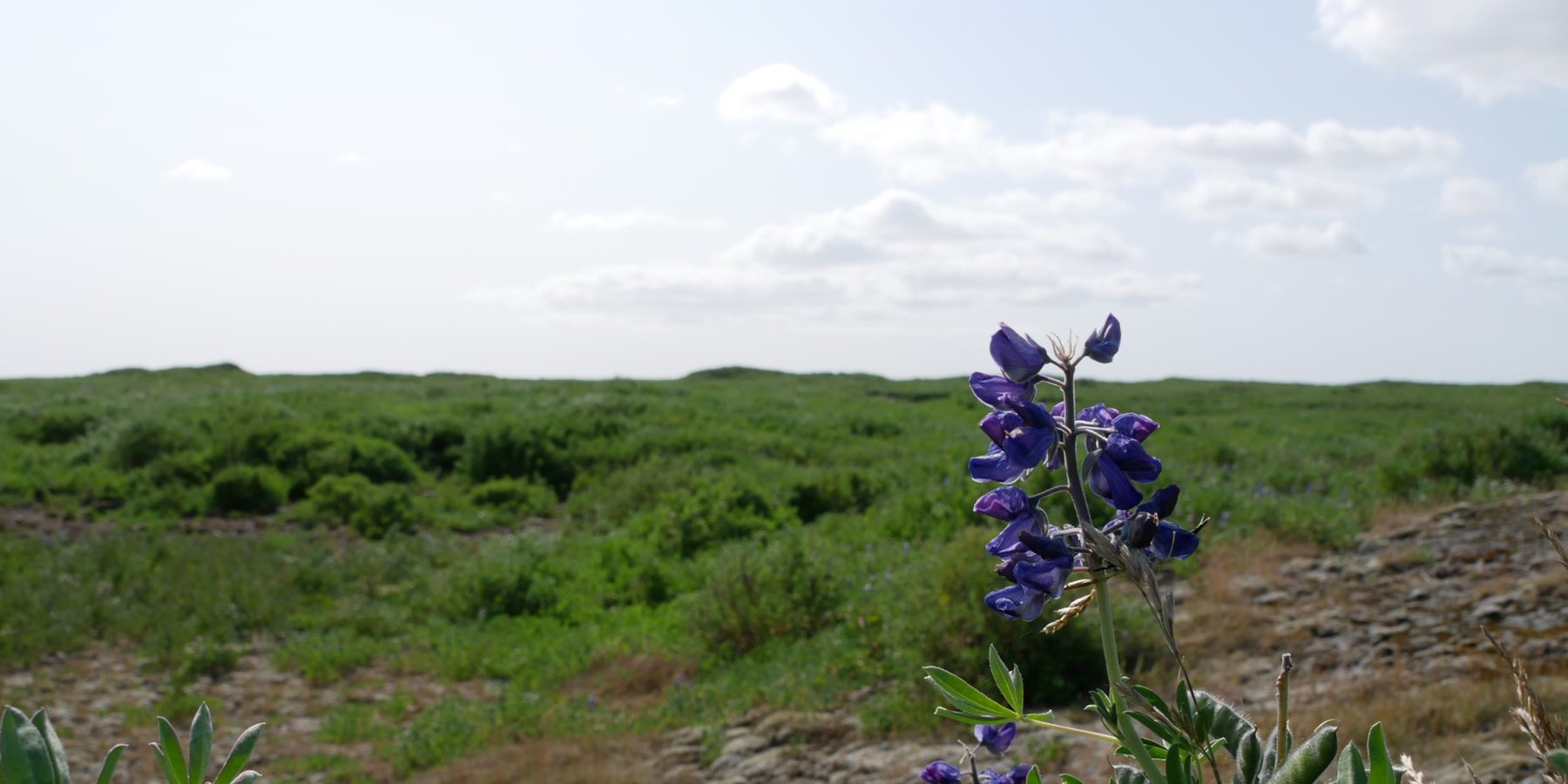
Seeding lupine for land reclamation and to protect the soil against wind erosion [ไอซ์แลนด์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jan Reichert
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Hanspeter Liniger
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Hanspeter Liniger
Nootka lupine or Alaska lupine
technologies_5750 - ไอซ์แลนด์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Runólfsson Sveinn
Soil Conservation Service of Iceland
ไอซ์แลนด์
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The nootka lupine is sown in sandy and gravelly areas to increase the vegetation cover and fertilize the soil.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
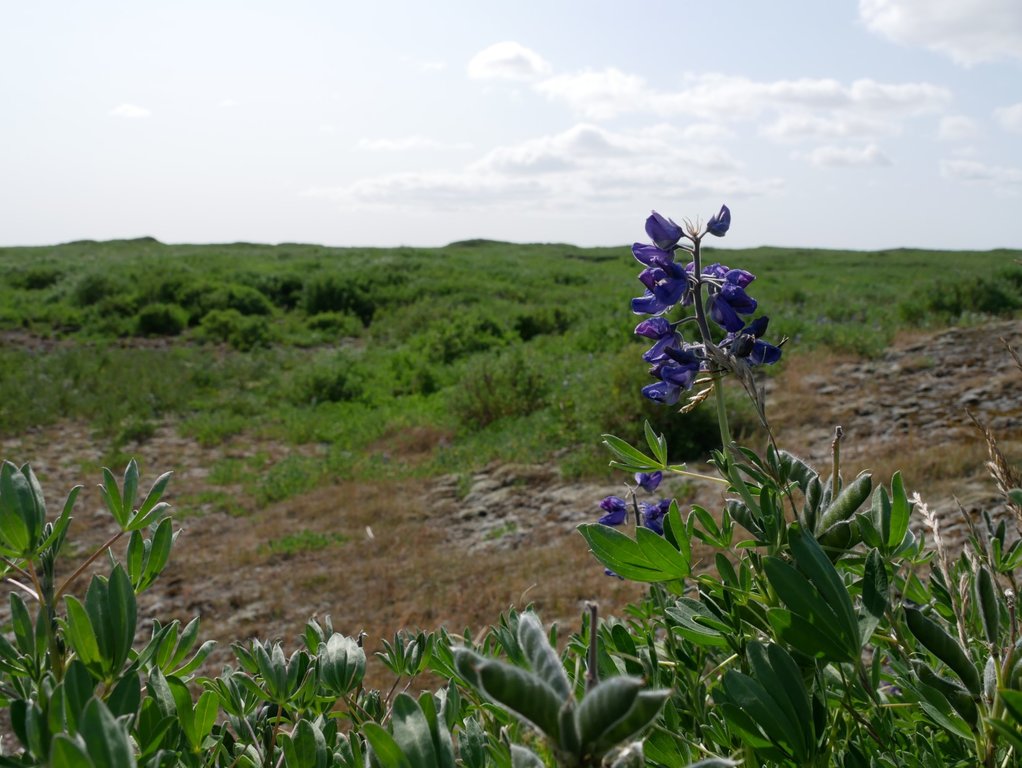
The nootka lupine (Lupinus nootkatensis) is a legume that can survive in the harsh climate of Iceland. It was introduced from Alaska to increase soil cover and fertilize the sandy and gravelly soil. For that purpose, it has been widely used from 1990 onwards in degraded areas all over Iceland. Because of its large amount of seed production, the plant is able to reproduce rapidly and spread. The ability of the lupine to fix nitrogen through its root system reduces the need for fertilizer - especially when planting trees. Increased vegetation cover due to the lupine plants minimizes vulnerability to wind erosion. The ground is protected and sandstorms can be reduced. This also protects neighbouring fields, and public and private infrastructure from sand and dust storms.
The lupine is seeded with machinery in spring or very late autumn. It is planted in strips – rather than all over the ground - because the plant readily spreads and colonise. Before planting, lupine seed have to be inoculated with rhizobium bacteria. These bacteria help the plant to fix nitrogen: without this inoculation the plant wouldn’t survive in the bare soil. These bacteria are produced during winter time in a laboratory. The lupine needs no fertilizer after planting. Planting of lupine is an extremely cost-efficient and effective way of increasing soil cover and soil fertility. It is a one-off operation: no further action needs to be carried out afterwards.
However, the nootka lupin is very controversial in Iceland despite its apparent advantages both on and offsite. The use of lupines should be carefully considered, especially in sensitive and protected areas. The reason is that this non-native plant is very invasive and leads to the displacement of the native vegetation. Grazing does not stop lupines spreading: only young plants are eaten by sheep, but once mature, its bitterness renders it unpalatable. On a small-scale, it is possible - with great effort - to slow down the spread by cutting the flowers. On a large-scale, the spread can only be stopped with herbicides which is highly controversial. From the land user’s view, the planting of lupine reduces the aesthetic value of the landscape because of monoculture: diversity is lost. That is why people try to plant trees in such fields. Because of the controversy surrounding the plant, the technology has been little adopted by farmers and due to its invasiveness, the Soil Conservation Service stopped using the lupine in 2018.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไอซ์แลนด์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
South of Iceland
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Thorlákshöfn, Hekla area
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
Animal type:
- horses
- sheep
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- whool

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
eroded land, degraded land
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Lupine is to bitter for sheep. That's why the land can't be grazed.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Can be combined with birch tree planting.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม
- Eo (Offsite degradation effect): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
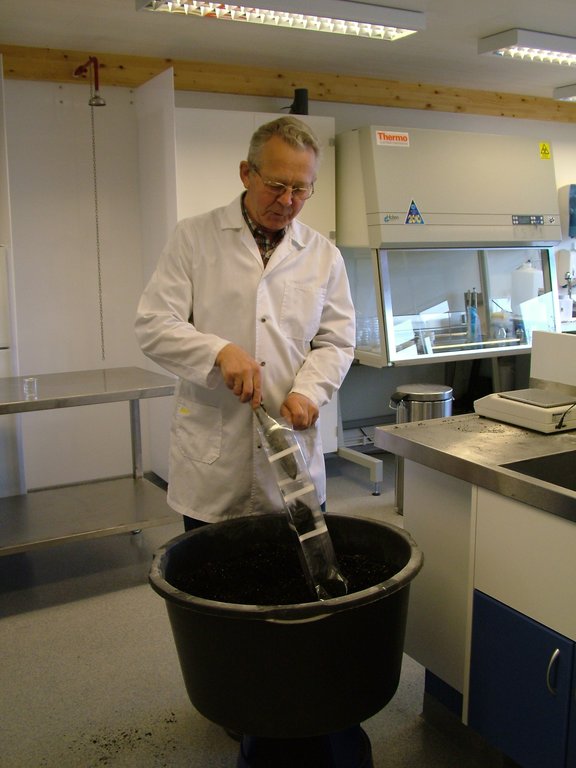
Lupine seeds are being inoculated with rhizobium bacteria prior to seeding. These bacteria help the plant to fix nitrogen. Without this inoculation the Lupine wouldn’t survive in the soil.
The seeds are seeded in by machinery in stripes because the plant spreads fast itself. No fertilizer is needed. Normally 5 kg of lupine seeds per ha is used.
ผู้เขียน:
Sveinn Runólfsson
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
Project costs in Thorlákshöfn
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
ISK
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
138.0
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | production of bakteria in labratory at Gunnarsholt | winter |
| 2. | inoculat the seeds before seeding | spring time and very late autumn |
| 3. | seeding lupine | spring time and very late autumn |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อื่น ๆ | Seeding lupine (total costs) | ha | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 30000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 217.39 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is no recurring activity.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is no recurring activity.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
workers, seeds, machinery
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less dust in the air during windstorms due to increased ground cover and therefore fewer health consequences.
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to its invasiveness and its enormously dense growth, other native plants are displaced by the lupine.
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to its invasiveness and its enormously dense growth, other native plants are displaced by the lupine.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ปานกลาง |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The lupine has been infested by a larvae in recent years. However, its population has collapsed and thus shrunk considerably.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
stopp further seeding
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Due to its invasiveness in Iceland, the Soil Conservation Service of Iceland stopped using the lupine in 2018.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The use of lupines is a very cost-effective application, which protects the soil well against wind erosion. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The use of lupines is a very cost-effective application, which protects the soil well against wind erosion. |
| Less artificial fertiliser has to be used because the lupine fertilizes the soil. |
| Sowing the lupine is a unique application. No further operations need to be carried out after that. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lupine is very invasive and displaces native plants. | The use of lupines should be carefully considered. On a small scale, it is possible with great effort to slow down the spread by cutting the flowers. On a large scale, the only possibility to stop the spreading would be the use of herbicides. |
| The aesthetic value of the landscape is reduced by the monoculture of lupines. | By planting trees in the lupines the aesthetic value can be increased. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The non-native plant is very invasive and produces large quantities of seeds why it is spreading rapidly. This leads to the displacement of the native vegetation. This can become a significant problem in protected areas (national parks). | The use of lupines should be carefully considered, especially in sensitive and protected areas. On a small scale, it is possible with great effort to slow down the spread by cutting the flowers. On a large scale, the only possibility to stop the spreading would be the use of herbicides. |
| The lupine is very invasive and spreads very quickly. | The SCS has stopped planting lupine since 2018. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/08/2019
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Webpage Soil Conservation Service of Iceland
URL:
https://land.is/english/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล