Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Manuel Fischer
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1559 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 28 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 28 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 30 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 9 พฤษภาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Muthoni Mary Njagy
0727 906 945
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
08/11/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
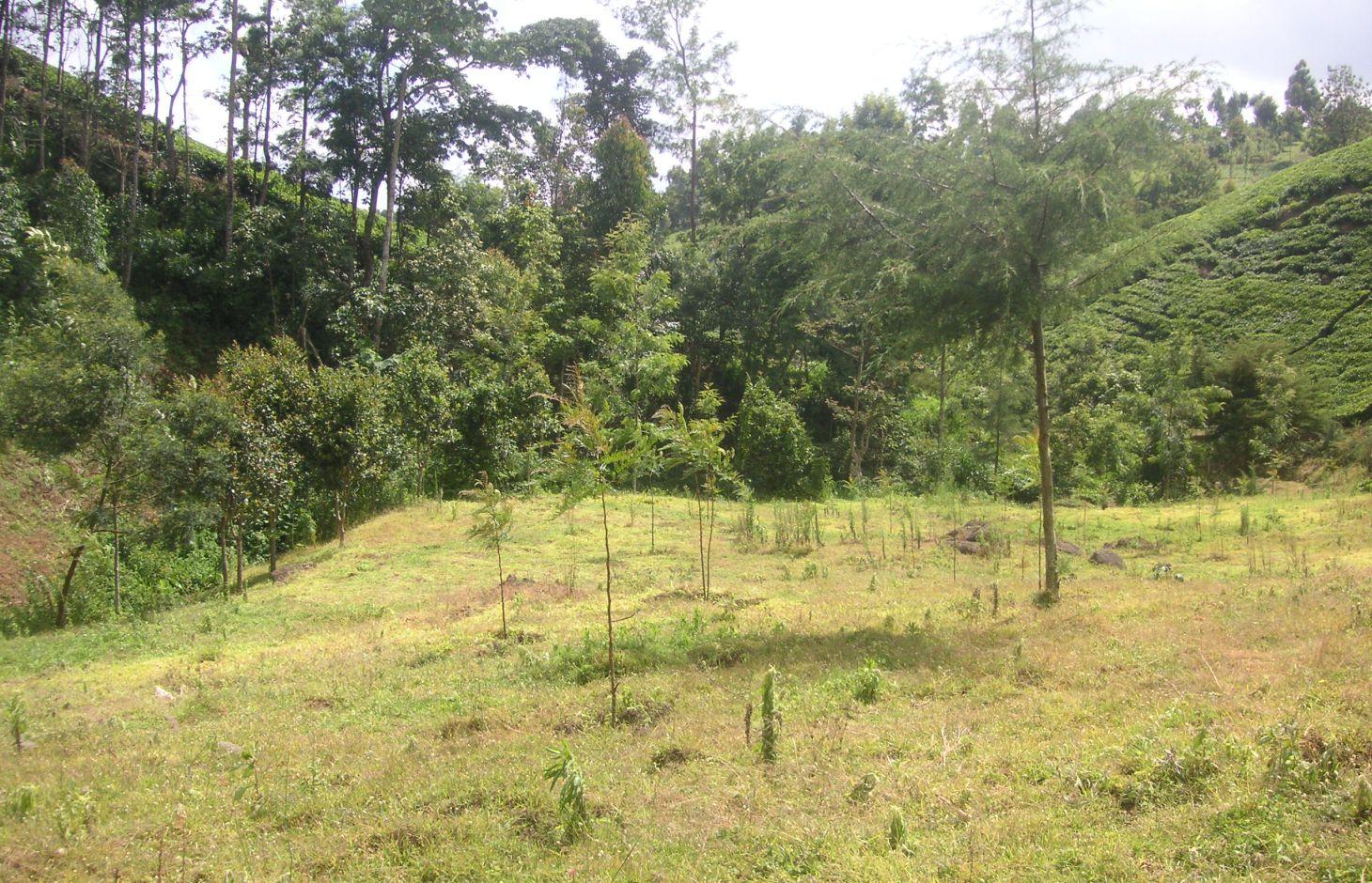
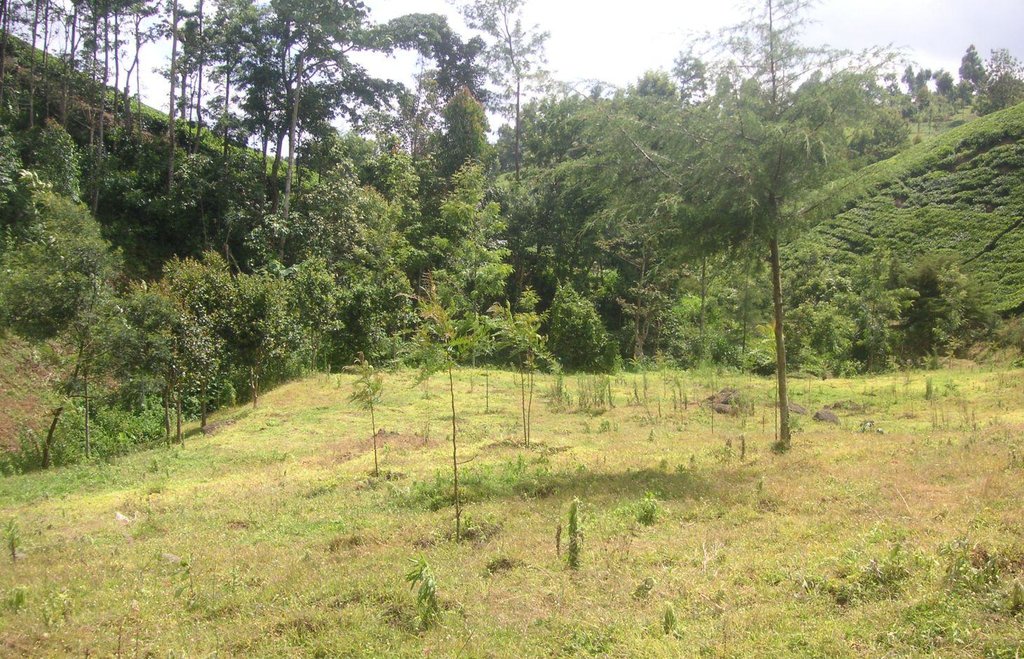
Tree line with adjacent grass strips as example of a productive and protective riparian area at Kapingazi River
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
On the south-eastern slopes of Mt. Kenya, the conditions are ideal for agricultural activities. There is plenty of rainfall (2100 mm/year) which is usually reliable. However in the year 2000, the river Kapingazi dried up for the first time since many decades during a dry spell. This led to community activities that finally came up with a system of vegetative interventions to strengthen the riparian zones. The intervention consists of tree planting and establishment of grass strips along the river. Napier grass is planted to stabilize steep slopes and to supply material for the construction of tea baskets.
Purpose of the Technology: The goals of this technology are manifold. Firstly, the vegetation prevents surface water and eroded soil flowing from the agricultural fields directly into the river. Therefore, sediments and chemicals used on the field are retained in the riparian soils and do not pollute the river. Surface water flow from runoff during heavy storms is slowed down and infiltration on soils covered by grass and trees is increased. As a result more groundwater is recharged during the wet seasons, which can be released during the dry season. Thus peak or flood flows are reduced and low flows are improved. Damage during flood flows on the riverbank (through erosion and destabilizing the riparian vegetation) as well as damages of floods downstream can be reduced or avoided.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Before planting the indigenous trees, water guzzlers like eucalyptus trees were cut down. Indigenous seedlings were planted right along the river at a distance of 2m. Between the trees and the tea plantation a grass strip of up to 10m is established. Some trees were planted scattered on the grass strip. The young trees are surrounded by grasses which are cut regularly every 2 weeks. This reduces competition and enhances growth of the trees. As soon as the trees are big enough, they function as a source of firewood, they can be pruned every 5 months.
Natural / human environment: The studied plot is situated right below the natural mountain forest of Mt. Kenya at the south-eastern slope. The source of Kapingazi River can be found at 1.5 km of walking distance upslope of the plot. Agricultural circumstances are good because of the fertile, volcanic plots and the abundant precipitations. However, the terrain is quite steep.
The zone which is used for tea production reaches from an elevation of 1700 m.a.s.l to 2000 m.a.s.l. Most tea farmers own between 4 and 20 acres. The area of the riparian zone covers 6 m from the river edge and belongs to the government. Since the harvest of the tea leaves requires a high labour input, local workers are hired. Most of the harvest is done during the rainy season because the tea plants are growing fast in this period. For the tea production only the youngest leaves are used, transported in a basket on the worker’s back to the tea factory in the evening.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kenya/Eastern Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Embu
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In the year 2002 the new constitution obliged the government to take care of the water resources. The instrument for this were the WRUA (Water Resource Users Associations), local initiatives of land users that promote protective measures along the rivers.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major cash crop: Tea
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main land use problems are pollution of the riverwater, low rainwater storage that provokes floods, too few water during the dry season and riverbank erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The main problem is the few water in the dry season that prevents irrigation.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Additionally, few food crops are planted in a relatively small homegarden.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: april to may Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: november to december
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Since the technology is only used by one farmer at a single spot, it does not make sense to indicate the area. Furthermore, the length along the river is more important than the area.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hp: decline of surface water quality, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Riparian trees were chopped down.), education, access to knowledge and support services (People didn't know about the consequences of the deforestation.), planting directly next to river
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
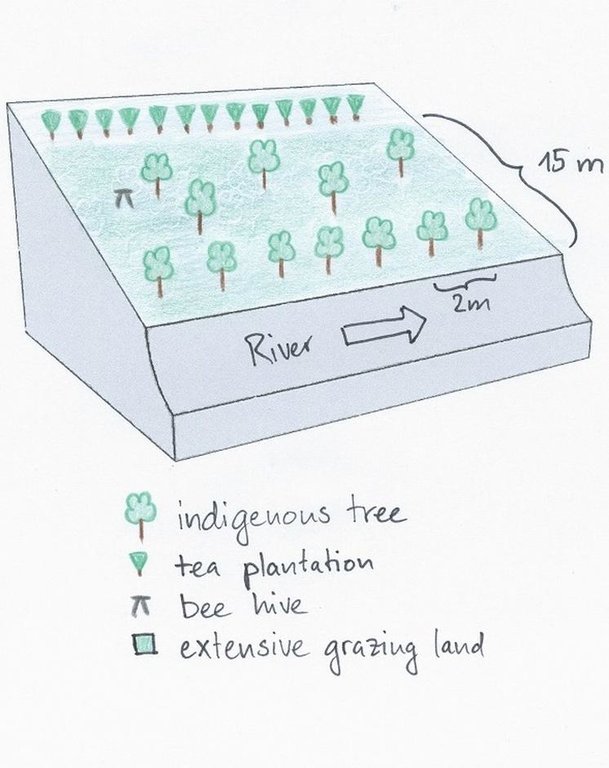
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The area between the river and the tea plantation is used to establish a riparian habitat. Trees are planted along the river and also on the adjacent grazing land. The grass is cut regularly and used as fodder. A bee hive was installed to generate additional income.
Location: Manyatta. Embu / Eastern Province
Date: 28.12.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 30
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: indigenous trees, Napier grass
Grass species: normal grass
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.33
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | ด้วยวิธีพืช | During rainy season |
| 2. | Replanting of seedlings which dried up | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Planting trees | ด้วยการจัดการ | At the beginning of the rainy season |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Tree planting during rain season | Persons/day | 6.0 | 3.3333333 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Replanting of seedlings | Persons/day | 2.0 | 3.333333 | 6.67 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting trees before rain season | Persons/day | 8.0 | 3.333333 | 26.67 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | pieces | 70.0 | 0.111 | 7.77 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings for replanting | pieces | 20.0 | 0.111 | 2.22 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Riparian seedlings | pieces | 90.0 | 0.034555 | 3.11 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 66.44 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding the area around the trees to get fodder and boost the tree growth | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every 2 weeks for 4 years |
| 2. | Weeding the lawns for better growth of the trees and for fodder | ด้วยการจัดการ | every 2 weeks during raining season |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Weeding the area around the trees | Persons/day | 16.0 | 3.33333 | 53.33 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weeding the lawns | Persons/day | 64.0 | 3.33333 | 213.33 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 266.66 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Jembe (Machete)
The costs were calculated for a riparian area with a length of 100m and a width of 10m, since hectares are difficult to apply on a riparian context. The determinant factor for the costs is labour. In this case, the costs are very low because the trees were only planted every 10 metres along the riparian. The seedlings have to be bought in a nursery. Most of the bushes regrow naturally and do not need any management.
Some of the seedlings had to be replanted, because they dried up. The required equipment like a spade is available on nearly every farm or can be borrowed from neighbours and is thus not added to the costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
2100.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Most of the rain falls during the rainy seasons from April-May and Oct-Nov.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: subtropics. http://www.mappedplanet.com/klima/klimadiagramm-39729-Nanyuki,Kenia
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very high
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: Also excess and poor/none
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Off-farm income specification: Owner is a member of the parliament.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land user was a former member of parliament
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Pruning of trees
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Grass for basket production.
Fuelwood
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Pruning the trees
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
aesthetics
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
Livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through the increase of the water quality, the technology improves the access to clean water.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
10% of all the riparian land users have adopted the technology
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 10-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 10% of all the riparian land users have adopted the technology. The external support was the provision of seedlings.
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Through the action of several organisations, the attention of the land users is drawn to a proper riparian management.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
The river does not dry up easily during dry seasons. The grass yield can be used for fodder purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? disseminating the knowledge among the farmers. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
A vivid and stable riparian ecosystem is the key to ensure biodiversity and stability of the riverbanks. This leads to a smaller vulnerability to floods or droughts and combats degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? continuous awareness raising among the land users. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Labour input for weeding is high | cutting grass at a bigger height |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล