Artificial Reef [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano
Gango
technologies_3116 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
Sustainable Livelihood Officer (SLO):
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Danajon Communities WATCH ( DCW)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Philippine Partnership for the Development of Human Resoruces in Rural Areasy (PhilDHRRA) - ฟิลิปปินส์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
05/04/2017
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Artificial Reef is installed at the bottom of the sea and anchored in all corners, thus, any weather and climate condition can not directly affect the situation of the technology as an alternative marine habitat.
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Social Enterprise (SE) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
Social Enterprise (SE) aimed to provide social protection among its members and generate additional family income. Above all, this approach will encourage the conservation, preservation and protection of the resources available in the community.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Artificial Reef is a fish aggregating device that is considered as a sustainable alternative in the islands of Bohol. This technology can withstand the effects of gale warning, typhoons and extreme heat.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
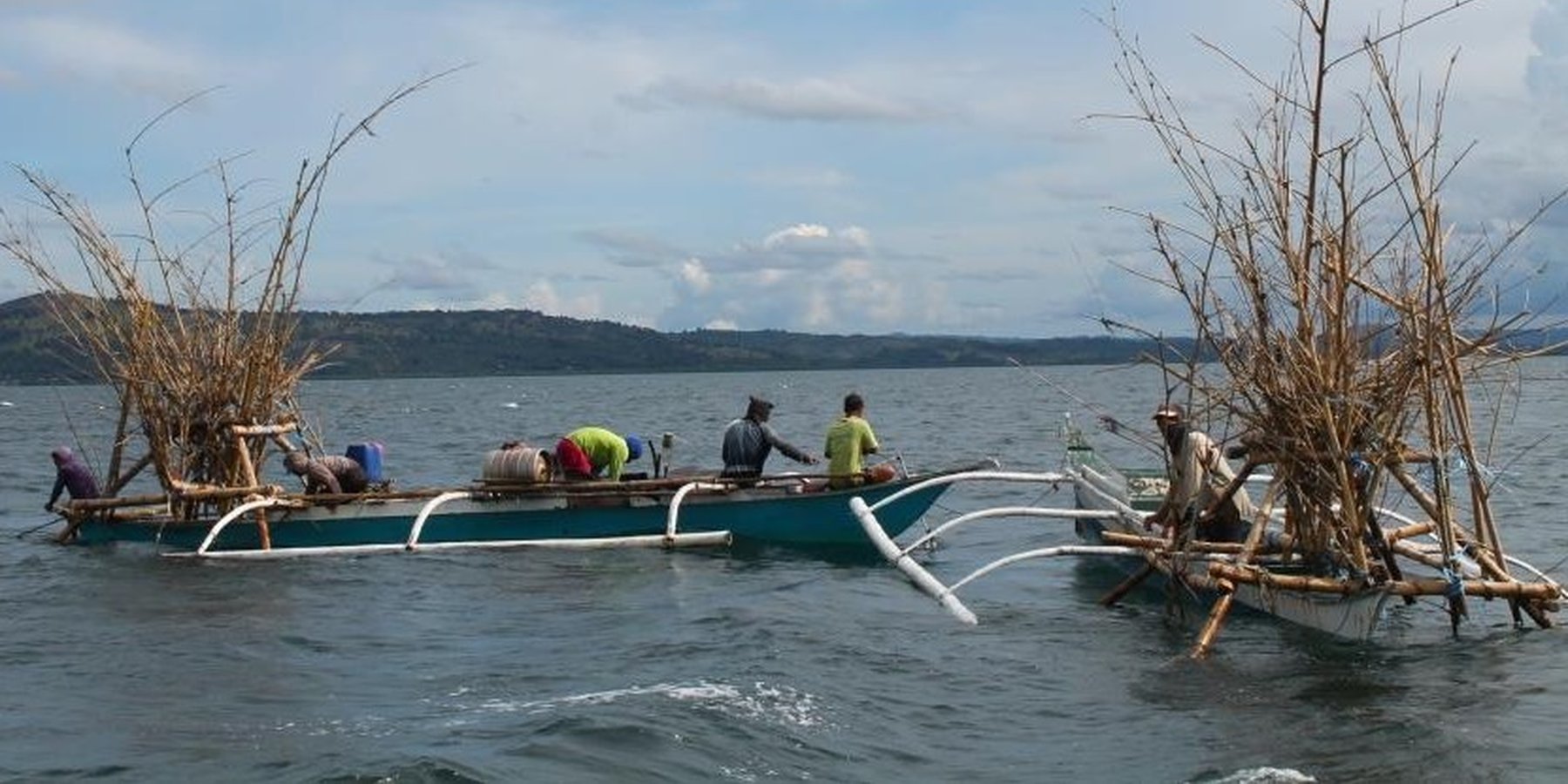
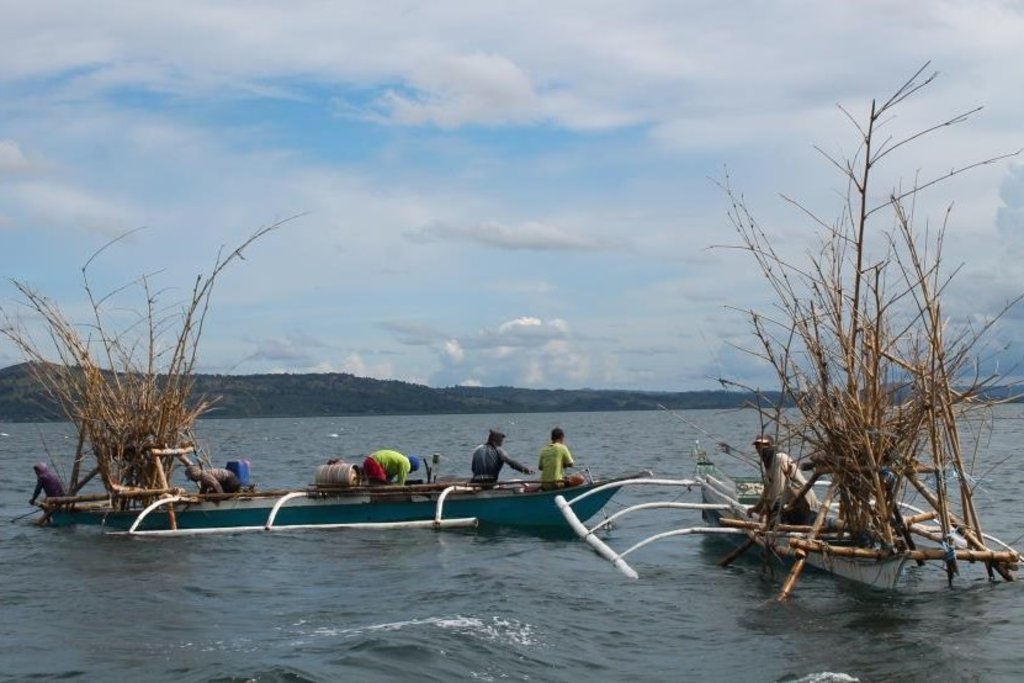
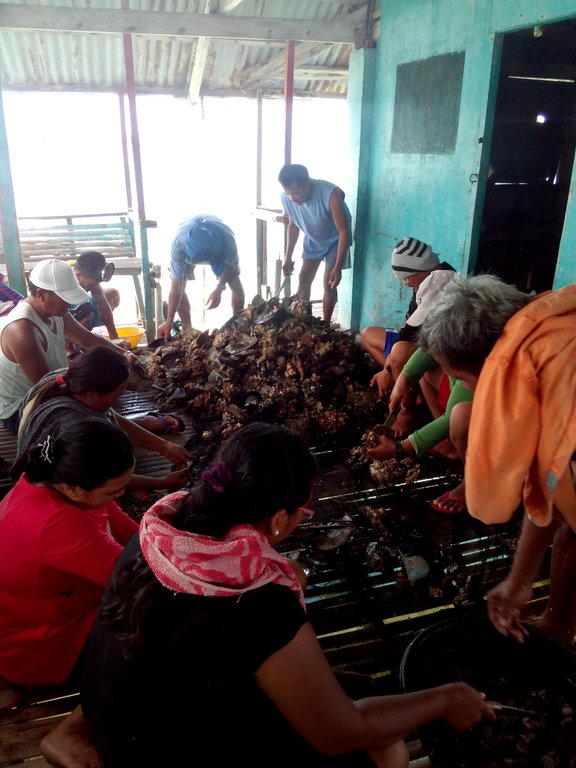
The fishers of Bohol have been using Artificial Reef over a long period of time. This is a fish aggregating device but at the same time, used for brown lip culture. Aside from the above mentioned functions of Artificial Reef, the Island of Bilangbilangan East in Bien Unido, Bohol installed this technology around the buffer zone of the marine sanctuary because the floater will serve as indicator of the marine protected area.
Artificial Reef Technology is a project of Bilangbilangan East Fishers Association (BEFA) from Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Bien Unido, Bohol; Calituban Fisherfolks Association (CFO) from Brgy. Calituban, Talibon, Bohol and Nasingin Fisherfolks and Mangrove Planters Association (NasFiMPA) from Brgy. Nasingin, Getafe. This technology is owned and managed by the People's Organization found in these three island barangays namely BEFA, CFO and NasFiMPA.
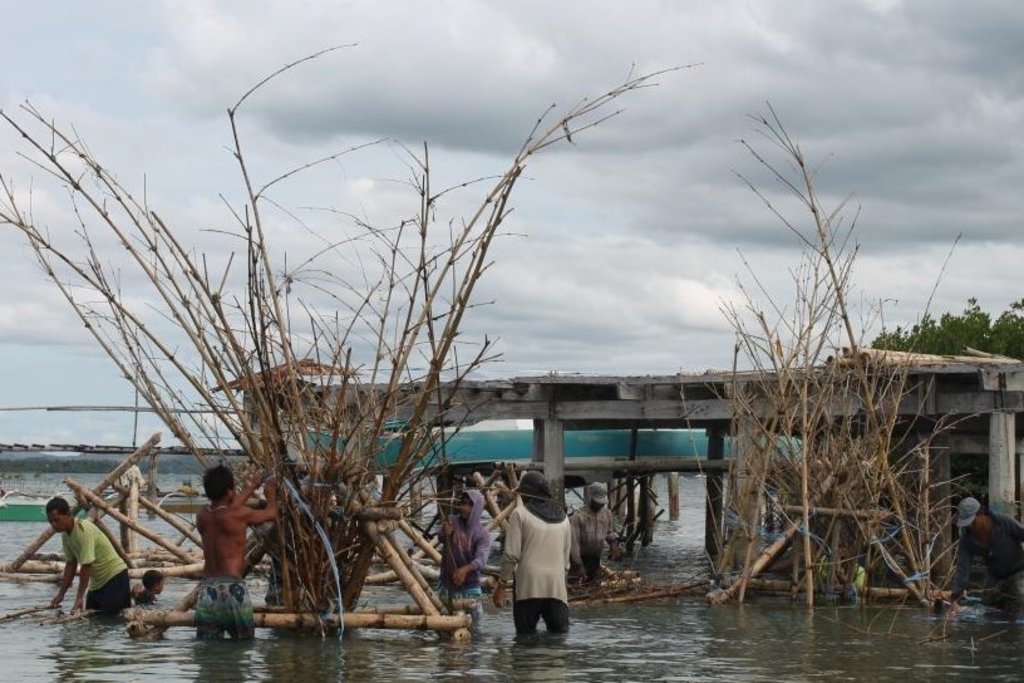
Artificial Reef if is primarily made of bamboo with a life span of 3 to 5 years. For stability, it is anchored in the four corners using a cemented container tied to every end of its corners. For markings, floaters are placed in the sea surface but Nasingin and Calituban fishers preferred not to use floaters for the security of their installed artificial reefs, rather, they used terrestrial points to identify the location.
This technology was installed within the municipal waters (15 kilometers from the shoreline) to help minimize fishing cost and avoid the hazards of sudden change in weather condition. The PO are now vigilant because they already installed Artificial Reefs before but were destroyed by the dynamite fishers. This encouraged the PO members to practice safe and legal forms of fishing in order to sustain their project. Above all, artificial reef will enhance fish spawning and provide alternative shelter to fishes during hot season.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
Brown lips will naturally grow in the artificial reef. After 3 months of installation, fishers can already harvest fish while the first harvest of brown lip can be done a year after the installation.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Monitoring of the Artificial Reef in Bilangbilangan Island, Bien Unido, Bohol after 3 months of installation.
A Social Enterprise Project of Danajon Communities WATCH (DCW) Project. Implemented by PhilDHRRA, LPFI and A2D Project. In Partnership with Caritas Switzerland and JTIF.
วันที่:
01/06/2016
สถานที่:
Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Bien Unido, Bohol
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Bilangbilangan East Fisherfolks Association (BEFA)
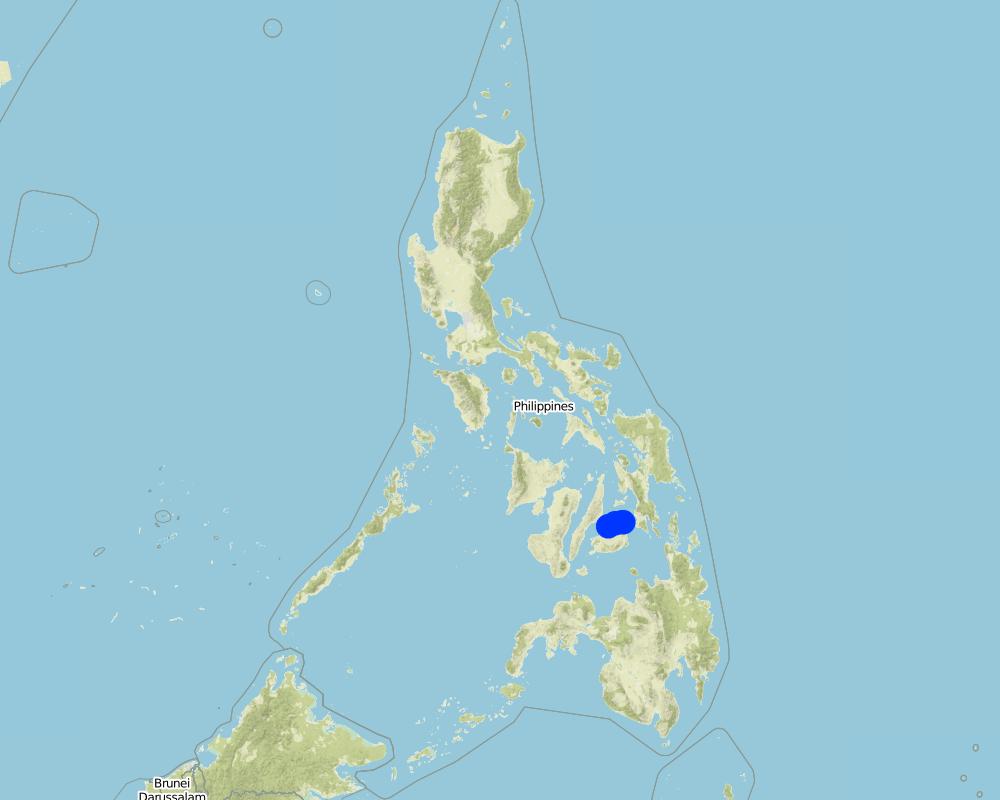
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Bohol
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Municipality of Bien Unido; Brgy. Calituban, Municipality of Talibon; Brgy. Nasingin, Municipality of Getafe
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The team decided to get the coordinates of the 2 ends and middle part of the Artificial Reef installed due to the weather and current of the tide. Also, these technologies were installed in a linear position.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The 3 areas have tried this kind of method even before DCW Project. However, it was not sustained mainly because of illegal fishing and illegal entry of fishers from the neighboring municipalities and barangays.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- sea
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Brown lip culture and fish aggregating device
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Before the installation of Artificial Reefs, the fishers are obliged to go beyond the municipal waters which increased their production cost and risk to sudden change of weather.
The Artificial Reef was installed within the municipal waters (15 kilometers from the shore line), fishers will lessen their production cost particularly their fuel consumption. This technology also increased fish spawning and marine conservation.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
อื่นๆ (เช่น หลังจากน้ำท่วม):
- not applicable
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Each Artificial Reef was installed 10 meters apart from each other.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S9: ที่พักพิงสำหรับพืชและสัตว์
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
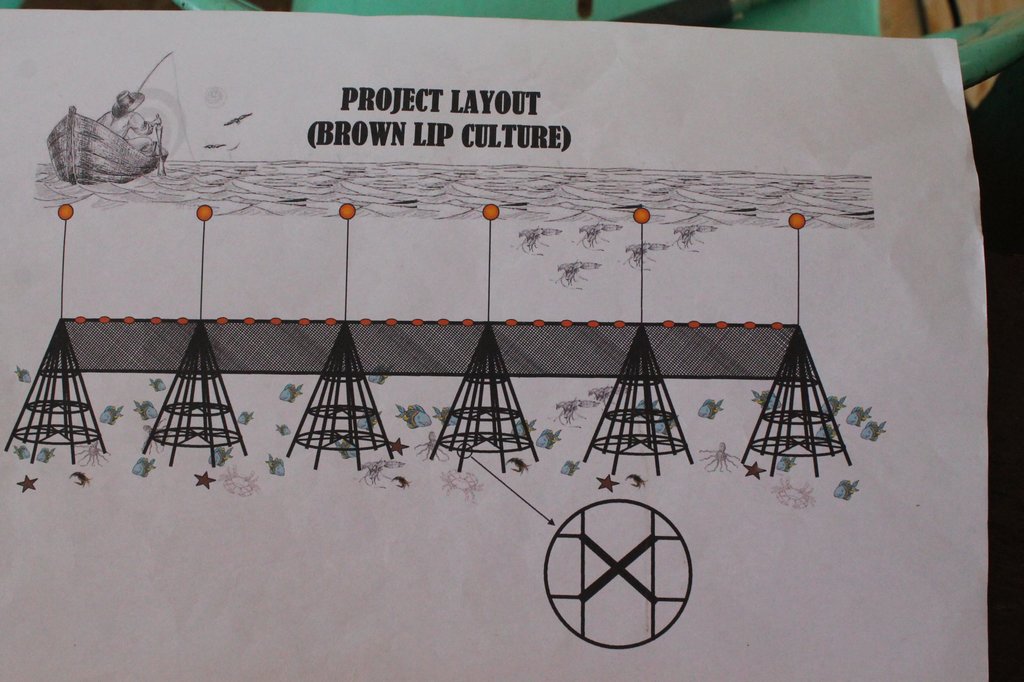
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Materials: bamboo pole, spiny bamboo, nylon #10 and coral stone as sinker
For this project with seed capital worth Php 30,000, 10 Artificial Reefs are targeted to be installed in a linear position.
Artificial Reef is pyramid in shape with the following dimensions:
Height: 12 - 15 feet
Base: 6.6 feet
Installation process:
Interval: 10 meters
Depth: 12 - 15 meters
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Php 3,200 per unit inclusive of installation; Php 32,000 for the 10 Artificial Reefs installed
ระบุปริมาตร ความยาว เป็นต้น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
Length of spread: 90 meters
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Philippine Peso
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
51.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
Php 250.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | canvass of bamboo poles and spiny bamboo | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before construction |
| 2. | purchase of construction materials | ด้วยการจัดการ | before construction |
| 3. | construction of artificial reefs | ด้วยการจัดการ | every 3-5 years |
| 4. | site selection | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 5. | installation of artificial reefs | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 6. | monitoring | ด้วยการจัดการ | 3 months after installation; monthly basis afterwards per artificial reef |
| 7. | harvest | ด้วยการจัดการ | 3 months after installation; monthly basis afterwards per artificial reef |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | motorboat rental | piece | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Bamboo Pole | piece | 10.0 | 120.0 | 1200.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Spiny Bamboo | piece | 4.0 | 50.0 | 200.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Nylon #10 | kilo | 10.0 | 120.0 | 1200.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3200.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No labor cost because the organization agreed that they will do it voluntarily.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | 3 months after installation, monthly basis after that |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | monitoring | persons-day | 2.0 | 250.0 | 500.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 500.0 | |||||
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Supply of bamboo poles and spiny bamboo since they have to find it from the interior part of the mainland.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
9999.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
as of 2016 data
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
https://weather-and-climate.com
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The technology must be installed along the path.
5.3 ดิน
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Not Applicable
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Not Applicable
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- กลุ่ม
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
Solid Waste Management:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By installing artificial reefs the fishers are not obliged to go further.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decrease in fuel consumption
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The fishers can catch fish even if there is gale warning.
risk exposure to sudden change of weather conditions
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology will not be affected directly or indirectly by the effects of gale warning and typhoon.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
Not Applicable
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | ลดลง | ดีมาก |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ดีมาก |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดีมาก |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| การสูงขึ้นของระดับน้ำทะเล | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
It's an organizational project with 80 - 120 members each organization.
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 10-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Instead of using bamboo poles, one organization decided to cement the poles because it is very difficult to find bamboo in the mainland. Also, bamboo will only last for 2-3 years.
Another organization planned to use plastic straps instead of spiny bamboo so that it will be easier and convenient for them to harvest. Another reason is the availability of brown lip spawn that will stream either at the bottom of the sea, in the middle or along the sea water level. The PO strategize to use plastic straps because they will just hang it above the artificial reef to have better harvest on brown lip.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| According to the management team, the advantage is having alternative site for fishing even if there is gale warning. |
| It will minimize expenses because of lesser fuel consumption. |
| Having an Artificial Reef (AR) project encouraged the members, including their wives to protect the artificial reef site from illegal fishers especially dynamite fishing and trawling. As a result, the people became aware of the effects of illegal fishing and the destruction it will bring to their marine ecosystem. |
| The longer the Artificial Reef (AR) stayed undisturbed, the greater the income. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Artificial reef enhanced fish spawning, food chain and improved marine ecosystem. |
| Catalyst of behavioral change among the members of the People's Organization namely BEFA, CFO and NasFiMPA. |
| The organization work together for the preservation, protection and conservation of the project site. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Monitoring assignment of the members. | Be strict with the Sustainable Enterprise (SE) Management policy. |
| The harvest cost is very expensive because it needs diving gears and large fishing nets. | Collaborate with Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR) for harvest paraphernalia. |
| The organization has no police power to arrest the intruders and illegal fishers that will take advantage. |
Close coordination with the municipal fish wardens (Bantay Dagat). The organization will establish security measures to protect their Artificial Reefs (AR) installed. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The duty bearers should implement Philippine Fisheries Code of 1998 (Republic Act No. 8550). | Capacitate the People's Organization to lobby and and implement the law. |
| The local government unit lacks support mechanism for resource-based technologies promoting environment friendly and disaster resilient enterprise. | Partnership among the local government units, people's organization and non-government organizations. |
| Limited exposure to market, business ideas and linkaging. | Conduct Value Chain Analysis (VCA) training, financial coaching, Occupational Safety and Health Standards (OSHS) and on-site mentoring. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
monthly monitoring visits to project sites
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
2 respondent per area
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Sustainable Livelihood Officer
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Social Enterprise (SE) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
Social Enterprise (SE) aimed to provide social protection among its members and generate additional family income. Above all, this approach will encourage the conservation, preservation and protection of the resources available in the community.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล