Primary strip network system for fuel management [โปรตุเกส]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Celeste Coelho
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli
Primary strip network system for fuel management
technologies_1361 - โปรตุเกส
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Louro António
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
โปรตุเกส
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ventinhas Marta
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
โปรตุเกส
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bragança Nuno
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mariano Inês
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
โปรตุเกส
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - โปรตุเกสชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Forest Association of Mação (Aflomação) (Aflomação) - โปรตุเกส1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
16/10/2011
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) [โปรตุเกส]
Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) is a territorial unit, where the main land use is forestry. This approach assembles and organizes small forest holders and defines a joint intervention for forest management and protection. Defined by law in 2005, and revised in 2009, each ZIF of private forest has to include …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Celeste Coelho
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
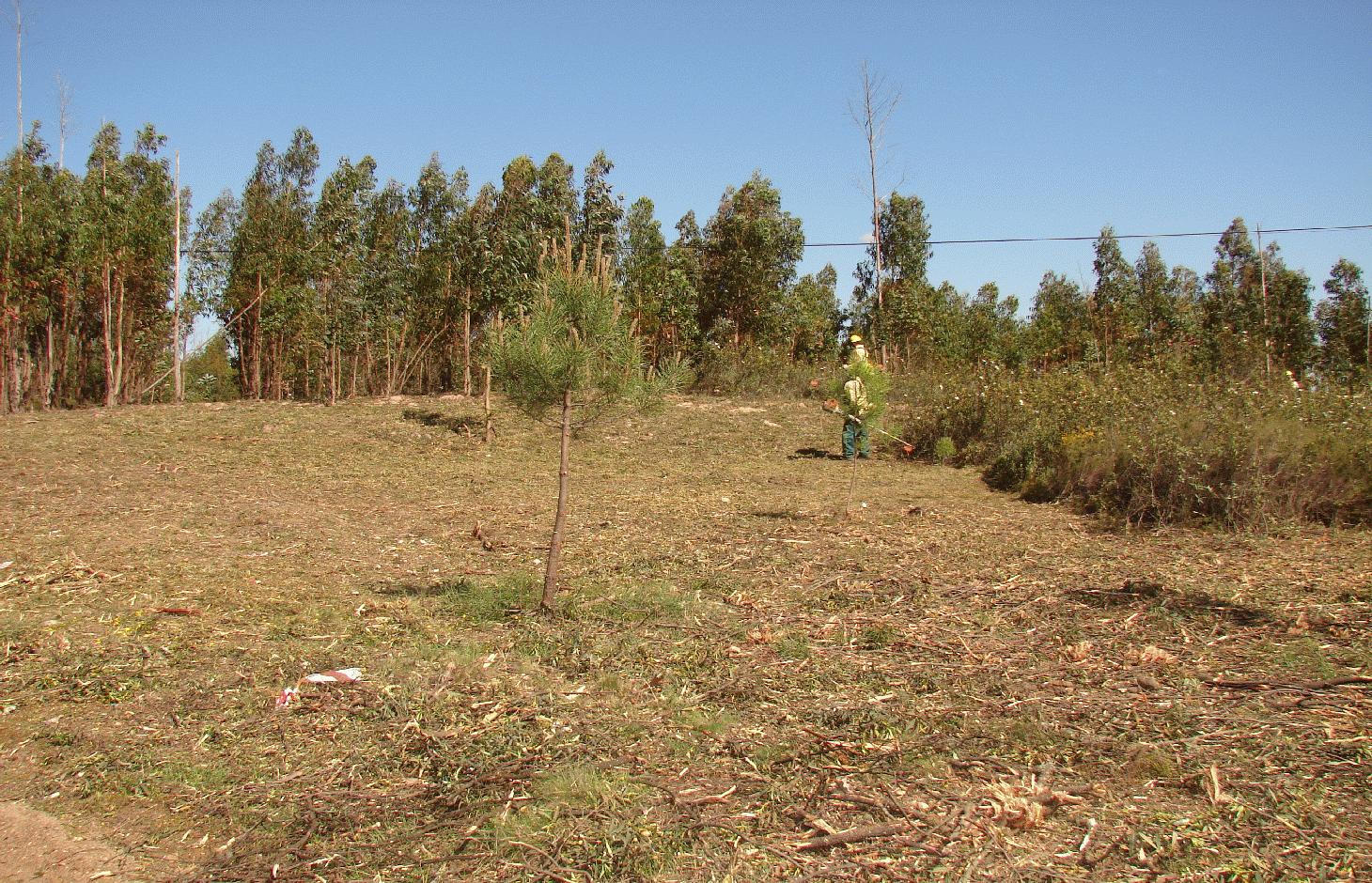
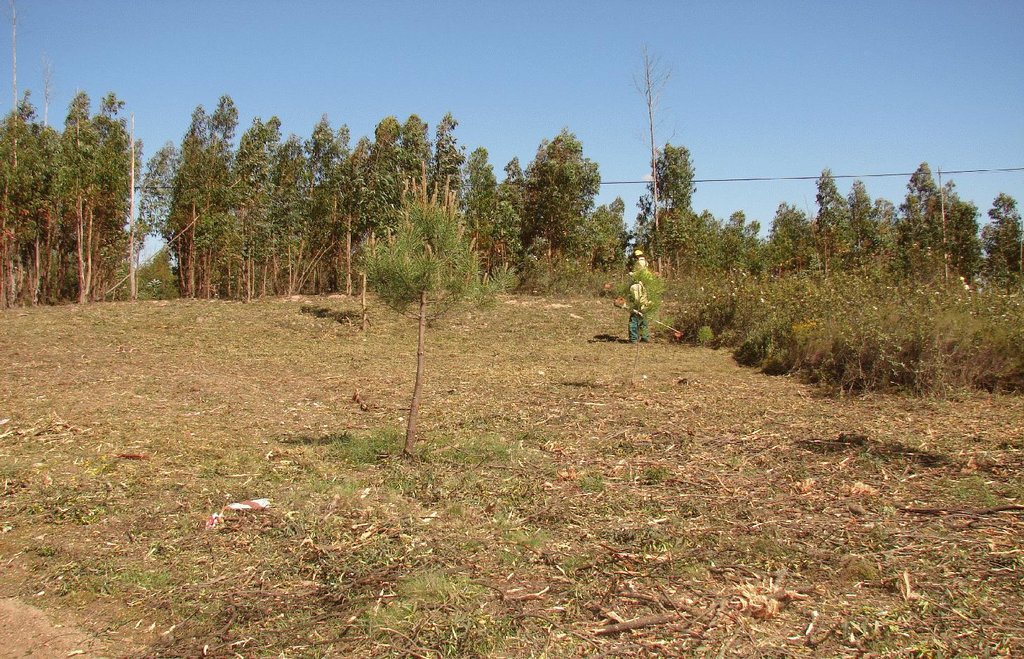
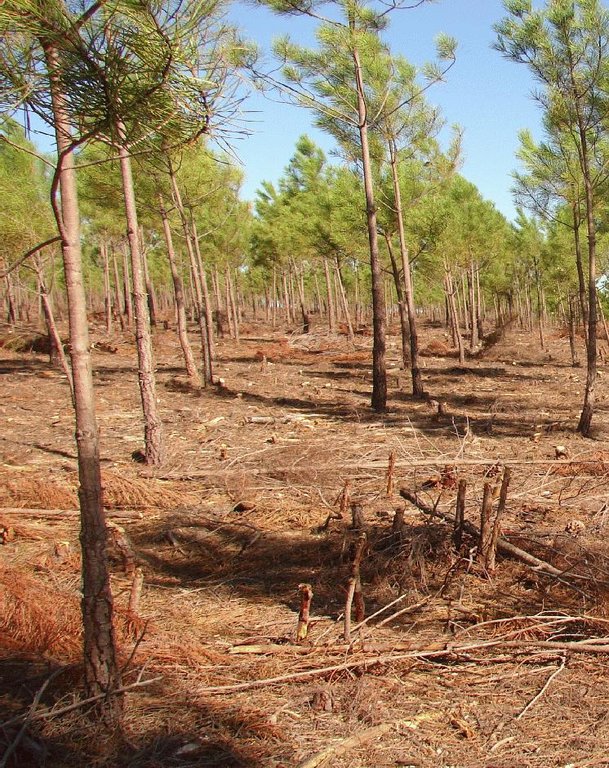
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
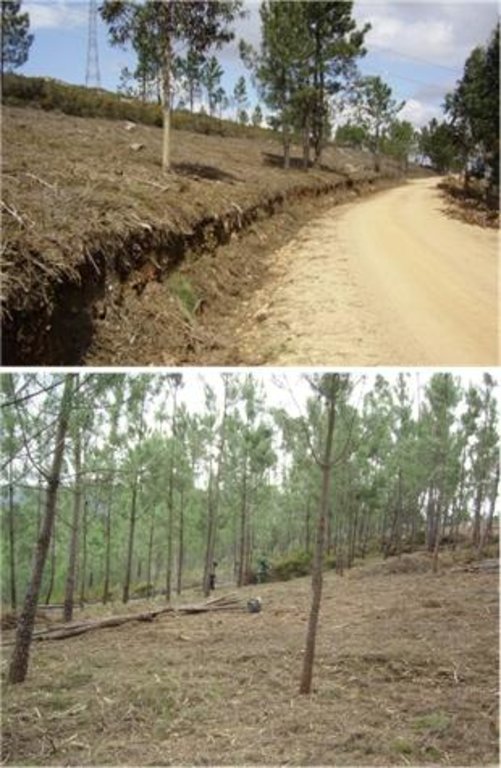
There are three types of strip for fuel management in forest areas: primary, secondary and tertiary, defined by the Law 17/2009. The most important differences between them are in terms of size (primary being the widest and the tertiary the narrowest) and scale (primary referring to the district level, secondary to the municipal level and tertiary to the parish level). The primary strip network system for fuel management (RPFGC) is integrated in the National System to Prevent and Protect Forest against Fires and it is defined by the National Forest Authority (AFN).
Purpose of the Technology: The RPFGC aims to re-arrange landscape elements, through the establishment of discontinuities in the vegetation cover, in forest areas and in the rural landscape (for example using water bodies, agricultural land, pasture, rocky outcrops, shrubland and valuable forest stands). Land tenure is private in most of the areas covered by the RPFGC. The main objectives of this technology are: to decrease the area affected by large fires; to enable direct access by fire fighters; to reduce fire effects and protect roads, infrastructures and social equipment, urban areas and forest areas of special value; and to isolate potential fire ignition sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These primary strips are ≥ 125 metres wide and preferably between 500 and 10,000 ha in area. The tree cover should be less than 50% of the area and the base of the tree canopy should not be lower than 3 metres. The RPFGC concept should include the adoption of a maintenance programme. The implementation and maintenance operations can be performed through different agro-forest technologies, such as clearance of bushes and trees, pruning, prescribed fire, harrowing and cultivation of the ground beneath the trees. Timber products can be sold and the removed litter can be used in a biomass power plant or applied to the fields to improve soil fertility, using mulching technology.
Natural / human environment: This SWC Technology needs considerable financial resources in terms of labour and equipment at the implementation phase. Costs, however, undergo considerable reduction thereafter. The implementation of this infrastructure to prevent and protect the land from forest fire is entirely funded by the government and implemented by the forest municipal services.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
โปรตุเกส
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Portugal
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Santarém / Mação
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้:
- การตัดไม้ที่มีคัดเลือก (Selective felling)
- การตัดหมด (Clear felling)
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Main species: Goats and sheep.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Forest fires increase due to rural depopulation and to land management abandonment.
Other grazingland: silvo-pastoralism: Goats and sheep.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Pine.
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: Eucalyptus.
Other type of forest: clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: Eucalyptus.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
Constraints of settlement / urban: Proximity of forest to urban areas.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): Ignition sources.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 1Longest growing period from month to month: 1 per year
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการป่าธรรมชาติและกึ่งธรรมชาติ
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 400 m2.
There has been some work carried out to develop the secondary system of linear strips for fuel management. These will provide the basis for the implementation of the primary system. The PROF | PIS - Plano Regional de Ordenamento Florestal do Pinhal Interior Sul (Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning of the Pinhal Interior Sul) has designated an area of 1752 ha with a total length of 141 km as the contribution to the primary system of fire prevention by the Mação municipality.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bf (Detrimenta leffects of fires): ผลเสียหายจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Forest fire frequency and intensity.), Property size (Small pieces of land (< 0.5 ha).)
Secondary causes of degradation: Population density (Ageing population structure and depopulation.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เขียน:
João Soares, University of Aveiro, Campus Universitário de Santiago, 3810 - 193 Aveiro, Portugal
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
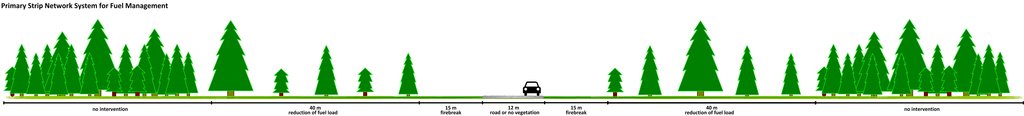
This technical drawing indicates the technical specifications, dimensions and spacing for the Primary Strip Network System for Fuel Management. The figure shows a road as the axis of the RPFGC, but it can also be a river or a ridge, amongst other breaks in the forest cover.
Location: Portugal. Santarém / Mação
Date: 16/01/2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of fires
Secondary technical functions: reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euro
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
0.76
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
18.75
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Primary System design | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | n. a. |
| 2. | Shrubs cleaning + Thinning (reduction of fuel load) + Pruning | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Dry season |
| 3. | Removing the cut waste material | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 4. | Litter Shredding | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 5. | Transport to the Biomass Plant | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1076.0 | 1076.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 568.0 | 568.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Transport | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1744.0 | |||||
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs calculation was made for the implementation of the first section of the RPFGC. The implementation phase lasted for 2 or 3 months during the dry season. This section included 28 ha and 4 teams of forest sappers were involved.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The costs include the activities to ensure the vertical and horizontal discontinuity of the fuel load and also the activities needed to manage the waste produced from the shrubs cleaning and thinning.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The rainfall ranges from 1000 mm in the North to less than 600 mm per year in the South of the municipality.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average is very shallow: Thin and stony terrains
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative; 2%
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Level of mechanization is manual labour or animal traction (Small machines are used)
market orientation is mixed (more subsistence than commercial).
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 2-5 ha
Size of forest/ woodland area per hosuehold: 25 plots.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Individual, not titled: Usually, legal documents for the property are missing.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
telecommunications:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, produces fresh growth for grazing.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The new growth provides more diverse and nutritious fodder.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The low fuel load can be maintained through grazing.
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Most of the primary system will be implemented in zones of low productivity. However, in some areas tree thinning can cause a decrease in wood production.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase of by-products from grazing.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The use of wood as a fuel for a power station and the use of vegetation to feed the cattle can promote the development of new crops and land uses.
In some areas, the implementation of the primary system can occupy productive land. The main aim of this technology is always to provide protection from forest fires instead of creating productive land.
การผลิตพลังงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After cutting the shrubs, biomass is taken to a plant to energy production.
The cleared ground, on mountain summits, of the primary system is used for wind farms. Cleared vegetation could be used as fuel for a power station.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The strips will mainly occupy areas of low productivity. The vegetation removed can be used as fuel for a power station. The maintenance of the primary system through grazing will create opportunities in terms of cattle grazing and all the resulting by-pr
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Costs of implementation
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The implementation of the primary system is very costly.
Maintenance costs
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved air quality by reducing forest fires risk.
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Some forest owners can have some difficulties in accepting the loss of their land to this technology. This can be even more difficult if they have some wood production on such land, so that it represents an income reduction.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduced risk of wildfire
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Associated with the vegetation removal.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Associated with the vegetation removal.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the diversity of the new vegetation cover. In some cases thinning the trees will have a positive effect by reducing the competition for water, sunlight and nutrients and (...)
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sometimes a loss which is associated with the immediate effects of vegetation removal.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants.
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The fuel load management in the primary system, involving the implementation of good forest practices, including the removal and control of invasive species.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants and consequently of new associated animals. The installation of fodder on the strips will promote grazing activities, increasing the number of goats, (...)
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
But also increased habitat fragmention
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In some cases, where there is a total removal or a huge reduction in vegetation cover.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Risk towards adverse events
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
This technology is an impediment to forest fire propagation and therefore reduces fire risk.
Soil erosion
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Usually, the soil in the areas designated for the implementation of the primary system is thin and poor. The use of machinery and vegetation removal can accelerate the soil erosion processes.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Forest area.
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology aims to reduce forest fire frequency and intensity, and the associated damage.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The maintenance will only start 2 or 3 years after the technology implementation, so no returns are expected at short-term.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 100% of the technology was implement by local administration, with support from the government.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: After the implementation period there was a high local acceptance of the technology. It is also expected that grazing activities contribute to the technology maintenance
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Fuel load reduction How can they be sustained / enhanced? This will be achieved using prescribed fire and specialised machinery. The efficacy of prescribed fire depends on the collaboration of technicians and forest sapper teams. To guarantee the effectiveness of RPFGC implementation, long-term maintenance has to be ensured. |
|
Reinforcement of the forest path system How can they be sustained / enhanced? Clearing the strips of the RPFGC can enhance the forest track network. |
|
Forest fire prevention and fighting How can they be sustained / enhanced? The know-how of the local stakeholders and communities will contribute to the design of the RPFGC . This information should be integrated into the Municipal Plans to Prevent and Protect Forest Against Fires (PMDFCI). Any further information should be provided to the Civil Protection Agencies and to the Forest Technical Office and also to the local fire-brigade team. |
|
Increase in landscape resilience How can they be sustained / enhanced? This will only be effective if the RPFGC is continuous and without gaps. The acceptance of the RPFGC by the landowners is fundamental to widespread the use of this technology. Information and awareness about the need to change vegetation cover is also very important, in order to avoid extensive areas of monoculture. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil erosion increase | Forestry good practices should be used in the RPFGC implementation, especially concerning the use of machinery and avoiding disturbance of soil at depth. Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). |
| Soil cover reduction | Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). |
| Runoff increase | Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). Excessive vegetation removal should be avoid, especially near water courses where the removal should be nil or minimum. |
| Budget for implementation and maintenance | European and national funds. Collaboration of the local government providing equipment and labour force. Information and awareness to the landowners about the importance of this technology. Campaigns of national awareness and definition of this technology as ‘public use’ to overcome some potential social conflicts concerning the land rights. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Decree-Law n. 124/2006, 28 June. Official Gazette n. 123 – I series: 4586-4599; Decree-Law n. 17/2009, 14 January. Official Gazette n. 9 – I series: 273-295.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) [โปรตุเกส]
Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) is a territorial unit, where the main land use is forestry. This approach assembles and organizes small forest holders and defines a joint intervention for forest management and protection. Defined by law in 2005, and revised in 2009, each ZIF of private forest has to include …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Celeste Coelho
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล