Lining irrigation canals [มาลี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Dieter Nill
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli
Revêtement des canaux d’irrigation (French)
technologies_1651 - มาลี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Traore Minamba
tbaminan@gmail.com
IICEM
มาลี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses, and to reduce pumping time and costs.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
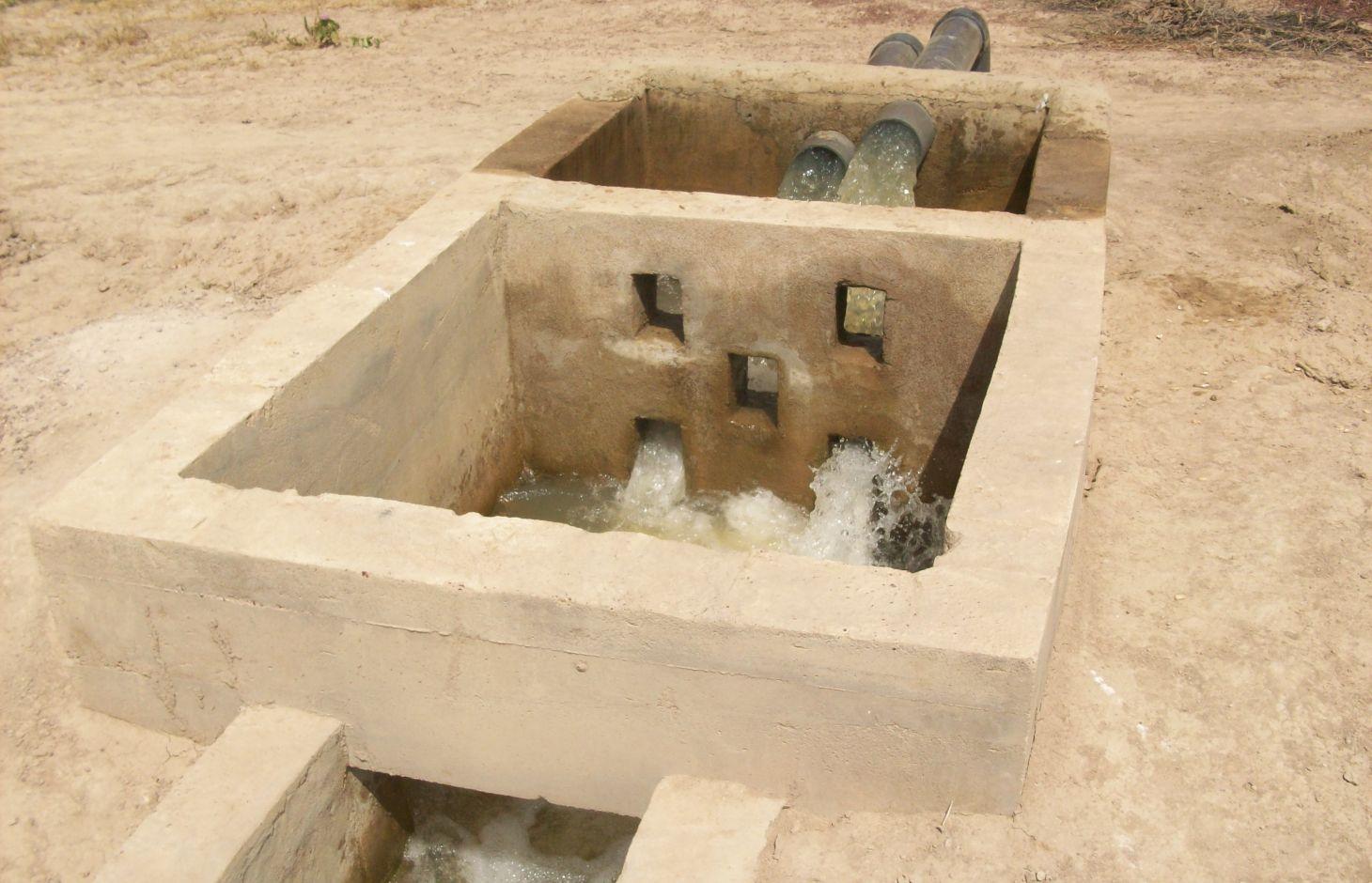
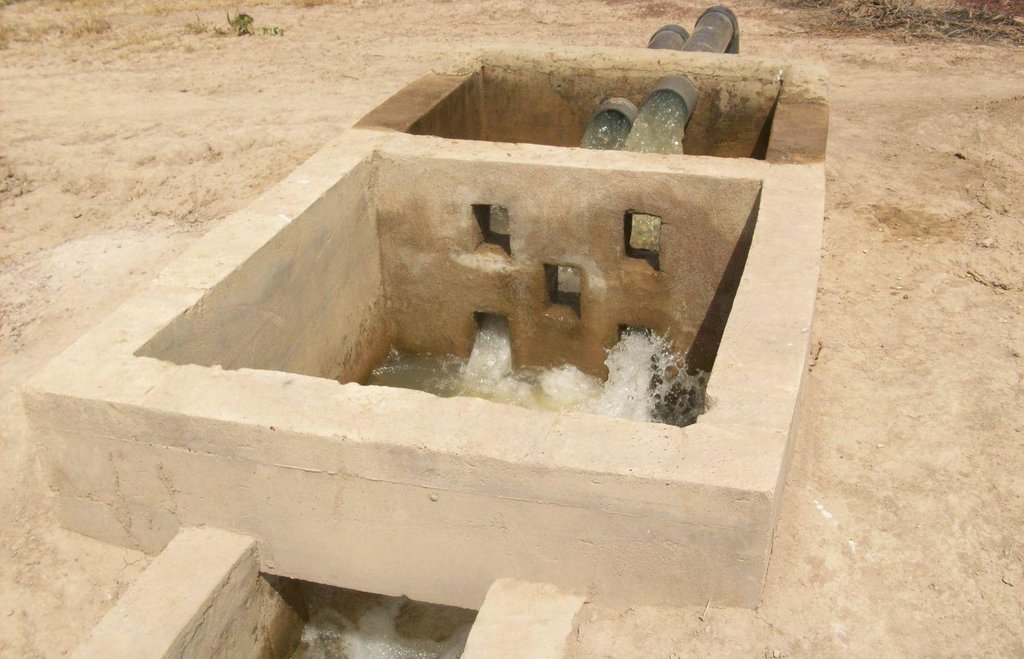
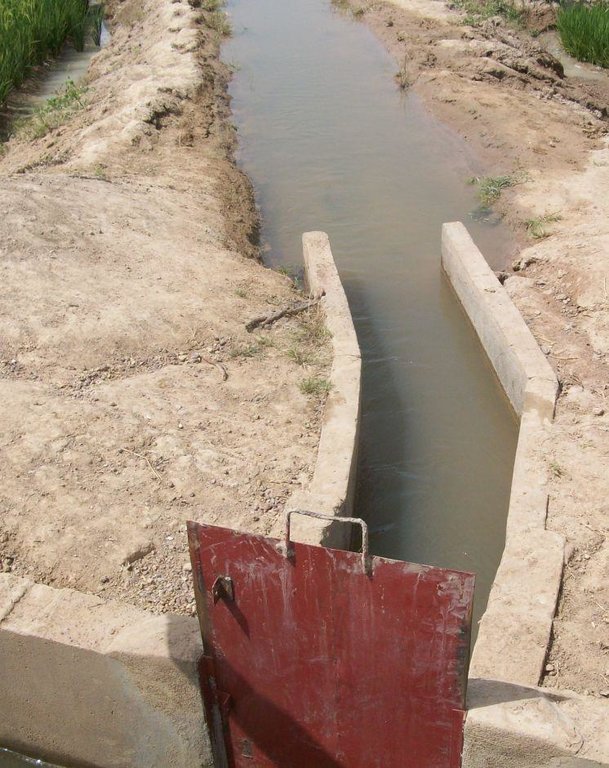
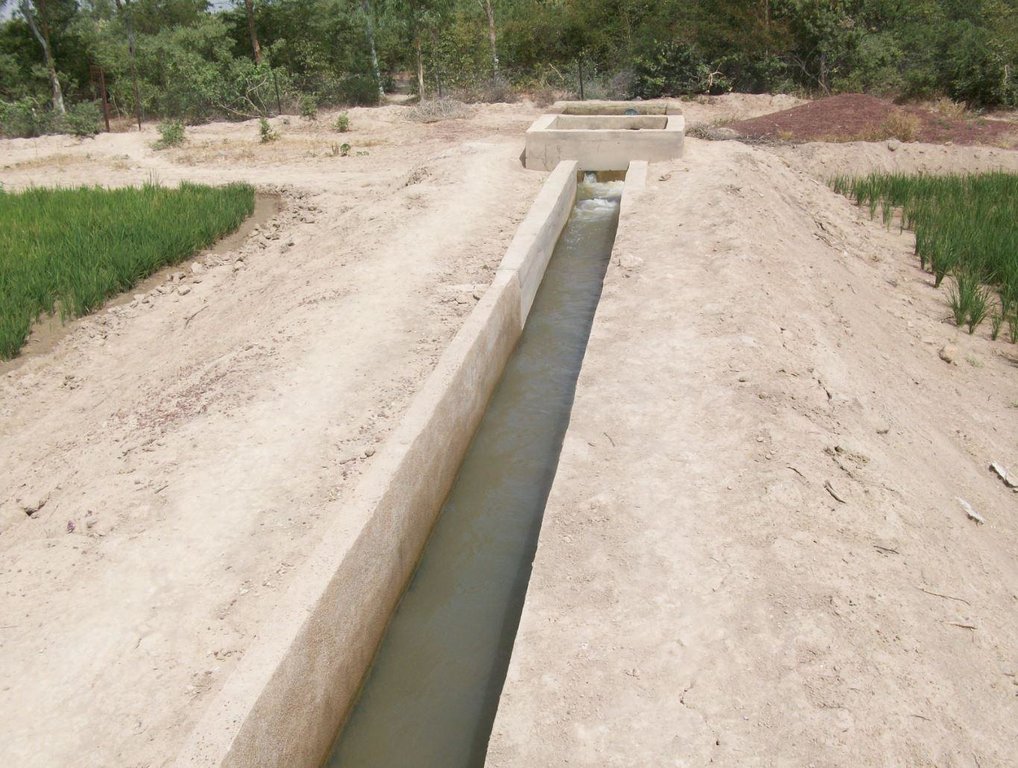
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required.
Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Lining is mainly used to improve the efficiency of existing irrigation systems. Once the canal has been lined, yields increase by between 35% and 80%. This is because crops receive the water they need to ripen as and when it is required. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. Pumping hours per hectare are considerably reduced (by 25% in the rainy season) because the canals ensure the correct distribution of irrigation water. Consequently, irrigation costs per tonne of produce drop due to the reduction in pumping hours and the costs of periodical maintenance and increases in yields.
Together with the growers, a memorandum of understanding was drawn up with IICEM and then signed by the mayor. The memorandum describes all the activities that form part of the collaboration between IICEM and the various beneficiaries. The works were carried out either in-company or constituted part of the highly labour-intensive work (HLIW).
a) Work delivered in-company (turnkey basis): Works are carried out in several stages: 1) Identifying the sites requiring lining. This involves locating the sites to develop and making contact with the NGOs that represent the project in the region, as well as regional directorates of rural engineering and economic operators working with the farming organisations in question. 2) The delimited sites chosen for development must undergo technical studies, which are entrusted to engineering consultancies recruited through an open tender process in accordance with the terms of reference for the studies to be conducted. 3) The technical feasibility studies comprise topographical, geotechnical, soil and environmental studies, as well as the creation of a development plan and quantification of materials required for the construction work. 4) Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses. In lieu of a ToR, an ITT is created by the project according to the requirements of the site. It is then published so that interested consultancies can put forward their bids. 5) Works are carried out under the control and supervision of the oversight office to ensure they adhere to professional standards.
b) Highly labour-intensive work: 1) The same as above. 2) Topographical surveys are carried out by IICEM specialists to calculate the calibration of the canals to ensure they are able to submerge plots over a large area. 3) After calibrating the schemes (energy dissipation basin and division box, main canal and secondary canal turnout, channel), a work plan is drawn up. This uses the measurements calculated to quantify construction material and equipment requirements. 4) Teams of (preferably local) builders are recruited to line the canals. The teams comprise master builders, reinforcing ironworkers, bricklayers and surveyors. 5) The materials and equipment required for each site are provided by an appropriate supplier recruited through a tendering process. 6) Provision of labour and farmer participation. Only the building contractors are paid for working on the project. Labour is supplied by the local community who are provided with lunch to maintain motivation and to prevent lost time caused by workers going off-site. 7) In villages where schemes are proposed, teams of shift workers from the local community are set up and trained in proper conduct for working on a canal lining project and in the keeping of a construction project log book.
Once the canal lining works are complete, IICEM provides a pump unit and subsidises the required fuel and consumables for one growing season. Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee.
The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years if small repairs are regularly undertaken. Ensuring linings are impermeable is of the utmost importance because water penetrating through micro-cracks as it flows through the network can lead to rapid and major water loss. It is therefore essential that producers can maintain installations and repair cracks.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มาลี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Mali
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao, Sikasso
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์ (Agro-pastoralism)
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): unequal distribution of irrigation water, ineffective irrigation systems (water loss)
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12 m2.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1200 hectares have had their canals lined
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required. Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
CFA Franc
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
512.0
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identifying the sites requiring lining | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 2. | Launching the invitation to tender for the technical studies / Undertaking topographical surveys to calibrate schemes | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Performing the technical studies / Quantifying building material requirements | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 4. | Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses / Recruitment of masons, bricklayers and reinforcing ironworkers | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 5. | Delivery of works under the supervision of the oversight office / Invitation to tender for the provision of materials and equipment | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 6. | Provision of labour and farmer participation | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 7. | Training workers from the local community in building site conduct | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | small repairs are regularly undertaken | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. Total costs: 1,587,865.50 US Dollar
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Lining of canals is an investment which is generally only feasible with external assistance.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Irrigation system canals in Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao and Sikasso have been lined.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses. |
| Pumping time and costs are also greatly reduced through the speedy distribution of irrigation water supplies, and reducing the use of motorised pumps lowers maintenance costs. |
| Yields increase by between 35% and 80%. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. |
| Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee |
| The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
www.iicem.net
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล