Improved grazing land management [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Daniel Danano
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Gitosh masheshal
technologies_1049 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - เอธิโอเปีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2003
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Local level participatory planning approach [เอธิโอเปีย]
An approach used by field staff to implement conservation activities, involving farmers in all stages of planning, implementation and evaluation.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Daniel Danano
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
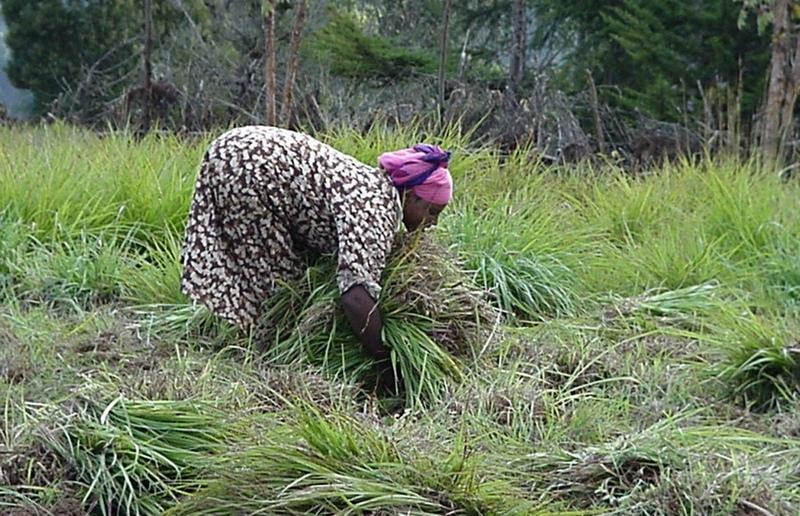
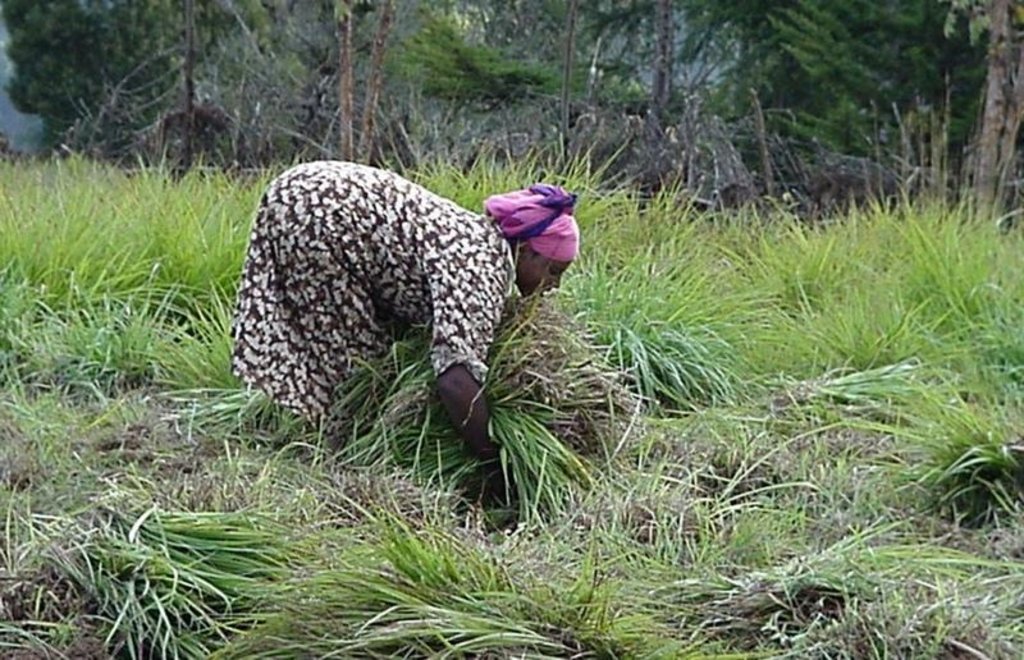
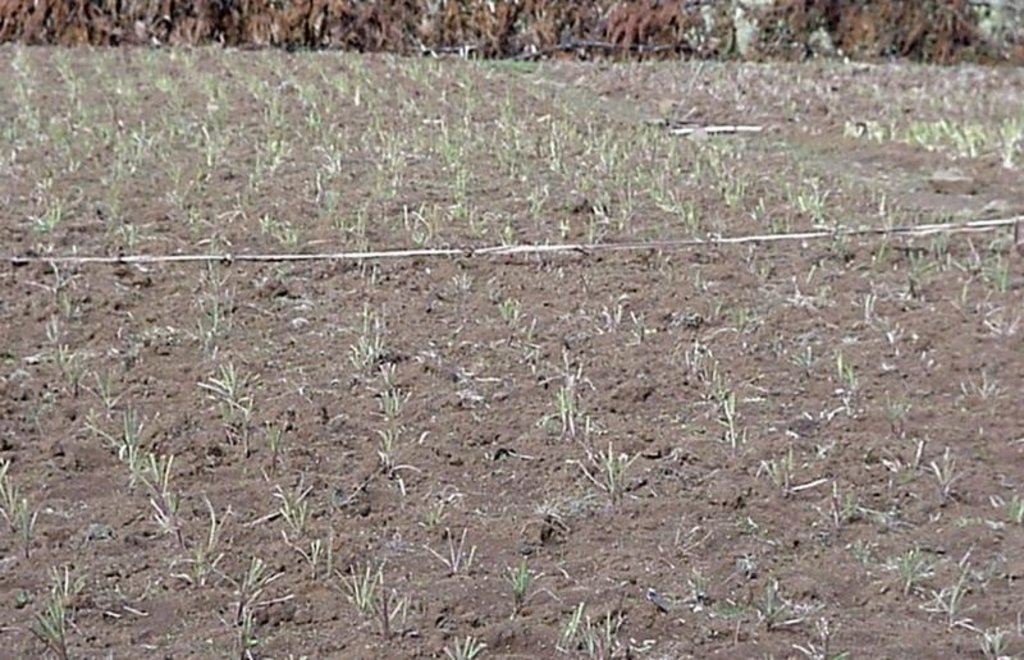
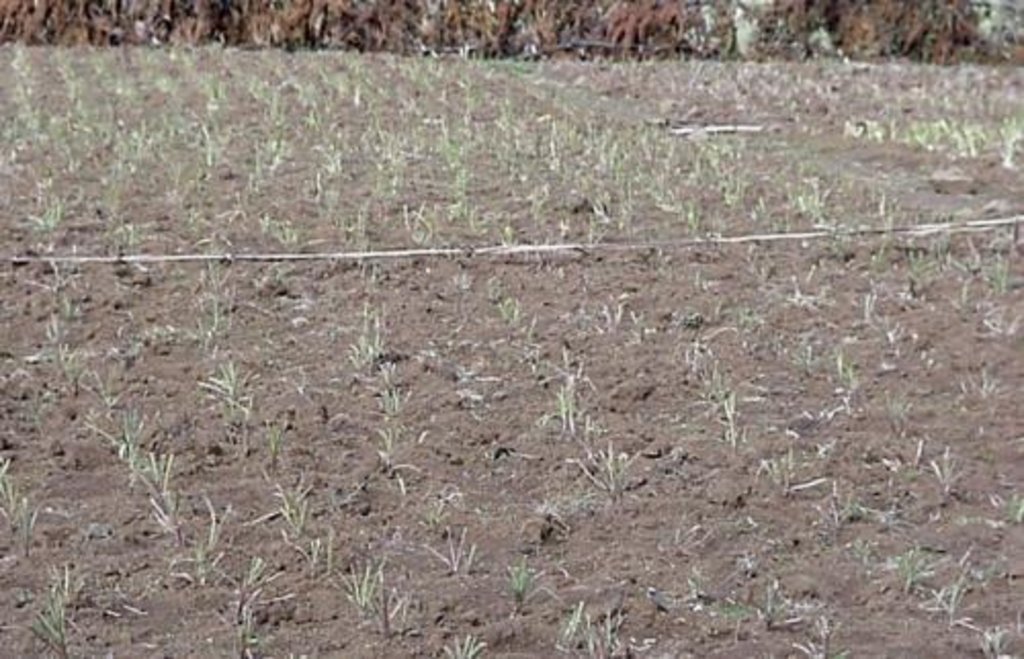
Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands, through planting of improved grass and fodder trees and land subdivision, to improve fodder and consequently livestock production.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
This case study focuses on the highly populated, humid highland regions of Ethiopia that experience serious shortages of pasture. Due to rapid population growth, communal grazing areas are increasingly being converted into cropland. This has led to enormous pressure on the little remaining grazing land, through overstocking of dairy cows and oxen, and thus overgrazing, resulting in considerably decreased productivity.
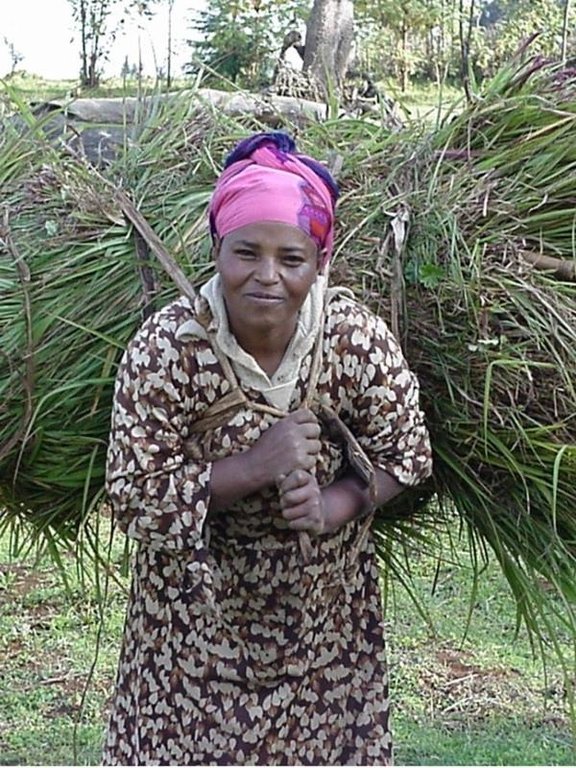
Improved grazing land management is vital to increase food security and alleviate poverty, as well as to bring environmental rewards. To address these problems, the national SWC programme in Ethiopia initiated a grazing land management project over a decade ago. Implementation of the technology includes the initial delineating of the grazing land, and then fencing to exclude open access. This is followed by land preparation, application of compost (and, if necessary, inorganic fertilizers) to improve soil fertility, then planting of improved local and exotic fodder species, including multipurpose shrubs/trees such as Leucaena sp. and Sesbania sp. and the local desho grass (Pennisetum sp.). Desho has a high nutritive value and regular cuts are ensured. It is planted by splits, which have high survival rates and establish better than grasses which are seeded. Other grass seeds, as well as legumes, including alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa) and clovers in some cases, are mixed with fodder tree seeds and then broadcast.
Maintenance activities such as weeding, manuring and replanting ensure proper establishment and persistence. Fodder is cut and carried to stall-fed livestock. Once a year, grass is cut for hay, which is stored to feed animals during the dry season. Experience shows that such grazing land is best managed when individually owned and used. In the study area, the community has distributed small plots (<0.5 ha) of communal grazing land to individual users to develop, manage and use.
The overall purpose of the intervention is to improve the productivity of grazing land and control land degradation through the introduction of productive techniques and improved fodder species, which consequently improve livestock production. Commercialisation of animals and marketing of their products increases the income of farmers. The government provides technical assistance, close follow-up, and some inputs for initial establishment. Land users are trained in compost/ manure application, planting of seeds, splits and seedlings, and general maintenance.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Chencha
Map
×2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
before SWC

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
After SWC - cut-and-carry (desho gras (Pennisetum sp.)), legumes (alfalfa, lucerne: Medicago sativa), trees (Leucaena sp, Sesbania sp.)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population growth has resulted in a substantial reduction in land holdings (<0.5 ha per family) and this in turn has led inevitably to encroachment onto communal grazing lands for cultivation. Livestock numbers on the other hand have remained unchanged, and this has led to overstocking of the few areas left. Livestock production, which accounts for 40% of the average household income, is thus reduced and farmers’ income declines correspondingly.
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: March - September
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปิดล้อมพื้นที่ (หยุดการใช้ประโยชน์ สนับสนุนการฟื้นฟู)
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Splits of desho grass (Pennisetum pedecillatum) are plantet in lines, using a hand hoe, after good seedbed preparation. Spacing between grass splits is 10 x 10 cm. The white line is a boundary between two households' plots (width of plot: 15-20 m). Trees are planted at rirregular spacing (around 5 m apart), layout is not specified.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of dispersed runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure, control of concentrated runoff
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: animal manure, leaf litter, wood ash, soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena sp., Sesbania sp.
Grass species: Desho grass (Pennisetumsp.), alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa)
Other type of management: change of intensity level
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delineation of the area to be conserved and establishment of a fence | ด้วยวิธีพืช | before the onset of rain |
| 2. | Subdivision of communal land into individual plots of 0.3–0.5 ha. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Planting material preparation in nurseries: grass splits (desho) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 4. | Good seedbed preparation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | (at the onset of the rains). |
| 5. | Planting of grass splits and tree/shrub species in lines; sowing of grass | ด้วยวิธีพืช | (early in the rainy season). |
| 6. | Weeding. | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 320.0 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Grass splits (tillers) | ha | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1052.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compost/manure preparation. Material used includes animal manure, | จัดการพืช | / initial establishment |
| 2. | Compost application | จัดการพืช | / one month after planting, initial establishment |
| 3. | Cut-and-carry, to stall-fed animals, begins when fodder is ready. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | (after 2–3 months growth) /2 -4 times |
| 4. | A final cut for hay is taken early in the dry season when the grass has matured well. | ด้วยวิธีพืช | (end of October) / |
| 5. | Weeding | ด้วยวิธีพืช | /each year. |
| 6. | Compost/manure application, mixed with soil, during seedbed preparation (only where plants have died and need replacement and fertilisation). | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 7. | Enrichment planting and gap filling | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after a year / repeated each year. |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 126.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Seedlings are given by the government for initial establishment. For further extension of area and replanting, the
land users set up their own nurseries. After 2-3 years maintenance costs decrease substantially as the grass cover closes up and maintenance activities such as replanting/enrichment planting and compost application are reduced or cease. The local daily wage is about US$ 0.70 a day, but varies depending on the intensity of the work. In this calculation the standard rate has been applied.
Farmers usually cannot afford fertilizers. Milk production compensates for some of the high investment costs (previously, production was low).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Local term: wett dega
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and foot slopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 2) and low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Off-farm income specification: source of off-farm income includes petty trade and weaving
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha: Ranked 1
< 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha: Both ranked 2
2-5 ha: Ranked 3
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase in livestock production
การผลิตไม้
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase in the availability of livestock products on the market
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Decrease in size of grazing plots due to land fragmentation
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Selling animals and their products
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Dependence on incentives
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Initially high. Incentives such as free seeds, seedlings, tools
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improvement in household diets (milk)
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased willingness
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
Sediment transport
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 50 households who accepted the technology in the initial phase, did so with incentives. They were provided with planting materials (seeds, seedlings, grass splits) and hand tools.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The rate of spontaneous adoption is very high. At present over 500 households have taken up the technology and the total area covered is about 20 km2.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Increased national income due to export of animals and their products. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Availability of fodder (grass, hay, shrubs) in sufficient quantities, and all year round How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the area under such development. |
|
Reduction in soil loss and land degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain adequate cover by planting more grass. |
|
Introduction of high yielding species as well as increase in land productivity and livestock production How can they be sustained / enhanced? ntroduce bigger variability of quality species and improve maintenance activities such as weeding and cultivation. |
|
Improved diet: livestock by-products such as milk, butter and cheese are essential food items required by the households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep on increasing/improving quantity/quality of livestock feed. |
|
Increased income through commercialisation and marketing of animals and their by-products. Meets financial needs for paying taxes, school fees, clothes etc. |
| Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands is both a technical and social challenge. Here is a promising example from Ethiopia that is spreading quickly. The key is subdivision of land into individual plots where cut-and-carry of grass and stall-feeding of livestock is practiced. This is only a possible option, however, where rainfall is favourable. land use rights: individual for cropland, open access (unorganised/communally used) for grazing land, except for the case study area where the rights to rehabilitated grazing land are given to individuals |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| At the initial stage of establishment it is very labour intensive | Use of improved land preparation methods such as oxen ploughing. |
| Substantial cash for inputs, particularly seedlings, is required | Produce seedlings of improved species and making compost in backyards. |
| Needs high fertilizer application | Focus more on organic fertilizers. |
| High pressure on remaining grazing areas | Keep animals in stall (stable) or park, at least part of the day and during the night, and introduce cut-and-carry more widely. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Adane Dinku, Chencha Wereda, Natural Resources Management Annual Report,. 2001 and 2002.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Local level participatory planning approach [เอธิโอเปีย]
An approach used by field staff to implement conservation activities, involving farmers in all stages of planning, implementation and evaluation.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Daniel Danano
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล