Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakha Chuke Tole for domestic use. [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sabita Aryal
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1655 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bajracharya Reena
Kathmandu university
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Maharjan Satish
Kathmandu university
เนปาล
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kathmandu University (KU) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [เนปาล]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sabita Aryal
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
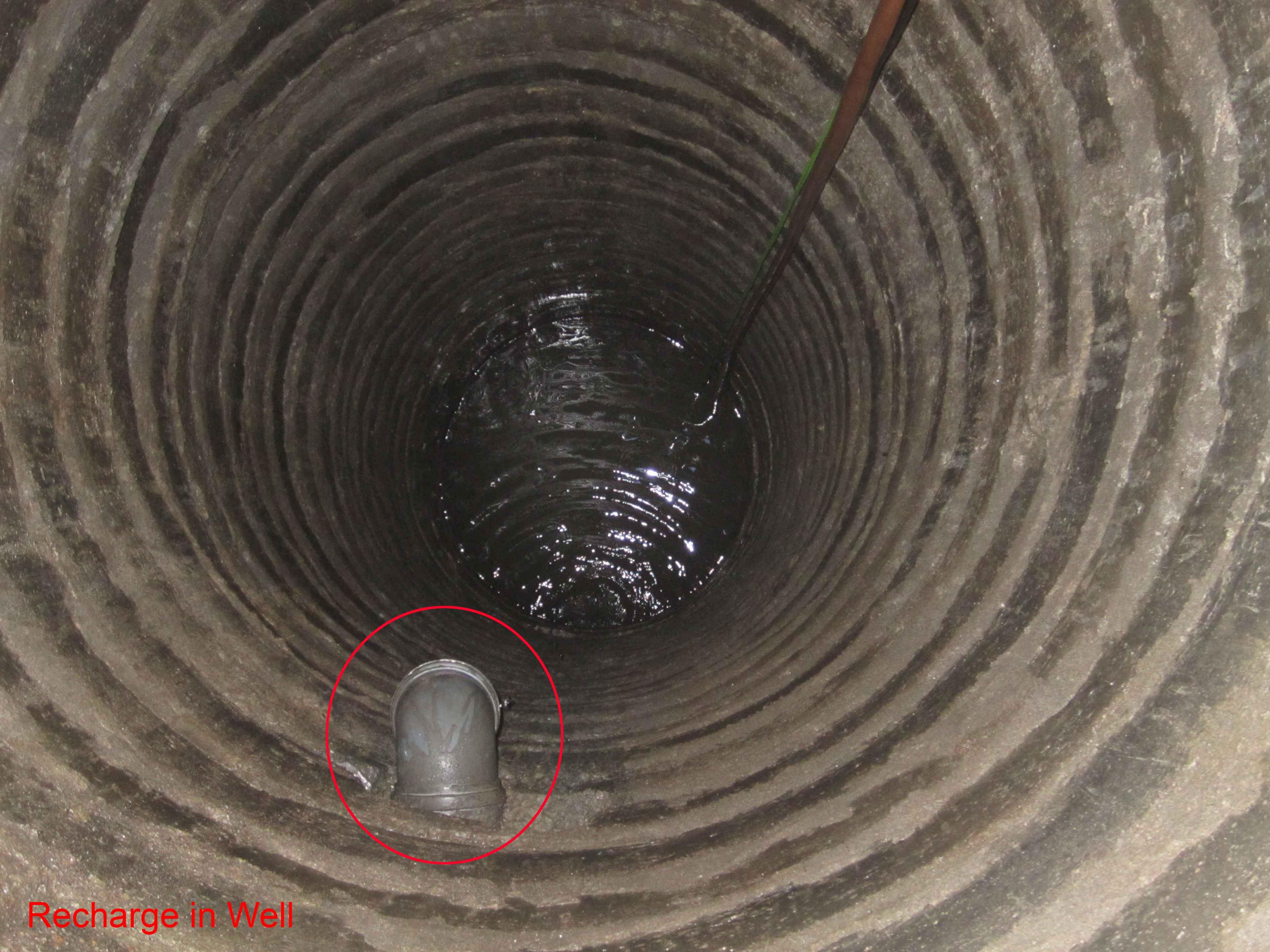
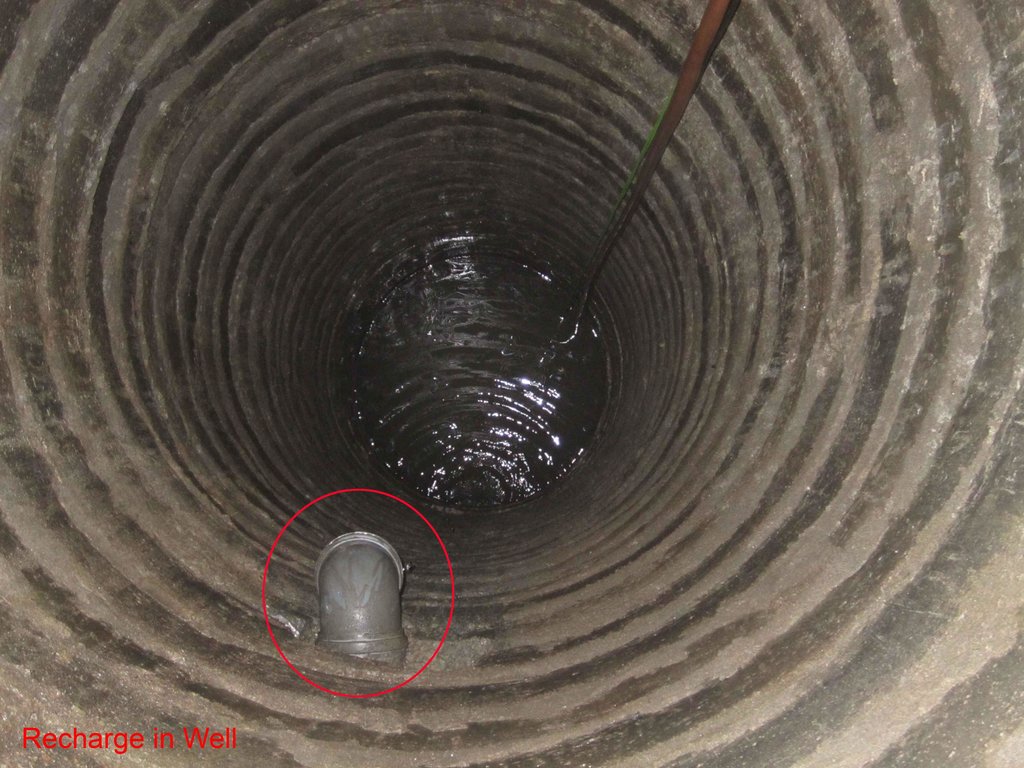
Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakka Chuke tole for Domestic use.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
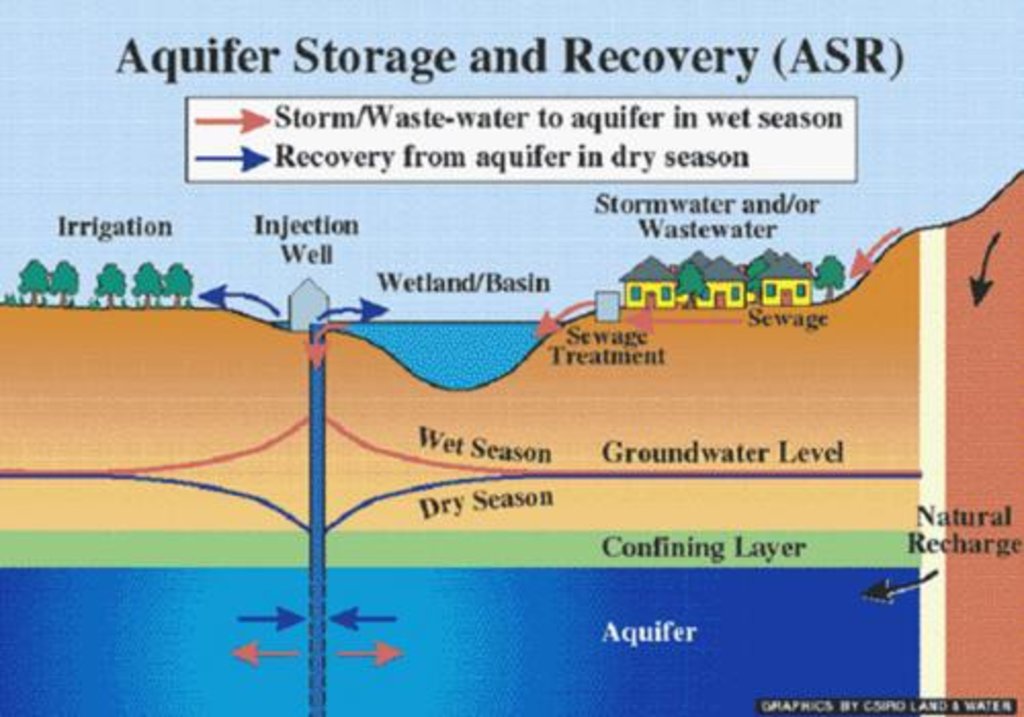
Due to increasing population and urbanization along with unmanaged settlements in and around the core city areas in Lalitpur existing ground water dries up while the water levels in well is decreasing alarmingly. However with initiation of rainwater recharge programs in areas in 2009
locals from around 150 houses around nyakha chuke tole and adjoining areas in lalitpur get their water supply with sucessful replerishment of their underground aquiter through rainwater harvesting.the dugwells are being sucessfully replerished due to rainwater recharge system.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is mainly applied to replerish ground water aquiter to support around 20 different committee in Lalitpur.
This aims to make people aware of the recharge mechanism and augument ground water level.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The credit for implementing this technology must go to local people participation. It is only because of the cooperation among themselves that make them realize current alarming problem and made them collect money for implementing recharge system.They have done it with external material support such as food-work, payment, subsidized machinery.
Regarding maintenance activities , women living around nyhakha chure tole are responsible for cleaning areas where technology has been implemented. Besides , water content in dug well are tested every six months to make sure that water is suitable for drinking that is free from ions and other chemicals . As well as different machine such as pump are checked every six months and are replaced if damaged, with the money collected from different house hold.
Natural / human environment: The implementation of this technology or system has made availability of water for various domestic use by supplying the water in each and every houses.It also has helped increasing harmony and mutual understanding among the people living there by. In past years people use to fight for getting water. there were fight between two locality for water . Ground water recharge system has increased water sources . There is proper distribution of water. Now people do not have to disturb their sleep for getting water like before.this has even helped to improve living standard and health of people.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
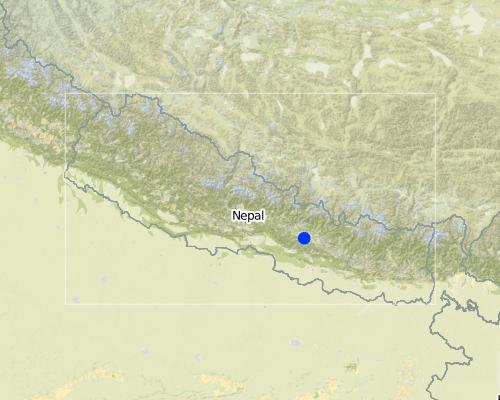
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Nepal
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Lalitpur
Map
×3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- Protect ground water
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major cash crop (CA): Rice
major cash crop (CP): Potato
major cash crop (CT): Orange
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
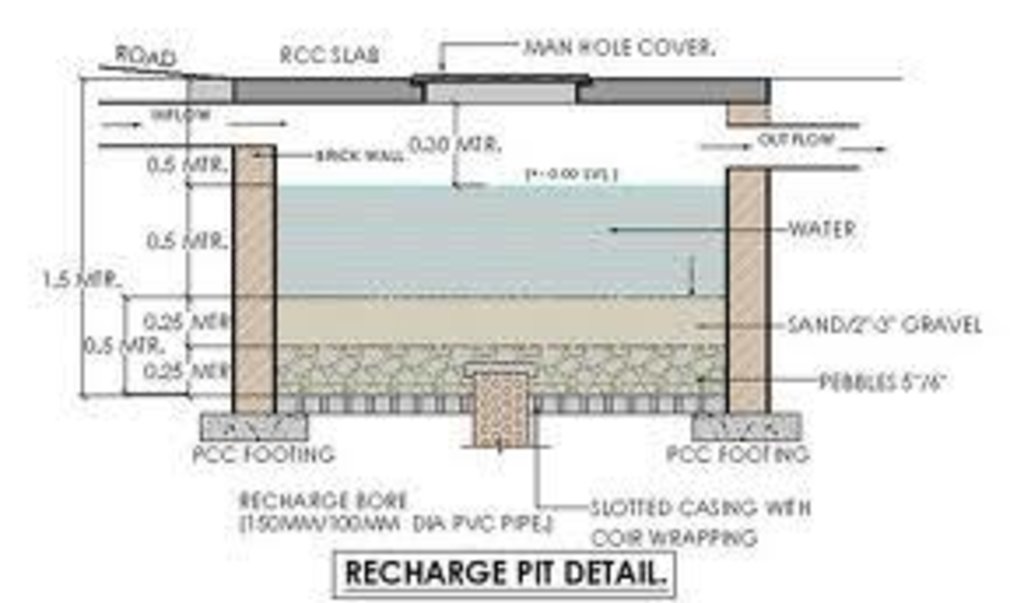
Underground water from dug well is drawn to stone filter through electrical pump. Water is purified in wash stone filter. purified water is pumped and drawn to surface water tanks from where water is distributed and supplied to people.
Location: nyakha chuka tole. lalitpur
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 200ft
Structural measure: rechargewell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20ft
Structural measure: dugwell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 29ft
Structural measure: underground
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15ft
Structural measure: water tank
Construction material (earth): used for construction
Construction material (stone): used for purfying
Construction material (concrete): used for construction
Construction material (other): used for construction
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Water harvesting system
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | dug well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 2. | underground water tank | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 3. | recharge well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 4. | others | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | 8hrs for 7 days |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Dug well | pieces | 1.0 | 124.0 | 124.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Underground water tank | pieces | 1.0 | 257.0 | 257.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Recharge well | pieces | 2.0 | 28.5 | 57.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Others | unit | 1.0 | 128.5 | 128.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 566.5 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | electricity | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | every month |
| 2. | dump | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | every month |
| 3. | others | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | every month |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อื่น ๆ | Electricity | month | 1.0 | 18.57 | 18.57 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Dump | month | 2.0 | 85.5 | 171.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | others | ,onth | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 206.57 | |||||
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
labour and constructing wells are the most determinant factors affecting the cost.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1114.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
Level of mechanization: tractor
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- กลุ่ม
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The Technology helps providing pure water for drinking which is one of the basic factor for drinking
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
การระเหย
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
proper drainage system
better plantation
diversity
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The establishment and maintainance cost is not so high compared to benifit and facility that are provided by the technology which has solved the problem of water in more than 200 household in one locality
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
150 households
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: the technology have been developed traditionally with local knowledge. therefore locals manage and maintain the pumps, controlbox.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: water is basic fundamental needs of life. peoples are also searching for alternatives for minimizing and solving the problems.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
now people dont need to disturb their sleep for collecting water How can they be sustained / enhanced? further educating people about benifit of ground water recharge we can make them participate in various program of maintainance and development of this technology |
| water supply is easily facilitated |
| local participation |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
there is proper supply of water in each and every houses How can they be sustained / enhanced? making all people aware of recharge mechanism, we can enhance this technology and supply water to people |
| peace and unity among people |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| land investment is required even different modern technology should be made available to purify water and make them iron free | government should make their concerns regarding such problems |
| participance from local communities is not enough for such large investments and implementing new technology |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| in some places the % of iron is high which makes the water unsuitable for drinking | different water purifying technology should be applied such as pets, sand, gravel etc |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [เนปาล]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sabita Aryal
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล