Addressing shallow landslides by using wooden pole structures. [บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Milenko Blesić
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: THEODORA FETSI, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter
Zaustavljanje plitkih klizišta drvenim šipovima
technologies_4285 - บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Čustović Hamid
University of Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bajrić Muhamed
University of Sarajevo, Faculty of Forestry
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
Municipality Kladanj Agronomist:
Hajdarević Hajda
Department of Finance, Entrepreneurship and Local Economic Development, Municipality of Kladanj
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Hotović Huso
Land user, Borak Locality, Kladanj Municipality
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Utilization of wooden pole structures placed in parallel, to reduce shallow landslides (2-3 m) in relatively small surfaces. Possibility to be combined with drainage system for better results.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
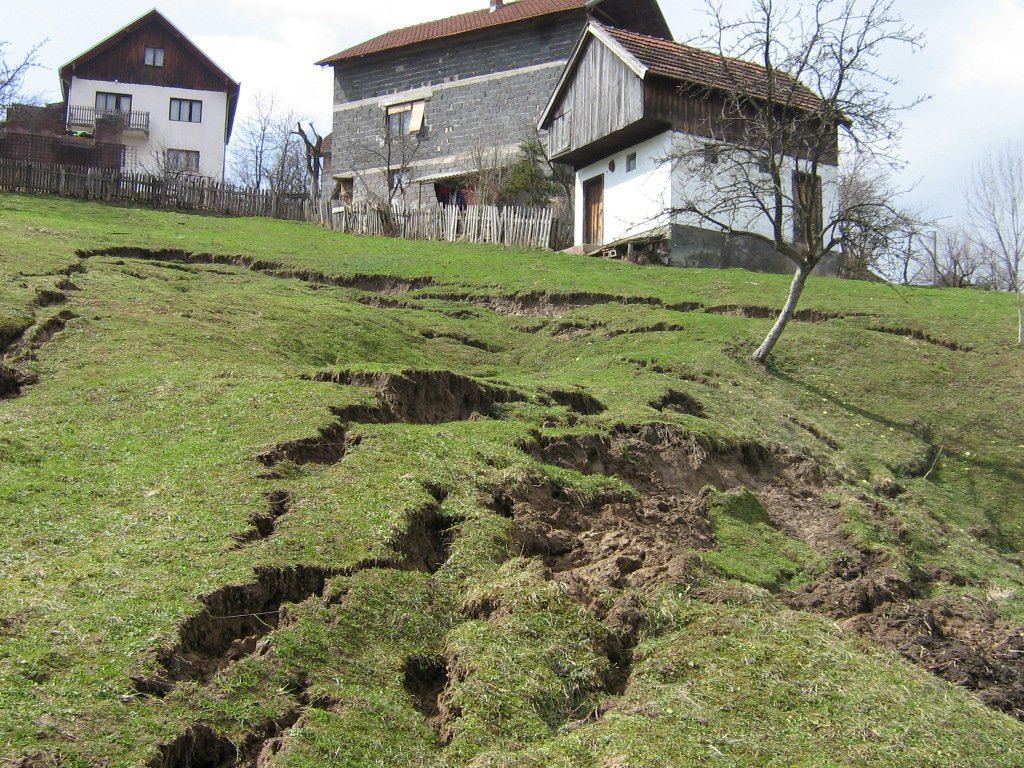
Farmers in northeast parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina traditionally applied the technology to address shallow landslides, surface erosion or loss of top soil due to sheet or interrill erosion. Movements of the upper layers of the soil appears due to unfavorable properties of the soil layers (clays, pseudoclays), set on impermeable geological substrates, all under conditions of intense and long-term rainfall. During the last decades, it has been frequently applied in the area of Kladanj municipality, whose administrative services for agriculture and forestry technically specified and promoted the technology. Landslides are one of the major problems in the hilly areas of Bosnia and Herzegovina, threatening particularly the agricultural lands. The technology is being applied by farmers on their own properties, but it is also part of public interventions, e.g. for the protection of roads or other infrastructure from landslides or in the context of roads recovery programs damaged by landslides. The technology aims to reduce the impact of the shallow (up to 2 - 3 m in depth) landslides of relatively small surface, by preventing further movement of the soil. So far, it is sporadically applied on around 20 – 30 locations in Kladanj Municipality, whose territory is around 355 sq. kilometers.
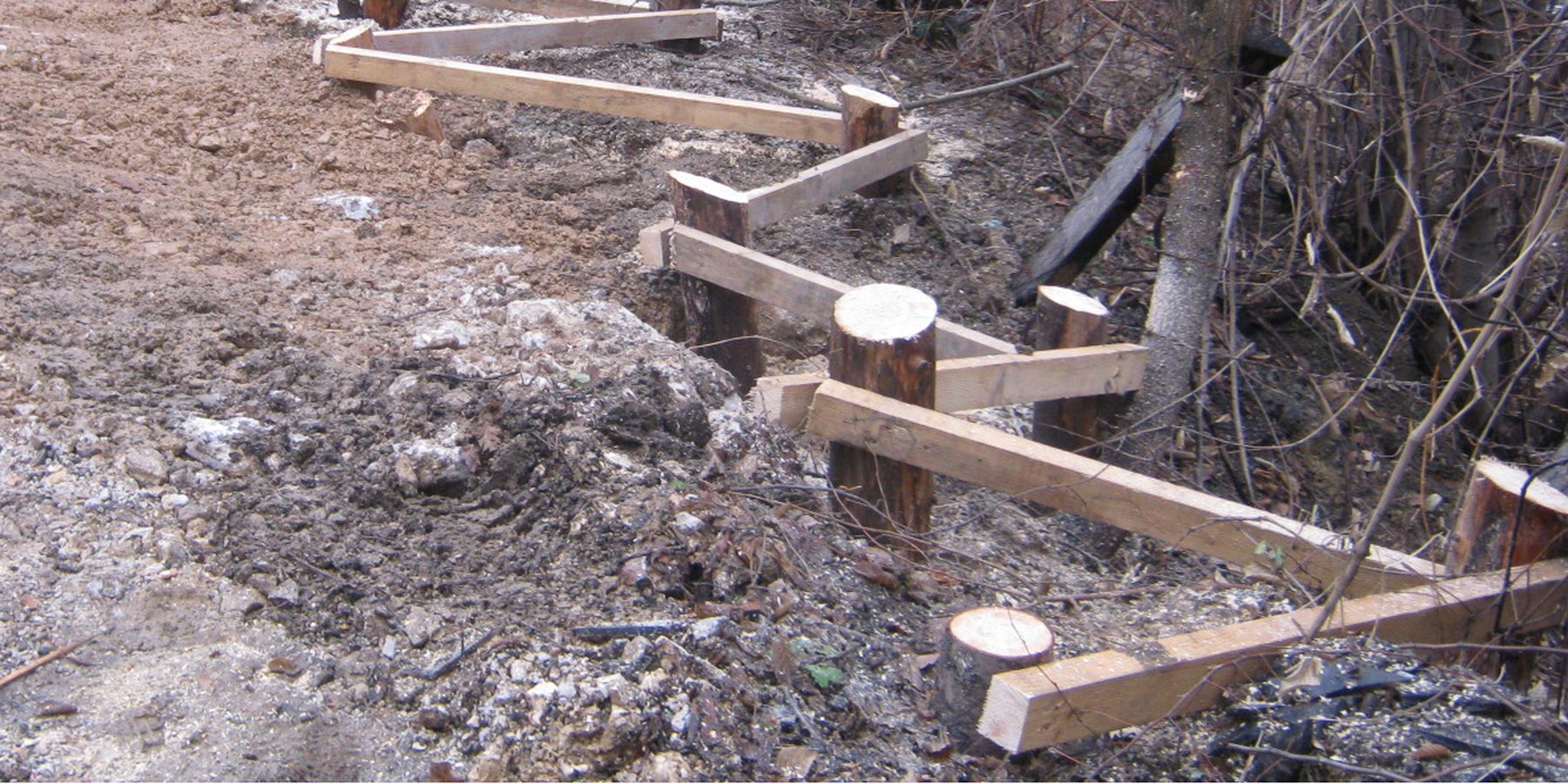
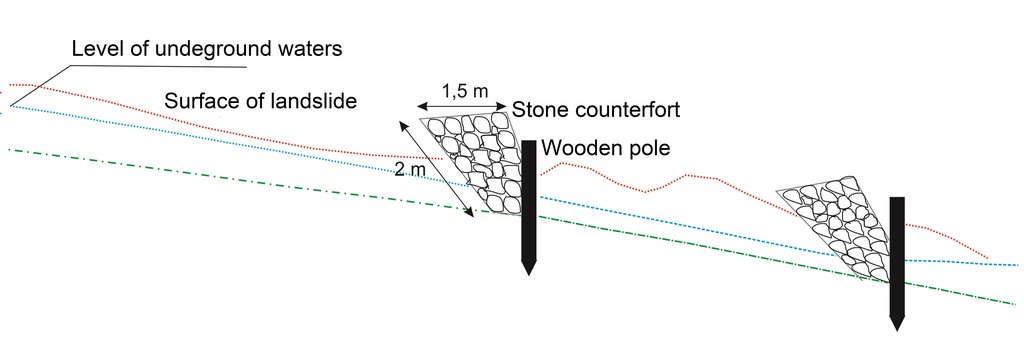
The technology implies pounding wooden poles in front (below) of the frontline of the landslide, along the contour, perpendicular to the slope. Land users recommend oaken pols due to their durability. The poles are usually 3.5 – 4 m long and 20 – 30 cm in diameter. One pole formation consists of two parallel lines of poles, with 1.5 to 2 m distance from line to line. The poles are positioned in a staggered way that a zigzag is formed. The poles are interconnected with wooden laths. One pole formation is usually enough to address smaller landslides, but in case of larger landslides, two formations are recommended. In the latter case, in combination with a drainage system, stone counterforts are formed in front (above) the poles' formation. See technical drawing for more details.
The primary purpose of the technology is to recover shallow and small landslides on slopping terrains. Stopping the movement of agricultural land after reparation of cracks and land gaps caused by landfall enables re-utilization of the land for either agricultural production or agro-forestry. In the municipality of Kladanj walnuts or other wooden fruit species with strong roots are often planted on recovered landslides.
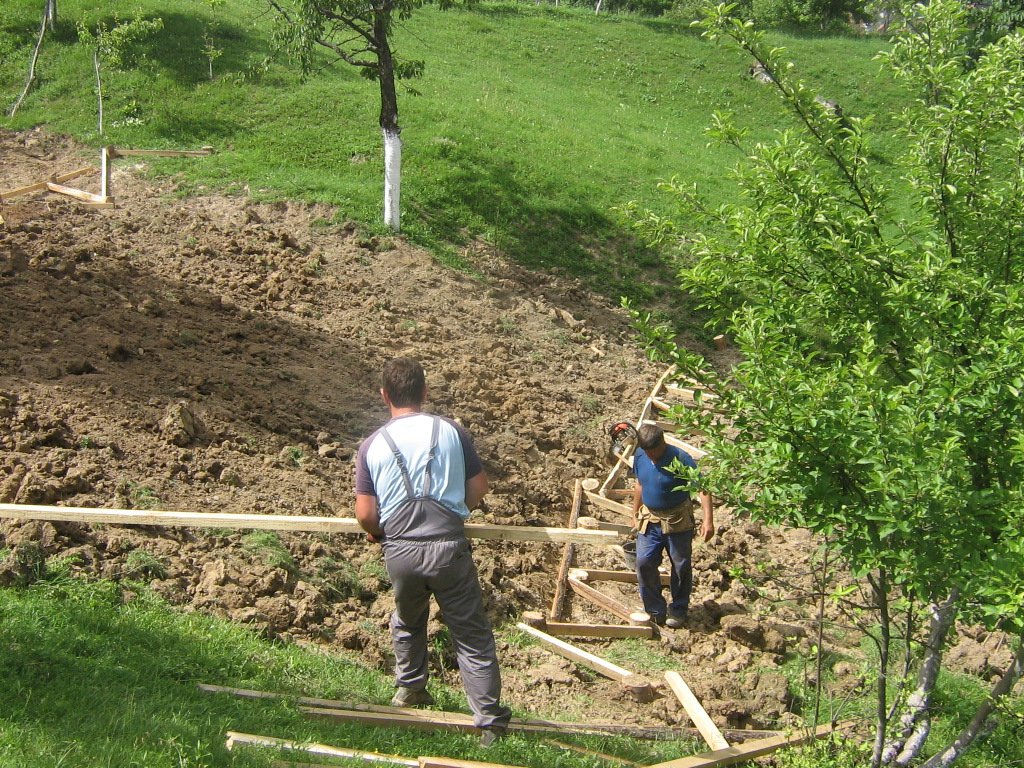
After a prior assessment of the depth and surface of the landslide, an expert or a technician prepares simple project sketches. The sketches define configuration of pole formations and materials needed for the construction (oak poles, laths). The realization of the technology is not particularly demanding. Nowadays machines are used to pound poles in the ground (mainly by a dredge's spoon).
It is a relatively inexpensive technology which could be financed by even small farmers who can protect or recover their, under Bosnia and Herzegovina conditions, usually small agricultural land parcels.
Although not an integral part of the technology, modification with water drainage from the body of bigger landslide ensures additional, long lasting stability of the terrain. If performed, the drainage is carried out by depositing drainage material (perforated pipes, pebbles, tiny stone fractions) in the lower zone of drainage trenches whose configuration and depth depends on the terrain conditions. Another modification of the technology could include construction of a stone counterfort in front (above) the pole formation. These modifications are briefly presented in the technical specification of the technology, but they were not applied on the site (Borak locality) where activities, establishment and maintenance costs of the technology were observed.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tuzla canton
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kladanj municipality
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - other
- fodder crops - alfalfa
- fodder crops - other
- vegetables - other
- Apples, Plums, Pears, Berry fruits
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Vegetables in orchards

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- cattle - non-dairy beef
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การจราจร ทางถนน รถไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology could be applied on various types of land use. In the northeast region of Bosnia and Herzegovina it is commonly applied on: grazing land, cropland (annual, perennial, trees and shrubs), and mixed land uses. In Kladanj municipality the technology is frequently applied for protection or reconstruction of roads damaged by landslides.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- stopping landslides, recovery of landslides
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
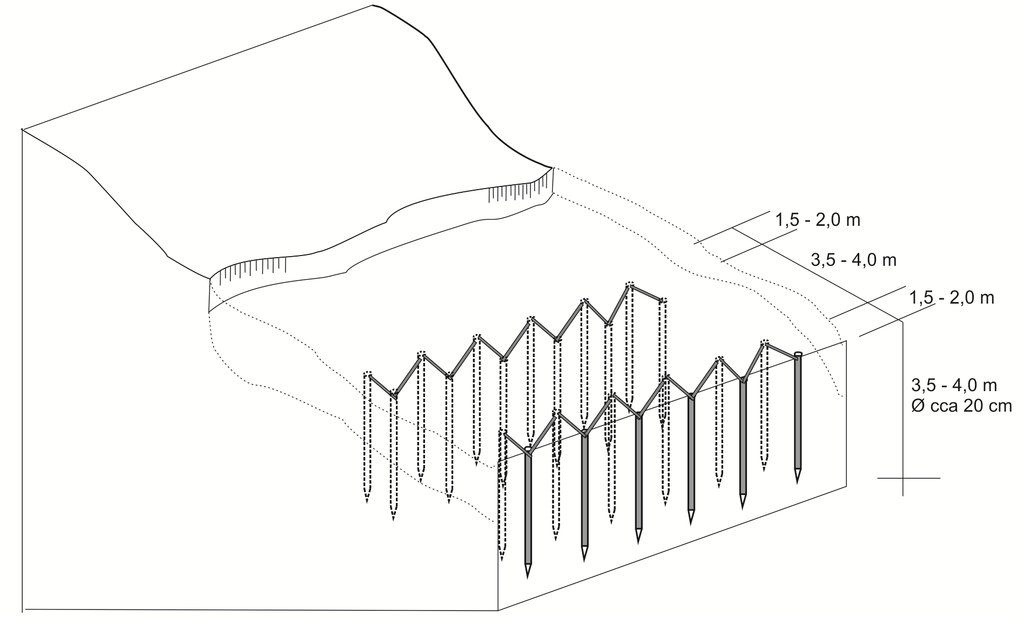
The sketch depicts the cross-section of the terrain, illustrating the wooden poles’ structures and the technical characteristics of the technology. Two wooden structures are being placed in parallel, at a distance of 3.5-4 m. Each structure is consisted by wooden poles positioned in a zigzag form. The poles are pounded in the ground at a depth of 3.5 m and are connected to each other with wooden laths. The distance between the poles is 1.5-2 m. The number of poles to be used, depends on the size of the area where the intervention is needed. The recommended distance between the two parallel structures is 3 – 4 m, depending on the characteristics of the terrain.
The implementation of the technology does not bring any change on the slope and could be applied on various slopes. The technology is mostly applied on agricultural or infrastructural land, i.e. on slopes not above 30%.
ผู้เขียน:
Muhamed Bajrić, Milenko Blesić
วันที่:
20/10/2018
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
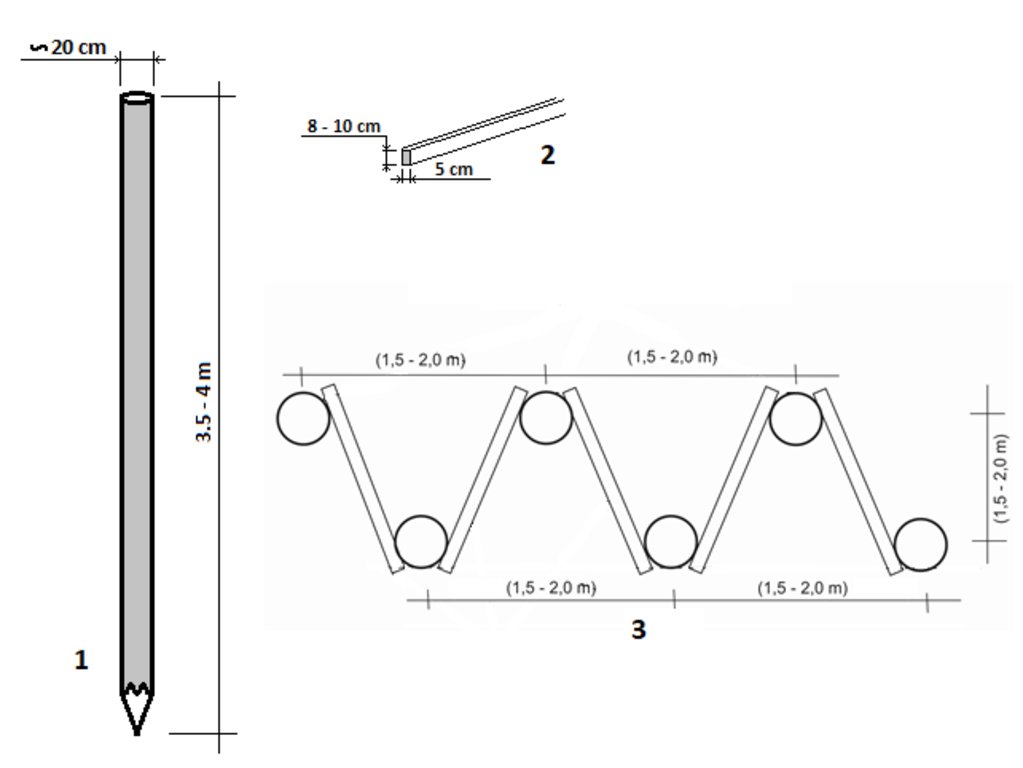
Drawing 1 shows the recommended dimensions of the poles.Drawing 2 illustrates the technical characteristics of the laths (2) which connect the poles. Drawing 3 shows the top view of the overall structure with the required dimensions.
ผู้เขียน:
Milenko Blesić, Muhamed Bajrić
วันที่:
20/10/2018
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
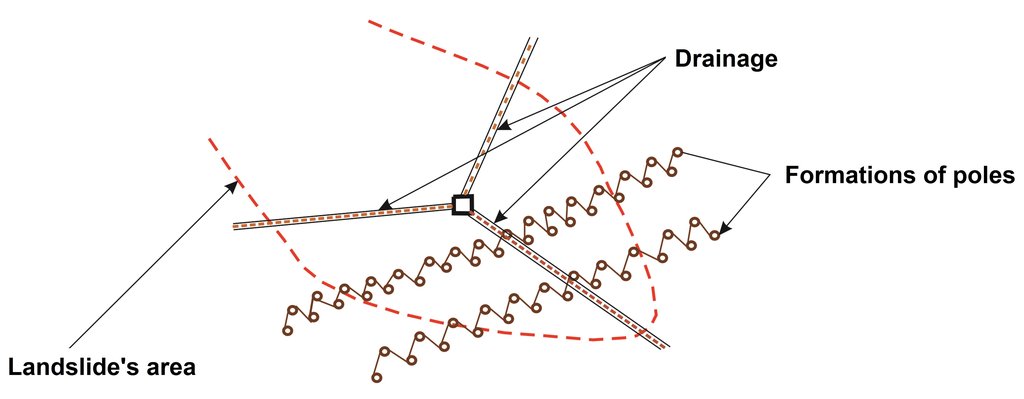
Modification (improvement) of the technology with a drainage system. The modification (drainage) was not applied on the site where the technology was observed.
ผู้เขียน:
Muhamed Bajrić
วันที่:
10/11/2018
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Modification (improvement) of the technology by construction of the stone counterforts just above the line of poles. The modification (stone counterforts) was not applied on the site where the technology was observed.
ผู้เขียน:
Muhamed Bajrić
วันที่:
10/11/2018
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Landslide on Borak locality - Kladanj municipalitay
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
0,35 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
29.24 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Expert's characterization of landslide | Any time |
| 2. | Designing the structure and identifying the materials | Any time |
| 3. | Purchase and transport of materials (poles, laths) | Any time |
| 4. | Pounding poles in the ground | Spring - autumn |
| 5. | Connection of poles' heads (above ground parts) with laths | Spring - autumn |
| 6. | Machine leveling of the terrain | Spring - autumn |
| 7. | Planting of walnut seedlings | Autumn |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Establishment activities are presented in accordance withe the activities on one specific (Borak) locality. The surface of landslide on this locality was around 0,35 ha, and after its stopping with the formation of wooden poles, its full recovery was done by leveling of the terrain and planting of 300 walnut seedlings (further walnut orchard). The list of final recovery activities could be different on other localities and it depends of landowners' intentions and financial possibilities.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Expert's characterization of landslide, designing of construction, specification of materials | Working day | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Pounding the poles into the ground | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Connecting poles with lathes | Working day | 1.0 | 29.24 | 29.24 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting of walnut seedlings | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Heavy machinery (dredge) work on pounding poles into the ground (hired) | Hour | 16.0 | 46.78 | 748.48 | 30.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Heavy machinery (dredge) work on leveling of terrain | Hour | 4.0 | 46.78 | 187.12 | 30.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Walnut seedlings | Piece | 300.0 | 2.92 | 876.0 | 30.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wooden (oak) poles | Piece | 100.0 | 17.5 | 1750.0 | 30.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wooden connecting laths | m | 200.0 | 0.5 | 100.0 | 30.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Other auxiliary materials (nails, wire, etc.) | Lump sum | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4487.64 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4487.64 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
So far, introduction of the technology in Kladanj municipality is supported from the municipality's budget (contribution in purchase of materials and hiring of heavy machinery).
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The presented activities and costs are related to the landslide (0,35 ha) on Borak (Kladanj municipality) locality. On this particular site, the technology is applied without drainage system and stone counterforts next to wooden pole lines. Though they are not linearly connected, costs on other sites may be smaller or higher, depending on the size of landslides and concrete conditions on the ground.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After establishment, the technology does not need any particular maintenance activities.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to the fact that after establishment the technology does not need any major maintenance activities, there are not any significant costs for maintenance. The maintenance is limited to annual checking of joints between lathes and poles and necessary minor interventions (replacement of possibly damaged lathes, re-connection of laths).
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Prices of the construction materials (poles, laths).
Hiring costs of heavy machinery (dredge).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
894.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The highest precipitations appear during spring and early summer, (June 111 L/m2; February 55 L/m2). Heavy downpours during summer is one of the climatic features of this area.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Tuzla
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
According to information from Kladanj municipality administration, on the municipality territory there are around 30 localities with the applied technology.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most of the interventions on private properties were partly supported by specific municipal/cantonal programs for recovery of lands, damaged by heavy rains, flash floods and landslides. All interventions on infrastructure (mainly roads) were fully supported by municipal/cantonal budgets.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
Improvemnts of the technology effects and durability
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
The original technology (wooden poles barriers) has been recently modified by parallel installment of drainage of landslide, and most recently by stone enforcement just above the line of wooden poles.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Relatively affordable way to stop and recover landslides on agricultural land |
| Wide availability of construction material (wood) in the region |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Costly effective way to recover agricultural land on small private parcels (usual in Bosnia and Herzegovina) endangered by landslides |
| The technology keeps land from further degradation or possible loss of soil and allows continuation of its current or different functional use |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It is not always easy to find/hire heavy mechanization for pounding of poles into the ground | Organization of farmers who want to introduce the technology and request for municipality support in hiring heavy machinery |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Limited durability of the wooden poles. | |
| The technology itself (i.e. without extensive drainage) is not efficient in stopping and recovering larger and deep landslides | Added investment in properly projected and implemented drainage system |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Field surveys from May to December 2018, valuable information from Ms Hajda Hajdarević, Kladanj municipality's office for agriculture.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
During filed surveys five land users who applied the technology were interviewed.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Besides field surveys, precious information regarding the landslide issues and possible technology effects were provided by professors Hamid Čustović and Muhamed Bajrić (University of Sarajevo).
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Field data compilation was done through six field surveys performed between May and December 2018.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล