Sunken streambed structure [อินเดีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: David Gandhi
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
DOH
technologies_1471 - อินเดีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Agrawal VK
danidain@mantrafreenet.com / pmdanida@sancharnet.in
Comprehensive Watershed Development Project
22 Pratap Nagar, RATLAM – 457 001, MP, India
อินเดีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
28/09/2002
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Comprehensive watershed development [อินเดีย]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- ผู้รวบรวม: David Gandhi
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Excavations in streambeds to provide temporary storage of runoff, increasing water yields from shallow wells for supplementary irrigation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
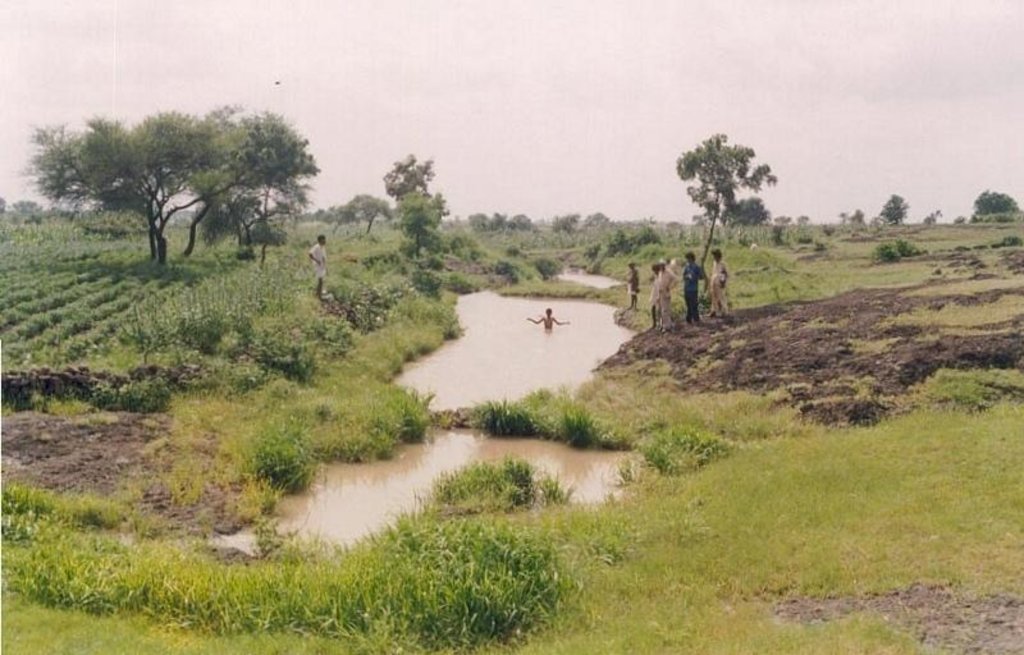
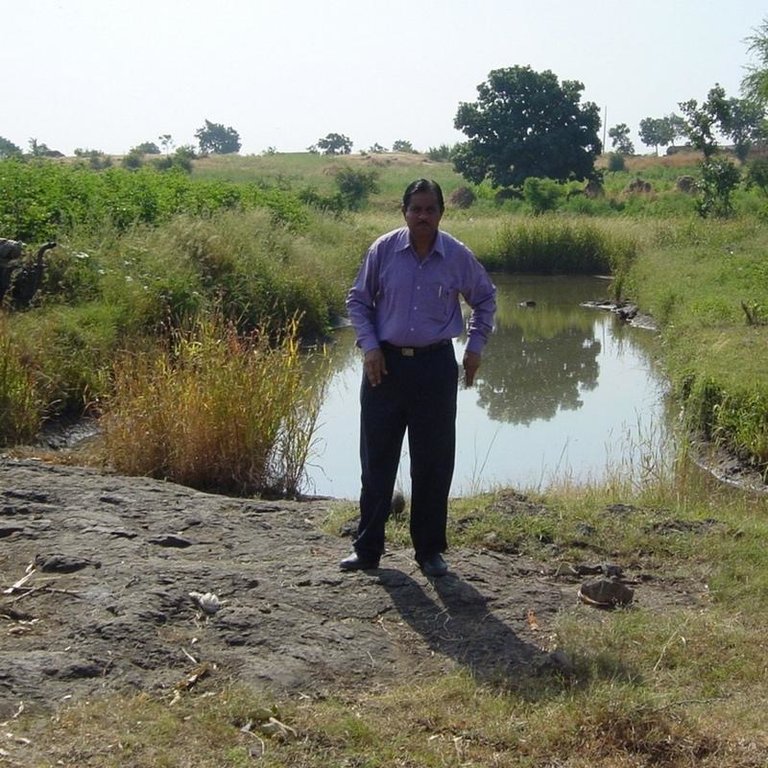
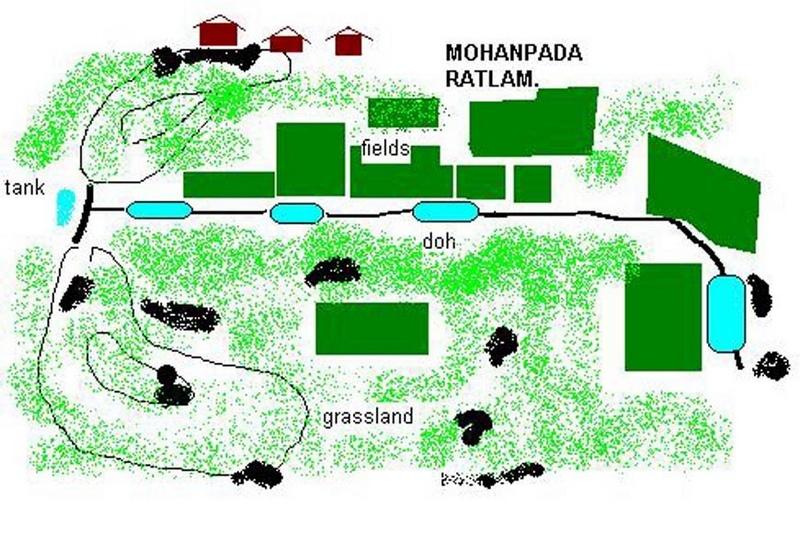
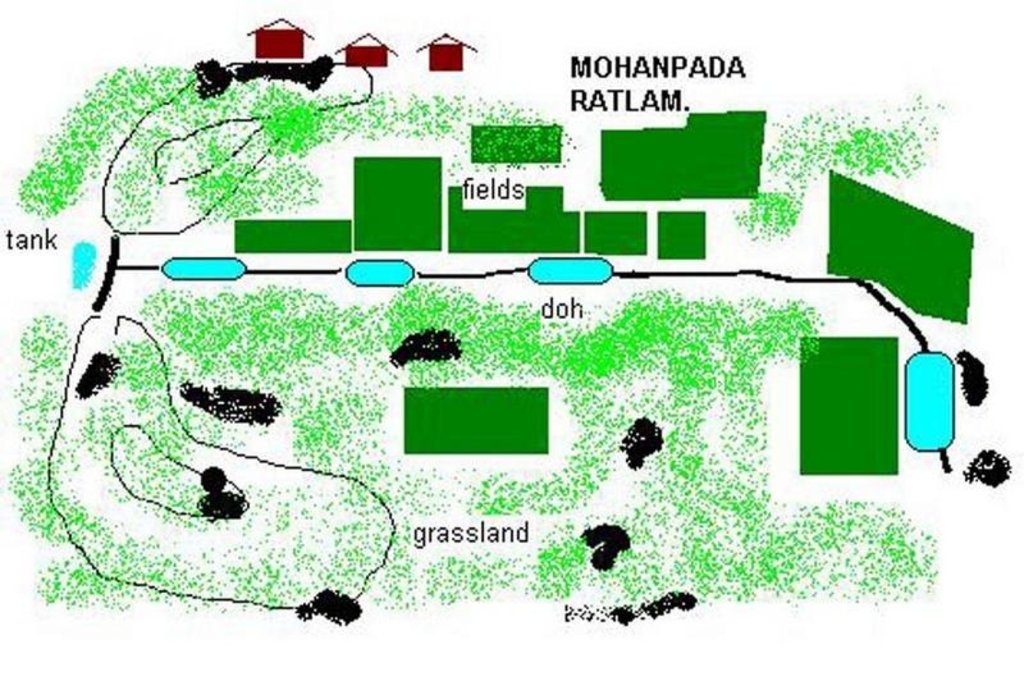
Dohs are rectangular excavations in seasonal streambeds, which are intended to capture and hold runoff to enhance groundwater recharge, thus increasing water for irrigation from nearby shallow wells. They also collect and impound subsurface flow. Dohs are built in semi-arid areas where rainfall is low and seasonal. The dimension of a typical doh is 1.0-1.5 m deep with variable length (up to 40 m) and width (up to 10 m) depending on streambed section, with an average capacity of 400 m3.
Purpose of the Technology: The excavated material is deposited along the stream banks as a barrier against siltation from surrounding areas. The slopes of the excavation are gentle (an upstream slope of 1:6 or 17% and a downstream slope of 1:8 or 12%) so that water flows into it, and excess water out again, carrying silt rather than depositing it. The sides however are steep, to increase capacity - and would benefit from stone pitching to stabilise them. A silt trap comprising a line of loose boulders is constructed upstream across the streambed. Dohs are generally built in sequence. They may be as close as a few metres apart. Bends in the stream are avoided as these are susceptible to bank erosion.
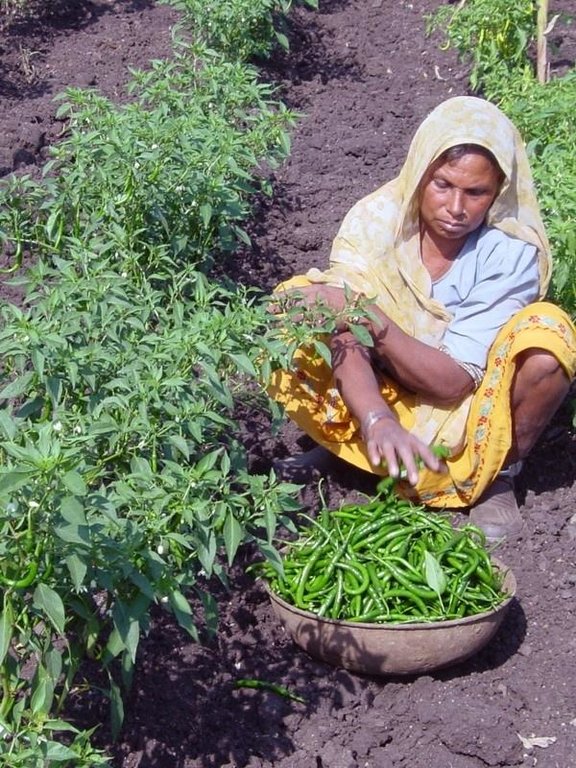
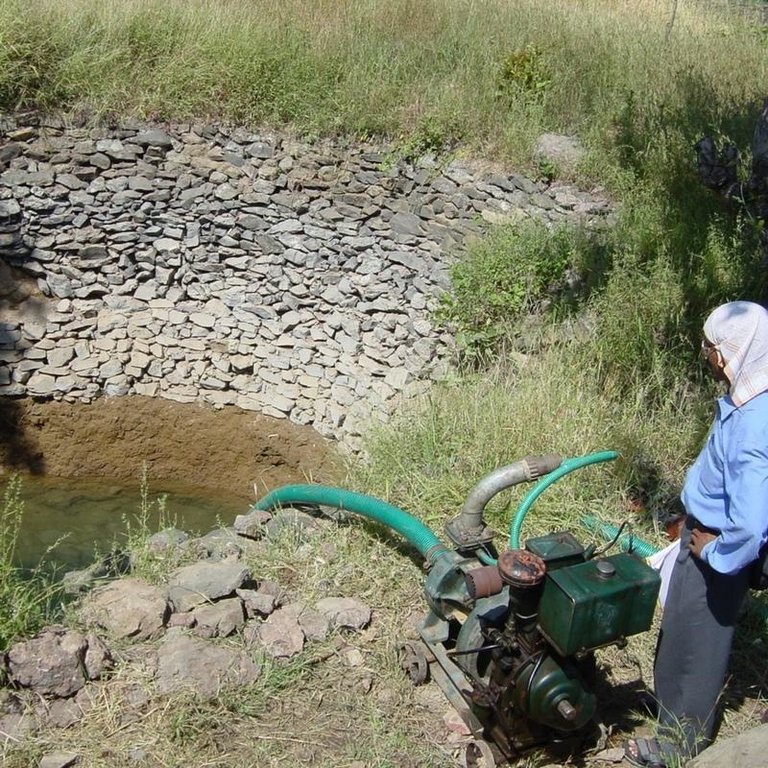
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology is used in conjunction with shallow wells (odees), which enable farmers to harvest the increased groundwater for supplementary irrigation of annual crops- including vegetables such as chilli peppers. Water is pumped out of the wells. In the case study village, Mohanpada, each doh basically supplies an underground source of extra water to one well. Communities together with project staff carry out site selection, and then detailed design/estimates/layout is done with project technical assistance. As a supportive measure the catchment area is treated with gully plugs (small stone checks in gullies). A water harvesting tank (small reservoir or dam) may be excavated above the series of dohs where this is justified by a sufficiently large catchment area/suitable site. The capacity of the tank at Mohanpada is around 600 m3 and thus also has a positive impact on groundwater recharge.
Natural / human environment: Maintenance is agreed through meetings of user groups: manual desilting is planned and repairs of gully plugs also. In summary, dohs are low cost water recharge alternatives for poorer communities, and in this case study, the extra area brought under production has meant that all families that require it, now have access to some water for irrigation.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อินเดีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Madhya Pradesh
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Ratlam, Mohanpada
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology which is a modification of the traditional 'DOH' observed in river beds was implemented on an experimental basis in village Ambaohondan Tehsil 0 Mau, Dist. Indore under NWDPRA by Mr. V.K.Agrawal & Mr.V.V.Karmarkar.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop: Wheat, cotton,vegetables etc (irrigated)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There are regular poor yields of agricultural crops on the degraded, rainfed fields. A further constraint is the limited amount of water in wells, restricting both the extent of irrigation, and the number of people with access to irrigation. There is an underlying problem of poverty, which in turn leads to seasonal out-migration to find work.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Agricultural lands: sloping fields, soil loss, poor yields. Common lands:competition from surrounding villages for grazing resulting in low yields. Private pastures (bir): small patches which are not sufficient to meet the fodder needs. Settlement area: 28 huts already erected. Additional space not available.
Other grazingland: extensive grazing: on patches of waste lands within fields
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During monsoon (kharif) season the main crop is cotton + maize. In addition minor pulses are taken. If water is available for irrigation, this is followed by wheat+gram in winter. Major area is fallow in winter except for the cotton crop which is of longer duration. No cultivation was observed in summer.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Oct
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1 m2.
The project area for phase 1 comprises 18 villages (3314 Households) mainly tribal. A significant portion of the area is barren and used for open grazing. The sunken wter harvesting technology was initially demonstrated in few villages as an alternative to the high cost heading type approach to water harvesting bieng implemented on a large scale by main line programmes.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Social causes = Lack of awareness and mobilisation amongst the communities.), Top down approach (Macro planning rather than micro (village level) planning.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
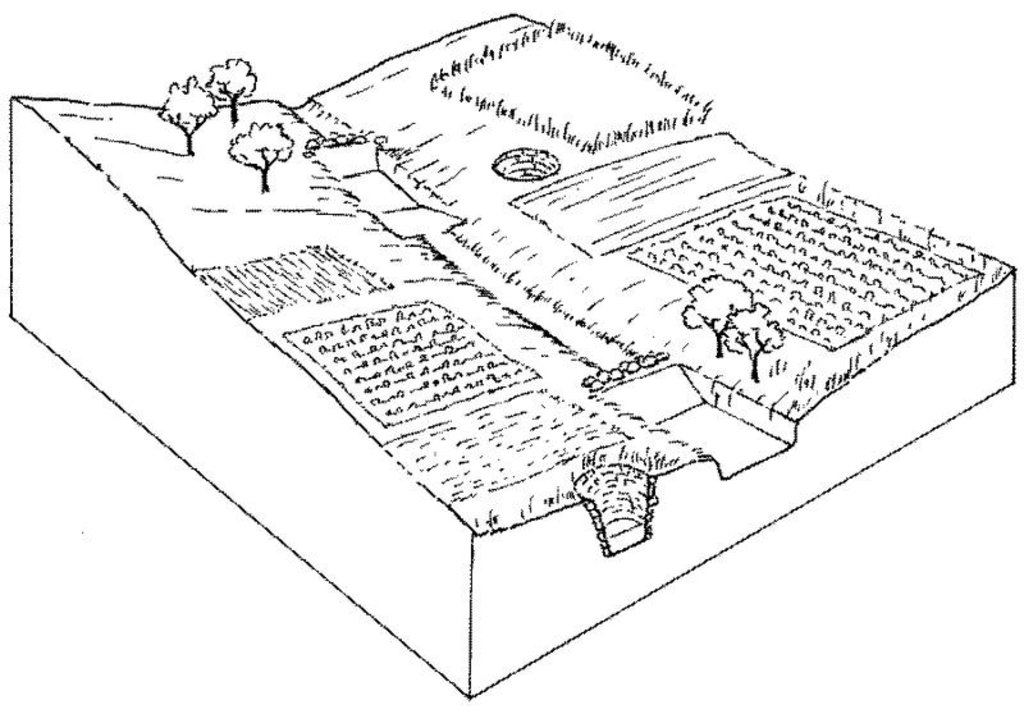
Overview of sunken streambed structures (doh) with associated wells and irrigated plots. Note that several dohs are applied in series along the waterway.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: doh (sunken streambed structure)
Structural measure: dam, gully plugs (supp.)
Construction material (stone): used for silt trap on the upstream side
Construction material (other): weathered section is excavated manually, while hard rock beds may be excavated by machine, dynamite.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Rupees
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
48.85
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection with community by eye | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 2. | Identification of beneficiaries and user groups | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 3. | Design & estimation by project staff | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 4. | Agreement of village committee. | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 5. | Treatment of catchment with gully plug | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 6. | Excavation of Dohs (200–400 m3) as last action with silt traps upstreamof each made from loose stone. | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 7. | Wells (odees) may be deepened and pumps bought | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 225.0 | 225.0 | 25.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 240.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of catchment treatments (desilting of gully plugs etc) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry Season/if required |
| 2. | Meeting of User Group | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Monsoon/After heavy Showars |
| 3. | Repairs to Silt-trap | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | During monsoon/After heavy shower |
| 4. | Desilting of DOH | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry Season/annual |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 5.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The construction of one doh costs between US$ 200-400, depending on the size of the doh (approximately one cubic metre can be excavated per person day at a cost of one US dollar). On a per hectare basis the costs are very variable, since they are related to the extra area brought under irrigation. In this case study there are four dohs within a total village area of 50 ha. Ten of the 50 ha have been brought into irrigated production (extra to the 5 ha already irrigated) due to the four dohs and the ‘tank’ and the costs outlined above are spread over those 10 ha. In this case half of the costs are directly attributable to dohs (average capacity 400 m3 each), and half to catchment treatment where the water-harvesting tank (a reservoir of approximately 600 m3) is the main cost. Where there is underlying rock, mechanical drills and blasting by dynamite may be required, which increases the costs. That was not the case in this village. The cost of deepening/widening the five wells (odees) has not been included here: that is carried out by the villagers themselves. While the project normally pays around 85% of labour costs, here at Mohanpada village the project only needs to pay 75%, due to a high level of commitment by the villagers.
The total of 4 doh structure were constructed along a stream length of 451 m having gradient of 1.2%. Total storage capacity is 1646qm. It is observed that during past year (2002) the structures were completely filled & subsequently emptied (percolated) 5 times.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Presence of hard stata (bed rock) increases cost of excavation
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
800.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
However since past 4 years rainfall has been below average
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Located on the tropic of cancer, characterised by hot dry summers (max 46 deg C) and cold dry winters. Monsoon (July-Sept) is characterised by high intensity showers followed by prolonged dry spells.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and moderate (ranked 3)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1, eroded wastelands, fields on slopes) and shallow (ranked 2, fields in valley portion)
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, present in valley sections) and coarse/light (ranked 2, present along slopes)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, fields along slopes,waste lands) and medium (ranked 2, fields in valley section)
Topsoil organic matter: High (ranked 1, fields along slopes, waste lands) and medium (ranked 2, fields in valley sections)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
1% of the land users are average wealthy (One family has bore-well).
19% of the land users are poor (Few farmers have access to shallow wells.).
80% of the land users are poor (Majority are small/marginal farmers without access to irrigation).
Off-farm income specification: some migratory work in nearby towns and in large scale mechanised farms during peak periods (note: now there is less migration as a result of increased irrigation)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased economic inequity in some villages, between those with wells and those without
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased economic inequity in some villages, between those with wells and those without
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Where cultivated
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In catchment
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
Amount of water to downstream users
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1600 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers in Mohanpada have constructed one doh with only 10 % subsidy on the total cost.
Spontaneous adoption is growing in neighbouring villages.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Dohs are a low cost alternative method of increasing groundwater in a semi-arid area where production of high value legumes depends on irrigation – and dohs represent the best way in this situation of expanding the extent of irrigated land, and bringing irrigation to more families. |
|
Small, multiple recharge points for replenishing groundwater for irrigation from wells How can they be sustained / enhanced? Breaking hard pan in stream bed mechanically by drills or blasting to deepen dohs and thereby make them more effective. |
| No risk of breaches of bunds as the structures are sunken below ground. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Group maintenance is required | Form user groups. |
| Villagers are more used to (and may prefer) larger and deeper ‘tanks’ | Establish more dohs to create more impact. |
| Dohs are limited in capacity and thus dry up quickly, as do the wells | Establish more dohs to create more impact. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Comprehensive watershed development [อินเดีย]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- ผู้รวบรวม: David Gandhi
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล