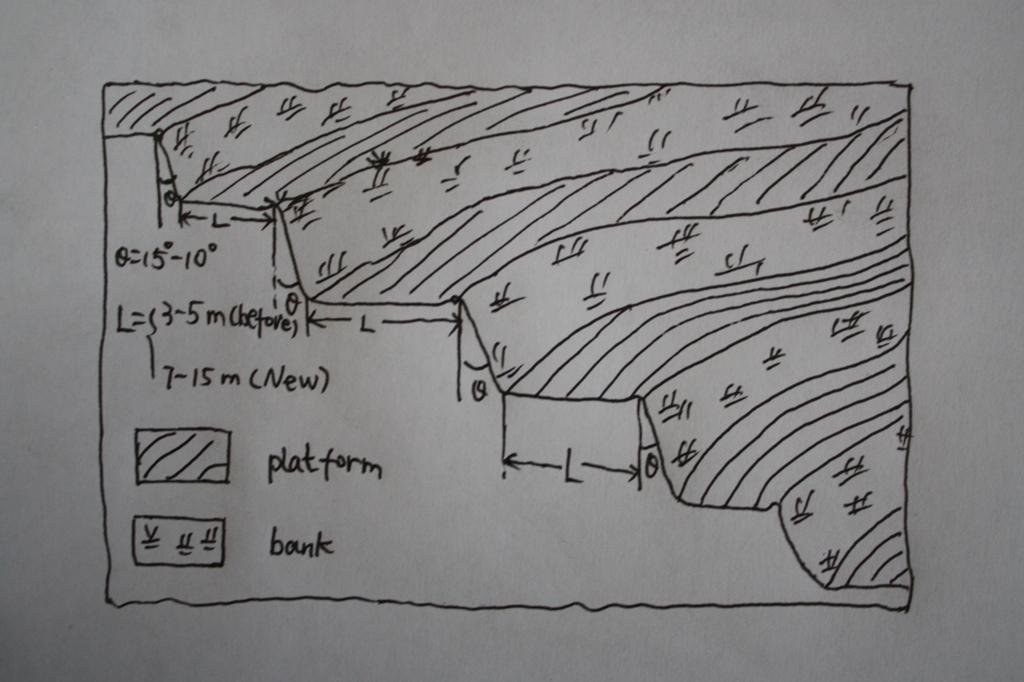
The brief structure of terrace in the Yanhe River Basin.
Location: Zhifanggou Watershed. Ansai County, Shaanxi, China
Date: 2008-12-15
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The location selection and how to build a good terrace need special knowledge on soil engineering.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is easy to know the benefit for all the local farmers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 50000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Grass species: Natural grass to protect the bank of terrace.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-100
Construction material (earth): The terrace in the Loess Plateau are used local soil/earth directly.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 30-60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Wild grassland or range land before mostly. Some time the cropland on the slope.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The labor is less intensive on the plain platform.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
0.83
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
8.8
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and design | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before construction |
| 2. | Move the topsoil to other place | ด้วยการจัดการ | 1st step of construction |
| 3. | Built the platform and bank with soil digged | ด้วยการจัดการ | 2nd step of construction |
| 4. | Backcover the topsoil on the surface of platform | ด้วยการจัดการ | 3rd step of construction |
| 5. | Check and accept the terrace | ด้วยการจัดการ | After the terrace finished |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Survey and design | Person/day | 45.0 | 8.8 | 396.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Building terraces (machine price included) | Person/day | 75.0 | 19.0 | 1425.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1821.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce the bank | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | annually |
| 2. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | annually |
| 3. | Build the edge in some terraces | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | annually |
| 4. | Reinforce the bank | ด้วยการจัดการ | annually |
| 5. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | ด้วยการจัดการ | annually |
| 6. | Build the edge in some terraces | ด้วยการจัดการ | annually |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Keep Terraces in shape | Person/day | 30.0 | 8.8 | 264.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 264.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Crawl dozer and small traditional hand tool., crawler tractor, spade
In general condition, slope and soil, in the middle reaches of Yan River Basin. The prices of labour-day and Machine-hour are around 2005.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The terrace on the steep slope need more input for more soil and earth should be moved. It is the most important factor.The soil depth is not so important for the deep soil layer here.The cost of labour increases greatly in the last several years and the cost of construction of terrace increased.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms also: mountain slopes and hill slopes
Slopes on average also very steep
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm.
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM.
Topsoil organic matter: The average Top-SOM of cropland is about 0.05%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration of Loess is very fast, but it is prone to sealing when flashing.
Soil water storage capacity low: It is easy to evaporation and drainage.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region.
Availability of surface water also poor/none: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal river.
Ground water table: It depends on the landform. In valley and alluvial land, it is shallow.
Water quality: Good quality for there are few pollution sources.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
It is very stable in this region.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy (The terrace are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national subsidy.).
Off-farm income specification: The yield of terrace is much high and stable.
Level of mechanization manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand, even the tillage on the nerrow terrace
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly in the wider terrace.
Market orientation mixed subsistence/ commercial: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
According to 0.054 ha per capita.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Like other rural area in China.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
600
หลังจาก SLM:
2200
การผลิตสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
43.9
หลังจาก SLM:
120
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
Livelihoods and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Evaporation form the wall of terrace, Especially for the narrow terrace
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More inflitration of rainfall, but the evaporation near to the wall increases
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10000t/km^
หลังจาก SLM:
2000t/km^2
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Loess is very prone to erosion and extreme storms would destory the bank of terrace. In the study site sesonal rainfall increased and the loess terrace could retain more soil water and reduce the runoff.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The yield of terrace is stable and relative higher. The income from terrace is high and the maintain cost is low.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
100 households
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Most land farmers have some terrace. I do not know the exact number of land user families who adopted the technology.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: the old narrow terraces, now a very small area left, are build voluntarily.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nearly all the people know the benefit of terrace. the benefits of terraces are very good for crops and orchards are high enough in this region.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Increase yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the terrace is maintained well, the water condition would be better than that on the slope land even in dry year with low precipitation. |
|
Convenient to till and harvest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tillage and harvesting is much easier on the plain flat land than on the slope. The maintainance of terrace is important. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Reduce soil erosion on the slope. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The loess soil is prone to erosion because of its loose character induced by fine sand content and low soil organic matter. The plain flat makes the dispersion and transportation of soil particls difficult. |
|
Reduce runoff and increase the soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? The runoff generation is smaller on the plain than on the slope. Slow movement of surface water lead to more soil infiltration. |
|
Increase yield. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water is the limit factor in the loess plateau. The yield would increase if there is enough water available. |
|
Decrease flood risk. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is a kind of off-site benefits because less runoff generation and gentle process of runoff decrease flooding. Reduction of sediment also diminish flood risk because the drainage capacity of channel and adjusting capacity of reservior increase when sedimentation decrease. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The output is also low in contrast with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The total and net income is too low because the area of terrace per capita is very small. |
| The income is relative compared with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The net income is low because the labour costs are increasing, and the total income because labour cost and very small area of terrace per capita. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| There is possible damage of terraces because the loess is very loosen and prone to collapse. | Keep upmaintaining the bank and land well. |
| Decrease runoff of lower stream. | No way to overcome it, but it also could decrease the risk of floods. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of ISWC, CAS
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The soil and agriculture of the Loess Plateau. 1989. Zhu Xianmo, Agriculture Press, Beijing City, China
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of ISWC, CAS
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Statistical tearbook of Yan'an. 2003. Compiled by Editorial Board of Statistical tearbook of Yan'an
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of ISWC, CAS
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Impact of human activities on runoff and sediment change of Yanhe River based on the periods divided by sediment concentration. 2008. WANG Fei , MU Xing-min ,JIAO Ju-ying, LI Rui. Journal of Sediment Research
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Changes of soil erosion intensity due to conversion of farmland to forest and grassland in Yanhe River. 2007. BasinWang Bangwen, yang Qinke, Liu Zhihong, Meng Qingxiang, Science of Soil and Water Conservation
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล