Integrated Production and Pest Management (IPPM) [มาลี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Dieter Nill
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Gestion intégrée de la production et des déprédateurs (GIPD) (French)
technologies_1653 - มาลี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Dako Jean Parfait
parfaitdako@yahoo.fr
Direction Nationale de l'Agriculture
มาลี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - เยอรมนีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Direction Nationale de l'Agriculture (DNA) - มาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
IPPM reduces the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
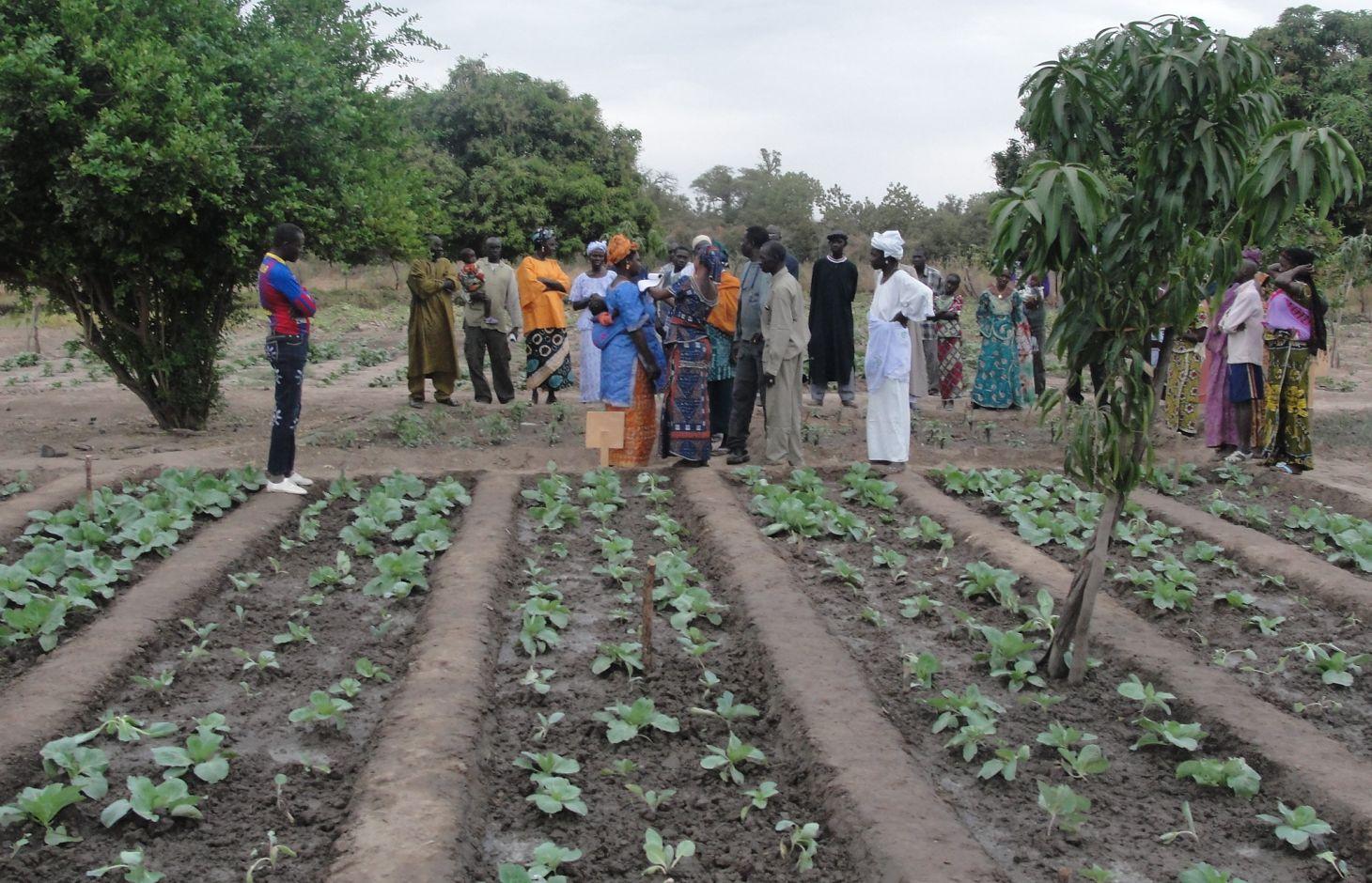
Integrated Production and Pest Management (IPPM) curbs the environmental degradation caused by current farming practices (intensive and extensive), reducing the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind. IPPM promotes the adoption of farming practices that are as respectful of the environment as they are productive and profitable.
Purpose of the Technology: IPPM works with all available techniques for combatting pests, while keeping pesticide use at economically justified levels. It reduces risks to human and animal health and to the environment. It is put into practice in farmer field schools (FFSs).
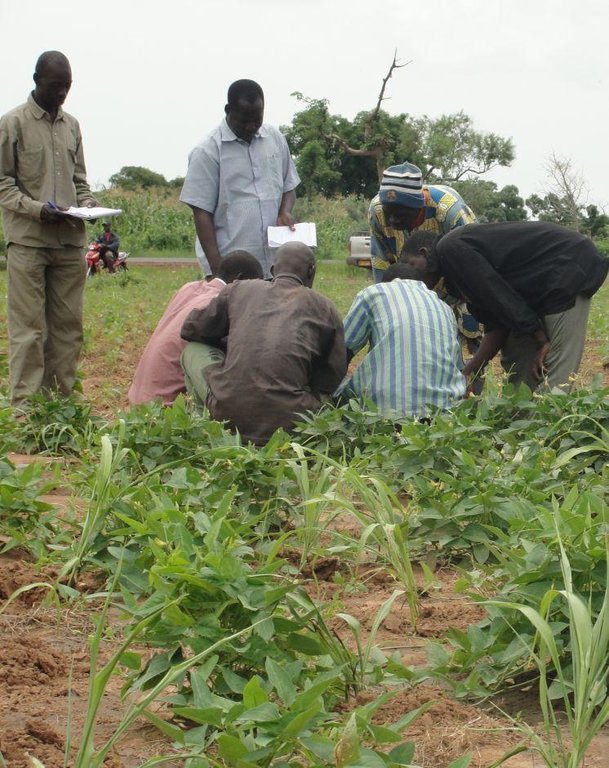
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Implementation: Men and women farmers are informed about the harmful effects of pesticide use. A group of local farmers are offered the opportunity to form a farmer field school led by a facilitator (with 25 farmers in each FFS group). The weekly sessions of the FFS focus on studying the presence
of insects and diseases and the condition of plants. The results are recorded in a study-findings logbook. Biopesticides like neem extract are used and their effectiveness is studied. Operation: Setting the critical thresholds for pest infestation of crops and evaluating the treatments required; Composing and applying pesticides according to the level of infestation.
Roles of the actors involved: Producers participate in the FFS and apply the techniques on their lands. Technical services provide training in good farming practices and link up the plant-disease and insect experts with the FFS facilitators. Research institutions make their plant-disease and insect experts
available and train up the technical services.
Natural / human environment: Implementation locations: All regions throughout Mali. On going for around 12 years. This technique is particularly popular with farmers. Trained facilitators and farming advisors are available.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มาลี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Mali
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): environmental degradation caused by current farming practices (intensive and extensive)
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M7: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other management measures: combatting pests
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (negative impact of pesticides, neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: combatting pests, change in farming practices
Other type of management: IPPM works with all available techniques for combatting pests, while keeping pesticide use at economically justified levels. Adoption of respectful farming practices.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium and poor
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: Also poor/ none
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The irrigated area is allocated by the chief
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced use of pesticides
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced risk to human and animal health and to the environment
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
IPPM promotes the adoption of farming practices that are as respectful of the environment as they are productive and profitable. It reduces risks to human and animal health and to the environment.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
คุณภาพน้ำ
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Implementation locations: All regions throughout Mail.
Scope of application: All farmed basins.
Duration of application: On going for around 12 years
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Reduction in pest control costs |
| Farm production is healthier and the environment is better protected |
| The use of pesticides for safeguarding production in rural areas is now very low. |
| Reduction of the negative impact wrought by pesticides on the environment (wildlife, water, soil) and on humankind |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The village facilitators and farmers participating in the FFS must be literate | |
| IPPM requires inputs from plant-disease and insect experts |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Annual reports for 2010, 2011 and 2012 – IPPM/DNA
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
URL:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล