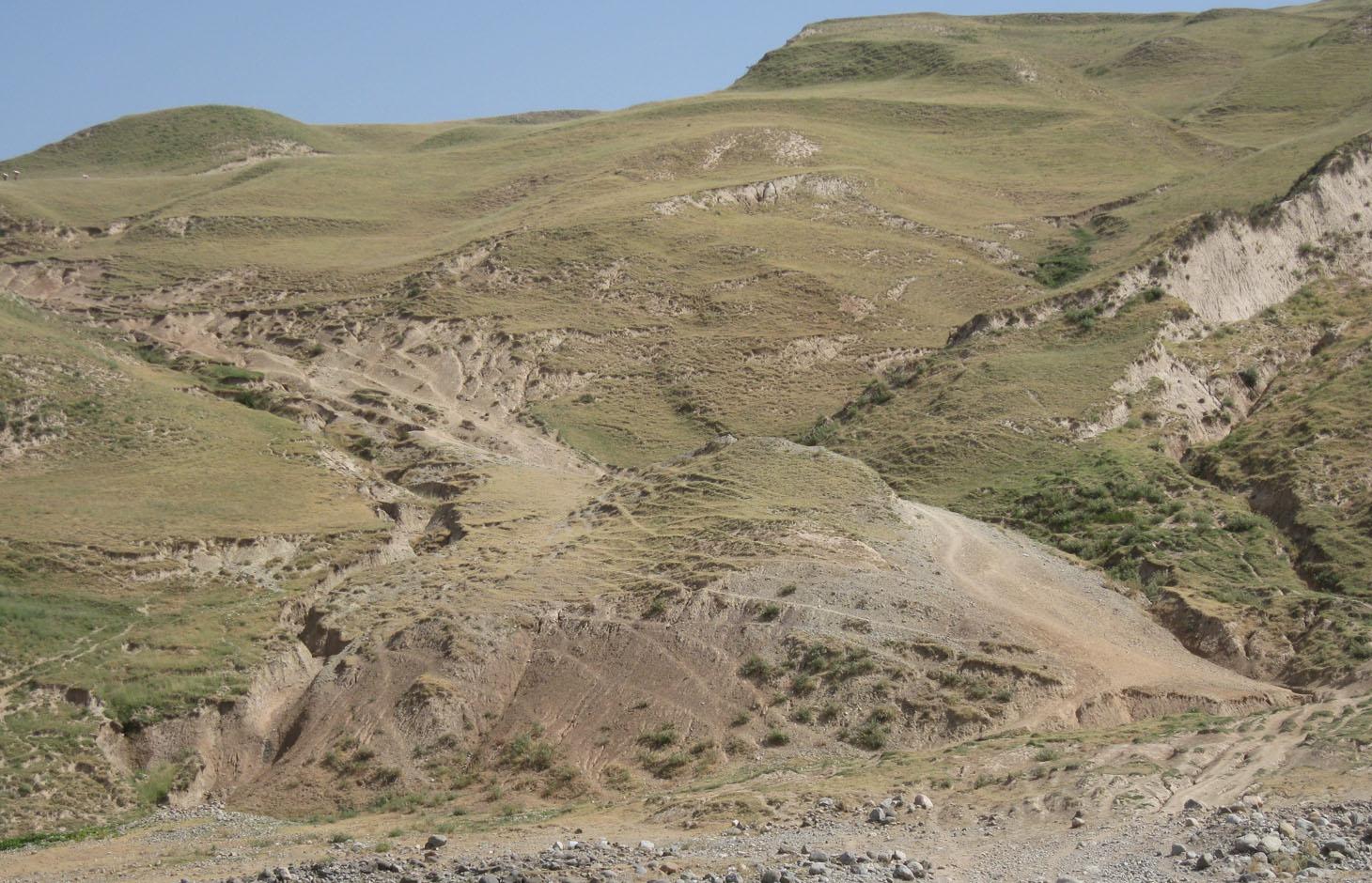
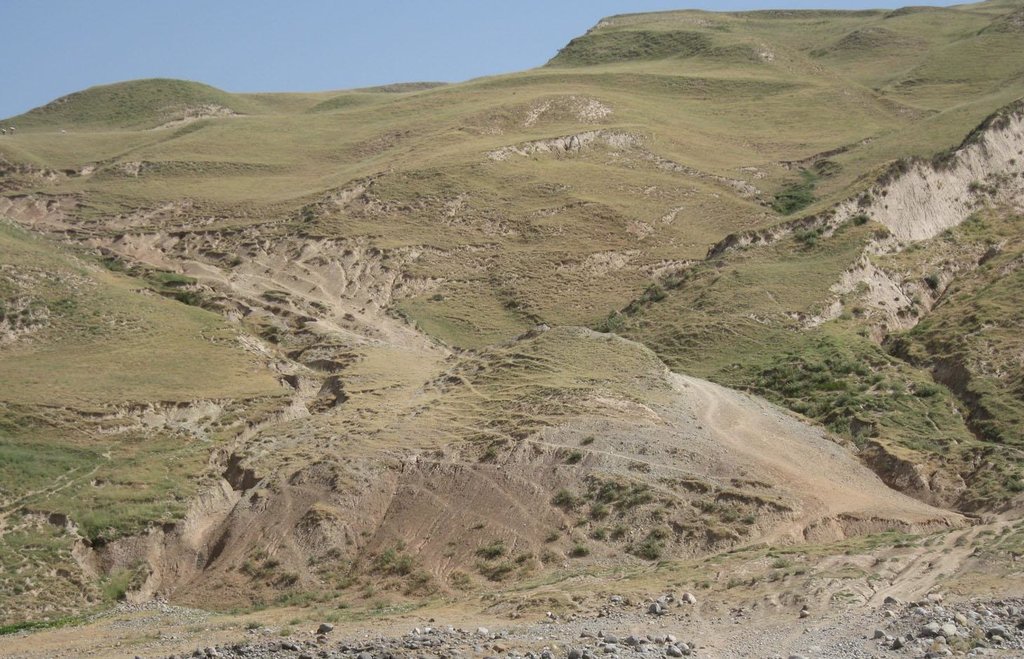
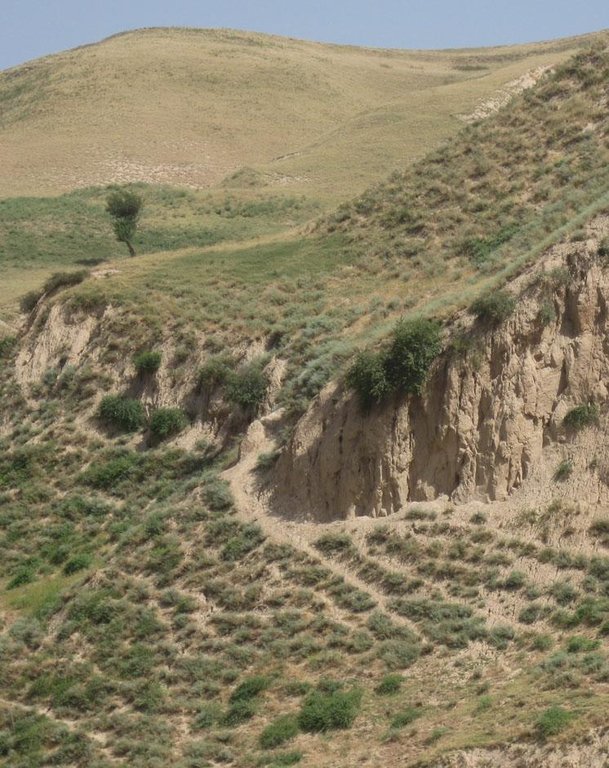
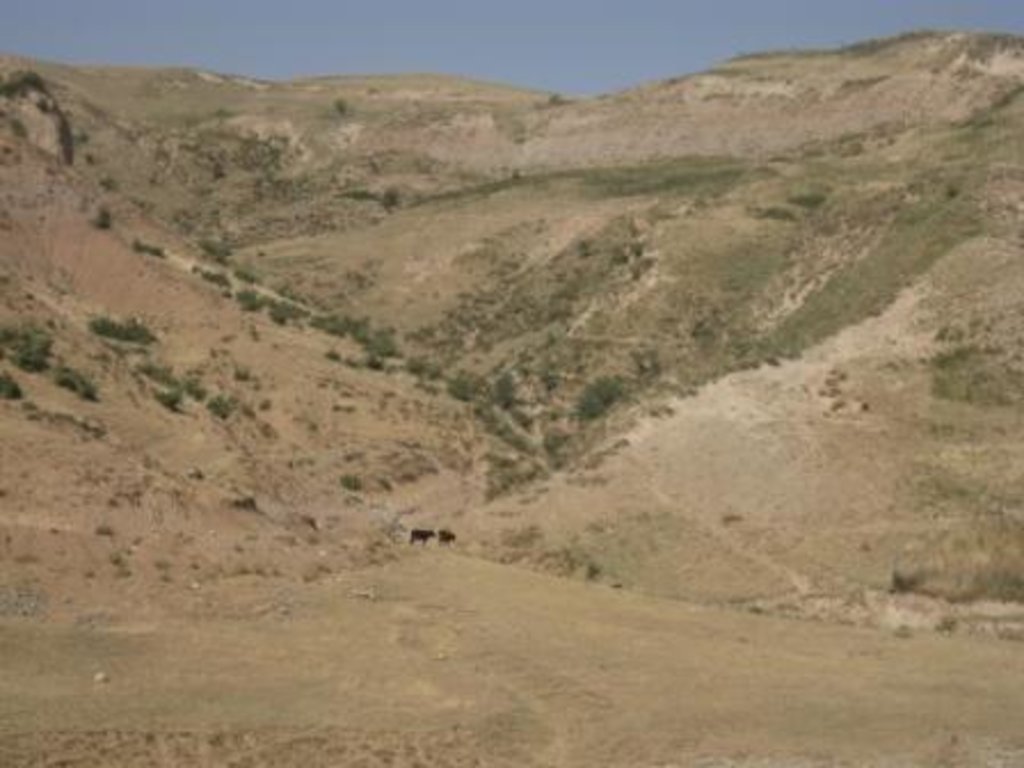
Degraded communal pasture Obishur [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Malgorzata Conder
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1545 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
28/07/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Degraded communal pasture without grazing management and sufficient waterpoints
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
On the communal pasture, located at the foothill around 85 households graze their livestock totally 500 cows and 100 sheep and goats. Half of the households of the village Momandion have livestock which is meant to graze at different places on that pasture. As there is no water point higher up in the pasture area, livestock grazes near the village where a water point is installed. The rolling zone is totally overgrazed and shows several deep gullies. Cows and the small livestock are divided for grazing. Every family is looking after a herd for a day every month. Although the families of the herding livestock communicate with each other, there is no planning for a sustainable grazing management.
Purpose of the Technology: The whole plot is overgrazed and livestock is increasing, so at least controlled pasture management could be expected to decrease the degradation process. Additionally, more vegetation would be available for feeding livestock. More water points have to be installed higher up in the pasture, to decrease pressure on soil and vegetation. More waterpoints would extend the area to be used for grazing. Another issue is that nobody really feels responsible for the pasture and its management. This explains why no pasture management exists at Jamoat level. Farmers are not organized in terms of pasture rotation and control. Livestock owners pay very small rent, which does not make them vakue the pastureland. Additionally, the tax is not enough for projects or investments (like installing water points).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Every household pays 12 Somoni per year for pasture rent, which is in total around 1000 Somoni. Rent is per household not per livestock number. No maintenance is done.
Natural / human environment: The pasture extends from the foothill to the upper parts of the hill with a high percentage of overgrazed, trampled, erosive area. Except for the water point near the village, there is no water and no shady points for livestock. 85 households graze their livestock, which total 1500 cows and small livestock. Every household is responsible for grazing the herd one day every month. Apart from that, no management exists between the families and Jamoat.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muminabad
Map
×3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Main animal species: Cow, sheep, goat
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing, soil compaction, soil and gully erosion, increasing vegetation cover and hence lower resilience for disaster risks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): More livestock reduces vegetation cover through overgrazing and trampling. Gully formation. Not enough water acces in the pastureland.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cow, sheep, goat
Grazingland comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
Type of grazing system comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: March-Sept
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- Water points
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 km2.
Farmer (Vakil) did not know at all the area extent, data based on Google Earth
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Eo (Offsite degradation effect): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Eo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (No controlled grazing), population pressure (Increasing livestock), land tenure (Communal property=No individual responsibility)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (one or two decades ago), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), poverty / wealth
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Bare vegetation cover, no trees, soil erosion, trampled paths, rill building, no waterpoints are all calling for pasture management among the villages.
Location: Obishur watershed, Momandion. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Controlled access, staged grazing
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Somoni
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
4.83
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
12.40
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Possible solutions: Pasture ManagementWorkshops, Meetings, Round table | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 2. | Water points | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 3. | Reduce Livestock quantity | ด้วยการจัดการ |
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
It wouldn not be expensive to hold regular meetings between the livestock keeping families for a better organization of the grazing area. The installation of a water point is very costly and labour intensive in contrast.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, approx. 40%) and hilly (ranked 2)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
2.4 ha, if 7.7 pers/household counted. In total 3040 ha pasture
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เช่า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land ownership is based on Land user certificates
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less forage available for livestock due to reduce vegetation cover
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
important clear-cutting in the past
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
no organizational task without pasture management
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
no organizational task without pasture management
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
lack of water points for livestock
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
lack of water points for livestock
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
more fodder has to be bought, because grazing is insufficient
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less forage for livestock
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
no organizational task without pasture management / feeding animals
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More difficult to feed livestock
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Pasture rotation would improve vegetation cover, infiltration, slope stabilization and natural disaster resilience
Rotate within the grazing land and less energy needed by livestock, which leads also to less consumption and hence overgrazing
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Establishment of rotational grazing is not expensive and does not require further equipment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Empower communication and decision-making also between the farmers |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Importance of rotational grazing depends on Jamoat and farmers level | Strengthen communication between Jamoat and farmers through consultancy, meetings etc. Farmer as tenants should get a voice. |
| Pastureland rent is too cheap and is not valued. There is no incentive to change, because nobody feels responsible for that area. | Increase the rent and discuss communally where money should go to (e.g. water points). |
| Pasture management does not show benefits immediately which makes it difficult to evidence good Technology. | Explanation/ education about short and long-term benefits |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล