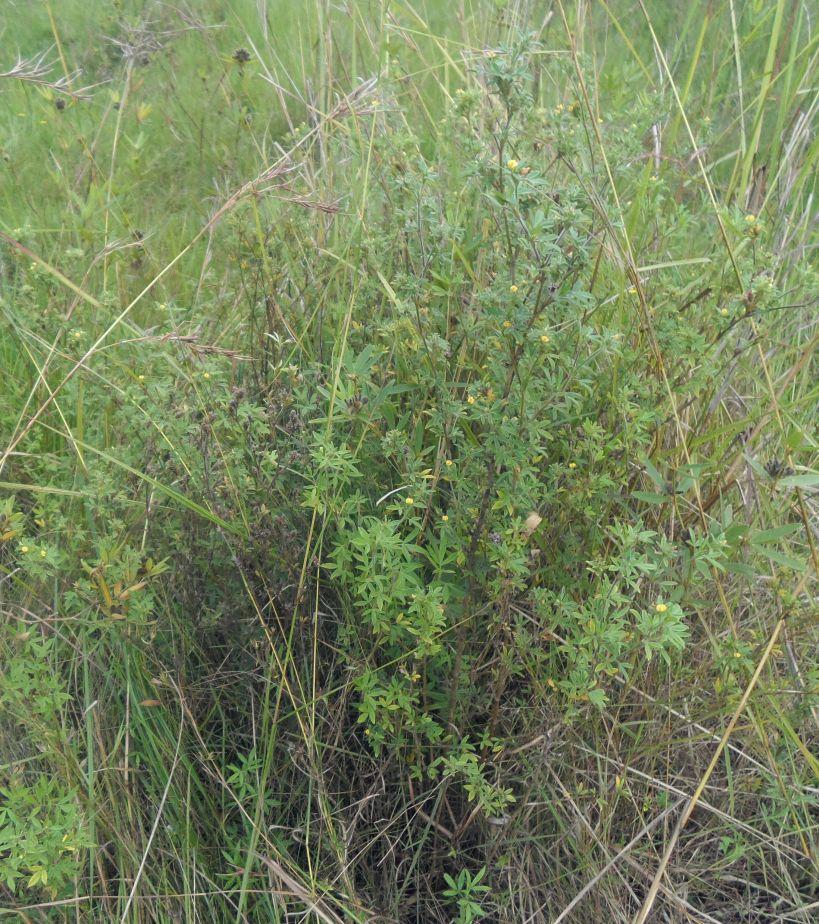
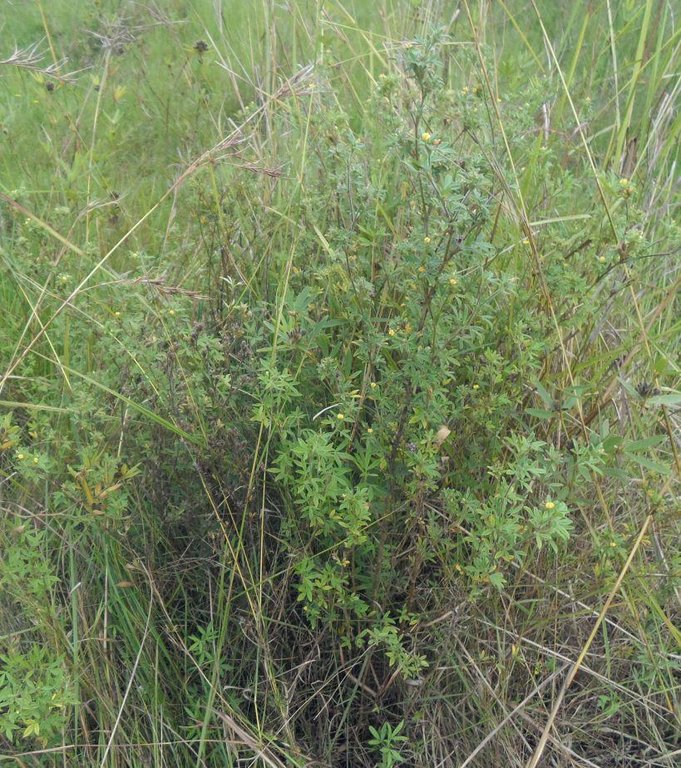
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
แทนซาเนีย
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
03/06/2014
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [แทนซาเนีย]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tanzania/Kagera
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปิดล้อมพื้นที่ (หยุดการใช้ประโยชน์ สนับสนุนการฟื้นฟู)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M7: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tanzanian shillings
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
1700.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.12
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | ด้วยวิธีพืช | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | ด้วยวิธีพืช | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | ด้วยการจัดการ | once |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.13333 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | |
| แรงงาน | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | |
| แรงงาน | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.13333 | 17.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | Number | 5.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 235.29 | 235.29 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 117.65 | 117.65 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | kg | 125.0 | 0.588 | 73.5 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 651.9 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | ด้วยวิธีพืช | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | ด้วยการจัดการ | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | ด้วยการจัดการ | Weekly |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.76466 | 26.47 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.53 | 52.95 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10.0 | 17.647 | 176.47 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10.0 | 17.647 | 176.47 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 432.36 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
5.0 ton/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
6-7.0 ton/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2 acres/annum
หลังจาก SLM:
10 acre/annum
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3
หลังจาก SLM:
8
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1200litres/cow/yeer
หลังจาก SLM:
2000litres/cow/year
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
weak
หลังจาก SLM:
strong
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Resultant of vergetation cover
การระเหย
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved vegetation cover
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
การอัดแน่นของดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Controlled fire burning
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Controled bush fire
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [แทนซาเนีย]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล