Cover crops [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Noel Templer
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Yeshifan Sebil (in Amharic)
technologies_6628 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Falaha Fanaye
Farmer
เอธิโอเปีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
With good management, a legume known as desmodium is a very good cover crop that can be integrated into perennial and annual crops. It improves soil fertility, repels insects and caters feed to the livestock.
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
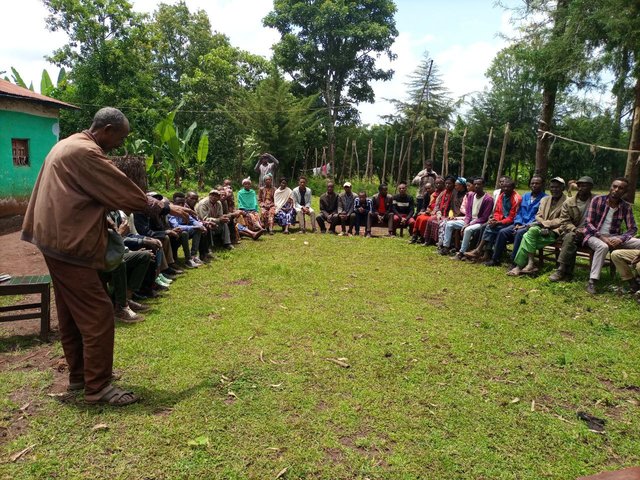

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [เอธิโอเปีย]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Cover crops are crops grown on bare, fallow farmland or under a main crop to cover and conserve the soil by protecting it from exposure to the sun, wind, and direct impact of rain. It fixes nitrogen (if a legume), improves soil fertility, supplies livestock fodder, and helps manage both pests and weeds.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
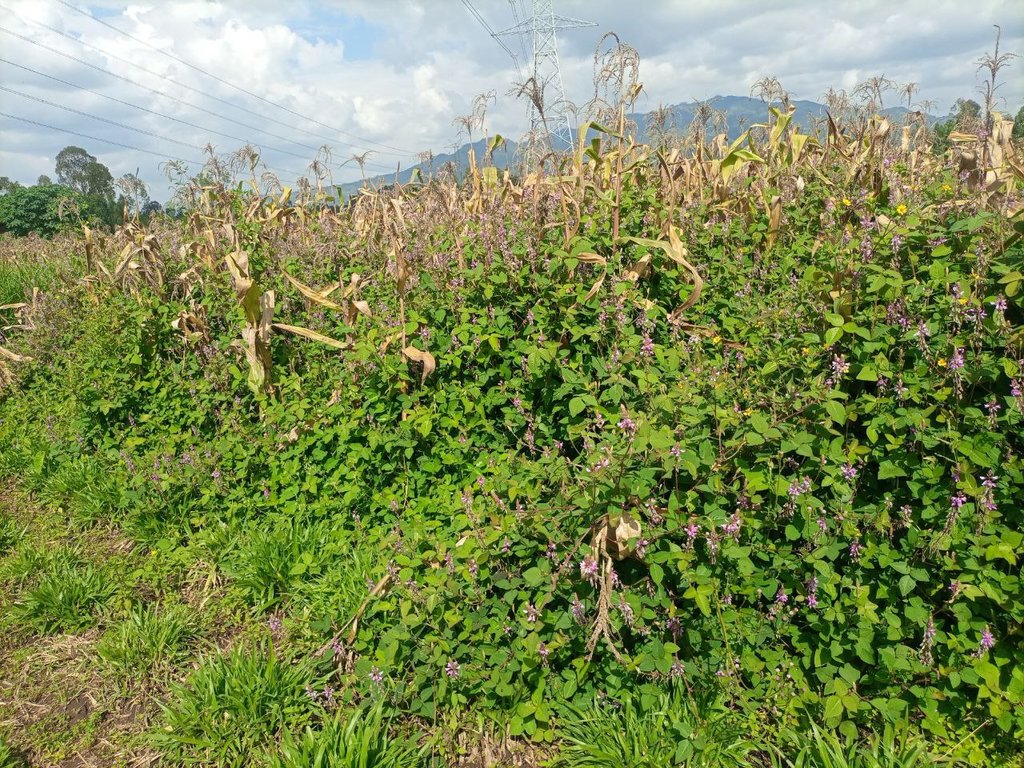
Cover crops are planted to conserve the soil on bare, fallow farmland or under a main crop. They can be grown on their own or between rows of annual and perennial crops such as maize, coffee, and fruits. The main purposes of growing cover crops are to cover the soil with low-growing vegetation, protect the soil from exposure to sun and rain, suppress weeds, improve soil fertility, supply livestock feed, and manage insect pests. Cover crops may be nitrogen fixing (if legumes), and they make productive use of spaces between crop rows, as well as controlling wind and water erosion. They also have the potential to restore soil fertility and help in climate change adaptation, as well as sequestration of atmospheric carbon above and below soil surface. Furthermore, cover crops can be fed to livestock, helping to bridge periods of shortage of feed when grazing lands are not available – which is an increasing problem because of growing population pressure and expansion of croplands. Land users give huge credit for its role as a pesticide by deterring armyworm and stalk borer when used as a border, and stopping their advance into the maize crop.
Desmodium is an example of a leguminous cover crop, improving soil fertility via fixing atmospheric nitrogen, increasing infiltration and productive use of soil moisture, and catering for livestock via a “cut-and-carry” fodder system. Desmodium is planted between rows of maize crops as well as between grass hedgerows around the farm. For its establishment, access to desmodium seed is essential. Once established, it remains to serve as a permanent source of planting material. Nevertheless, there are some disadvantages of desmodium: seed collection is difficult, it may trap honey bees and it can compete with the crop for light and space if allowed to grow too tall. Thus, efficient management of desmodium is essential. Nevertheless, as part of an agro-ecological intervention, cover crops like desmodium deliver multiple benefits to resource-poor farmers and can be viewed as an investment in improving soil fertility as well as soil health. Overall, cover crops improve productivity, and help ensure yield stability and contribute to a healthier ecosystem.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
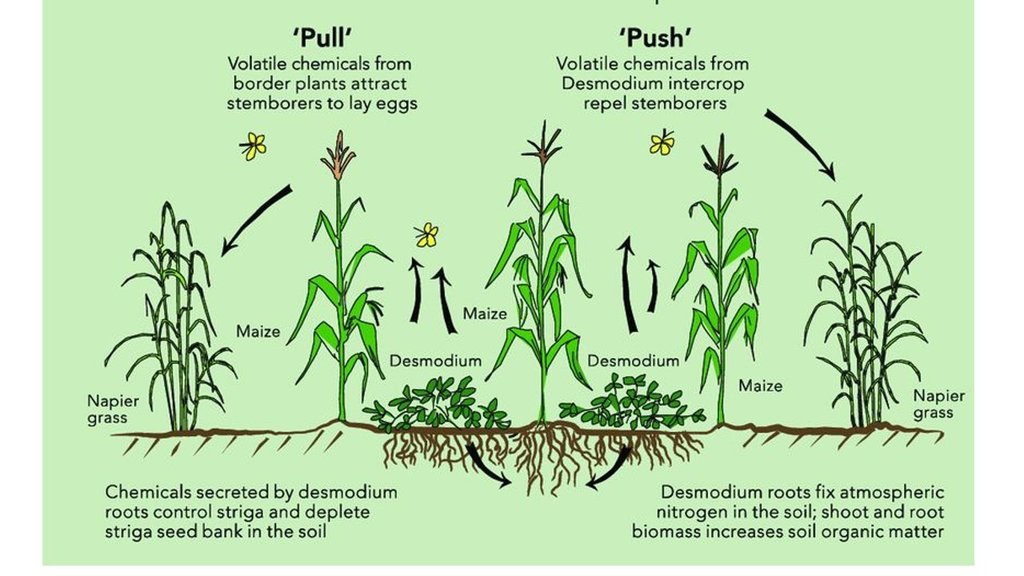
The photo portrays the location where desmodium and other grass species mutually play distinct but complementary push-pull roles of attracting and repelling insect pests from infesting the main crop past the visible hedgerows.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Videos of this technology is not taken.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
SNNPR
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kuto Sorfela kebele, Sodo Zuria
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user is a member of the the ISFM+ implementing farmers group and recently evolved to the Agro ecology since the kebele is an agroecology site.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2022
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The cover cropping practice has introduced via ISFM+ farmers group.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- Desmodium
Annual cropping system:
Maize/sorghum/millet intercropped with legume
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Belg (short rain) when maize is planted and Meher (long rain) when other crops are planted.
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Desmodium/haricot beans is intercropped with maize.
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Cereal crops such as maize/tef is rotated with root crops such as sweet potatoes/taro or the legume crops such as haricot beans.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Desmodium and the grass (Brachiaria species) serving as push-pull technology to the pest. Adopted from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/desmodium-legume-cover-crop-solution-food-insecurity-africa-ndiritu/. In this particular case, Brachiaria play the "pull" function on the periphery of the maize farm.
ผู้เขียน:
Africa Sustainable Agriculture Biweekly Newsletter, ICIPE Push Pull Project
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
Timad = 0.25 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 4 Timad
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
ETB
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
53.6283
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
250
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
We believed to address only the maintenance costs of desmodium as it demands only seeds, skills, and knowledge as compared to the other SLM technologies.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
We jumped to the following session as maintenance cost is rather decisive for the cover crops.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation and planting | Before and at planting |
| 2. | Cutting desmodium to use as feed for cattle | During the growing season |
| 3. | Harvesting desmodium biomass and /or seed | At harvest maturity |
| 4. | Access to planting materials, if newly started | Anytime in the offseason |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land preparation | PDs | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Cutting for use as feed | PDs | 8.0 | 250.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Harvesting total biomass and /or seed | PDs | 5.0 | 250.0 | 1250.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Desmodium seed | kg | 3.0 | 120.0 | 360.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 5610.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 104.61 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Agroecology/ Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Prices of agricultural inputs are frequently changing in Ethiopia.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The prevailing economic crisis and rising of inflation in the country contributes to inputs and other services price uncertainty.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall distribution is uniform except in El Nino cases or recurrent drought experienced in the country and the region.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The visited farmland lay on gentle slope and less vulnerable to the effects of erosion.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Not available.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Seldom, when heavy rainfall is intercepted, there is a flood event.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The farming system in the area features the best agroecology practices with diverse agrobiodiversity. The type of crops grown in the area ranges from root crops (such as sweet potato, cassava, and yam), cereals (teff and maize), to perennial crops: coffee, fruits and enset.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
In addition to crop production, the land user engaged in off-farm activities such as making local liquor to support her family's livelihoods. Furthermore, the land user adopted diverse ISFM technologies such as biogas/bio slurry and vermicomposting.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As compared to the local people, the adoption and implementation of diverse agricultural activities and the size of the farm put the land user on a relatively larger scale.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
The farmland was inherited from the predecessors.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Parts of the land used by the user are leased in from the other land owners.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user accessed electricity in rural areas. She also used biogas for energy production.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase with proper management of the companion crops on a gradual basis.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Simultaneously increase with good harvest per unit of land as the integration allows to combat against pests.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Desmodium gives high biomass production. So it supplies more fodder if timely trimmed and supplied to the livestock.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Believed to increase with the application of appropriate management practices.
การผลิตสัตว์
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Desmodium fixes atmospheric nitrogen that improves the fertility of the soil in addition to the production of large biomass that supplies organic matter to the soil.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Slightly decrease as desmodium fix atmospheric nitrogen in the long run and partly complements urea fertilizer.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It demands follow-up and frequently monitors and manages the growth of desmodium to reduce its competition with the main crops.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As it creates evidence-based learning, it improves land user's SLM knowledge.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
High biomass production and the ground covering traits of desmodium assist to slow down surface runoff and promote infiltration deep into the soil.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the companion crop fixes atmospheric nitrogen, it improves nutrient cycling.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Land users suggested the pesticidal role of desmodium as compared to the hidden contribution to the improvement of soil fertility through its natural traits of fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It increases biomass production that absorbs carbon above and below the surface of the soil.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Contributes to groundwater recharge by reducing surface runoff.
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Facts are not available to complement this allegation since the implementation is on smaller areas of farmland.
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It breaks the speed of flood that overflow and damage neighboring areas.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูแล้ง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ขยายออกไป | ดีมาก |
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The benefit from desmodium can be made in the short term. Its high biomass production to enrich grass fodder and suppression of weeds and pests are promptly seen as compared to some other SLM technologies.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology improves soil fertility. |
| It manages insect pests and stops their advance and negative consequence they might causes on the main crops. |
| Supply protein-rich feed to the animals. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Cover crops provide multiple benefits to the family farmers such as the best uses of land between the rows of maize crops. |
| It smothers weeds and improves soil fertility and crop productivity which have a positive contribution to the livelihoods of family farmers. |
| Cover crops and the practice itself have a beneficial role in agroecology intervention and improvement of the ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Fast growing and overwhelming the main crops (competition for space). | Applying intensive management such as cutting and feeding to the animals. |
| Feeding the animals with fresh harvest is not friendly to the livestock. | As it is a protein-rich fodder crop the harvest must be slightly dry and mixed with grass fodder that reduces the adverse effects of either bloating or diarrhea. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to manage and harvesting desmodium seeds. |
1. Intensify the management of desmodium and reduce harvesting inconvenience on main crop. 2. Replace desmodium with other farmer's friendly legume species such as Dolichos lablab...as cover crops. |
| Hooky nature of the seed that sticks to the clothes. |
-Wear nylon wears/clothes that reduces the effects of hooky seeds. - Produce seeds on separate plots. |
| Quick growth and climbing traits that dominate the main crops. | - Apply intensive management and use the above-ground parts as fodder for the livestock by adopting cut-and-carry feeding system. Also, needs to keep the green parts under frequent management practices. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
4 people
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
1
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
3
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Cover Crops for Sustainable Crop Rotations. Clark, Andy. 2015
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.sare.org/resources/cover-crops/
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Greenleaf desmodium. A Fact sheet index describing about the cover crop
URL:
https://keys.lucidcentral.org/keys/v3/pastures/Html/Greenleaf_desmodium.htm
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is wide. Also, it requires many data sources including the sketching of the technical application of the technology, video graphic description, etc., which seems ambitious to be addressed by an expert.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [เอธิโอเปีย]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล