Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Harry Wells
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Donia Mühlematter, Barbara *, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Hanspeter Liniger
technologies_3381 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing: 16 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing: 6 พฤษภาคม 2019 (inactive)
- Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing: 3 กันยายน 2018 (inactive)
- Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
- Rangeland Restoration by cutting invasive species and grass reseeding and managing grazing : 23 มีนาคม 2018 (inactive)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
26/01/2018
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
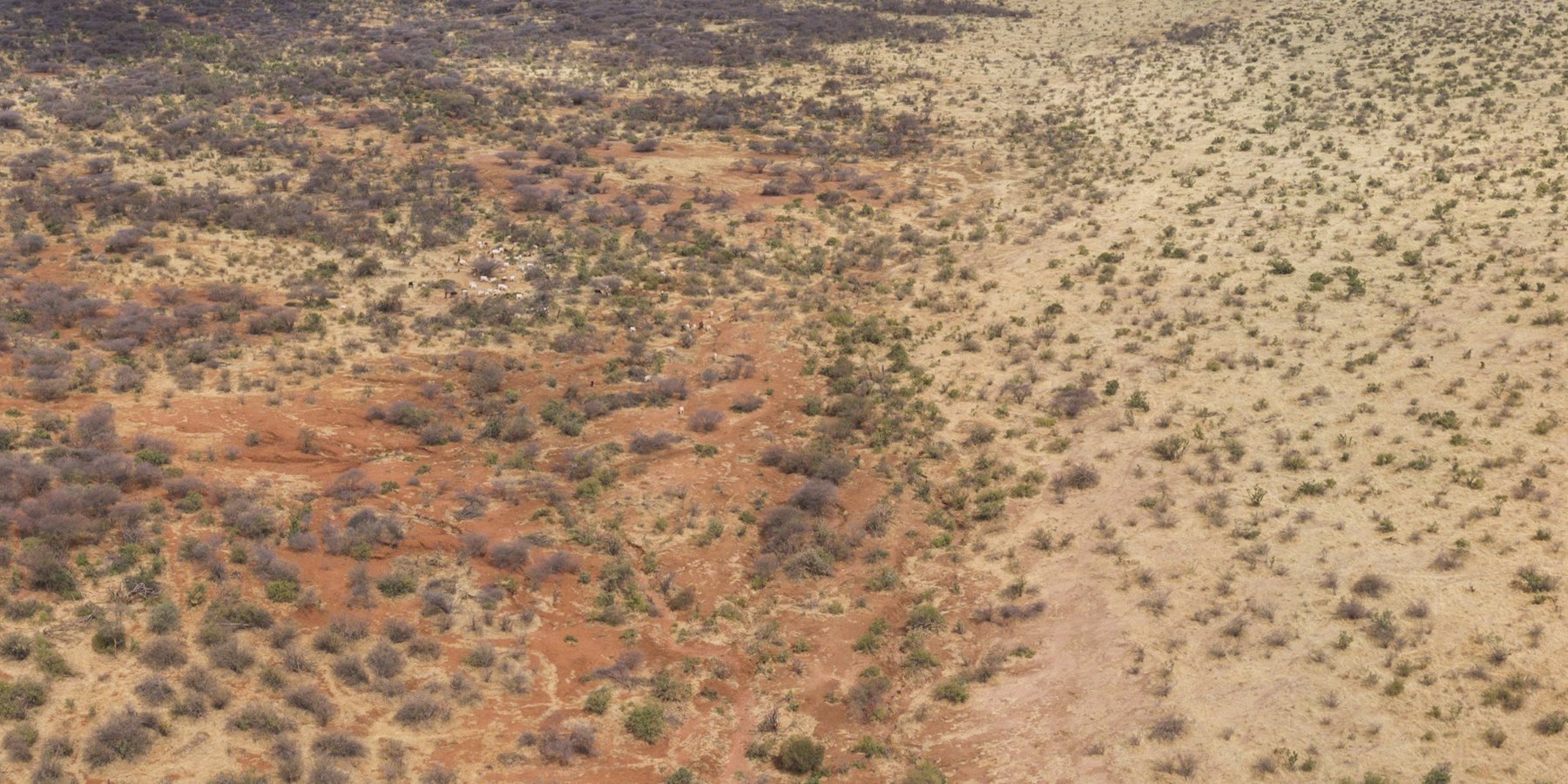
This 'Rangeland Restoration' technology is part of a 'Holistic Rangeland Management' approach. It involves clearing of invasive vegetation (predominantly Acacia reficiens) and reseeding with grass (Cenchrus ciliaris) and allowing resting and reduced grazing pressure to rehabilitate degraded communal grazing land.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
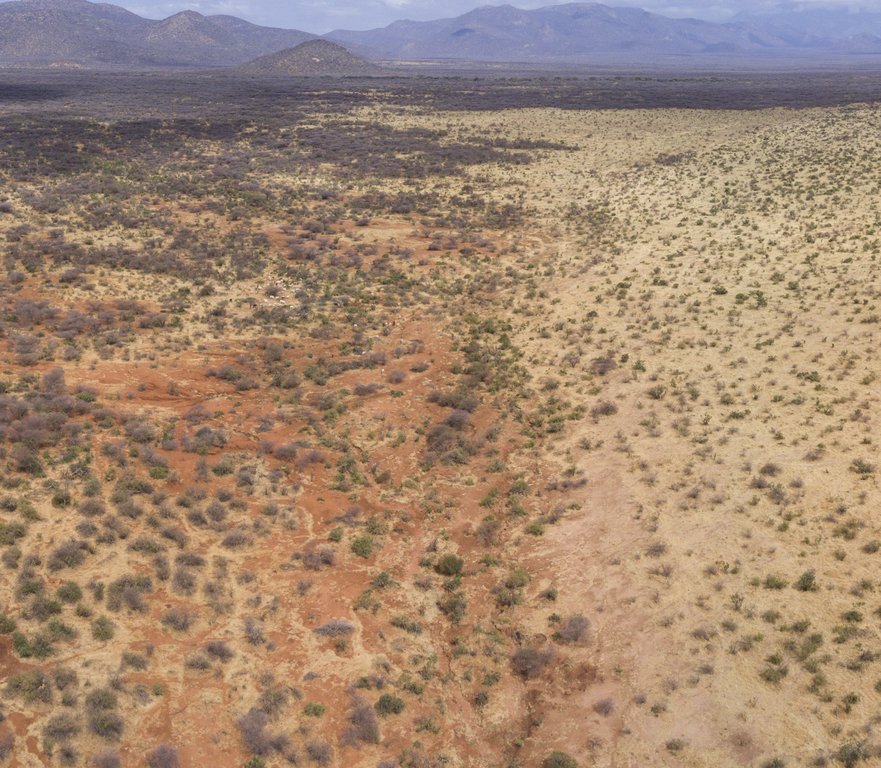
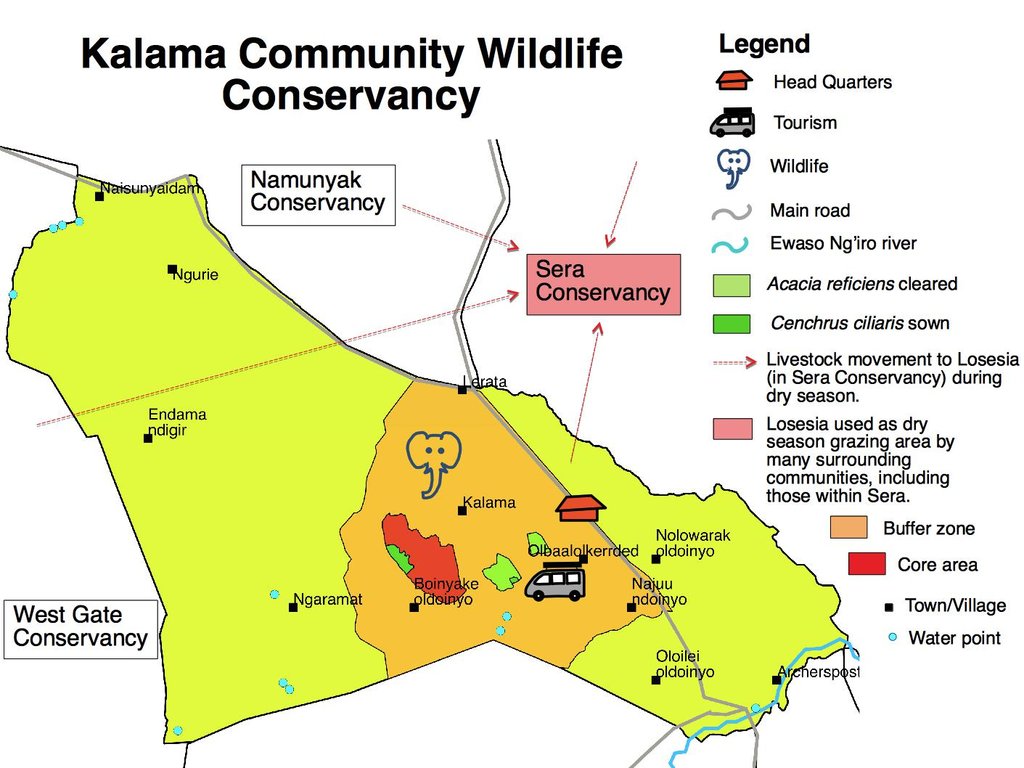
The 'Rangeland Restoration' technology is applied in degraded sites within the 3,100 Ha 'core conservation area' (an central area with minimised grazing pressure designated for tourism) and 'buffer zone' (an area surrounding the 'core conservation area' with reduced grazing pressure) of the Kalama Community Wildlife Conservancy (total area: 9,500 Ha).
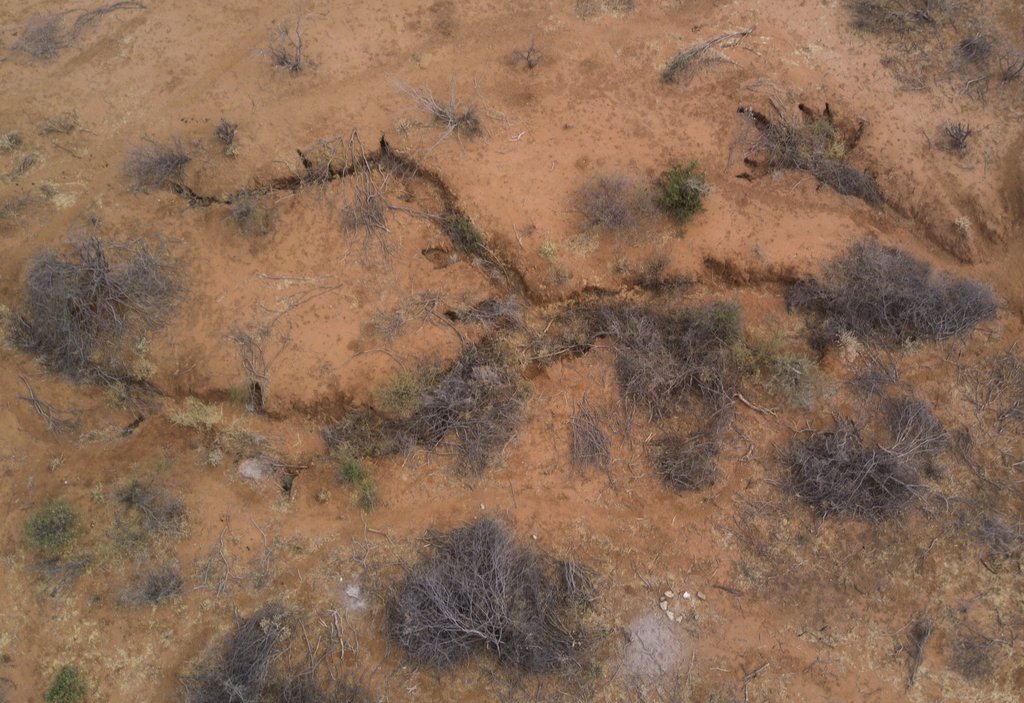
The main characteristics are clearing of invasive woody vegetation (predominantly Acacia reficiens) and reseeding with grass (Cenchrus ciliaris). Acacia reficiens (commonly known as red-bark acacia, red thorn or false umbrella tree or thorn) is a native tree or shrub but is considered an invasive species as it can encroach degraded areas with bare and disturbed soil. It is very opportunistic and hardy and can subsequently take over large areas of native vegetation. The invasion can reach a closed or nearly closed canopy with A. reficiens thickets, which are hindering animals to enter and access fodder thus making the area inaccessible for grazing and browsing. Additionally it can be observed that the soil underneath the canopy remains bare and the grass growth seems to be suppressed. As a result the top soil is compacted or forms crusts, which hinder infiltration. During the erratic but heavy rains most of the water flows away as runoff (research in close by areas show that runoff is between 60-80 % of the rainfall) and increases soil erosion and further degradation of the land despite a rather good tree cover. Rangeland grass and fodder productivity in these areas are reduced to a fraction of their potential.
The main activity is the cutting of the trees and shrubs at a height of ~1 m. The main trunks and branches can be used for fencing, temporary house constructions, firewood and charcoal. Most of the cut trees and the remaining branches are used to spread on the bare land where the trees and shrubs are cut. Underneath this dead material the bare soil receives some cover, which creates favorable conditions and microclimate for termites and other fauna in the soil to brake the hard top soil and crust and enable infiltration of the water during the next rains. This allows regrowth of grasses, particularly in the areas protected by the branches. In the following seasons the spread of the grasses can increase also the the area not protected by the branches. Additionally, seeding with Cenchrus ciliaris (buffel-grass or African foxtail grass), a grass species which is native to most of Africa, enhances the growth of a highly valuable fodder grass. Seeds are hand-broadcasted in the treated areas and germinate during the next rainy season. The first greening is visible in the places where the branches and the wood pieces cover the soil. From there the local annual and perennial grasses start colonising and expanding in the following seasons until, ideally, the whole area that has been bare is covered by valuable perennial grasses. Parallel to the cutting and reseeding is reduced grazing pressure and a resting period over at least one dry season, which is facilitated by the fact that treated areas are situated in the core conservation area or in the buffer zone. This involves the cooperation of the members of Kalama Conservancy, who agree to restrict grazing in the buffer zone and more so in the core conservation area. The exact duration that grazing is allowed in each of these two areas varies year to year depending on drought severity and forage availability. Whereas the grazing pressure by livestock can be regulated, there remains uncontrolled grazing by wildlife. The major herbivores are zebra, elephants and a number of different gazelle and antelope species the grazing pressure by wildlife varies but can be substantial at certain times.
Rehabilitating degraded grazing land is the primary purpose of the technology. Other benefits of the technology include: 1) augmented forage availability for the community; 2) increased livestock production; 3) reduced soil erosion and flooding. Land users enjoy these benefits but would like larger areas to be similarly restored. However, the limiting factor is the funding required to pay for labour, which is the major input required for the clearing and reseeding activities. Establishing a market for removing the main stems and producing and selling charcoal is still an opportunity to further explore immediate benefits and cash income in order to pay for the investment into the clearing.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Samburu County
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2006
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Acacia reficiens was already selectively cleared traditionally when constructing livestock corrals ('bomas'), but the introduction of more extensive clearing and grass-reseeding to rehabilitate specific areas was facilitated by Northern Rangeland Trust and Grevy's Zebra Trust.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Cattle (milk, beef), Sheep/Goats (milk, meat), Camels (milk, meat), Donkeys

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Bare and/or degraded land
ข้อสังเกต:
The area has been overused and continuously grazed for a long period of time without given the land and vegetation a break to recover. Thus a vicious spiral developed: the reduced grass cover lead to degradation of the soil to compaction and crusting, reduced infiltration thus reduced runoff and reduced vegetation growth, which in turn increased the pressure on the remaining vegetation and thus more base soil etc.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Rainiy seasons from April to June and from October to December but with high variability in time and amount
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
likely continuously growing till technology was introduced
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
- V4: การแทนที่หรือการนำพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น/ที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา ออกไปจากพื้นที่

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
A total of 279 hectares were treated with this rangeland restoration technology (clearing invasive Acacia reficiens and reseeding with Cenchrus ciliaris). Treated areas were relatively flat (slope < 5%). A. reficiens were cut ~1 m above the ground and well before the onset of the rains to discourage regeneration. C. ciliaris seeds were hand-broadcast at a rate of ~45 kg/Ha.
Holding membership of multiple community conservancies facilitates the movement between wet season and dry season grazing areas. For example, many of the local communities move their livestock to Losesia, in Sera Conservancy, for dry season grazing. These porous boundaries relieve pressure from Kalama Conservancy during some parts of the year, potentially facilitating recovery of treated areas, but also allows neighbouring communities to access treated areas rendering their grazing management challenging.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
279 hectares (total over 6 sites)
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Kenya Shillings
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
101.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
450 Kenya Shillings
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing Acacia reficiens (cutting and spreading) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | During dry season, well before the onset of rains to prevent Acacia reficiens regrowth from stump. |
| 2. | Reseeding with Cenchrus ciliaris grass seed | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Prior to the onset of rainy season to maximise germination and establishment of Cenhrus ciliaris.. |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Clearing Acacia reficiens | person-days | 1200.0 | 450.0 | 540000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Hand-broadcasting Cenchrus ciliaris seeds | person-days | 1200.0 | 450.0 | 540000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machettes | units | 40.0 | 500.0 | 20000.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Cenchrus ciliaris seeds | kg | 2520.0 | 50.0 | 126000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transport of workers to and from site | litre | 600.0 | 100.0 | 60000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1286000.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Funding raised by Northern Rangelands Trust and Grezy's Zebra Trust (including USAID and FAO funding).
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
These are the costs associated a 55 Ha treated area. Six sites of a similar size were treated with similar budgets totalling 279 Ha.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No maintenance activities.
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No maintenance costs.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Hiring labour, as it was the most costly component.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
351.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Archer's Post
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
pH ~7-8.5; SOC 4.7 g/kg of soil; Na ~0.1-0.4 cmolc/kg
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Rangelands in Kenya are generally characterized by high bio-diversity. The particular sites have been degraded in terms of vegetation ans soils. After the restoration diversity increases but has not reached its full potential.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Kalama Conservancy receives considerable income from the high end tourism (~60% of total income) and donations (~25% of total income).
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
communally owned
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to degradation fodder production before was minimal both for grasses (hardly that survived the grazing pressure) as well as accessible browse material
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
perennial grasses were brought back
การผลิตสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
cut wood of the invasive species can be used for charcoal production, and construction material. The amount is high but the marketing is still weak, so most of it is left to be spread on the ground
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
one dominate invasive wood species was removed to give way for other native species to repopulate the area
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is still potential to decrease runoff further as the system is still recovering and improving.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
damage on major bridges but also on smaller within the conservancy
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Land that was previously considered unproductive is now considered grazing land. |
| Increased infiltration and decreased runoff and water erosion. |
| Recolonisation by local grasses and forbs to replace reseeded Cenchrus ciliaris after 1-2 years provides nutritious forage (particularly the forbs) for livestock. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Decreased impact of the invasive Acacia reficiens on vegetation and soil within treated areas. |
| Increased biomass of herbaceous vegetation for livestock and wildlife forage. |
| Augmented biodiversity after reseeded Cenchrus ciliaris replaced by local grasses and forbs. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Creates overly high expectations from the community regarding the potential to restore larger areas. | Raise awareness among community members regarding the limitations of large-scale restoration. |
| Lack of funds to pay labourers. Paying community members to undertake restoration activities rather than these activities being voluntary is now, in hindsight, perceived to have been a mistake. | There will never be enough funding as labourers will continue to expect ever-increasing wages. However, over time, community members may decide to restore land voluntarily. Explore the potential for marketing the main trunks for charcoal production of firewood to pay for the labourers. |
| Controlling grazing in recovering areas. | Raise awareness about the restoration projects within immediate and neighbouring communities. Also, ensure grazing by-laws are implemented and offenders fined. |
| Land users unwilling to voluntarily take part in restoration activities. | Increase ownership by conducting restoration projects at more local zonal-levels rather than at the conservancy-level. Create additional incentives by using and marketing of some of the wood material (for legal charcoal production) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Inability to provide adequate rest to treated areas (i.e. by controlling grazing pressure) leading to unsuccessful establishment of Cenchrus ciliaris or other herbaceous vegetation in treated areas, particularly in 'buffer zone'. | Implement grazing rules more stringently. |
| Lack of capacity regarding how to reseed Cenchrus ciliaris in some treated areas. In one case, seeds were buried (as farmers do with maize seeds), which is reported to have contributed to low establishment success of C. ciliaris seeds. | Capacity building. |
| Germination and establishment of Cenchrus ciliaris depends on timing in relation to the onset of rains, which are unpredictable and led to unsuccessful rehabilitation of some treated areas. | Provide most accurate weather forecasts available. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
2 field visits to the sites
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
3 informants
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
1 report
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
'Northern Rangeland Trust: Baseline assessment of rangeland health - Kalama and Namunyak conservancies', Tor-G. Vågen & Leigh A. Winowiecki, 2014
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/bitstream/handle/10568/65671/nrtReport_march2014.pdf?sequence=1
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Northern Rangeland Trust: Baseline assessment of rangeland health - Kalama and Namunyak conservancies
URL:
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/bitstream/handle/10568/65671/nrtReport_march2014.pdf?sequence=1
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล