Vegetation cover management on an organic, mixed livestock-crop farm [ฝรั่งเศส]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Alan Radbourne
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: David Robinson, David Norris, Sabine Reinsch
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
technologies_5680 - ฝรั่งเศส
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
co-compiler:
Joubioux Christiane
Chambre regionale d'agriculture de Bretane: Regional chambre of agriculture of Brittany
ฝรั่งเศส
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Le Callonnec Patrice
NA
ฝรั่งเศส
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Guiet Sylvie
Chambre regionale d'agriculture de Bretane: Regional chambre of agriculture of Brittany
ฝรั่งเศส
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmersชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - สหราชอาณาจักรชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Association des Chambres d’agriculture de l’Arc Atlantique (AC3A) - ฝรั่งเศส1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Use of different mixes of plant cover for livestock fodder which are simultaneously favourable for biodiversity by improving soil health, and reducing the need for agrochemicals.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
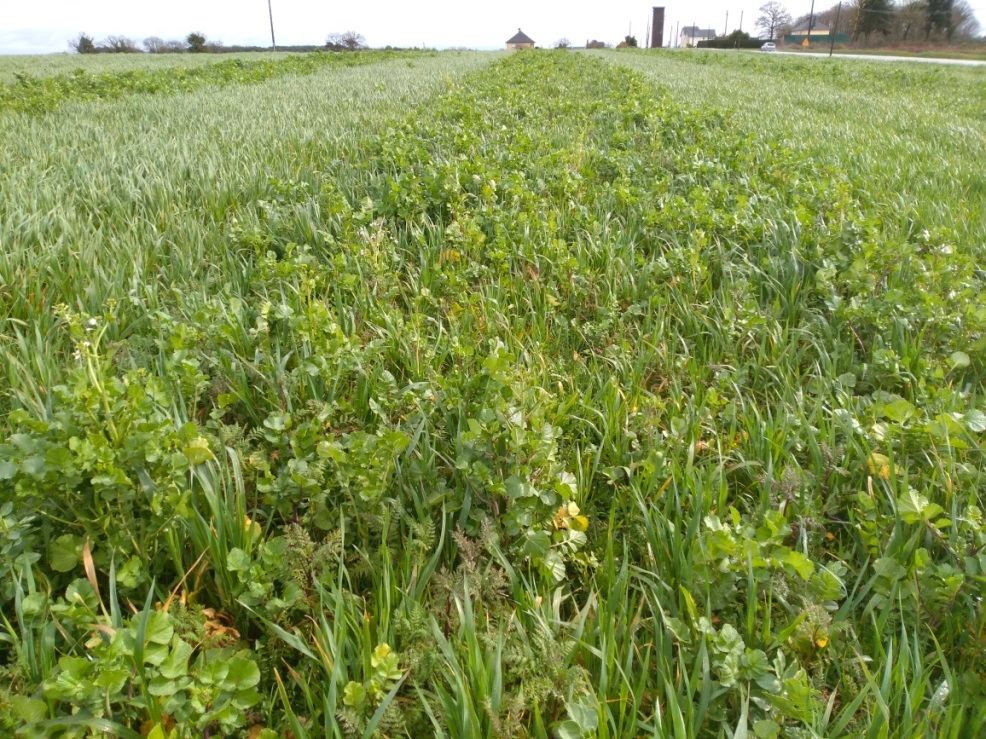
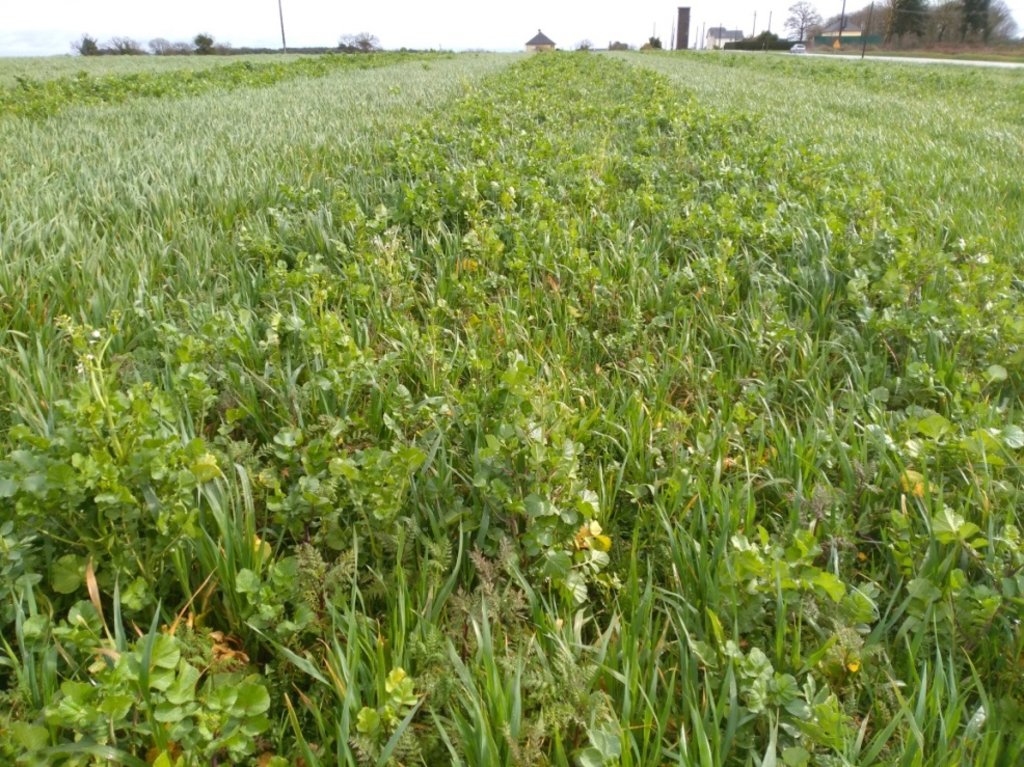
Agriculture in Brittany, in the north-west of France, is known for fish, beef, pork, poultry, vegetables and milk. Cover crops are used by farmers of Mauron, and the example described here is from a farm located in Morbihan in the basin known as Ploërmel. In this warm temperate area the average annual rainfall is 650-700 mm with an annual temperature of around 11°C.
There are three types of cover crops included in the rotation. These are selected on the basis of their benefits in relation to soil fertility and fodder production, in order to improve the farm's food self-sufficiency. There are three basic types of cover crops, as follows.
1) “Protein mixes” are composed of 35% faba (broad) beans, 26% oats, 17.5% peas, 17.5% vetch, and 4% clover. These are sown in early October after grass or maize are made into silage at the end of April.
2) "Green manure" cover crops are sown at the beginning of September after cereals, and are composed of various complementary species with the main objective of preserving and strengthening soil life (i.e. worm abundance), and winter feeding of heifers. For example, the commercial "Biomax" mix contains seeds of broad bean, vetch, clover, phacelia and radish. These cover crops are enriched by the presence of approximately 50% ryegrass regrowth, supporting the development of soil life.
3) Rapeseed is sown after cereals as a crop rotation feedstock and are made into silage.
Cover crops are either broadcast and rolled, or direct seeded depending on the conditions of the post-harvest plots. The seed drill used is equipped with discs to minimise soil disturbance as a reduced tillage technique, but more important in this respect is the presence of crop residues (i.e. straw). The seed drill is also equipped with tines.
The cover crops are grazed by heifers in a rotational 2-day paddock set-up. After grazing and regrowth of the ryegrass present, the fields may be left to develop into pasture, or seeded to crops using a minimum tillage drill.
The purposes are:
•Improved production
•Countered land degradation
•Protected watersheds
•Preserved biodiversity
•Adaptation to climate change/extreme events
The benefits are:
•Sustained ecosystem health: no pest and disease problems, good herd health
•Enrichment of the soil by the addition of carbon in organic matter and by the work of earthworms - favouring ecosystem functioning
•Protection of the soil and surface biodiversity because of maintained plant cover
•Increased weed control due to plant canopies and fertilisation effect of green manure
•Planted cover crops used as livestock feed during winter
The challenges are:
•Potential difficulties in establishing plant cover (especially in dry areas)
•Late sowing of cover crops reduces beneficial effects
•High costs of seed mixtures with high protein cover crops
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฝรั่งเศส
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Brittany
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mauron
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2019
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In order to make their production system evolve, farmers and their associates are eager for information. They do not hesitate to go and see what is happening elsewhere and to consult: training, visits, reading, internet, exchanges. The land user is a member of the BASE (Biodiversity Agriculture Soil and Environment) network and the Ecosystem association. Breeders do not hesitate to test new production practices on their farms.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- Cover crops
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rye
- fodder crops - clover
- fodder crops - grasses
- fodder crops - other
- legumes and pulses - beans
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
protein mix, a multi-species green manure, and a rapeseed mix
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Maize, grassland

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- poultry
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Dairy and poultry moved across crop for fodder and cross benefits of fertilisation.
Species:
cattle - dairy
Count:
115
Species:
poultry
Count:
4500
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
- broadcast sowing or direct sowing of species mixture in late August / early September or late September / early October
- protein mix: peas 40 kg / faba (broad) beans 80 kg / vetch 40 kg / clover 8 kg / oats 60 kg per hectare
- Biomax mix: radish 2 kg / clover 3 kg / faba (broad) bean 20 kg / phacelia 2 kg / vetch 10 kg per hectare
- Rapeseed mix: 8 to 10 kg per hectare
ผู้เขียน:
Revue agricole Terra
วันที่:
21/06/2013
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
€
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.9
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
Gross hourly minimum wage: €10.15 on 1 January 2020, i.e. €1,539.42 monthly on the basis of the legal working week of 35 hours.
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation and subsequent sowing of rapeseed/rapeseed after harvest cereals | End of August |
| 2. | Soil preparation and sowing of the Biomax mixture after harvest cereals | End of August |
| 3. | Soil preparation and sowing of meslin after grassland or corn on the cob | End of October |
| 4. | Rapeseed/rapeseed grazing and growing of green manure | December to March |
| 5. | Meslin silage | April |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Direct seeding (compil) | ha | 40.0 | 60.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Broadcast sowing | ha | 72.0 | 15.0 | 1080.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Roller spade before sowing (1 pass) | ha | 72.0 | 23.0 | 1656.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Maceration by a roller with blades | ha | 224.0 | 23.0 | 5152.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds - protein blend | ha | 60.0 | 394.0 | 23640.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds - forage rapeseed | ha | 17.0 | 28.0 | 476.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds - green manure "biomax" fertilizer | ha | 18.0 | 60.0 | 1080.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 35484.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 39426.67 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs for seeds refer to purchased seed, if farm-saved seed, the cost is reduced
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No maintenance costs just time to rotationally graze livestock and poultry
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No maintenance activities, future years would repeat establishment activities
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Direct sowing equipment, destruction with 2 passes of rolling spade, cost of purchasing "biomax" mixture
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
675.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The farm is located on the commune of Mauron in Morbihan and is in an early agro-climatic zone. The average annual rainfall of 650-700 mm is the lowest in Morbihan. The average annual temperature of around 11°C and is also the lowest in Morbihan.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Ploermel
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
The climate of Mauron is warm and temperate. It is in the basin known as Ploërmel, the most continental of Morbihan with colder winters, hotter summers and rainfall of around 650-700 mm/year. Heavy showers fall all year round in the area of Mauron. Even in the driest months, rainfall remains fairly heavy.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The minimum and maximum altitudes in Mauron are 47 m and 130 m respectively.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
The farm is located in the commune of Mauron in Morbihan and is in the geological zone of the Briovician shales.
It contains :
UCS n°4034 Brown soils gradually leached from the plains and plateaus from locally soft schist sandstone.
UCS n°4022 Shallow, sometimes podzolic soils of locally sandstone mounds and brown leached soils of open plains, derived from soft schist.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The farm has been involved in organic farming since 1964 when Claudine's father settled on a 45-hectare dairy farm. The regrouping was carried out in 1968.
As the associates' facilities have been installed, the size of the farm has increased to reach a useful agricultural area of 220 hectares in 2020.
The farm has 3 main operating areas:
- dairy cattle with about 115 dairy cows (average of 7 to 8000 litres/year),
- poultry with 4500 laying hens, and a
- production of cash crops.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- provisioning
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
lease
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Better diversity of fodder available is producing healthier and better quality animals
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sward mix in cover crop is very diverse
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water related loss impacts
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved crop and animal production
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Greater workload to rotationally graze and manage crop effectively in an organic system (i.e. can't rely on spraying to solve problems). Yet, benefits outweigh extra workload.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vastly improved understanding through SLM expert advice and practical learning from doing SLM technology.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced tillage techniques and less passes across fields with machinery as no spraying due to organic system reduces compaction.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Selected species of cover crops help recharge nutrient availability in the soil
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crop rooting system & waste inversion as green manure increases the soil organic matter below ground.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Greater crop cover and thus more biomass above ground
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Well designed mixed cover crop seed mixes, although more expensive, provide a specialised plant diversity ideal for the farm system requirements.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
A diverse vegetation supports greater habitat diversity
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface run off and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows in storm events
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing drought impacts
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ | |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
Livestock feeding, economic interest, societal expectations
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Species are selected according to their ability to cover, feed and work the soil. To do this, species are chosen for their diversity and complementary according to their root system: tap roots, adventitious roots, surface lateral roots, etc.
For the past 2 years, the Biomax green manure + RGA regrowth mix has been grazed by heifers.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Sustain ecosystem health: no pest and disease problems, good herd health. |
| Carbon sequestration by enrichment of the soil with organic matter and by the work of earthworms favouring ecosystem functioning. |
| Protection of the soil and surface biodiversity because of maintained plant cover. |
| Increased weed control due to plant canopies and fertilisation effect of green manure. |
| Planted cover crops used as livestock feed during winter. |
| Sustained ecosystem integrity reduces/counters ecosystem degradation by using multiple ecosystem functions: Complementarity, Continuity of soil life, Green fertilizer essential in the farming system, Feeding the livestock. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Multi-species cover is conducive to soil quality: production of a high above-ground and root biomass that promotes soil life, soil structuring at depth (tap roots) and on the surface (superficial roots) by the effect of organic matter inputs. |
| Multi-species cover provides shelter and cover for small fauna: seeds for the winter survival of the fauna, plants that are tiered at different heights without being too dense for wild game to move around while being protected. |
|
The different families that can be planted under cover are: - Grasses are generally easy to grow and are valued by animals (oats, rye and sorghum). - Leguminous plants improve the performance of cover crops. They are regulating plants that trap nitrogen and fix it in the soil. This is then used by the crop that follows. - Cruciferous plants are to be reserved for cereal rotations without rapeseed or vegetables. - Compounds (nyger and sunflower) are interesting for biomass production. |
|
Well-developed canopies have a competitive effect against weeds (germination inhibition, smothering, allelopathy). The aim is to have a rapidly developing canopy. It is necessary to limit the risks of shot blasting by sowing the canopy on clean soil, especially for early sowing (especially for short-cycle weeds: ragwort, bluegrass, Persian speedwell). Some species have allelopathic effects, i.e. they secrete inhibiting substances (the intensity of the allelopathic effect is taken from the Sem-Partners catalogue, see bibliography): - Diploid oats: allelopathic effect not demonstrated. Little is known about the mechanisms and molecules involved. - Spring Oats, Fenugreek, Gesse, Moha : average allelopathic effect, mechanisms and molecules involved are not well known. - Camelina, Radish: strong allelopathic effect (glucosinolates). - Winter mustard, Spring mustard: action of glucosinolates against nematodes (Heterodera Schaati and Meloidogyne chitwoodi) in biofumigation. - Buckwheat (Sarrazin): strong allelopathic effect. Little is known about the mechanisms and molecules involved. |
| A plant cover provides additional fodder, 3 to 4 tonnes of dry matter can be produced depending on the species and sowing date. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Difficulties in establishing cover: difficult lifting in dry areas |
Conditions for successful plant cover Sow as soon as possible Take advantage of the humidity just after harvest |
| Late sowing of cover crops: no or little flowering and therefore little beneficial effect | Early establishment of complementary species |
| High cost of purchased seed of mixed protein cover crops | Self-production of farm-saved seed |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| In order to increase the potential of the canopies for bees, it is necessary to sow in the first half of August for flowering in the autumn. Some species are rich in nectar or pollen: rapeseed, white mustard, phacelia, radish, sunflower, clover, vetch. However, some species have extra-floral nectar such as sunflower, vetch and faba beans. That is to say that they secrete nectar outside the flowering period. | Sow in the first half of August as soon as the cereals are harvested to take advantage of the residual moisture which is conducive to good emergence. |
| The development of RGA on the farm. | Ploughing can slow down the development of RGA. |
| The cost of destroying the canopy is high (45€/ha excluding labour) with the 2 cross passes of rolling spade. |
3) Cost of some tools for destroying the cover crops: Independent disc stubble cultivator 3m= 33€/ha Cultivator 3.5m = 20€/ha Mulcher 3m = 27 €/ha Cambridge roller 8m = 16€/ha Blade roller 3m = 17€/ha Assumptions: replacement value depreciated over 10 years + maintenance, tractor cost 20€/hour, labour not included |
| Before grazing a multi-species canopy, it is advisable to check the absence of toxic species (e.g. buckwheat) | Not known |
| The doses and costs of implementing protein blend cutlery in interculture are high. |
- Adjusting Mixed Doses - Self-production of farm-saved seeds - Mixture with recommended doses (OBS: Do not exceed 120% pure dose) |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
GAEC Bio-yvel
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Performed by Patrice Le Callonnec
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Chargés d’études élevage et machinisme CRA Bretagne
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Couvert végétal, une culture à part entière, Terra du 21 juin 2013
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Terra (Réussir terragricoles de Bretagne) du 21 juin 2013
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Couvert végétal, de réels avantages agronomiques, Terra 12 juin 2015
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Terra 12 juin 2015
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Couverts végétaux, la destruction possible dès le 1er février, Terra du 15 janvier 2016
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Terra du 15 janvier 2016
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Liste de plantes attractives pour les abeilles, Ministères de l’agriculture et de l’alimentation, 2017
URL:
https://agriculture.gouv.fr/decouvrez-la-liste-des-plantes-attractives-pour-les-abeilles
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Implanter des cultures intermédiaires à effet allélopathique ou biocide, biofumigation
URL:
https://geco.ecophytopic.fr/geco/Concept/Implanter_Des_Cultures_Intermediaires_A_Effet_Allelopathique_Ou_Biocide,_Biofumigation
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล