Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Michael Herger
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Hanspeter Liniger, Alexandra Gavilano, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Brigitte Zimmermann, Donia Mühlematter
technologies_2092 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 4 กันยายน 2019 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 22 กุมภาพันธ์ 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 11 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 3 กันยายน 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 4 ตุลาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 1 กุมภาพันธ์ 2018 (inactive)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Leresi Patrick
+254721153572
ilngwesi@nrt-kenya.org
Il Ngwesi Group Ranch
Mukogodo Division, Laikipia North District, PO Box 263, 1042 Timau, Kenya
เคนยา
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
22/01/2017
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Yes and no, only time will tell here. Grazing principles and management (with partly applied Holistic Managment) of Il Ngwesi Group Ranch are said to be exemplary for group ranches in the area. In evaluation processes since the introduction of the new principles and also in reports, they were rated as "best practice". Land recovery is according to these reports in full swing. However, in the field the picture looks partially different. The land is in large areas (still) heavily degraded. Data suggests that vegetation and soil is in a rather bad condition - many erosion features characterize the land. Nevertheless, according to land users, land coverage has significantly improved since the introduction of the new technologies.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
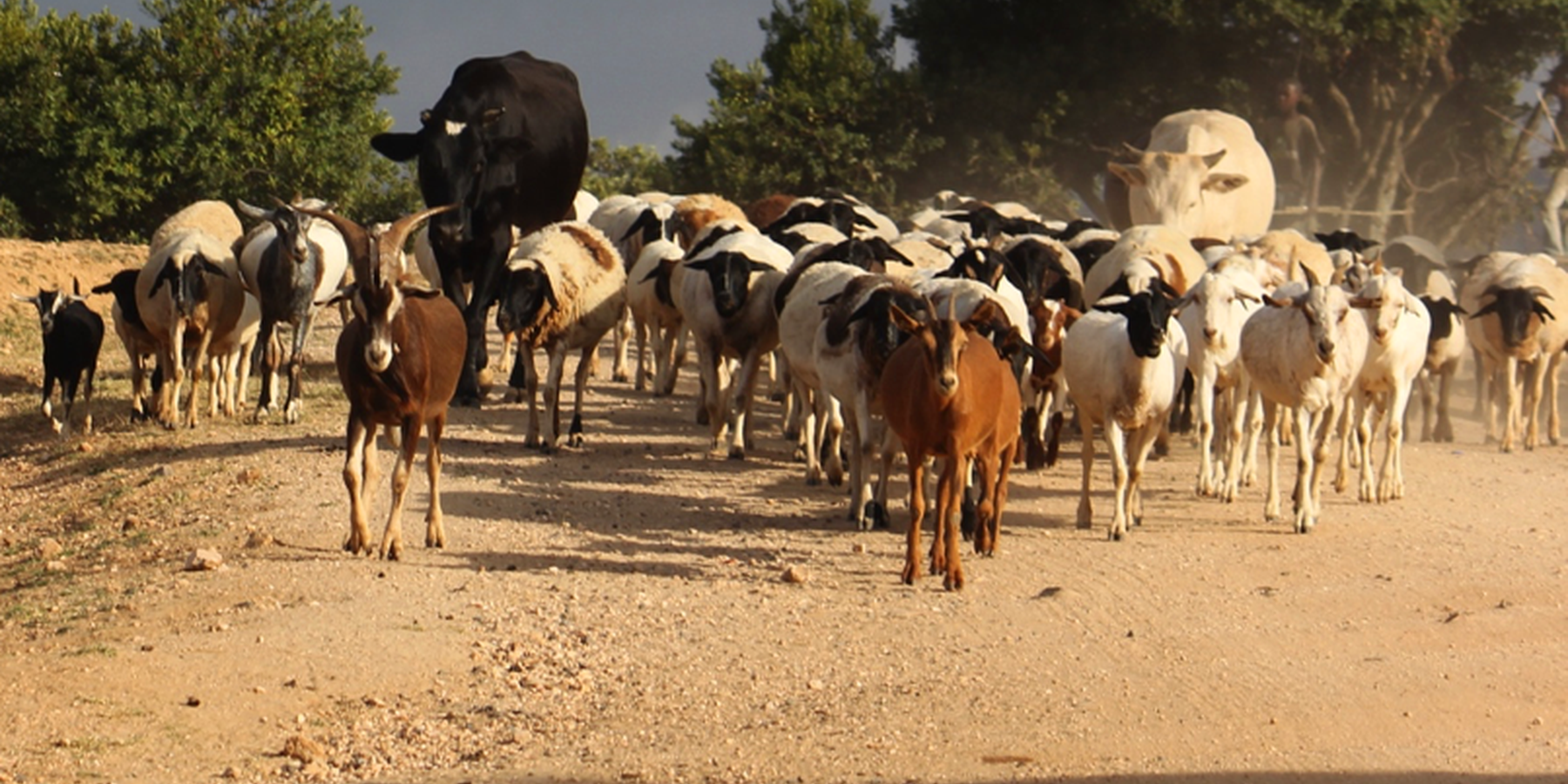
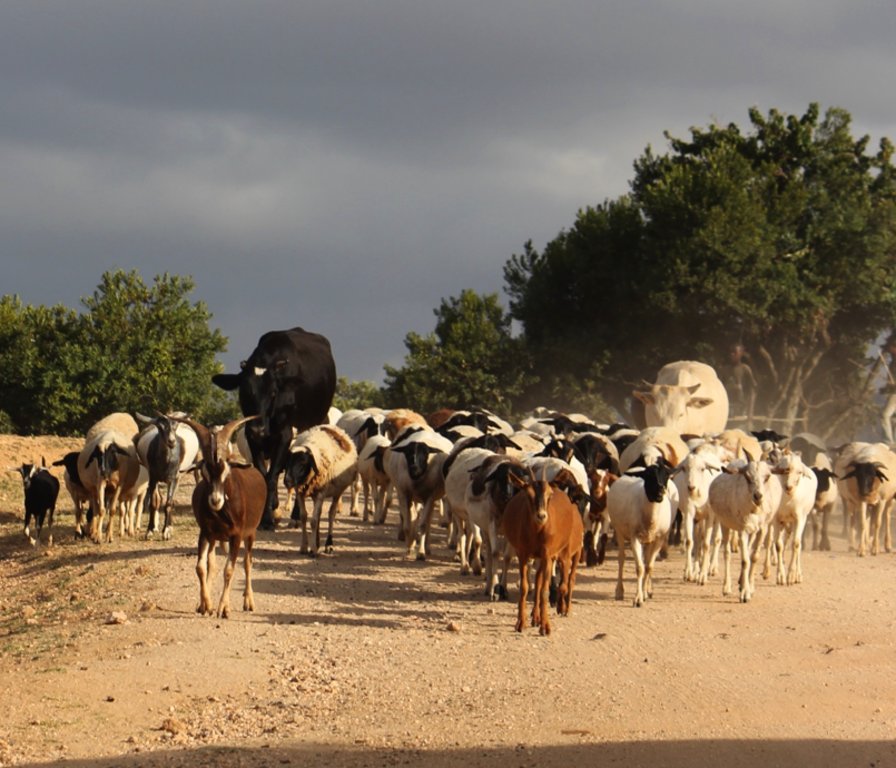
A group ranch belonging to the Masai (traditionally, nomad pastoralists) has applied "Holistic Management" grazing principles. The principles consist of separate, planned grazing in villages during the rains, then “bunching” and moving of all animals in herds during the dry season. Denuded land is recovered by a "Boma” technology: i.e. strategic corralling of animals overnight, and reseeding.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
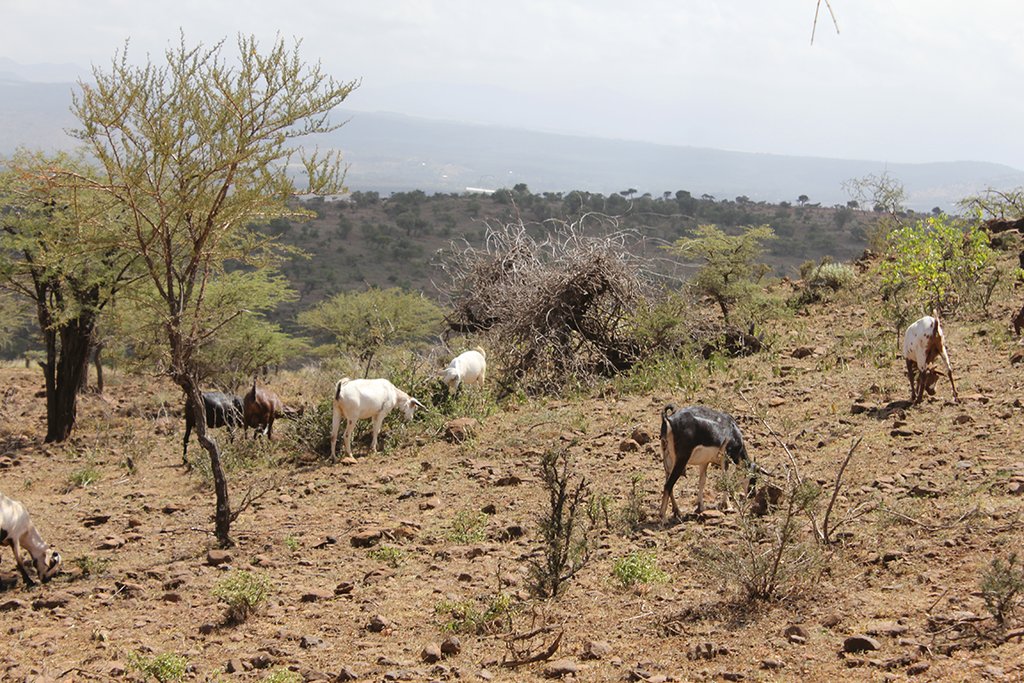
On Il Ngwesi Masai Group Ranch, livestock production management is a combination of traditional livestock keeping and holistic grazing management principles which were introduced in 2007. Livestock production at Il Ngwesi is for subsistence and sales - and has very high cultural significance. 80% of the land is used for conservation, where wildlife and their habitat are protected. The vision is to integrate community development and sustainable environmental management. Holistic Management (HM) was originally conceived by Allan Savory (1988), and is promoted by the Laikipia Wildlife Forum. It integrates decision-making, planning, and livestock keeping. On the land, this means bunching of all livestock close together (in order to act as a "plough" and break the soil to allow seeds, nutrients, and water to infiltrate) resulting in better plant growth. By moving the animals together from block to block, HM aims at managing high numbers of livestock while restoring degraded land. Instead of individual livestock-owning families herding and trekking their own animals, consolidated herds are now managed and moved together, and overseen by herders and supervisors. This allows intensive grazing in restricted areas while resting the remaining land - instead of continuous open grazing. However, Holistic Management principles are still a matter of controversy. While advocates of these management principles do not limit herd sizes, opponents see the root cause of degradation exactly in too high stocking rates. Criticism is plentiful and reviews of the method state that there are no peer-reviewed studies that prove that Holistic Management is superior to conventional grazing systems in outcomes (Carter et al. 2014, Briske et al. 2014).The group ranch land consists of a settlement and a conservation area. The conservation area is further subdivided into a small core zone, measuring 500 hectares and a larger buffer zone of 6,000 hectares. Within this buffer zone, pastoralists are permitted to graze livestock during the dry season.Besides these two main grazing areas in their group ranch, they use additional grazing areas outside their territory such as pasture in forests. In one forest - Mukogodo - they have settled officially; in Ngare Ngare and on Mount Kenya, on the other hand, it is more of an informal agreement. In Il Ngwesi, HM principles are very strictly applied in the conservation area; elsewhere only partly or not at all. During the movements to the forest glades and Mount Kenya, HM principles are maintained as far as possible. This documentation describes the combined grazing management system. During the rains, the grazing system is largely by traditional management: animals remain in and around villages managed individually by households. During the dry season, all livestock are bunched together and managed as one herd.During the wet season, grazing at Il Ngwesi Group Ranch is organized by elders within their seven villages. HM principles are only partly applied. During the dry season, once all the grazing land is eaten, livestock are bunched together and managed by a few herders and overseers. The block system rotation starts. To seek new pasture and water, cattle and smallstock are led to forest glades, and then to the Il Ngwesi conservation area. As soon as the forest pasture is gone, they move on to the conservation area. Usually, this movement of livestock to forests and conservation area starts in February; then they return to the villages in April; and then back to the forests and conservation area until the next rains in November. Whilst the livestock are bunched together, large bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) are constructed for overnight enclosure. Bomas are sited on bare land where dung accumulation and crust breaking by hooves helps rehabilitate land. Every year the boma sites are shifted slightly according to a plan. The total area that can be restored per year is almost 1% of the area of Il Ngwesi.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
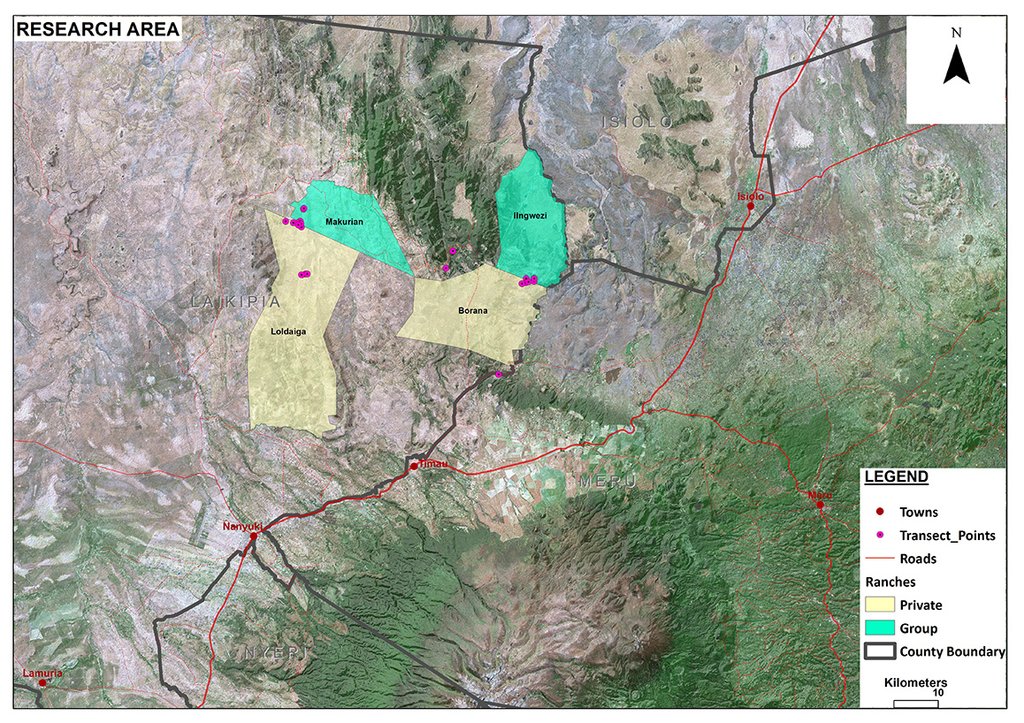
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Laikipia
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mukogodo Divison
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2007
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory.
In Laikipia, it was introduced by Richard Hartfield, Laikipia Wildlife Forum and funded by Laikipia Wildlife Forum (LWF), Lewa Conservancy and Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT) (approximately 50% of all additional costs of Il Ngwesi since the implementation were covered by funding). Agreement with elders was reached first, then the community was trained.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Livestock: Cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, camels
Meat and milk production (also blood) and as a bank/ value asset. Mainly subsistence and local production.
Livestock: 4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU (calculated with the total affected land by livestock: 157km2)
Pressure on land including wildlife: 3.3 ha/TLU (stays the same, calculated with wildlife biomass density estimated by Georgiadis et al. 2007).
Livestock numbers:
Lower Il Ngwesi: 4000 cattle, 20'000 shoats, 50 donkeys, 100 camels.
Sanga: 700 cattle, 2000 shoats, 20 donkeys.
Mukogodo: 1500 cattle, 5000 shoats, 20 donkeys
Livestock fluctuations (per year): -10% sales, -5% loss due to drought/diseases, -5% slaughtered,
+30% natural breeding, new purchase and deaths are mutually offsetting.
Steers are for fattening on private ranches and during droughts other livestock can be moved to private ranches (up to 3000).
Wildlife: elephant, antelope/ gazelle (like gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle, dik-dik), hares, predators and more.

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
ข้อสังเกต:
Villages, bomas, manyattas.
8'000 inhabitans.
Lodge for Tourism.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
ความหนาแน่นของปศุสัตว์ (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU. Pressure on land: 3.3 ha/TLU
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Il Ngwesi has an area size of 87 km2. However, the total affected land by livestock is 157km2. The technology is also applied on other ranches (mainly private ranches, see the documentation for neighboring "Borana") in Mukogodo division.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
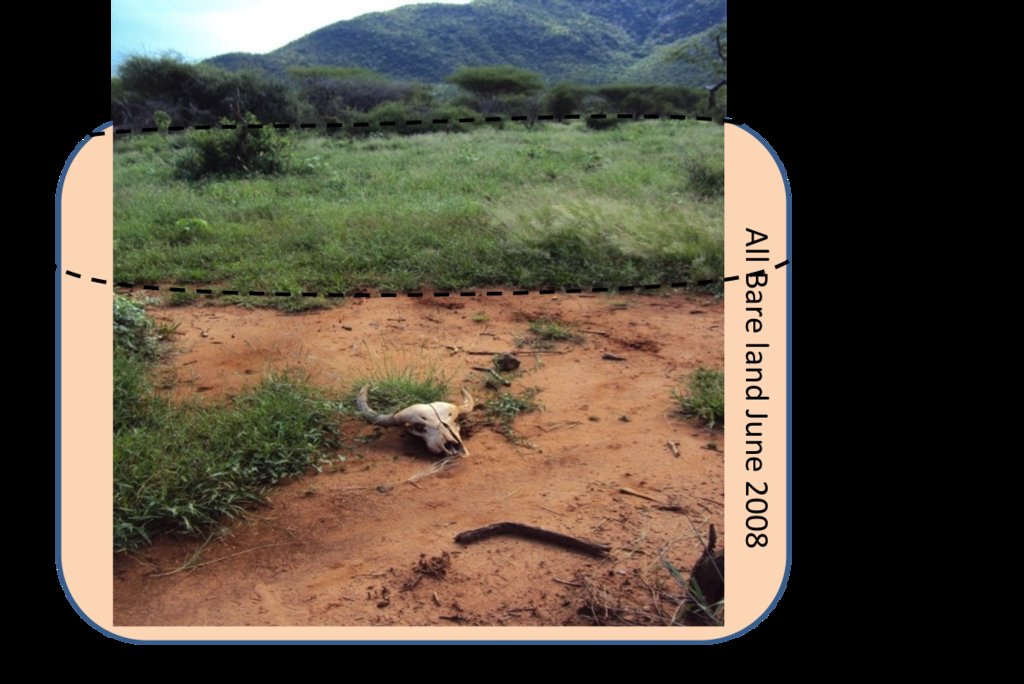
Across the grasslands and rangelands an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species. However, Il Ngwesi is not affected by the invasive species Opuntia stricta. For more information on rangeland health see Herger (2018). The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
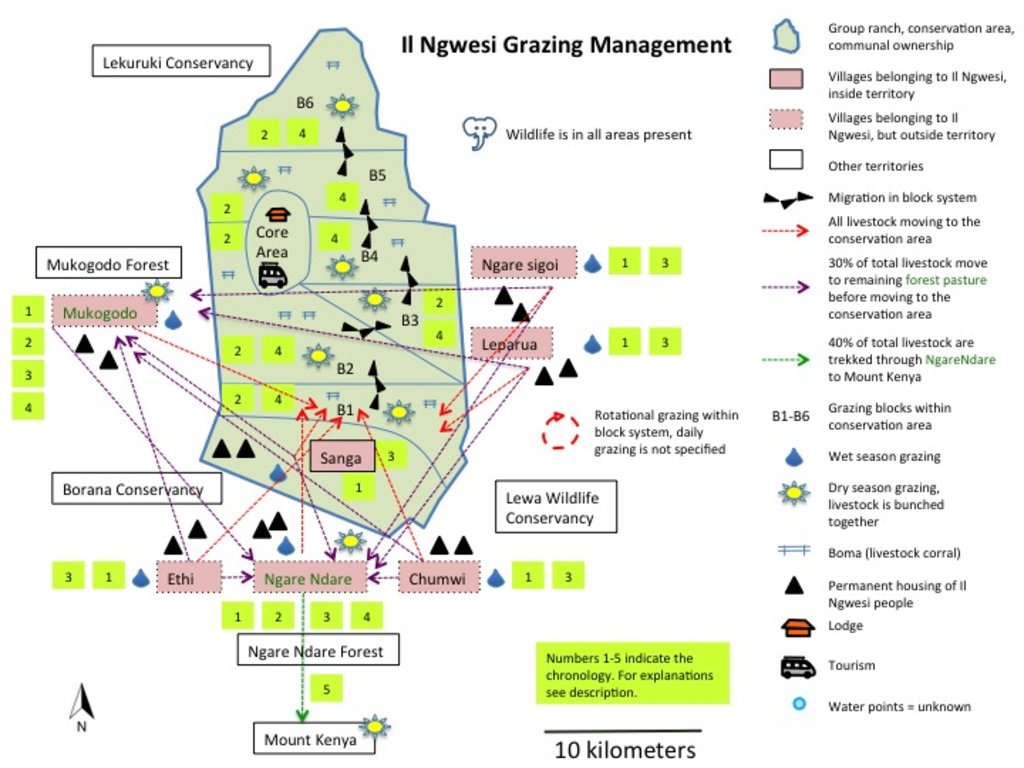
Grazing map of Il Ngwesi in Mukogodo Division
Grazing Principles:
- Rotational, planned grazing
- Bunching
- Resting periods for pasture
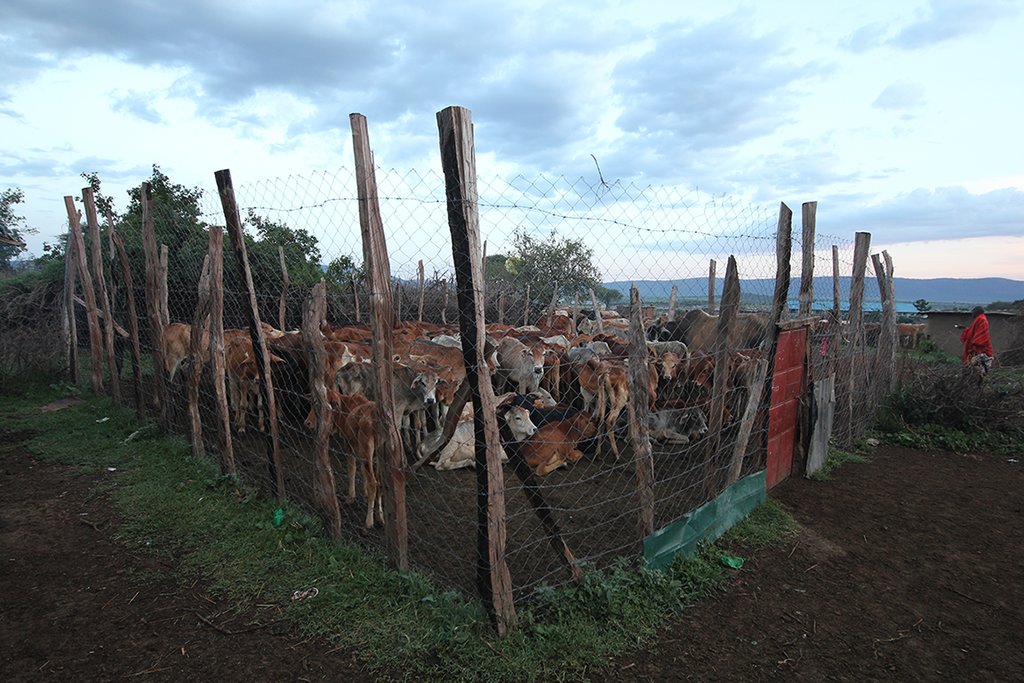
- Bomas for bare patches (night corrals)
Value Chain:
• Natural Breeding/buying (Ranches & individually)
• Grazing
o Settlement area (in red, during the wet season, until pasture is gone, organised by elders, bunching of all animals as soon as it gets dry)
o Mukogodo Forest / Ngare Ndare Forest (30% of total livestock, remainder to conservation area for grazing directly)
o Conservation area (6 blocks)
o Mukogodo Forest/Ngare Ndare Forest/Mount Kenya (Ngare Ndare Forest as corridor to Mount Kenya, about 40% of total livestock goes to Mount Kenya)
• Need-driven sales to local butcheries/NRT/Ranches
Il Ngwesi Masai also started to buy land outside their Group Ranch.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Herders, animals treatment. For the whole area affected by livestock (157 km2)
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
USD 2.5
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of elders and community by project leaders | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 2. | Grazing planning for bunched animals (livestock from all households) | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 3. | Hiring herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ด้วยการจัดการ |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Costs for establishment unknown |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Trainings were funded by NRT, LWF and Lewa Conservancy. No figures on this.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | จัดการพืช | |
| 3. | Planning activites | ด้วยการจัดการ | |
| 4. | Boma Management (mainly movement of Bomas) | ด้วยการจัดการ |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Herders, watchmen | Person-days | 250.0 | 540.0 | 135000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Supervisors | Person-days | 3.0 | 720.0 | 2160.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planning activities, management | Person-days | 20.0 | 1500.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Livestock-owning families (for wet season, no wages paid, livelihood) | Person-days | 8000.0 | 300.0 | 2400000.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Boma Movement | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | Animals treatments (spraying against ticks) | Per livestock unit | 5000.0 | 5.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Injections, vaccine | Per livestock unit | 5000.0 | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2607160.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Overall additional costs since introduction of new technology are estimated at 20% higher than before. 50% are covered by project funding (LWF, NRT, Lewa Conservancy).
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs per unit are multiplied by days.
According to the interviewed manager, total costs are only USD 18'000 (without herders). However, the listing of all costs results in much higher total costs. Total animal treatment costs for Makurian Group Ranch in comparison are USD 428'000 (labor USD 380'000, animal treatment USD 48'000, without livestock-owning families).
Also, people living in the area (population of 8'000 inhabitants) are involved in livestock keeping and are included here in calcuations as labor (for 3 months, wet season, 10% of total population).
Cost/benefit is currently negative for livestock keeping. Income due to livestock sales is roughly estimated USD 340'000 (price for cattle on average USD 400 per unit, sales around 500 p.a., price for goats and sheep each USD 40 per unit, sales around 2'000 p.a., slaughtered units (for subsistence use) cattle: 50, shoats: 1'000 - detailed figures available Herger 2018).
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
- Managing of one big herd, many supervisors needed.
- Movement of bomas.
- Livestock-owning families (although they obviously don't receive any salary): this is simultaneously their livelihood and used for subsistence. But once all their livestock is bunched in a big herd, they lose their nutritional source (milk, blood) and livelihood (sometimes they keep back a few units for this reason).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
497.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ average from 2013-2016 (neighboring ranch). Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes. Il Ngwesi is generally drier than Borana. Grazing areas are on different altitudes with different rainfall amounts. While Il Ngwesi Sanga (as one of the villages) is at almost 1700 m a.s.l. with similar rainfall like Borana HQ, Il Ngwesi Conservation area is at 1220 m a.s.l. with significantly lower precipitation (no rainfall gauge). Grazing glades in Mukgodo Forest are at 1850 m a.s.l. and in Ngare Ndare Forest at almost 2100 m a.s.l. (no rainfall measurements available, higher rainfall amounts) and varying heights with much higher precipitation on Mount Kenya (no defined areas).
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Hilly areas (e.g. Sanga village) and flat areas in lower altitude (conservation area).
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol.
SOC 1.1-1.4 %
pH: 6.3
Clay: 12%
Silt: 53%
Sand: 35%
More information in Herger (2018).
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Few springs, Ngare Ndare river, no boreholes. Source is Mount Kenya.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Grassed acacia bushland. Bare land up to 70% during the dry season. Loss of (native) vegetation. Invasive species coming in. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Solyneum inconum, Ipomea hildebranditi, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies. Dominant trees: Acacia tortilis, Acacia mellifera, Acacia nilotica, Acacia etbaica, Boscia angustifolia. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (see Herger 2018).
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Masai people. 8'000 Masai living in Il Ngwesi. Traditional lifestyle. Livestock with very high cultural value. About 10% subsistence use, 90% is sold for local and national markets (mainly local).
Very little agriculture; tourism (award-winning eco-lodge in conservation area); people start to diversify. Schooling of children has a high importance today (e.g. smallstock is sold for school fees). Children and young warriors are traditionally herders, however, it is shifting towards hiring herders and sending children to school.
Have been historically "squeezed" from all sides into smaller areas for livestock keeping. Future of pastoralism is in question.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Applies for one household. Herders on the other hand trek livestock over an area of more than 10'000 ha.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
การจัดการที่ดิน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas). Previously, every household managed their livestock individually.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
External! Better land cover attracts invaders (Invasion from northern tribes), envy
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Poorest livestock-owning families are better off now since their livestock are also bunched together with all the others. For instance, before they couldn't afford to trek their 5 cows to Mount Kenya for pasture, now their livestock are trekked with all the others - all have the same opportunities. Other households are complaining about this since they can't decide on their own anymore where they want to bring their livestock for grazing.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less runoff, more water stored in the soil.
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Il Ngwesi is not affected by the huge invasion of the exotic cactus, Opuntia stricta. However, there are some other invasives like Lantana in the area, but not as problematic as Opuntia. According to land users, native vegetation cover has improved, which results in fewer invasive species.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More stored in the soil. According to the land users, no measurements conducted.
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
All listed impacts are as perceived by land users according to Patrick Leseri, Conservation Manager. In his opinion, vegetation cover has thanks to the new technologies improved. Planning activities significantly increased and therefore also socio-economic and ecological conditions improved. Results from a rangeland health assessment (only ecological conditions) show on the other hand partly heavily degraded ecological conditions (poor soil and vegetation, erosions features, inability of producing annual grasses after rains etc) (Herger 2018). Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไปอื่น ๆ | Greater variation of seasonal rainfall, higher intensity of rainfall events, change in rainfall regimes in general (see Schmocker 2013 and Imfeld 2016). | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Improved rangeland health, better internal organization, and cooperations make them less vulnerable to climate change impacts.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Masai people have changed their livestock composition towards owning more smallstock (goats and sheep) than cattle. Goats are tolerant of drought, and as browsers, they don't need any grass. Also, they can be turned into money much quicker than a cow in times of need and because of their more rapid reproductive cycle. They can also recover number more quickly after livestock losses through drought.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Proper utilisation of pasture – controlled usage/grazing. |
| Land recovery (more cover, more water, more fodder, less erosion). |
| Carrying capacity increased. |
| Traditional knowledge is still used. |
| More dialogue in community: brings everyone in the community together – they have a common point – everyone has the same interest. |
| Improving breeds is easier (because all are bunched together). |
| Easy vaccination of all livestock at once. |
| Approving cultural lifestyle of Masai: the higher the livestock numbers – the better for the land. |
| Better for disadvantaged community members: for instance for those who could not afford to move their livestock to Mt Kenya on their own before. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The listed advantages from Patrick Leseri, the land user, are for the most part shared share with the compiler's view. Improved planning of livestock production with planned grazing and long resting periods, improved dialogue in the community, and the named advantages of a big herd (like easy vaccination etc) are important advantages. Regarding Holistic Management (HM) principles, there remains uncertainty about land recovery. On the one hand, it is generally questionable to state as in HM: “the more animals the better” (as long as they are managed properly they can even recover degraded land), which seems dangerous in areas with such high livestock numbers and cultural value of livestock keeping - without scientific proof of the principles in similar ecological conditions. We have witnessed rather poor condition of the land, and the much-vaunted good land was difficult to find. Favourable descriptions might also be related to funding of the project. Results from a rangeland health assessment show (partly) heavily degraded ecological conditions (bare ground, poor soil and vegetation, erosion features, partly an inability of producing perennial and annual grasses after rains etc) (see Herger 2018). However, an evaluation of change over time is impossible to assess. Further monitoring is necessary. Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches. However, the efforts towards good management and a sense of community was not difficult to notice. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Higher costs. Above 20% more than normal costs. Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT), Laikipia Wildlife Forum and Lewa conservancy as main funders for applying holisitc management principles. Since 2007, they covered about 50% of all costs.. | |
| More labour intensive. 20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas). | |
| Challenge to bring people together (and their livestock) and agree on a joint management. | |
| Some families still prefer to manage their livestock on their own and make their own decisions. There are no individual decisions anymore: principles apply to everyone. | |
| Breeding can also be a problem – those with good genetic material (better livestock) may lose and those with poor may win by mixing. | |
| Conflicts among animals; bulls fight a lot. No separation of heifers, cows, steers and bulls. | |
| Management of high numbers of big herds is a challenge. | |
| Diseases are easily transmitted. | |
| Once livestock is collected to big herds, individual families lose their nutritional basis (milk, blood). However, some also keep a few livestock units back. | |
| Sometimes trees are cut for bomas. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Il Ngwesi (mostly in Sanga village though) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Several meetings with the grazing coordinator, conservation manager, chief, elders, and other resource people of Il Ngwesi over half a year.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
University of Bern
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Modeling Seasonal and Annual Precipitation using long-term Climate Records and Topography. Master’s Thesis. Noemi Imfeld (2016).
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
University of Bern
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Savory, A (1988). Holistic Resource Management. Gilmour Publishing, Harare, Zimbabwe
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Online
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
•Carter, J., Jones, A., O’Brien, M., Ratner, J., Wuerthner, G. (2014). Holistic Management: Misinformation on the Science of Grazed Ecosystems.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
International Journal of Biodiversity.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
•Briske, D.D., Ash, A.J., Derner, J.D., Huntsinger, L. (2014). Commentary: A critical assessment of the policy endorsement for holistic management. Agricultural Systems 125:50-53.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล