Agroforestry parkland [เซเนกัล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Julie Zähringer
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli
technologies_1167 - เซเนกัล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CSE (CSE) - เซเนกัล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
19/08/2009
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
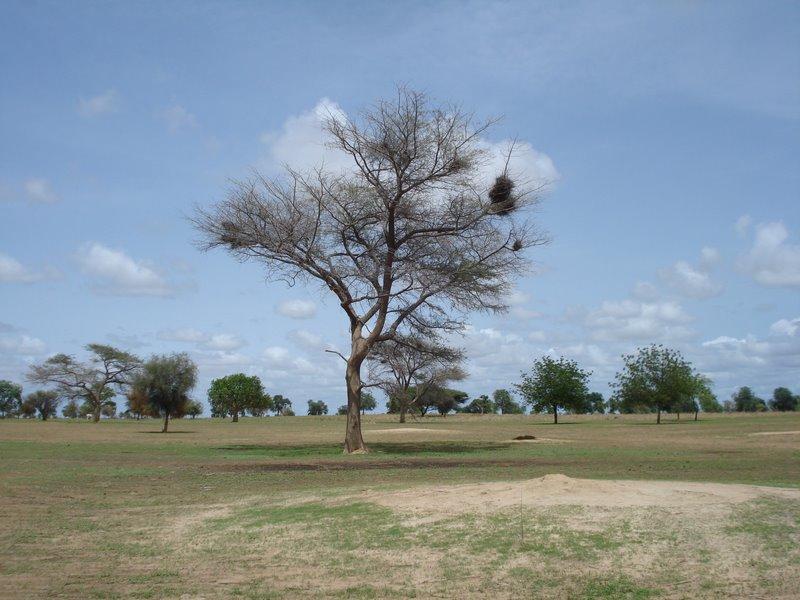
A traditional agroforestry parkland with scattered trees beneficial for soil properties (e.g. Faidherbia albida) or providing food for human beings and cattle (e.g. Sclerocarya birrea)
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Between scattered trees of which some were carefully selected for their positive influence on soil properties, either millet (Pennisetum typhoides), groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) or watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) are grown in rotation. The dominant tree species are Faidherbia albida (syn. Acacia albida), Sclerocarya birrea, Sterculia setigera and Combretum glutinosum. Some of the species were introduced from elsewhere and planted by land users when they settled in the area. Other species regenerated naturally in the fields and were protected till they reached mature age. F. albida sheds it's leaves at the beginning of the rainy season increasing soil nutrient stock for the cultivation period and reducing competition with crops for light. Sclerocarya birrea is widely appreciated by cattle for it's nutritious fruits. Cattle resting in the shade of the large trees provide free organic manure. Mulching and manure application are common means to improve soil organic matter and nutrient content in this remote area where access to inorganic fertilizers is very limited due to inaccessibility.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objectives of this parkland system are to enhance crop production through improvement of soil properties with the help of trees, the provision of supplementary food for cattle in the form of fruits and the availability of certain plants (or parts of them) for traditional medicine.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology has a long tradition in more southern regions of Sénégal and was brought to the Ferlo by Wolof people that moved to this zone in the search for cultivable area. Knowledge is transferred from parents to their children. Except for the purchase of seeds for cultivation of the fields there is no financial inputs required for this system.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. Rainfed agriculture under agroforestry parkland in a belt around the main village is the main landuse type in the area. In a second circle, extensive pastoralism is practiced and forest resources are being exploited. Presence of insects and wild animals (monkeys, warthogs) damaging cultures and the lack of sufficient rainfall are main constraints mentioned by landusers in the area. Degradation of vegetation cover is widespread. The bare soils are prone to wind erosion, a common phenomenon in the area, carrying away the arable soil horizon and causing a decline in soil fertility. In general, the local population has signaled a decline of land degradation due to the widely practiced tradition of SLM technologies.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เซเนกัล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Louga
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Linguère / Barkédji
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
introduced from the more southern parts of Sénégal by Wolof farmers
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Major cash crop: Millet, groundnut, watermelon
Major food crop: Millet, groundnut, watermelon
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): deforestation, wind erosion causing loss of topsoil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): rain insufficience and presence of insect pests
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul-Oct
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (due to domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (oversized herds of cattle), droughts, population pressure, poverty / wealth (poverty)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: plant residues after harvest
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure from cattle faeces
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 8
Trees/ shrubs species: Faidherbia albida, Sclerocarya birrea, Sterculia setigera, Piliostigma reticulata, Balanties aegypti
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | selection or planting of trees | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | removal of unwanted tree species | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | 1.0 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1.68 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Lifespan of the product: 1 season (120 days)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | application of manure and mulching | จัดการพืช | |
| 2. | sowing of millet / groundnut | จัดการพืช | june |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No cost is involved with organic manure as it can be obtained by giving nomadic Fula herders the right to let their cattle rest in the shade under the trees or feed on plant residues
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
300-400 mm during one rainy season / length of dry period: 9 months
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage / infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: High
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
30% of the land users are average wealthy.
70% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: livestock raising
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (by horse)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
fruits of Sclerocarya birrea
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
because of availability of plants used in traditional medicine
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
mulching
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
mulching
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
litterfall, organic manure
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
16
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology is already being practiced by the whole population of this village
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
increased crop production How can they be sustained / enhanced? protect trees in fields |
|
increased availability of fruits for humans and cattle How can they be sustained / enhanced? protection of trees producing fruits appreciated by humans or cattle |
|
increased availability of plant products used in traditional medicine How can they be sustained / enhanced? protection of trees providing these products |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
increase of soil fertility and organic matter through trees How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage further plantation or natural regeneration of tree species beneficial for soil properties |
| no costs involved with maintenance of technology |
|
carbon storage below and aboveground How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree density |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| loss of cultivable area due to trees in field |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| natural regeneration practically absent, continuity of parkland threatened | tree planting or assisted natural regeneration if present |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล