Minimum tillage in Mediterranean vineyards [โปรตุเกส]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Carla Ferreira
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Minimum tillage
technologies_2879 - โปรตุเกส
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Centro de Estudos de Rescursos Naturais, Ambiente e Sociedade (CERNAS) - โปรตุเกส1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
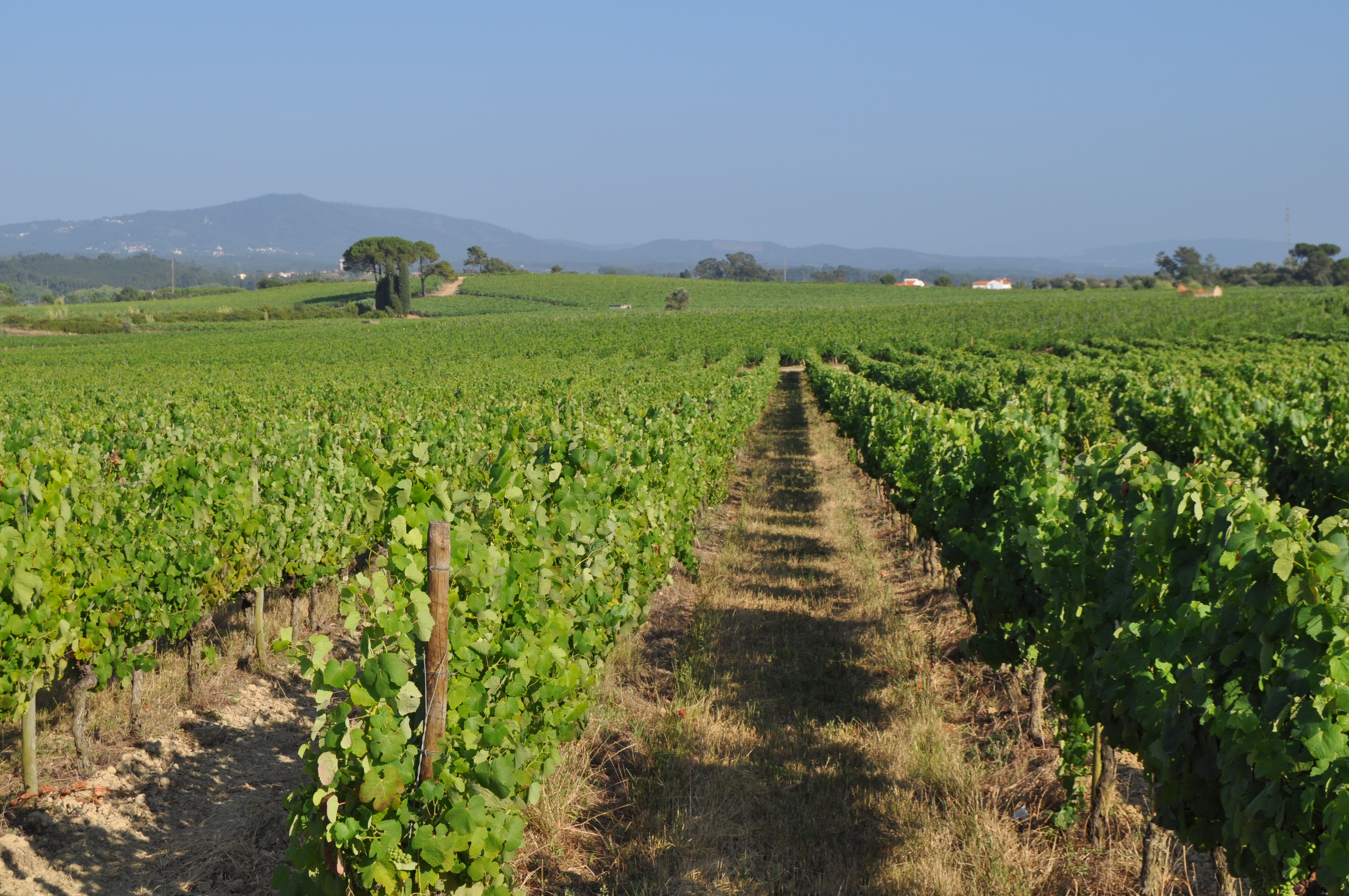
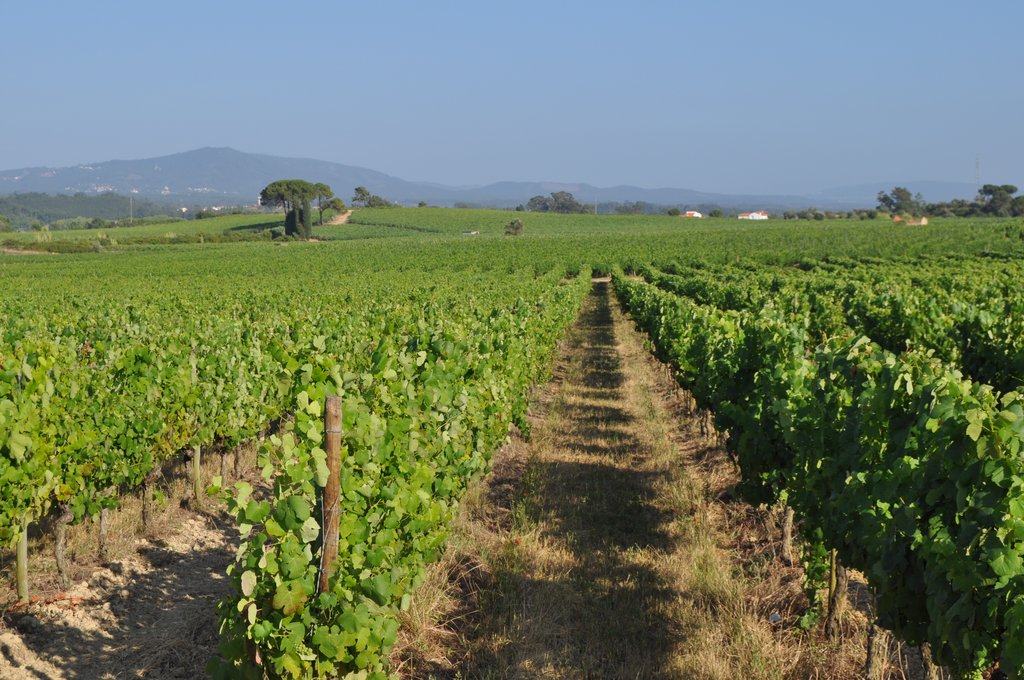
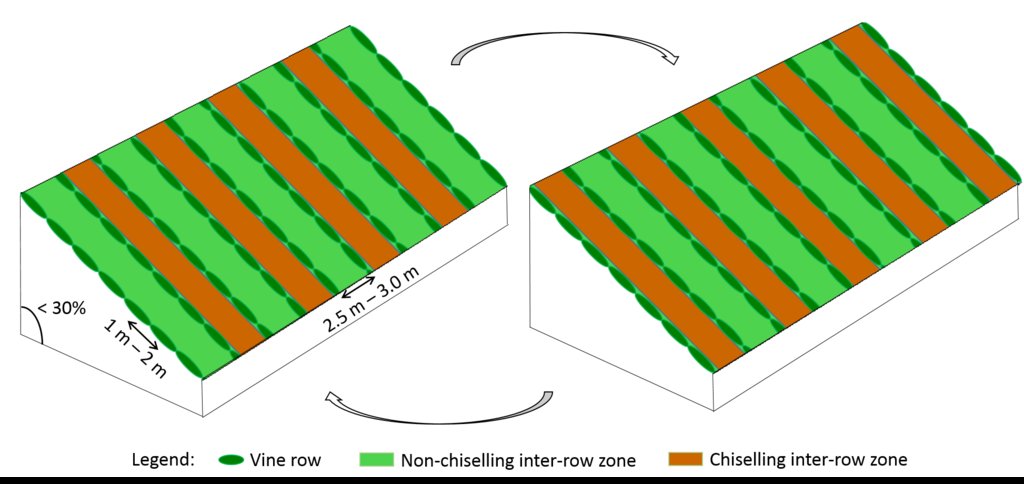
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in alternated inter-row zone, to promote soil decompation and maintain partial vegetation cover.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Portugal is one of the larger wine producers in Europe, with vineyard area covering 27% of permanent crops. Vineyards play an important role in the Portuguese economy, not only due to the impact of wine industry but also the important cultural heritage and great influence on tourism sector. There are thirteen specialized wine regions in the country, from which we highlight Bairrada region, located in central mainland, where minimum tillage is becoming popular. Bairrada has a Mediterranean climate, characterized by a long dry summer, although the strong influence of the Atlantic Ocean. Vineyard is the most relevant crop in Bairrada. In this region, farmland is mostly cultivated by landowners, comprising small winegrowers (5-10ha), most of them members of local farmers associations, as well as large producers (100-500ha) with a relevant position in the world wine market.
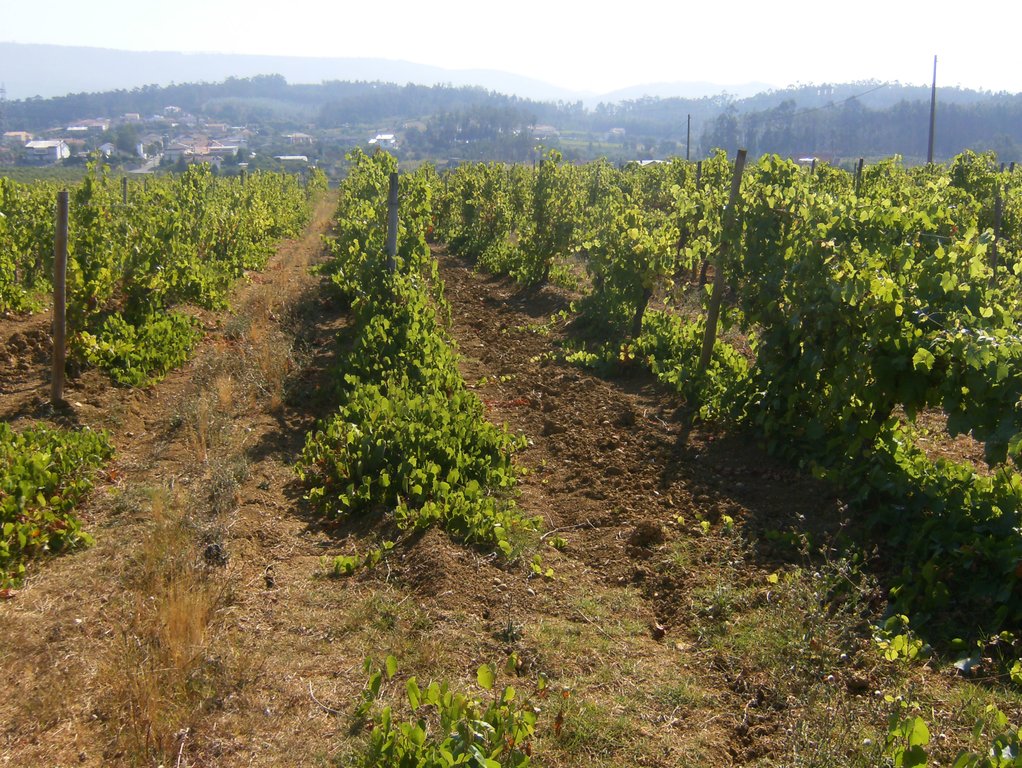
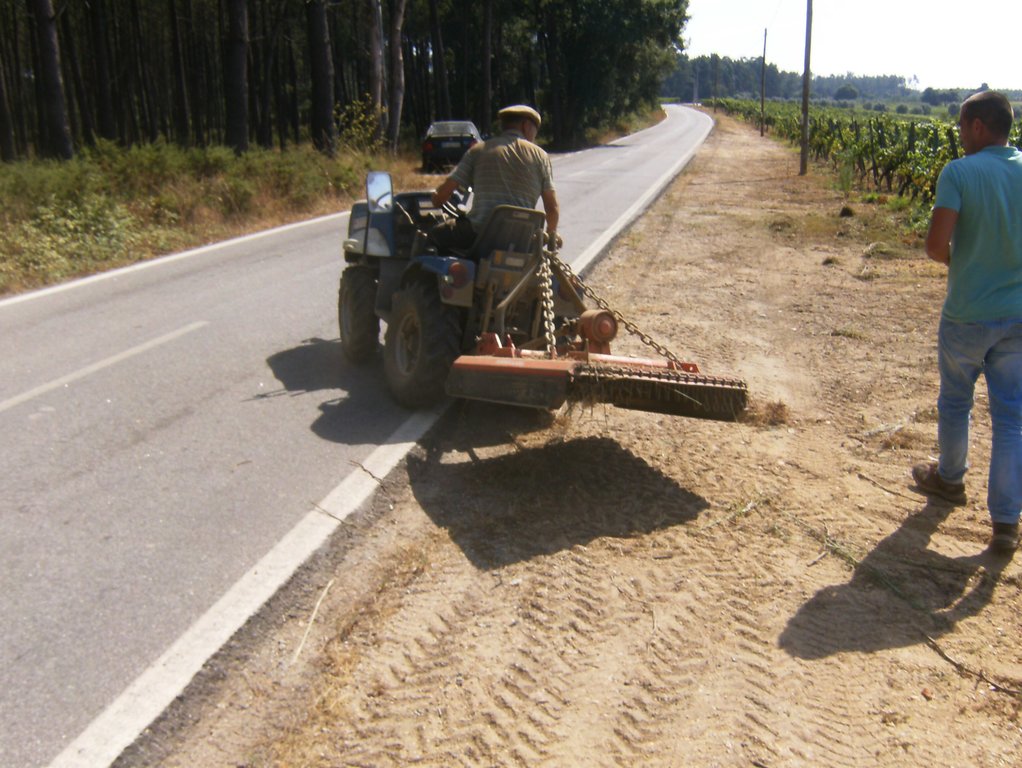
In vineyards, tillage is performed to promote de-compaction of the typical medium/fine soils and weeds control. In Bairrada wine region, soil tillage is usually performed twice per year – in autumn and spring, depending on weather conditions. Tillage is performed with a ripper and disc arrow (10-15cm), since mechanized vineyards require vines arranged according to horizontal wire bundles. However, tillage activities favour soil degradation, namely due to soil erosion and increasing mineralization of organic matter. In order to mitigate land degradation, minimum tillage of inter-row zone was adopted. No tillage is not applied by the farmers due to the need to de-compact the soil, favoured by the relatively high clay content. The minimum tillage is performed in alternated inter-rows, to keep vegetation cover in part of the vineyard. Tillage inter-row switch every time, so that each inter-row is not tilled more than once per year. Weeds control in the non-tilled inter-rows is performed using a rotary brush mower. In the plant zone, weeds are controlled with herbicides, applied twice per year: autumn-winter (before vine plant winding) and spring-summer (during vegetative growth). During the hot dry summer, weeds are naturally controlled due to water-stress. Mechanical intervention is also performed for pest and disease control, generally applied as preventive measures. Phytosanitary treatments are performed upon receipt of notices from Regional Directorate of Agriculture or technicians from local farmers association. These notices also include recommendations about the type of products and the application rate. In the majority of the Region, pruning and harvesting is performed manually. Pruning residues are typically mowed and left at the soil surface.
The adoption of minimum tillage was triggered by governmental subsidies. Farmers recognize the impact of this technology on the environment, namely on preventing soil degradation and enhancing biodiversity. However, soil compaction and water competition between vegetation cover and vines (over the summer) are major concerns.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
โปรตุเกส
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Bairrada, Central Region
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
- motivated by financial support from the government
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Technical recommendations provided by technicians of farmers associations.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- grapes
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
One harvesting per year
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Vineyard
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in the inter-row zone, in alternated lines switching between chiselling activities (10-15cm), usually performed in autumn and spring. There is no specific technical recommendations.
Vines are disposed horizontally, supported by wire or cord sustained by wood or metal support. Planting compass varies with soil fertility, type of wine, as well as expected quantity and quality of production, and desired height of the edges. Typically, distance between vine plants within each row ranges from 1m to 2m, and the inter-rows distance from 2.5m to 3.0m, leading to densities of 1000-3000 vines/ha. Generally vineyards are installed on natural surface profile for slopes lower than 30%, and in terraces for hillslopes of 30-50%. Vine plantation is forbidden for slopes greater than 50%.
ผู้เขียน:
Carla Ferreira
วันที่:
26/06/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha per year
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.86615
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
30
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chiselling of alternated inter-row zone | Autumn/Spring |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control in alternated inter-row | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chemical control of weeds in plant zone | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Chisel | Equipment | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Rotary brush mower | Equipment | 1.0 | 1600.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sprayer | Equipment | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 5100.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 5888.13 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Young farmers (<40 years old) may submit agricultural projects for partial government funding.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs provided do not include the tractor aquisition costs.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeds control with herbicides (in vine rows) | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chiselling (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | For chiselling activities | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | For mechanical weed control | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | For spraying of herbicides | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor with chisel | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor with rotary brush mower | 2.0 | 145.0 | 290.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor with spraying system | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicides | Litres | 6.0 | 12.0 | 72.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 802.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 925.94 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Machinery and labor
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1077.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The climate is Mediterranean but with a significant influence of the Atlantic Ocean. The dry season extends from July to September and the rainiest period extends from November to February.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
10G/01UG from the Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Csb according with Köppen climatic classification.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Óis do Bairro: 5%; São Lourenço: 10%; Estação Vitivinícola: 9%; Quinta do Valdoeiro: 10%; Pocariça: 14%. Altitude ranges from 25m to 55 m a.s.l.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
There is a lack of studies regarding biodiversity.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- สหกรณ์
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Some of the farmers belong to large wine companies, which export the wine to several countries
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area of land varies a lot. Individual farmers can have vineyards from 2-15ha, whereas large wine companies own up to 400 ha of vineyards in Bairrada region.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- บริษัท
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The state also own some vineyards devoted to research.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are no measurements.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Although there are no measurements, it is expected less sediment and nutrient export (linked to decreasing runoff), thus less impacts on aquatic ecossystems.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Associated with decreasing chiseling activities
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vineyards are relevant for tourism, thus, their sustainability is relevant.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers associations provide knowladge and trainning to farmers.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not measured, but available water in the water cycle is expected.
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is no data, but decreasing runoff will contribute for lower sediment and nutrient exports, thus, improving water quality.
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are no measurements, but field studies performed elsewhere report increasing soil moisture due to vegetation cover.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Maintenance of vegetation cover in half of the vineyard inter-rows. However, vegetation cover is limited during dry periods.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Based on bibliography.
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Although there are no measurements, farmers report that ploughing activities are relevant to reduce soil compaction.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
According with literature review, minimum tillage decrease the mineralization of organic matter.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not measured.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not measured, but expected given the partia maintenance of vegetation cover.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Decreasing runoff will contribute for decreasing downstream flooding
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less runoff and erosion will decrease downstream siltation.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less runoff will provide lower sediment and nutrient exports to rivers.
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Lower tractor activities contribute for less greenhouse gases emission.
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The impacts have not been measured. The response is based on literature review and field observations.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology does not have an impact on climate related issues.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Less herbicides and ploughing decreases maintenance costs. |
| It allows to reduce herbicide application to control weeds, thus favouring biodiversity. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Minimum tillage is best suited for heavy, compacted and/or poorly drained soils, typical of vineyards. |
| It reduces land degradation, by improving soil structure and vegetation cover, important to reduce soil erosion. |
| Improving soil cover will improve soil moisture and aeration conditions, relevant for crop development and soil biodiversity. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction due to lower ploughing | Improve soil structure |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to maintain inter-row vegetation cover during the dry season | Replace vegetation cover by other materials (e.g. mulching) |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
More than 10 field visits were performed over a three month period.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Seven
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Two
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Several
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/05/2017
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Biddoccu, M., Ferraris, S., Pitacco, A., Cavallo, E. (2017). Temporal variability of soil management effects on soil hydrological properties, runoff and erosion at the field scale in a hillslope vineyard, North-West Italy. Soil & Tillage Research 165, 46–58.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716301386/1-s2.0-S0167198716301386-main.pdf?_tid=22418bb0-5b58-11e7-980c-00000aab0f6c&acdnat=1498582154_0fb04affbfbcf3f6e729ccdd354527ee
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Byrne, S., Guire, L.M. (2005) Vineyard Floor Management. Final report to Grape and Wine Research & Development Corporation (RT 04/03-1)
URL:
http://www.mvwi.com.au/items/526/Vineyard%20Floor%20Management%20RT%2004%2003%201.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Cruz, A., Botelho, M., Silvestre, J., Castro R. (2012) Soil management: Introduction of tillage in a vineyard with a long-term natural cover. Journal of Viticulture and Enology 27(1), 27-38.
URL:
http://www.scielo.mec.pt/pdf/ctv/v27n1/v27n1a03.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Napoli, M., Marta, A.D., Zanchi, C.A., Orlandini, S. (2017). Assessment of soil and nutrient losses by runoff under different soil management practices in an Italian hilly vineyard. Soil & Tillage Research 168, 71–80.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716302604/1-s2.0-S0167198716302604-main.pdf?_tid=34c1a784-5b58-11e7-8e6a-00000aacb35d&acdnat=1498582186_a97504bbec990b26b9de92901fae9b9b
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Puig-Montserrat, X., Stefanescu, C., Torre, I., Palet, J., Fàbregas, E., Dantart, J., Arrizabalaga, A., Flaquer, C. (2017). Effects of organic and conventional crop management on vineyard biodiversity. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 243, 19–26.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880917301603/1-s2.0-S0167880917301603-main.pdf?_tid=1428ce58-5b58-11e7-a61a-00000aacb361&acdnat=1498582131_0ca1f7a72aa834a0345b38122a2f7a05
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Raclot, D., Bissonnais, Y.L., Louchart, X., Andrieux, P., Moussa, R., Volts, M. (2009). Soil tillage and scale effects on erosion from fields to catchment in a Mediterranean vineyard area. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 134, 201–210.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880909002023/1-s2.0-S0167880909002023-main.pdf?_tid=3a75799e-5b58-11e7-8adf-00000aab0f6b&acdnat=1498582195_b808271c0c5bcddc3fa189cccc11fea3
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล