Water Source Protection [ภูฏาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: ONGPO LEPCHA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Haka Drukpa
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Chhu Ka Soongchop (ཆུ་བརྐ་སྲུང་སྐྱོབ།)
technologies_6842 - ภูฏาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Dorji Sangay
Yakpugang Community
ภูฏาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - ภูฏาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
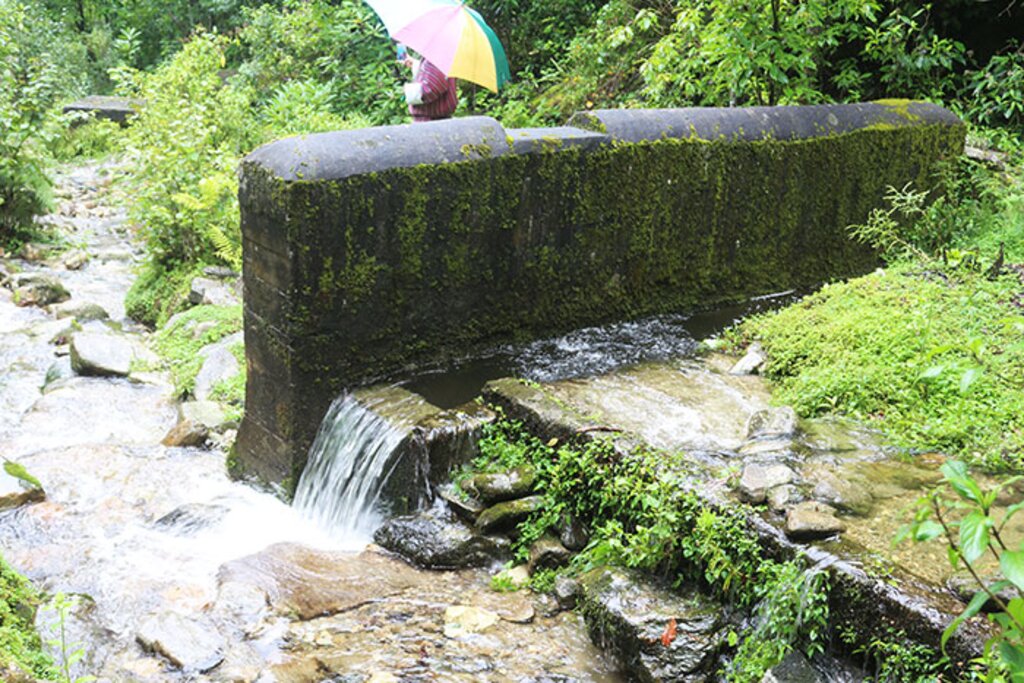
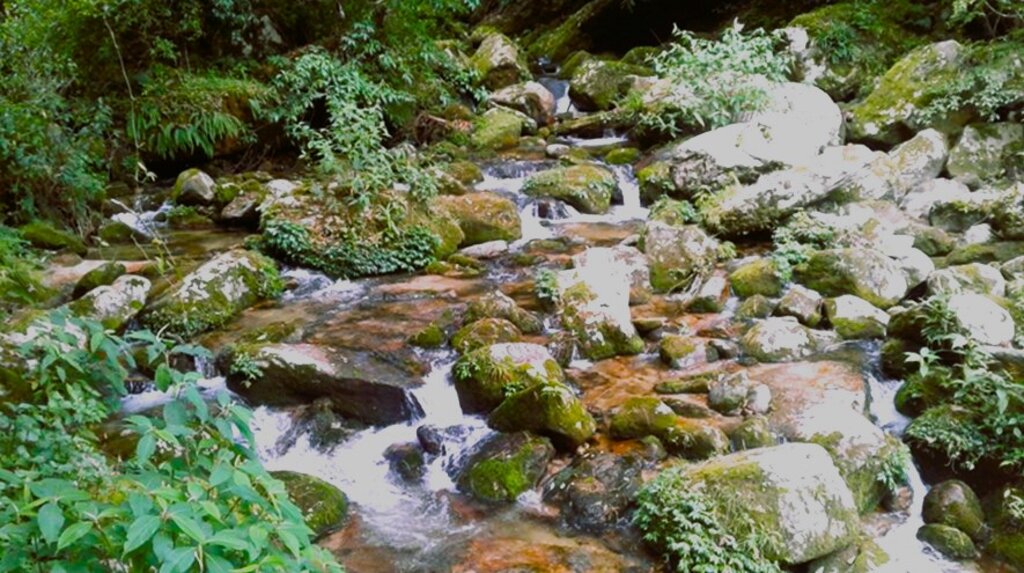
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs, or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past, the emphasis was on fencing and improving vegetation cover at the discharge point itself, but a recent focus is on groundwater recharge areas.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past this included fencing and enhancing vegetation cover at the discharge point – that is, where the water starts flowing. However, today, water source protection also focuses on improving groundwater recharge areas. The water source protection technology has many benefits. In addition to providing a clean and regular supply of drinking and irrigation water, it also enhances the vegetation cover of the catchment area.
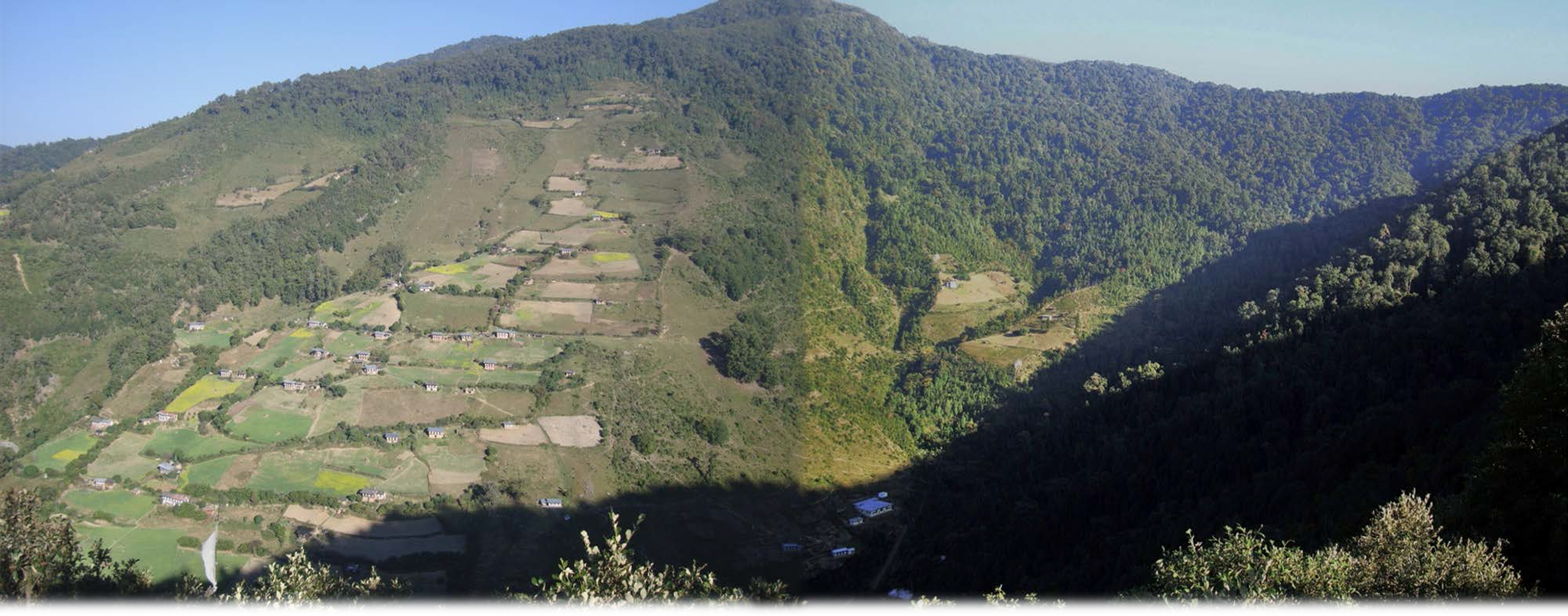
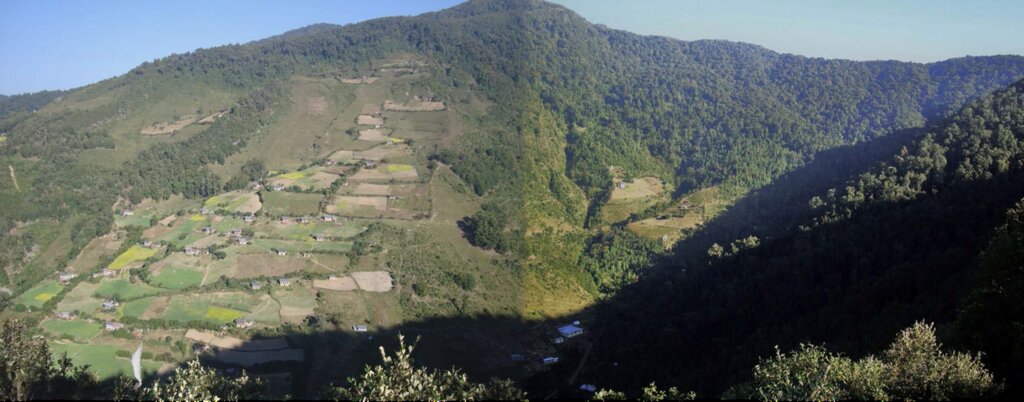
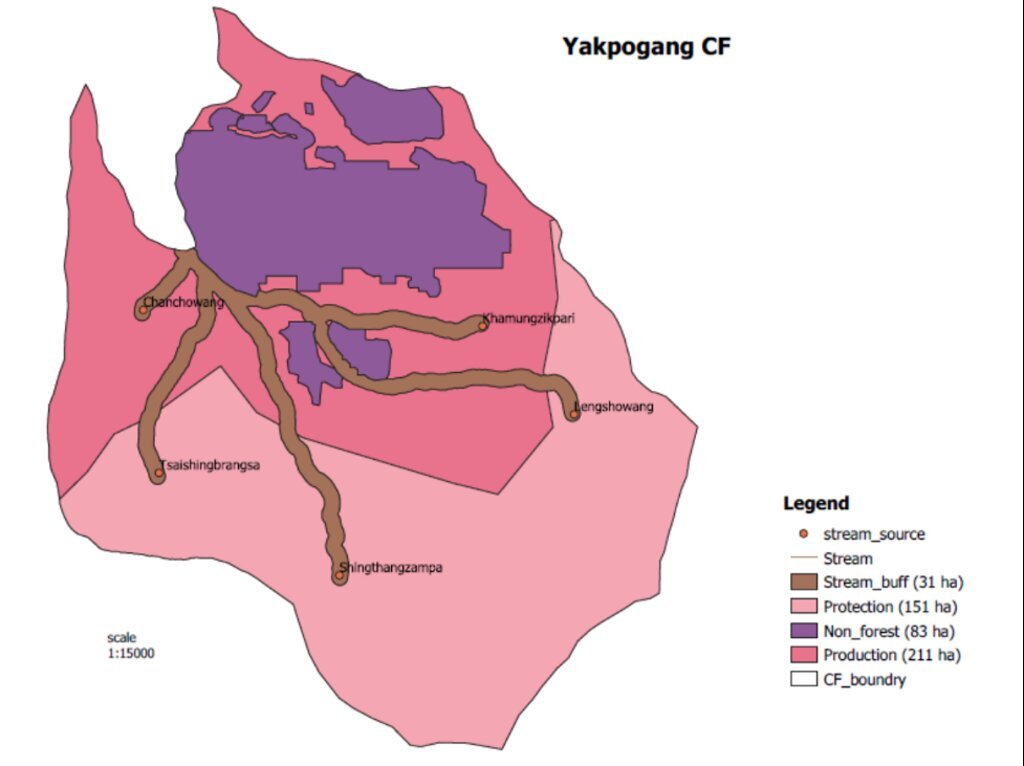
Strategies target maintaining adequate water levels in underground water reservoirs to ensure a continuous flow of streams and springs. In Yakpugang Community Forest, the technology has been applied specifically in the southern mountainous part of the village. An area of 638 acres (255 hectares) has been established as the recharge zone, and three springs have been identified for source protection. Native tree species have been planted annually in the degraded watershed to improve forest conditions. The main purpose is to protect the quality and quantity of the water for both drinking and irrigation purposes. The technology is supported by an approach that involves collective efforts of the community who realize that if their drinking and irrigation water supply is to be sustainable, they must work together.
The main purpose is to ensure a continuous supply of water for drinking and irrigation to the community. This is achieved through managing the catchment areas where rainwater soaks through the ground to reach a groundwater reservoir, and one of the key interventions is protecting the water sources from wild animals and livestock.
The water source protection technology involves 1) meeting different stakeholders, 2) signing agreements between the stakeholders, 3) site selection and survey, 4) planting of native tree species, and 5) conducting annual monitoring and evaluation. Inputs like fencing materials, planting materials, and human resources are required for the implementation and maintenance of the technology.
The technology is liked because it helps provide a continuous supply of both clean drinking and irrigation water. Furthermore, protecting water sources by the community is rewarded in monetary form by the nearby town as part of the Payment for Environmental Services (PES). This incentive helps the community to generate income which is ploughed back into the improvement and maintenance of water sources. What is disliked is the reduction in grazing land since the land users are not allowed to graze their cattle inside the water source areas.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ภูฏาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Mongar Dzongkhag (District)
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Yakpugang village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2007
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The project was conducted with technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and and funded through Blue Moon Funding with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services. Later Mongar Regional Referral Hospital was also involved as one of the major water users.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- vegetables - root vegetables (carrots, onions, beet, other)
- Chillies
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
- stone fruits (peach, apricot, cherry, plum, etc)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Vegetables are cultivated in one growing season, however, fruit trees are perennial.
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
The cole crops are rotated with root vegetables and legumes.

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- ทางระบายน้ำ ทางน้ำ
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Irrigation channels for farming and drinking water pipes
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The community was benefited greatly from the technology, and thus farming is mostly irrigated and rainfed is done, when rain falls in the area.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
GIS map of the recharge zone of the Yakpugang spings
Yakpugang village, Mongar Gewog (Block), Mongar Dzongkhag (District), Bhutan
ผู้เขียน:
Ugyen Norten
วันที่:
07/10/2023
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Recharge zone of 638 acres (255 hectares)
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
638 acres (255 hectares)
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
82.08
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1000
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community meeting | Conducted several times |
| 2. | Survey of the recharge zone and site selection | The survey took around 2 to 3 weeks |
| 3. | Agreement between the stakeholders | Agreement done thrice |
| 4. | Native tree species plantation around the watershed | Based on a specified date and each individuals from household came |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The establishment activities were done with the technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and the Department of Forests and Park Services since the water source falls under the community forest.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
258500.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The project was funded through Blue Moon in collaboration with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services and Global Environment Facility (GEF) was also involved.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of the water source | Thrice annually |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Community Forest members | person/day. | 102.0 |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Since the water source is a community asset, an individual from each household goes to the water source area for annual maintenance. This happens three times a year, and no cost goes into it except labour contribution from each household during which they bring their own tools and food.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
None.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The data was used from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Warm temperate zone
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
surface water
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Water quantity and quality have been greatly improved with the intervention of water source protection. These three water sources provide drinking water to Mongar town and Mongar hospital.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total land is 1.5 acres and total cultivated and is 1 acre
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the Land Act and Land Rules and Regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
15 baskets of maize
หลังจาก SLM:
20 to 25 baskets maize
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There has been an increase in the amount of maize, which has been credited to the increase in the amount of water than in the past.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
According to the land user, crop quality has been relatively better after the implementation of the technology than in the past.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the presence of water in the community, production has decreased.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
maize and some other cereals and vegetables were grown
หลังจาก SLM:
maize together with cole crops, tubers and fruits are grown
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1 acres
หลังจาก SLM:
1.5 acres
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In the past, the lack of water would lead the land users to keeping some of the land fallow.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Water would be scarce periodically
หลังจาก SLM:
Water is now available throughout the community
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Drinking water availability has increased compared to the past. This is mainly due to the protection of water sources. In addition, now community members also go for regular clearing of irrigation channels, drinking water pipelines, and sources to keep the supply steady.
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quality in terms of cleanliness of drinking water was reported to have enhanced because in the past nearby streams from where they get their drinking water used to get polluted by rainwater, animals, etc.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Water would be taken to the nearby streams
หลังจาก SLM:
Water is now provided near there house
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Since supply is continuous the water availability for livestock also increased.
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water for livestock are also improved than in the past.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Focused more on growing crops requiring less water
หลังจาก SLM:
Now grows variety of diverse crops
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Since the water flow is continuous, there is enough water to carry out multiple cropping.
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water quality for irrigation is better than the past
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
focuses mostly on commercialising maize
หลังจาก SLM:
now commercialises diverse vegetable crops as well
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The availability of water in the community, allowed for the land users to grow a diverse vegetable crops in large amount.
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Community members prone to water related disease
หลังจาก SLM:
Water is relatively cleaner
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Agreement for water source protection is conducted after every end of the agreement year, where water use rights are also discussed.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
water from the source would dry up most of the times
หลังจาก SLM:
water in the water source is almost always filled.
คุณภาพน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Would be dirty due to wild animals and grazing cattle
หลังจาก SLM:
Since water source is protected, water is relatively cleaner
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
in the past, drought would occur periodically
หลังจาก SLM:
Even during the absence of rain, water is still available
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Would normally be polluted due to wild animals and grazing cattles
หลังจาก SLM:
Water is now clean and also drinkable
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
| ไฟป่า | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| ไฟบนบก | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| ดินถล่ม | ไม่ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The income earned from the project goes into community development and the community forest, and the expense for the project is already funded.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
102 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Continuous supply of both drinking water and irrigation water |
| Water is supplied to Mongar town, and income is earned from it under Payment for Environmental Services (PES) arrangement b |
| Has helped in community development and improvement of community forest |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Water quality is preserved, and pollution and contamination of the water sources are prevented. |
| The plantation of native tree species helps conserve the ecosystem. |
| Long-term sustainability and enhanced climate resilience of the water source |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Decreased grazing land | Shift the grazing area outside the community forest or establish improved pasture land in their registered land |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
One household
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
One individual
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
11/07/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Norten, U. (2021). Impact of Water Management strategies- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) in Bhutan. International Journal of Science and Innovative Research, 2(8), 109-144.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://ijesir.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/0100072IJESIRnew.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
WWF. (2017). Valuing Ecosystem Services in Chamkharchhu Sub Basin: Mapping Sediment Using InVEST. WWF.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://wwfasia.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/final_invest_report_final_draft_may_17_spread_compressed_2.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/programs-initiatives/source-water-protection
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Water Source Protection
URL:
https://sswm.info/arctic-wash/module-4-technology/further-resources-water-sources/water-source-protection
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Basic Information about Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.epa.gov/sourcewaterprotection/basic-information-about-source-water-protection
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Conserving water resources with PES, an example from Yakpugang
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/conserving-water-resources-with-pes-an-example-from-yakpugang/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล