Almond and Apple sapling plantation [อิหร่าน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
تبدیل دیمزارهای کم بازده (گندم و جو) به باغات سیب و بادام (arab)
technologies_1742 - อิหร่าน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Majid Soufi
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Hasan Ahmadi Shiraz
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/05/2010
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
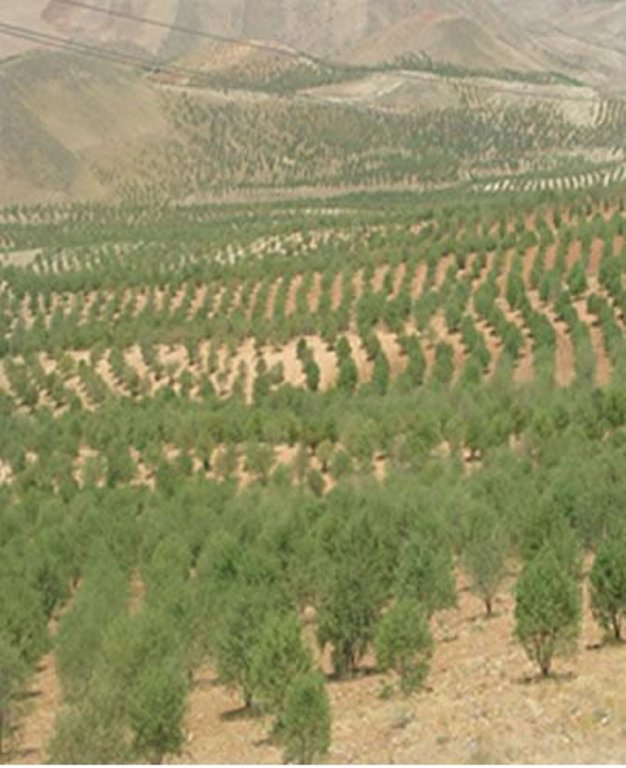
Plantation of almond and apple trees on the contour lines instead of annual rainfed crops such as wheat and barley on hills with 8 to 30% slope.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
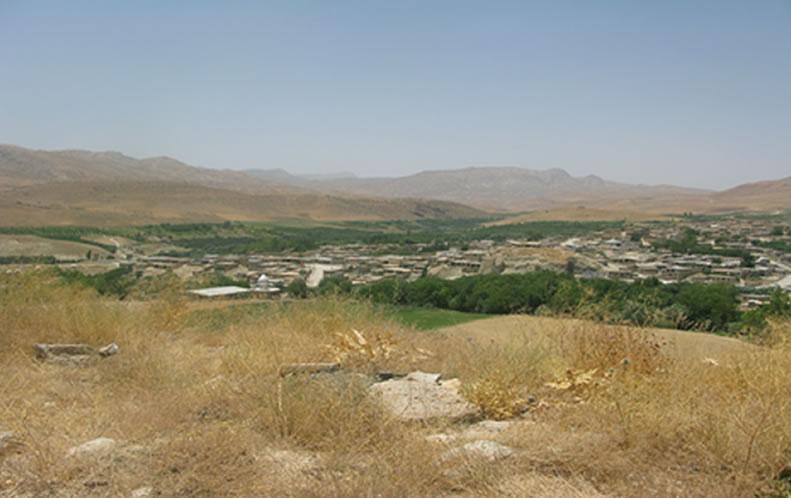
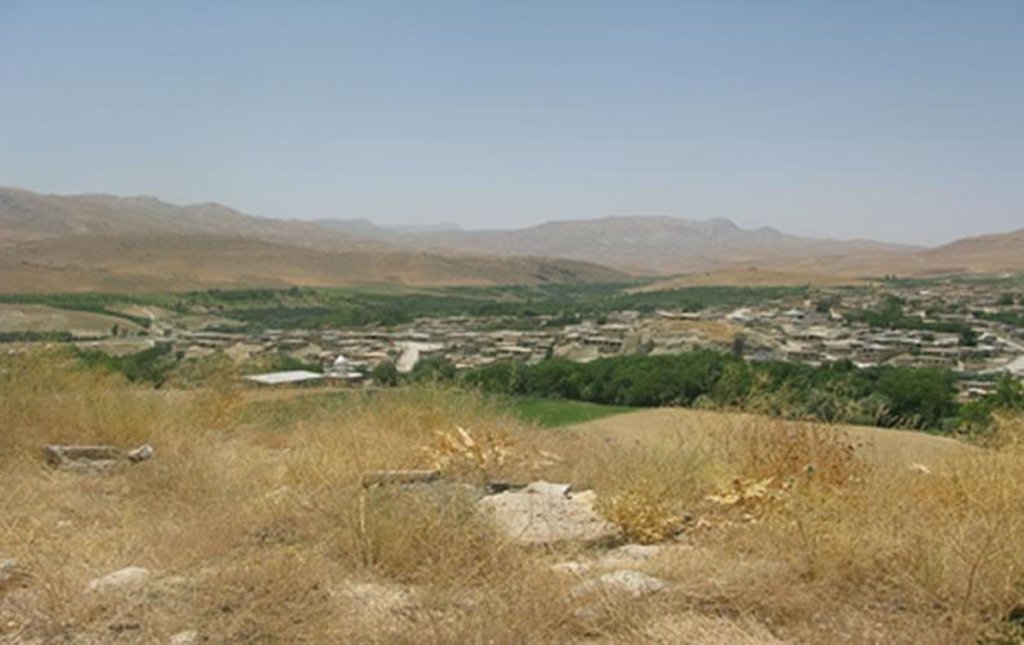
Dejkord village is located in north – west of Fars province and west of Eghlid dis-trict. This village is located on hilly steep land with 390 families. Climate of the village, according to Demarton classification, is situated in the Mediterranean temperate zone. The long-term mean annual temperature is 13.5ºc and long-term mean annual rainfall is 510 mm. The landforms of the study area are generally rolling (with slope 8-16%) and medium mountain ridges (with slope 16-30%). The site study is located between 2000 and 2700m above sea level. The average depth of the soil in this region is 50cm. Dominant top soil textures are sandy loam, loam, and sandy clay loam and are commonly shallow with low amounts of organic matter (usually below1% ). The results of soil analysis showed that silt decreases and sand and clay increase with soil depth. The range of clay, silt, and sand is respectively 16 to 35 %, 9 to 33 %, and 47 to 73%. EC (Soil Electrical con-ductivity) is less than 1(dS/m). The main problems in this area are poverty and soil erosion that reduce crops yield. Ploughing in slope aspect increased soil erosion in this area.
The impact of this technology depends on establish pits on contour line that caused to keep runoff and reduce velocity of rain water and also canopy cover of trees caused to prevent of rain splash and provides adequate soil cover, protect-ing the land from Erosion and roots of trees enhanced infiltration. Otherwise this system increased farmer income rather than before implementation technology.
Watershed Cooperative of Dejkord started its activities since 1998 with 548 mem-ber and covering 8 villages but today this watershed cooperative have 8000 members . In order to build capacity for the watershed resident, the Fars province office of natural resource started to give lands for non – irrigated plantation which are suitable for improving the watershed. The mentioned office gives US$ 800 loan as a very cheap facility against 1 hectare of the land to the members of watershed cooperative, and the time of paying back is 5 years after they get the loan. Nowadays 15000 hectares of those lands are converted to non – irrigated gardens of Almond and Apple trees. Out of 15000 hectares, 10000 include productive Almond garden, and 5000 hectares include Apple garden .As an average, for 1 hectare about 4.5 to 5 kg seed with the value of 1.5 US$ are needed. There are 270 to 300 saplings in 1 hectare and the distance between the saplings is 6 meter. Before the watershed program, the income of resident was US$ 80 per hectare per year, however after the project their income increased to US$ 1000 to 1200.per hectare per year. For maintenance of the project some measure like fertilizing, recession, spraying, cropping and etc will be done.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อิหร่าน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Fars Province, Iran
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Eghlid District, Dejkord Village
2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
1998
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There are several problems in this area, including: land degradation because of inter-rill, rill and gully erosion, lack of income economic resources for stockholders before implementation. income of resident was US$ 80 per hectare per year from annual crops but after the implementation, their income increased to US$ 1000 to 1200, plowing the lands by farmers along with slope in land with more than 10% slope topographical status, soil fertility decline.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 150 km2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, industrial activities and mining, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), floods, population pressure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
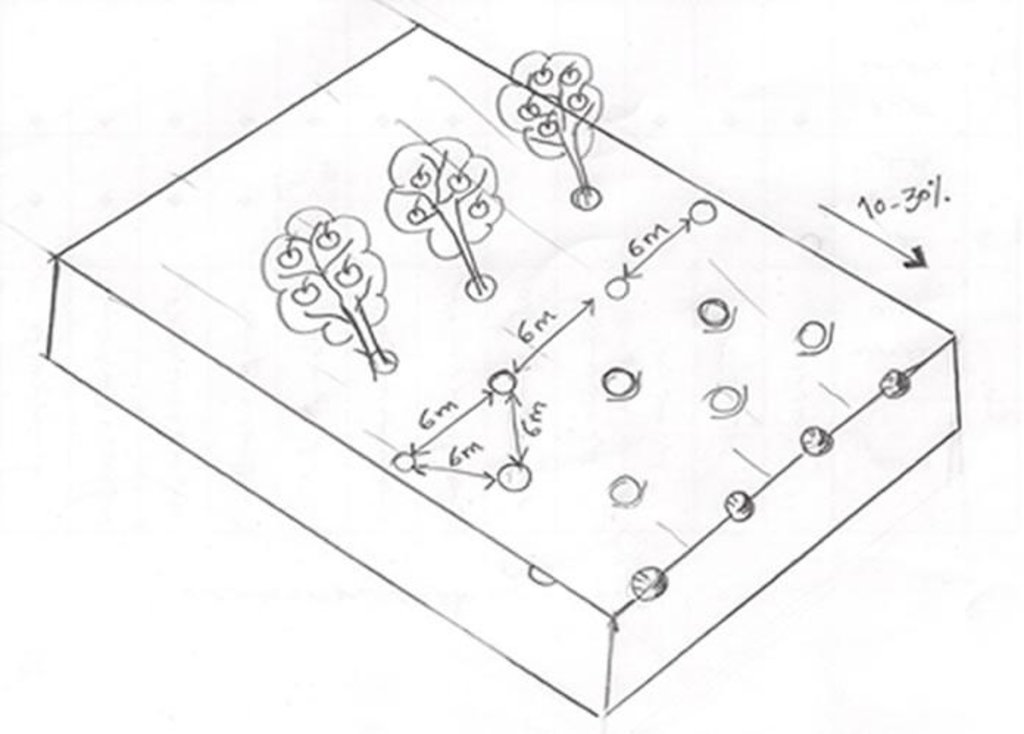
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Fruit trees cultivated on slope (10 - 30%) with a spacing of 6 between.
Location: Dejkord Village. Eghlid District, Fars Province, Iran
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Vegetative measure: Vegetative Measure
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Change of land use type: Change from grazing land and annual rainfed crops to tree crops.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging Pits carried out by labor on hilly steep land (approximately 270-300 pits per ha) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | before rainy season |
| 2. | Planting of fruit tree seeds (Almond and Apple) by hand | ด้วยวิธีพืช | spring |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Digging Pits and planting of fruit trees | ha | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 137.5 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plugging of land with tractor in contrast to the slope. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | Digging pits at the foot of the tree for water harvesting. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Pest management with chemicals. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | two or three times a year |
| 4. | Trees pruning. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every year |
| 5. | Create a slot for fertilizers/manuring | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 6. | Manuring. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after one year |
| 7. | Irrigation of new seedlings. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 8. | Harversting of fruits. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 9. | Pest control for trees and their fruits. | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | All the labour | ha | 1.0 | 410.0 | 410.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Toxin for pets | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 570.0 | |||||
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mediterranean
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: Near ground
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
There were many wild birds before, now there are only few.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- สหกรณ์
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Off-farm income specification: Most farmers depend economically entirely on their own crop production.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
livelihood and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
competition
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
wind velocity
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Establishment costs are high in the first year, but after 5 years the system becomes very profitable.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on adoption trend: At the first stage most of the land users who accepted the technology did so with incentives, but there was no spontaneous adoption.
- The project gives educational assistance, training, technical assistance in the field.
- Spontaneous adoption is growing in neighboring villages.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Different fruit harvested at different periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? gives better income in 1 year and therefore encourage family members participation |
|
Improved conservation/ erosion knowledge How can they be sustained / enhanced? This project has caused the resident acceptance and therefore caused to the extension of the technologies to the neighbor region |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Rehabilitation of degraded areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? reduced soil erosion and increased productivity |
|
Production increase and good fruit yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? Introduce low input demanding and fast producing tree species and varieties. |
|
Increased food security How can they be sustained / enhanced? with production and generation of different kind of fruits |
|
Reduction of erosion processes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the soil cover through implementation of planted trees |
|
Increased crop production and diversity (fruit, timber) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Apple and Almond |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Fruit trees consume more water (but they also help in drainage) these trees with consuming water and waste it to transpiration caused to Reduction in stream flow in downstream | through lowering the ground water table. Appropriate tree species need to be selected and bred. |
| Pest and diseases | pests on apples reduced the price of products (pets controlled by toxin and natural hunters). |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล