Double Basin Masonry Check Dam [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
NA
technologies_6716 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Abdi Amir
Dry valley Rehabilitation and Productive Use (DVRPU) project of the GIZ
เอธิโอเปีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The Check Dam helps to arrest the runoff of flood and rehabilitate the gully development.
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [เอธิโอเปีย]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
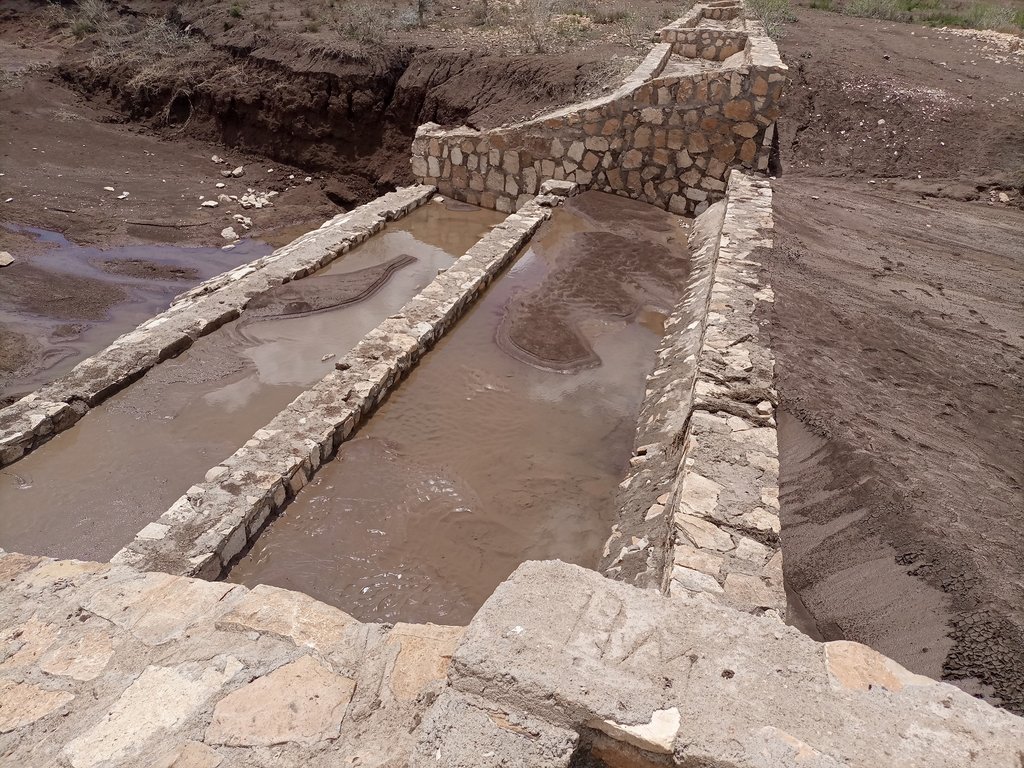
A double basin masonry check dam is a physical structure that helps to stop gully formation or further development of gullies in dry valleys. It rehabilitates small to a medium-sized deep gullies that are eating into the heart of adjacent land.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
A “double basin masonry check dam” is a structure built in a narrow gully or depression to stop further gully formation. It is made of stone, concrete, gabions and wooden bars and serves as a permanent barrier. In this particular site stone is used as the structure is masonry. The technology is applied in areas where there are concentrated flows of water or runoff. The double basin masonry check dam is sited across a slope or a deep gully to slow water flow and capture sediment from upstream in the basins and behind the structure, thereby preventing expansion of the gully. The width of a check dam is variable. This particular structure is 14 meter wide, three meters deep and about 52 meters long. By helping to fill up the gully with sediment, it leads to rehabilitation and makes productive use of the area for growing trees, forage, and other plants. Apart from reducing the speed of surface runoff, the structure also promotes water infiltration, and recharges the groundwater reserves in the aquifer.
The main inputs necessary to build the check dams are financial resources, technical skills, skilled and unskilled labour, and construction materials including sand, stone, cement, water and other materials. Furthermore, construction tools such as a theodolite, line level, string, hammers, spades, hoes, and other tools are essential for design & construction. Technical skills for designing and profiling, and further capacity-building training are essential also. Application of the technology is also supported by satellite image and ground truthing to ensure the precision of siting.
The agropastoralists in the dry basin areas are pleased to see a huge movement of the soil arrested by the structure. The reduced expansion of the gully into the heart of the farm and grazing lands raises hopes of their land become productive and remaining so for generations to come. This hope and expectation have motivated them to welcome the intervention and develop an understanding of the actual benefits accrued from it. This leads to their support for the construction efforts. The disadvantages are that the technology is labour and resource-intensive which can be unaffordable for resource-poor agropastoralist communities living in food-insecure areas where rainfall is unreliable. This may make the adoption of the technology difficult to establish and nurture on their own without outside support.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
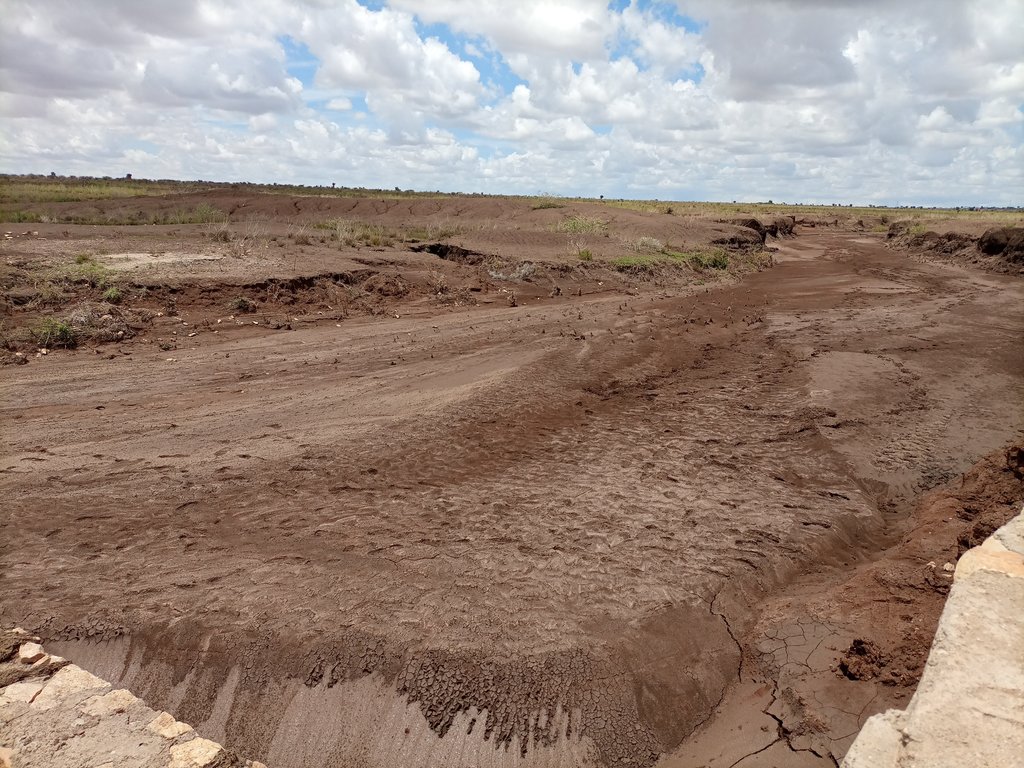
The photos display a large amount of sediment captured by a few days' shower post recurrent droughts experienced in the area over the last two to three years.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Video of the technology was not taken by this particular documentation exercise.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Somali
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Hadow kebele of south Jigjiga district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Locating the check dam closer to each other may help to stop the damage of heavy and concentrated flood moving in the drainage basin.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2021
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) project of the GIZ in Somali Region.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Rainfed is the type of water supply that often experiences erratic distribution characterized by the reception of lower amounts. Mostly characterized by erratic and erosive feature.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology stops the mass movement of soil and water. As a result, it reduces land degradation, rehabilitates the degraded dry valley, and makes the land available for productive uses.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
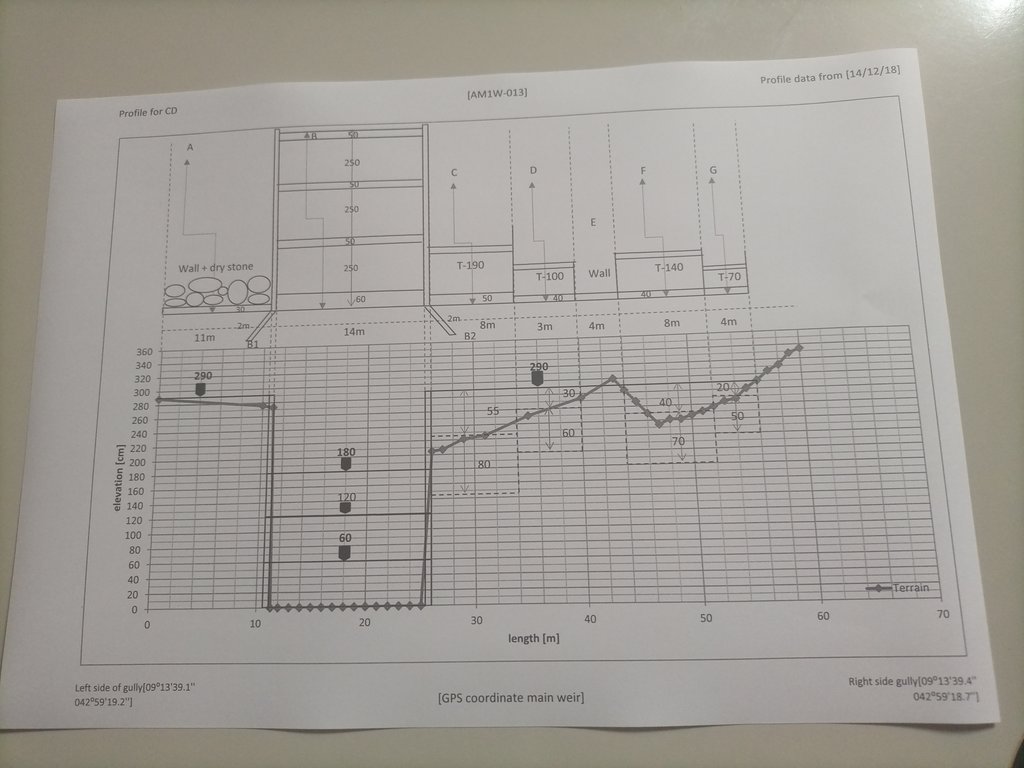
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The design (layout - top view) and profile (lower view) of the technology is presented with universal units to clearly read and understand by the SLM experts or engineers. In addition, there are section drawings of the main weir and Bill of Quantity (BOQ).
ผู้เขียน:
Amir Abdi
วันที่:
14/12/2018
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
check dam
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
14m*3m*52m =2184m3
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
8.5 - 16 USD based on their skills
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduct rapid assessment and Surveillance of intervention site | During the off-season |
| 2. | Finalize site selection | ditto |
| 3. | Layout, Design and profiling works | |
| 4. | Identify and train masonry workers | During off-season |
| 5. | Material supply | |
| 6. | Start actual layout and excavation work | |
| 7. | Supervision... |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Once intended to put the technology or the structure in place, a series of activities are conducted involving experts and contract workers until the activities are effectively finalized.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
9200.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The project is responsible to cover the cost.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost for an unskilled casual laborer a day is 8.5 USD whereas the daily cost of a skilled Masonry worker is 16 USD per day.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Oversee and identify damage | During and after rainy season |
| 2. | Measure the degrees of damage | ditto |
| 3. | Quantify cost and materials needed | |
| 4. | Schedule the maintenance work | Right before the off-season |
| 5. | Employ the workers and reconstruct the damaged parts or upgrade it. | During off-season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As some of the technology implementation sites are inaccessible during the rainy season, implementing the activities during the off-season is commendable.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
3244.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The project is expected to cover the entire maintenance cost. However, maintenance cost is attributed to various factors including the degree of damage, material costs at the time, etc. The figure merely represents an estimation of the cost, on average.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As the dry land receive erratic and erosive rain, damage to the structure is not uncommon. Combining fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial fodder grass stabilizes the sediment and reduces the speed of run-off on top of the structure. Therefore, associating the structure with biological barriers right after the first season of rain is a mandatory action that assists to reduce the damage and maintenance cost that is not affordable by resource-poor communities.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Inflation and increasingly changing material prices, labor and transportation costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall distribution is erratic and erosive.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Jijiga Meteorology station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
There are bimodal rainfall patterns but the distribution in each respective season is not uniform. Particularly, the past consecutive seasons have been characterized by drought.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The technology is implemented in the gully or depression to reduce the speed of runoff and hold back the sediment and running water itself.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Land users communicated the presence of a medium level of water salinity.
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
The water quality is a relative description as it is not supported by facts. Both livestock and human beings are using ponds and still water for drinking after rainfall.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
A few tree and shrub species are common in the area. Acacia, opentia (Euphorbia species), and some invasive weed species are common.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
Agro-pastoralist
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The agro-pastoralist settlement pattern is stable except their mobility with their livestock looking for water and feed. Land users of various age groups are benefiting from the technology.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
Land use is largely communal and individual inherit it from their lineage.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not much service is available in the pastoralist area except that the road paths through the area also create access to the market and other service centers.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
With the development of the sediments trapped by the structure by fodder crops of multipurpose tree species, it is possible to boost production and ensure the sustainability of the structure.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the sediment brings in fertile topsoil from the upstream catchments, the likelihood of producing quality fodder in the rehabilitated area is so high.
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The multipurpose tree species assumed to be planted in the rehabilitated area are expected to increase wood production.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the rehabilitated valley reduces runoff and increases the groundwater reserves, it caters to the opportunity to access drinking water.
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Succeeding vegetation covers enables to filter of the water and improves the quality of surface and subsurface water.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Slightly increases as the structure and rehabilitated areas improves water infiltration and formation of still water or micro ponds behind the structure.
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Simultaneously increases with the availability of surface and subsurface water.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction of gully formations that consume the rangeland allows accessing relatively more rangeland areas for the livestock to graze over. This inevitably improves the food security of the pastoralist community.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology and its function along the mainstreaming work with local development actors certainly improve the understanding and evidence-based knowledge of the land users.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology is believed to increase both surface and groundwater quantity in the intervention valley.
คุณภาพน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Surface runoff speed and volume are gradually decreased with the rehabilitation of the gully and the development of the area behind the structure.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil moisture in the rehabilitated area positively increased.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the structure on the upstream side reduces the speed of runoff, soil, and water loss decrease, and soil accumulation is increasing over time.
การสะสมของดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It increases with the deposition of sediments. Seeds of different trees and vegetation can emerge as succession species.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increases!
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The structure and rehabilitated areas reduces the speed and impacts of the flood.
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Overtime, tree cover reduces emission of carbon and green gases.
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
Assessment of on-site impacts desires long-term follow-up, data collection, and analysis.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the technology put in place in recent times, off-site impacts need assessment based on facts.
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The structure and rehabilitated areas inevitably reduces downstream flooding and siltation in the future.
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is visible siltation held back by the structure. However, quantifying demands empirical analysis.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The facts regarding the off-site impacts will certainly be assessed as a long-term impact.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดีมาก |
| ดินถล่ม | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Similar to on-site impacts, the off-site impact assessment needs, facts, and long-term follow-up.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
Adoption rate is yet to be evaluated. The technology put in communal land.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No community so far adopted and implemented the technology on its own.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Rehabilitate the gully, and stop and reverse the gully formation. |
| It creates the opportunity for productive use of the degraded environment. |
| Recharge the groundwater aquifer and supply still water for temporary use by local people and livestock. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Promote regeneration of the lost species through resilience building. |
| Improve the landscape feature. |
| Improve the ecosystem and its overall services. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High investment cost to implement the technology. | Promote government awareness and emphasis on the benefit and investment in developing the technology. |
| Lack of implementation skills. | Develop the skills and motivation of the community and other stakeholders. |
| Conflict of interest on the use of the rehabilitated land in the intersection of neighboring kebeles. | Awareness creation and promote behavioral change on the joint benefit of the technology. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Inability to put micro check dams along the drainage line before it cuts deep into the soil. | Improve surveillance and promote early intervention. |
| Lower level of participation from the land users. | Develop the capacity, awareness and motivation of the land users. |
| Stakeholders and land users lower level of environmental education, improper land management and the consequent climate change and other associated adversities. | Promote environmental education, emerging climate change and climate variability in adult and vocational education. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Four individuals
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Two individuals.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
23/03/2023
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The flash flood post three years of drought is so damaging. The fragile soil that has been exposed to the sun is easily detached and moved away by the flood. Substantial tons of soil stopped by the check dam signals the positive effects of the structure in changing the trends.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Criteria for optimizing check dam location and maintenance requirements. Hassanli, A. M. & Beecham. 2013; ISBN: 971-1-60876-146-3
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287636490_Criteria_for_optimizing_check_dam_location_and_maintenance_requirements
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Different Types of Check Dams & Design Procedures
URL:
https://forestrybloq.com/different-types-of-check-dams/
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is comprehensive. However, to answer every question, there must be a tradition of long-term data collection and documentation exercises by either the project or the partners government organizations. In that way, it is possible to fully address the multifaceted demands included in the questionnaires such as " the before and after SLM intervention" which is dire to address them for those projects at their early stages of implementation.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [เอธิโอเปีย]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล