Minimum tillage in UK arable cropping systems: Tivington [สหราชอาณาจักร]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
non-inversion tillage (eng); conservation tillage (eng)
technologies_984 - สหราชอาณาจักร
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Oborn Jo
Farming wildlife advisory group
สหราชอาณาจักร
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Farmin & wildlife advisory group (FWAG) - สหราชอาณาจักร1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
Individual experimental farmer: Tivington [สหราชอาณาจักร]
Individual farmer experimenting with machinery to maintain economic viability and reduce time spent on land preparation.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
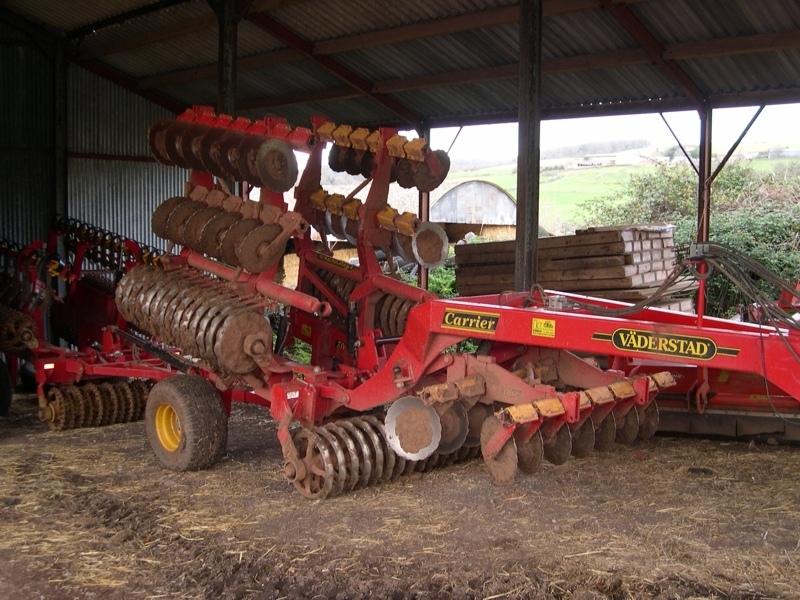
Non-inversion tillage to create a seedbed
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Non-inversion tillage to provide suitable seedbed for following crop.
Purpose of the Technology: Even and cost-effective crop establishment, saving time and benefiting the environment. Maintenance: annually, per crop,
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: innovative farmer reducing impacts of farming on the environemnt, expanding his businesss and saving time
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
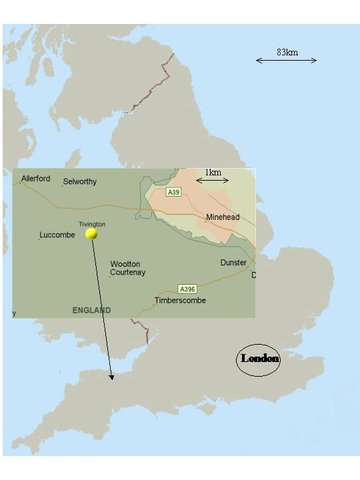
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สหราชอาณาจักร
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Somerset
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Minehead
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.78 km2.
Farm is a total of 126ha of which 28ha are grazed, 9ha are under environmental stewardship and 7ha are set aside
Map
×3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - wheat (spring)
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 300 Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Jul
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and compaction caused by inappropriate land use and intensive grazing respectively
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion and capping of the soil
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: winter wheat - winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - beans - winter wheat
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (economic viability), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility
Early planting
Material/ species: crop
Quantity/ density: depends on
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residue
Quantity/ density: 2-5 t/ha
Remarks: residue chopped + spread over width of combine
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Remarks: broadcast
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: biosolids (from Aug05)
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: when required
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
£
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.56
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Additional info: - Year2: surface cultivation: mid September / per crop - Year2: drill: mid September / per crop - Year2: roll: mid September / per crop - Year3: shallow sub-soil: November / per crop - Year3: drill: November / per crop
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Year1: shallow sub-soil | 3rd-4th week in August / annual |
| 2. | Year1: spray with non-selective herbicide (glyphosate) | late August/ early September / annual |
| 3. | Year1: drill | late August/ early September, 3-4 days after spraying / annual |
| 4. | Year1: roll (optional) | after drilling / annual |
| 5. | Year2: surface cultivation (more in Annex 3) | mid August / per crop |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Equipment (year1)-machine hour | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Equipment (year2)-machine hour | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Equipment (year3)-machine hour |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Vaderstad Carrier, Vaderstad drill and roller
Only crop establishment costs are included as all other costs - seed, fertilisers, pesticides - are equivalent with those for conventionally mouldboard ploughing. The costs highlghted include labour. Equivalent crop establishment costs by ploughing are 225 (year1), 231 (year2), 190 (year3)
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
slope (steeper slopes require more horsepower), state of the soil, climate, crop
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
800.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
85% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Contracting work forms greater part of income
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
126 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
- Other
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
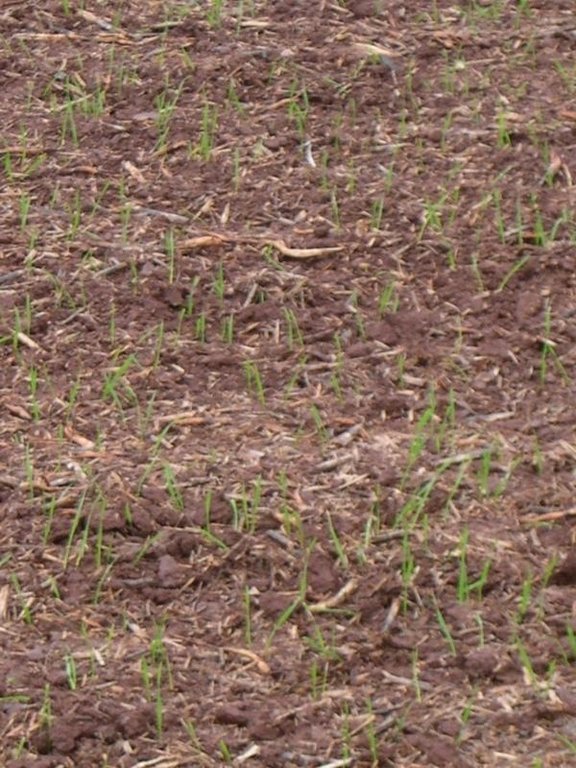
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In early years
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Timeliness of operations
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Operation twice as quick as ploughing
Economic viability
Input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Possible increasing herbicide costs
Hindered farm opperations
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
timing of operations critical
High machinery costs
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
High capital investment but low running costs
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
Preparation for new legislation
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
CAP reform, Soil Action Plan for England, EU Water Framework directive
Acceptance by society
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Age difference: Technology tends to be taken up by younger farmers
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0.01
หลังจาก SLM:
1
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Possibility
การอัดแน่นของดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More earthworms compared to land that has been ploughed
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Driven by economics
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Increased work rate making operations quicker |
| Better trafficability |
| Less at risk of weather |
| Earlier drilling. It is a systems approach - minimum tillage combined with early drilling and low seed rates |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Increased work rate How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better planning |
| Improved soil organic matter |
| (Possible) soil structure improvements |
| Improved soil ecology and other wildlife benefits |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Dependent on dry weather | Co-operation with other farmers or larger acreage |
| Machinery more complex and expensive | A combination of crop rotation, pesticides and stale seedbeds |
| Increasing grass weed populations | Does not necessarily mean spending money eg utilising old equipment on farm like subsoilers. However, need the right attitude |
| Need to be experimental | Accept advice for varying sources, talk to different people |
| Advice can be fragmented/ confusing |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Technological knowledge of farmer | Training and education, dissemination |
| Initial high capital investment | Extended finance |
| Possible increasing weed populations | More diverse management options - cultural and chemical |
| Need to expand acreage to cover capital costs | More diverse crop rotation but perhaps this is insufficient to retain economic viability |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SOWAP project
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
www.sowap.org
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
L and D farming
URL:
www.landdfarming.co.uk
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Vaderstad machinery
URL:
www.vaderstad.com
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Individual experimental farmer: Tivington [สหราชอาณาจักร]
Individual farmer experimenting with machinery to maintain economic viability and reduce time spent on land preparation.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล