Traditional irrigated rice terraces [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ramanand Bhattarai
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Tari khet (Nepali)
technologies_1099 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - เนปาลชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
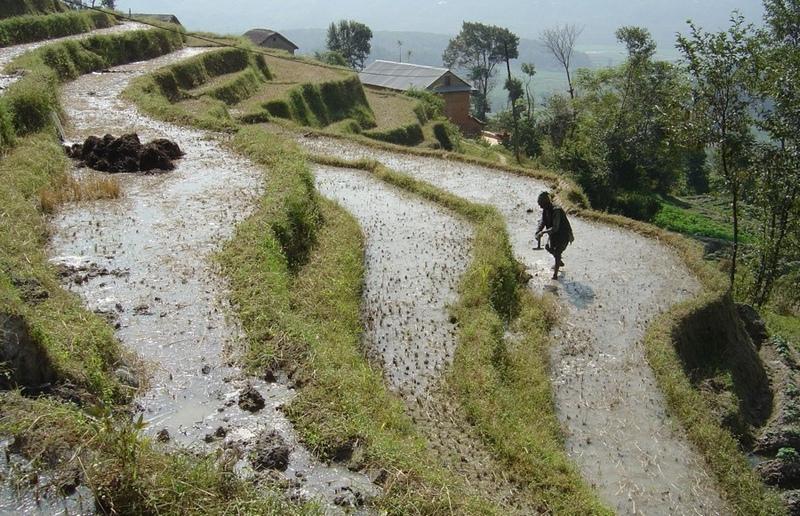
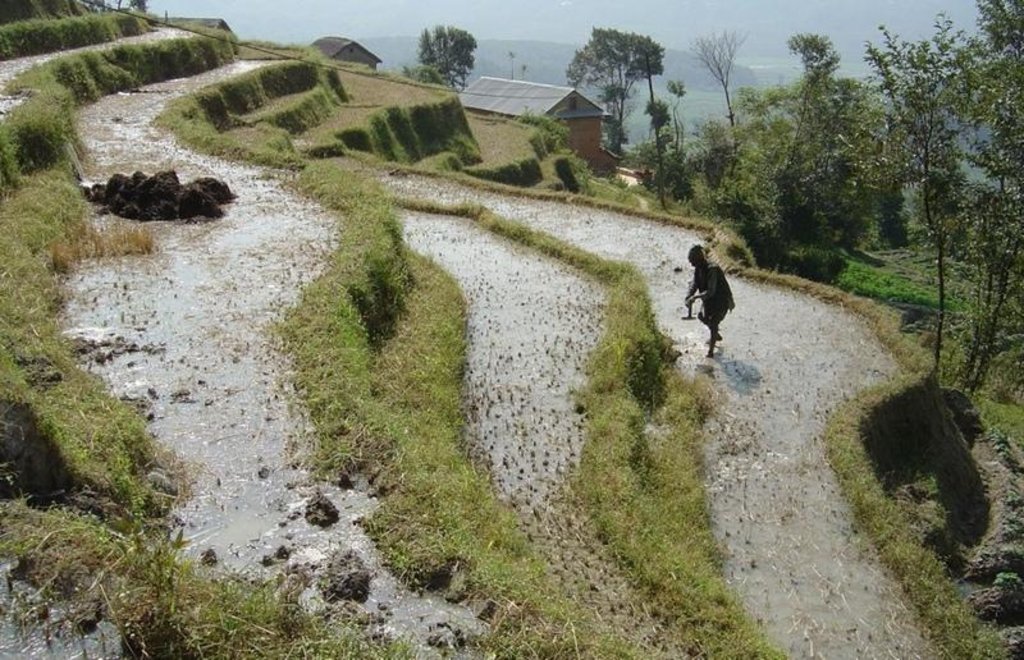
Level bench terraces with risers protected by fodder grasses, used for the irrigated production of rice, potatoes and wheat
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The level bench terrace is a traditional technology that makes irrigated crop production possible on steep, erosion prone slopes. The majority of such terraces in Nepal were constructed by hand many generations ago, but some new land - mostly already under rainfed cultivation on forward sloping terraces - is still being converted into irrigated terraces. The initial costs for the construction of the terraces are extremely high – and annual maintenance costs are considerable also. The climate is humid subtropical, slopes are steep (30%-60%) and soils generally have a sandy loam texture. Terraces are cropped by farmers who mostly have less than 0.5 ha of land each.
Two to three annual crops are grown per year starting with paddy rice during the monsoon, followed by potatoes and/or wheat.
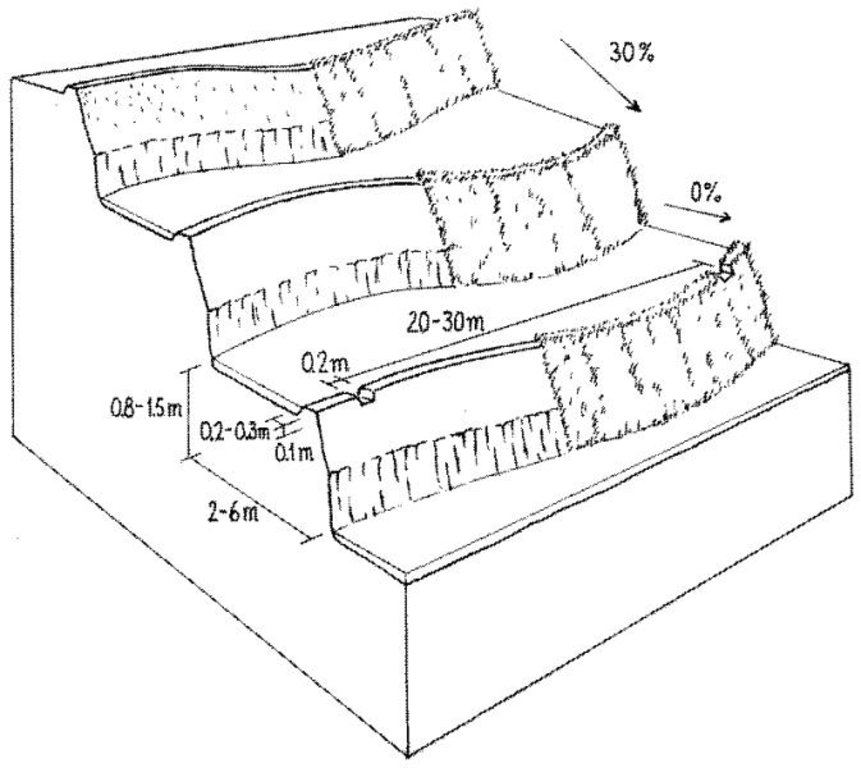
While terrace beds are usually 2–6 m in width, to save labour they are made as wide as they can be without increasing the danger of slips/land slides. Surveying was traditionally done by eye, but now a water-tube level may be used. Risers are 0.8-1.5 m high with a small lip (20-25 cm). The slope of the riser varies from 80 to 160%, depending on the initial gradient of the hill. Stones are incorporated in the risers if available, and grass species such as bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and napier (Pennisetum purpureum) may be planted for stabilisation and as cattle fodder. The risers are compacted (with hoes) to improve ponding conditions for the paddy rice. Twice per year the risers are scraped with a special tool: (1) at the time of land preparation for paddy rice the lower part of riser is sliced, but the upper part is left protected with grasses against the monsoon rains; (2) at the time of wheat planting the whole riser (including the lip) is scraped and spread as green manure on the terrace.
Terraces are flooded with water for paddy rice cultivation: a smaller amount of water is diverted into the fields for other crops. Excess water is drained to the lower terrace by openings in the lip, which are filled with rice straw in order to filter out sediments. The depth of water for rice - when flooded completely - is normally between 10 and 15 cm. Fertility is maintained by addition of farmyard manure, spreading the scraped soil from the riser, and also through sediment carried in the irrigation water. Nowadays, mineral fertilizers are also applied.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kathmandu
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Manmata subwatershed
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
1.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 km2.
Map
×3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - rice (wetland)
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- wheat
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major cash crop: Potatoes
Major food crop: Rice and wheat
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - steep slopes, not suitable for agriculture in their original state (better for forestry, agroforestry, horticulture, and fruit
trees)
- small and scattered plots of land
- land users find chemical fertilizers and water expensive
- there is water scarcity from September to May and too much rain in the monsoon period (June to August) with the danger of erosion and collapse of the terraces
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
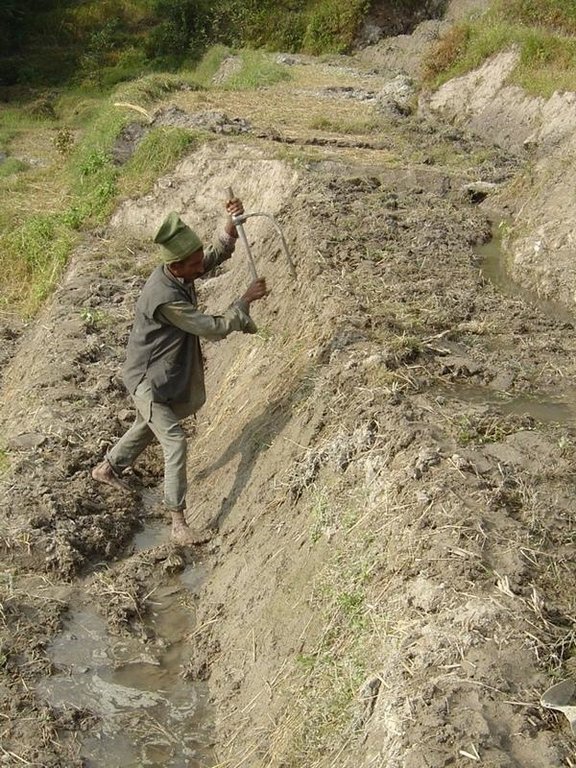
Layout of irrigated terraces. Openings in the lips drain excess water, grass cover stabilises lips and risers (right). After harvesting of rice, the grass is scraped off the lower part of the risers (left) and spread on the terrace beds
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, control of dispersed and concentrated runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green/farmyard manure
Vegetative measure: fodder grass at risers
Terrace
Material: earth
ผู้เขียน:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting grasses including bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon). | during monsoon |
| 2. | Construct bunds (risers) with soil from upper and lower sides | before monsoon |
| 3. | Level terrace beds (soil moved from upper to lower part of terraces). | before monsoon |
| 4. | Make lips on edges of terraces | before monsoon |
| 5. | Compact risers | before monsoon |
| 6. | Construct irrigation canal | before monsoon |
| 7. | Make openings in lips for drainage of excess water | before monsoon |
| 8. | Test-irrigate terrace for accurate levelling | during monsoon |
| 9. | Plant grasses including Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) | during monsoon |
| 10. | After 2–3 years: some narrow terraces may be merged to form single, wider terraces | during monsoon |
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flood the paddy fields .. | (June/July) / Repeated 3–4 times during |
| 2. | Slice/scrape grass and soil on lower part of risers and spread on terraces | (when flooded, June/July) / |
| 3. | Plant rice and apply mineral fertilizer | (June/July). / |
| 4. | Harvest rice | (October) / |
| 5. | Apply manure (cattle manure), after rice harvest | (October). / |
| 6. | Slice/scrape grass and soil from whole of risers and spread on terraces; repairsmall collapses/slumps in risers | (October/November) / |
| 7. | Pprepare land | (November) / |
| 8. | Apply mineral fertilizer | (November/December). / |
| 9. | Irrigate | Nov. / repeated several times during cultivation |
| 10. | Harvest of potato/wheat | (January-March). / |
| 11. | Planting of rice | June,July / |
| 12. | planting of potatoes, wheat | November / |
| 13. | Repair of small collapses/slumps in risers. | (Oct./Nov.)/ |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 185.0 | 185.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 840.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 840.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade, baskets, (doko), special tool for scraping
Current establishment costs are very difficult to determine since the majority of the traditional terraces were
established a long time ago. Costs depend closely on the present state of the land (forward sloping terraces or uncultivated) and the need for irrigation canals. Farmers say that construction now could cost up to US$ 10,000 per ha if carried out by hand at full labour cost. The cost given for maintening the terraces (approx. US$ 840 per ha) includes all associated annual crop production costs. In this case study, 100% of the construction costs were borne by land users.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because of the geology and soil texture (loam)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Off-farm income specification: hired labour (on other farmers’ fields) or as porters
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (rice/wheat) and commercial (potatoes)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land use rights: leased (90% of farmers), individual (10%)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
the technology is a part of a complex farming system
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not everyone has access to land for irrigation
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Livestock fodder
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
when the agreed and scheduled water extraction amounts are exceeded
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
poor maintenance of topmost terraces may cause landslides
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Soil fertility
Biodiversity
Number of crabs in irrigation water make holes in the terrace risers
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
which in turn can cause pipe erosion and riser collapse
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
Groundwater recharge
Soil moisture and nutrients downstream
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Income and production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the terraces (including all maintenance activities) |
| Easier to cultivate flat terraces/less labour required (after establishment of terraces) |
|
Work sharing: traditional terraces are part of a long tradition of work sharing within the community with no external labourneeded How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established traditions and norms |
|
Technology is easy to understand/apply. Increased opportunities for irrigation facilities: farmers without level terraces are not allowed (by the irrigation committee at village level) or do not claim irrigation water |
|
The irrigation element of this technology fosters social bonds within the community How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established norms and traditions. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Decreased grass production (grazing area reduced) | Promote planting of high value grass species on risers (such as bermuda grass). |
| The farmers believe that the terraces are too narrow (for efficient use of tractors); they would like to have wider terraces |
Investigate possibilities of constructing wider paddy rice terraces on steep slopes, which, according to present experience, is not possible. |
| High labour costs for establishment. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
There is considerable literature on the construction and maintenance of irrigated terraces in general, but no references thatspecifically describe the traditional paddy rice terraces in Nepal
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล