Vermicomposting: an effective liquid fertilizer and biopesticide [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: William Akwanyi
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: George Onyango, Innocent Faith, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
technologies_6685 - เคนยา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Mururi Wamunga Job
Welthungerhilfe farmer
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers who have used vermicompost and vermijuice have recorded good harvests and there are no adverse impacts on their farms.
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [เคนยา]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- ผู้รวบรวม: William Akwanyi
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Vermicomposting is an on-farm waste management strategy where worms are used for biodecomposition of wastes to produce a natural liquid fertilizer and pesticide.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
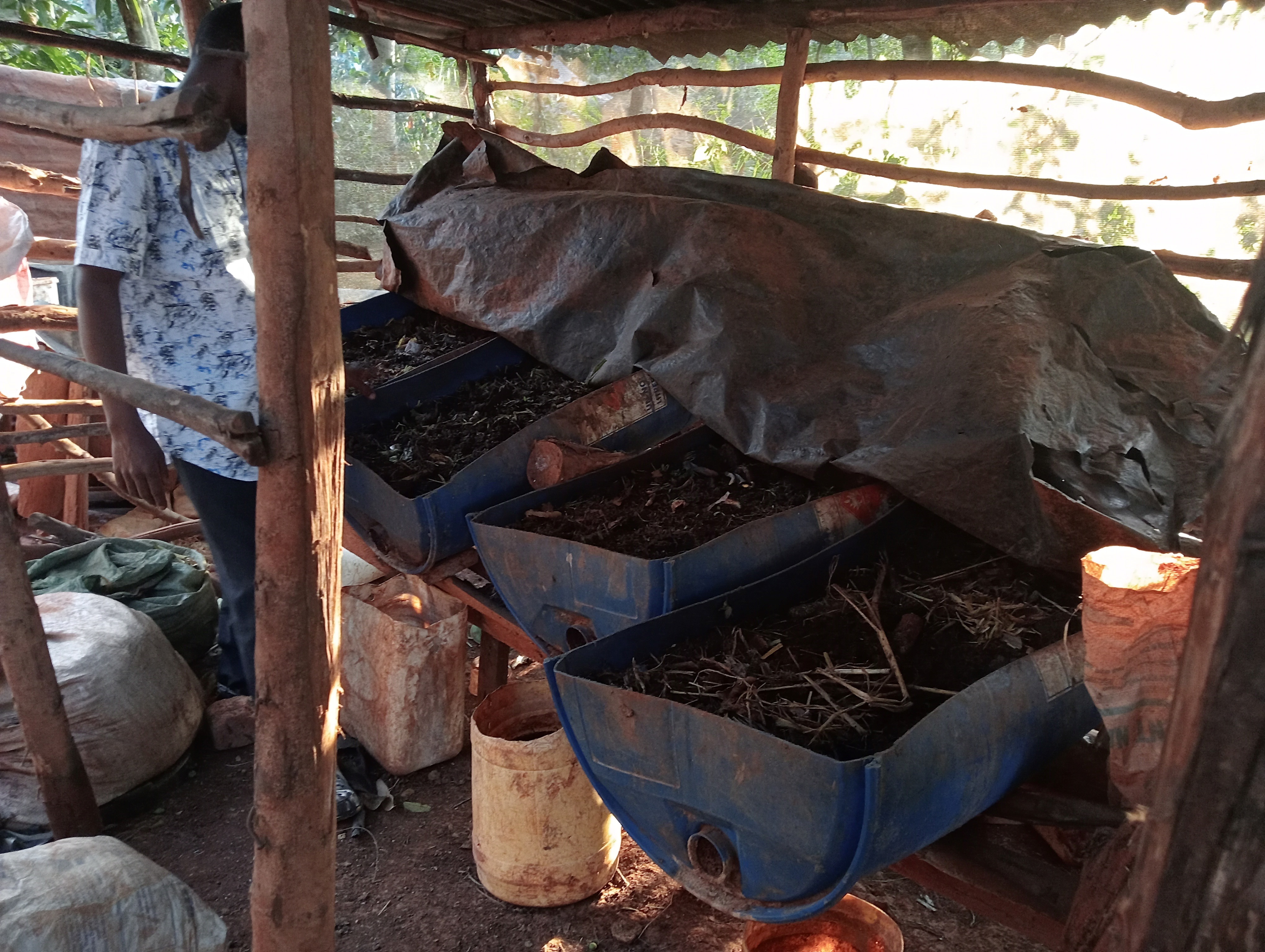
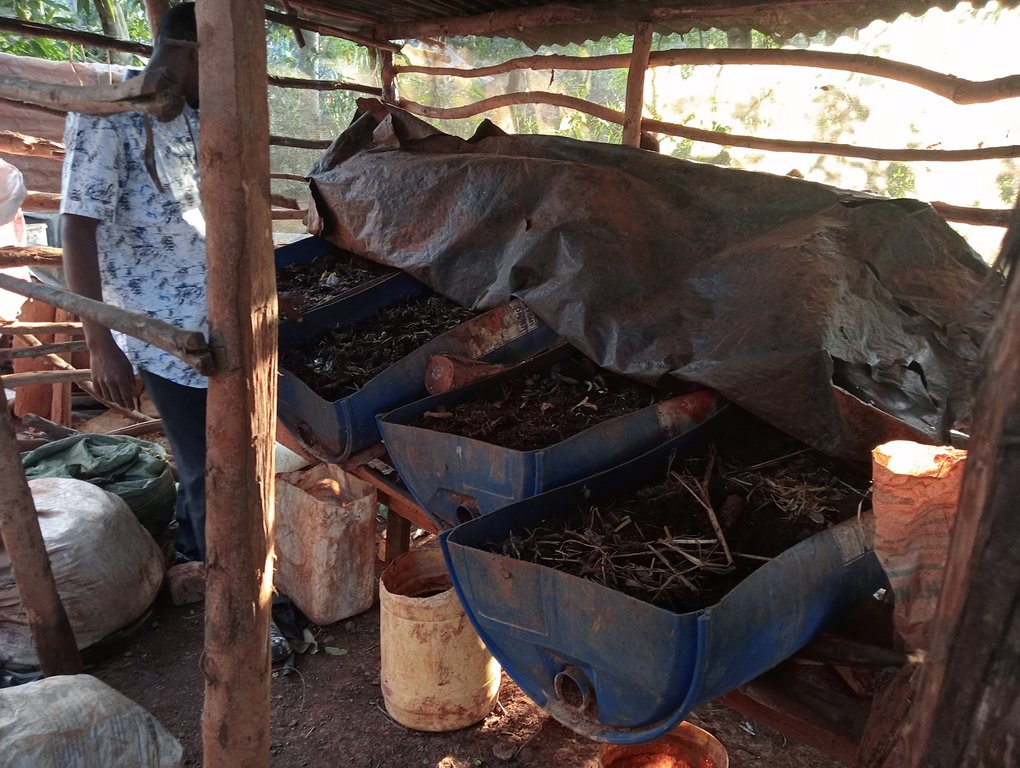
Vermitechnology is biodecomposition of wastes using worms such as red wigglers. It includes vermicomposting (production of compost) and vermiculture (production of worms to ensure sustainability of the enterprise).
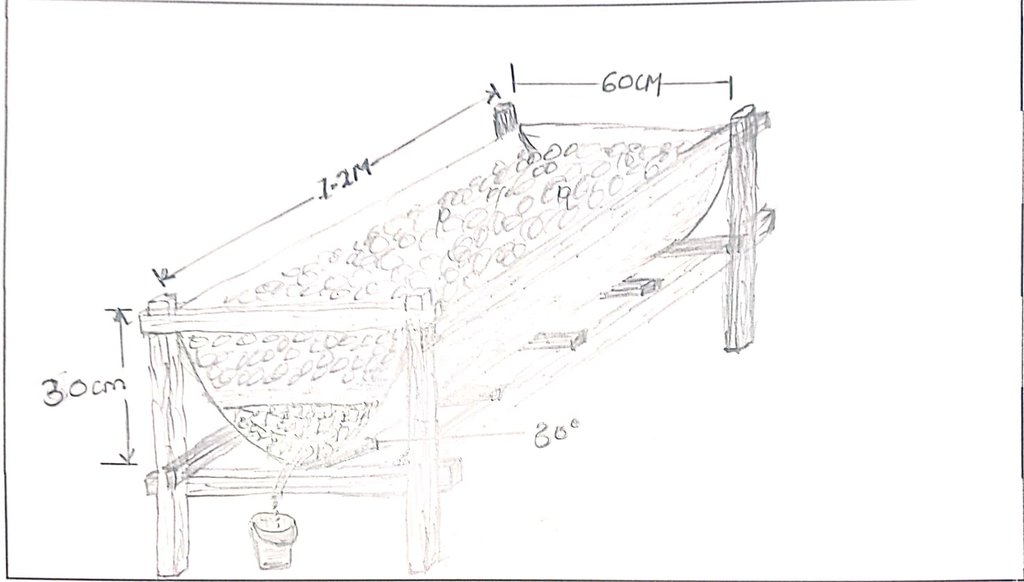
A vermicomposting structure is installed under shade and covered with a black polythene sheet to protect worms from the heat of the sun, and to prevent volatilization of nitrogen. The structure itself can be made by cutting a 60 cm radius and 120 cm height drum into two halves lengthwise. The half to be used must be thoroughly cleaned of oil or chemical residue. A hole is drilled at one end of the half drum for the installation of a tap. A base is made using wooden rails fastened on wooden posts using nails. The container is angled at 30° with the outlet pipe or tap on the lower side to allow free flow of leachate/ vermijuice. Materials are introduced in the half drum, including a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum, a 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food (kitchen and/ or animal wastes) on the bedding material. 20 litres of water are evenly sprinkled on the worm food. The worms and casts are introduced and evenly spread on the food. A bucket is placed at the outlet to collect drops of vermijuice.
Bedding materials include maize cobs, chopped maize straw, agroforestry tree bark, husks, old cartons and paper, and sugarcane bagasse. Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively. However, temperature can be checked by hand also. It is advisable that food (waste) is decomposed before being added onto the bedding material to maintain the temperature within the desired range of 15 - 20°C. Worms coil at the top of the material whenever temperatures go higher. Humidity is often higher in culture bins than in composting beds. Hence, more leachate in culture bins than in composting beds. However, humidity content in both culture bins and composting beds should not exceed 60% since the worms can take in a lot of water and die.
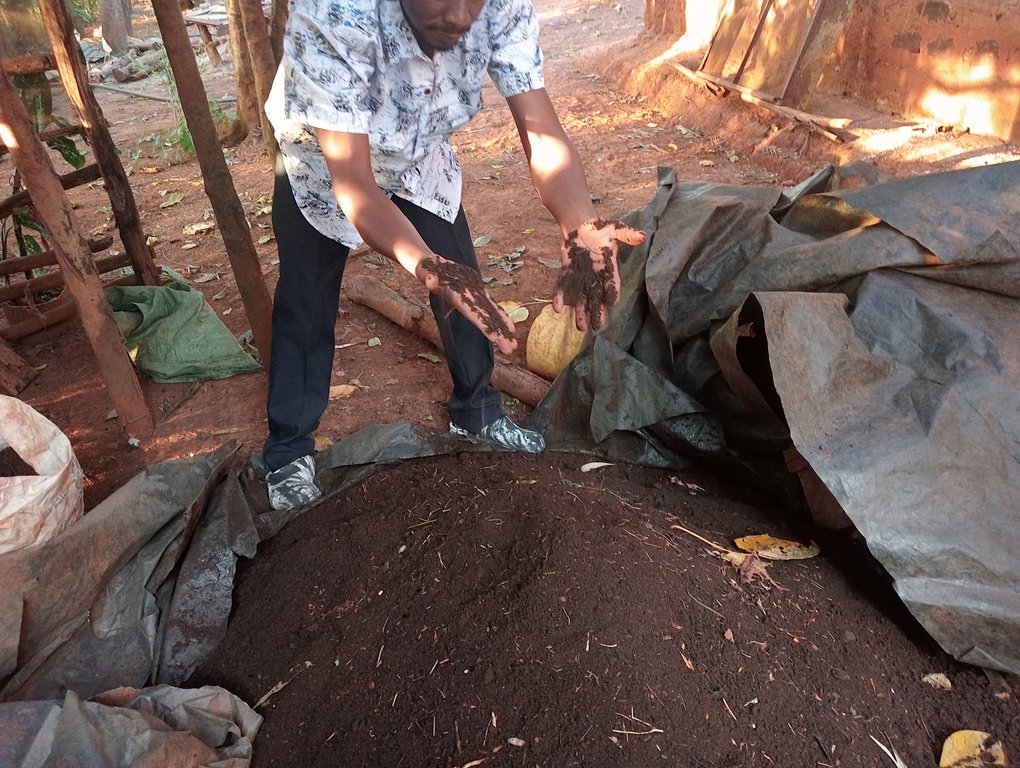
Feeding of the worms is done every 2 weeks where a mixture of 1 kg of chopped fresh tithonia, 3 kg of fresh cow dung, and 3 kg of cooked maize meal (“ugali”) is added and evenly spread on the decomposing material. Collected juice is returned to the system every 2 weeks for a period of 2 months. After the 2 months, the juice will be ready for use as folia fertilizer and pesticide. The casts become ready manure after about 2.5 - 3 weeks. It is harvested by dividing the container into 2 equal halves widthwise and not introducing food to the upper half to make the worms concentrate on materials on the lower half. The worm-free compost on the upper part is completely removed to be used as manure. The remaining material containing the worms is spread uniformly in the half drum. Worm food is then added evenly spread on top.
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. Provided that all inputs are available, a farmer can produce vermicompost and vermijuice 4 times from the same system in a year i.e., 40 litres of vermijuice and 120 kgs of ready-to-use compost in a year. Normally, a one-acre (0.4ha) farm requires about 20 tonnes of compost for planting maize. Vermijuice is mixed with water in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 10 parts of water when required as a folia fertilizer and in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 5 parts of water when required as a pesticide. 20 – 30 litres of vermijuice can be applied to a 0.4 ha farm. However, the amount required for fertilizer varies from farm to farm depending on the conditions of the soil and the crop(s) to be grown. It is important that soil testing is done to determine the conditions of the soil to ensure that the compost is added at the correct rate.
Vermicomposting requires less space and less maintenance labour compared to normal composting. It takes a shorter time to get compost from vermicomposting than from normal composting. On the other hand, large farms would require the installation of several vermicomposting units in order to meet the farm demand. The choice of either technology or both depends on a number of factors, including the size of the farm, the amount of compost required, the time required to produce the compost, etc.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kakamega County in western Kenya
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Matora A Village, Ebukuti Sub-location, Manyala Location, Marama South Ward, Butere Sub-county
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The are no protected areas within the area i.e., sub-county
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
ProSoil project under WHH as the implementing partner
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- vegetables - other
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
Annual cropping system:
Maize/sorghum/millet intercropped with legume
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- fodder crops - grasses
- passiflora - passion fruit, maracuja
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- fruits, other
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- papaya
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Crops planted during long and short rain seasons.
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Maize and beans
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- goats
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- poultry
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Cattle dung and poultry droppings are used as inputs in vermicomposting. Compost is applied on soil where livestock fodder is planted.
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- economic security, investment prestige
- milk
- eggs
- meat
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
2
Species:
goats
Count:
3
Species:
poultry
Count:
4
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There are assorted trees on the farm, and these provide litter that is an input in composting.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Crops are planted all year round due to availability of irrigation water from Eshiatukha and Luanda streams which supplement rain water.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
- การจัดการของเสีย / การจัดการน้ำเสีย
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A6: Residue management
A6: Specify residue management:
A 6.3: collected
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Some plant residues, especially leaves are collected and used as input in vermicomposting.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Ca (Acidification): การเกิดกรด
- Cp (Soil pollution): มลพิษในดิน
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Compost and vermijuice stabilize soil pH and have potential to suppress some soil-born plant pathogens that would have caused plant diseases.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Prevents pathogens
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The drawing above is of a half drum; 60 cm radius and 120 cm height.
The half drum is supported on rails fastened on wooden posts using nails.
The half drum is positioned in a slanting manner at 30° to the horizontal level to enable free flow of the juice.
The outlet of the vermijuice is on the lower side.
Materials introduced in the half drum include the following: a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum; 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food on the bedding material. The worm food material are determined by the required soil nutrients e.g., banana trunk for potassium (K)-rich manure and/ or vermijuice, crushed eggs for calcium (Ca)-rich, and tithonia for nitrogen (N)-rich.
The worms and cast are introduced and evenly spread on the food.
A bucket is placed at the outlet to receive dropping vermijuice.
ผู้เขียน:
William Akwanyi
วันที่:
30/01/2023
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
A half drum vermicomposting unit as described in 2.2
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
0.17 cubic metres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
KES
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
122.95
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
300
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of vermicomposting unit, inclusive shed | Before procuring worms |
| 2. | Adding materials | Before procuring worms |
| 3. | Introduction of worms | After completion of construction |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. The farmer should have the structure ready with all materials except food for the worms before procuring the worms.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Construction of the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| แรงงาน | Construction of shade over the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Hammer | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Hand saw | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Tape measure | |||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Bedding material | |||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Worms in cast | |||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Kitchen or animal wastes | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Half drum | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gunny sheet | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Nails | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Iron sheets | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | Gravel | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | Sand | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | Water |
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
7000.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The ProSoil project provided the worms
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The costs refer to the equipment described in 2.2. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 56.93 USD.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring humidity and temperature | Daily |
| 2. | Feeding | Biweekly |
| 3. | Watering | Biweekly |
| 4. | Predator control | Daily |
| 5. | Harvesting compost | Every 2.5 - 3 months |
| 6. | Collection of vermijuice | Daily |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
2000.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 16.27 USD.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another. It is not easy to attach monetary value to some of the input e.g., wastes and water.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1300.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Kakamega Meteorological Station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
The climate in the area favours most agricultural activities.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The farm is located at an area that is lower in altitude compared to other areas in the larger area. The altitude of the farm is 1,319 meters above sea level.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil pH of most farms in the area ranges from moderately acid (4) to moderately alkaline (7).
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The area has high agrobiodiversity since most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
ระบุ:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The farmer has an official title deed for his piece of land. He also leases other people's pieces of land for farming. Water in the streams such as Eshiatukha and Luanda and springs is freely accessed without restrictions. There is a borehole in the neighbourhood, and the managers of this borehole have set rules for accessing the water thereat.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3
หลังจาก SLM:
8
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Number of 90Kg bags of maize harvested per acre of land. Based on estimate by the farmer.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not easy to quantify by the farmer. Based on estimate by the farmer.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3
หลังจาก SLM:
5
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Number of harvesting cycles in one season. Based on estimate by the farmer.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on estimate by the farmer.
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2
หลังจาก SLM:
6
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Amount of milk in litres from one cow. Based on estimate by the farmer.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
70
หลังจาก SLM:
10
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the probability of crops failing to do well in any season.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Land management has been eased because use of manure from vermicomposting improves the soil structure making it easier to plough.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10,000
หลังจาก SLM:
0
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the amount of money in KES spend on fertilizers. The farmer no longer purchases fertilizers.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2,000
หลังจาก SLM:
50,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the amount of money earned from sell of farm produce. Currently, he sells manure, worms, and vermijuice and also offers services in construction of vermicomposting structures.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3
หลังจาก SLM:
5
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the number of farm products that the farmer sells to earn income. Based on estimate by the farmer.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
4
หลังจาก SLM:
1
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the number of months when there in no food in the house and the household has to purchase all food required in the house.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10
หลังจาก SLM:
20
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the percentage of moisture content in the soil during the dry season.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40
หลังจาก SLM:
80
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimation of soil cover on his farm.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2
หลังจาก SLM:
4
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil organic matter has increased due to use of manure.
ความเป็นกรด
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20
หลังจาก SLM:
50
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated vegetation cover at his farm.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
3
หลังจาก SLM:
8
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Quantity refers to the number of crops that the farmer establishes on his farm.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are earthworms at the farm.
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not easy to quantify. Compost improves carbon sequestration in the soil.
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Use of vermicompost and vermijuice reduces the farmer's dependence on inorganic fertilizers and pesticides.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
The project was implemented in the entire ward. Very few farmers have vermicomposting structures.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most farmers are not implementing yet they were taken through the vermicomposting training by the ProSoil project.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
Design
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
The farmer does not fit taps on the composting structures as outlets for the vermijuice since someone can accidentally close the tap and forget to open, especially during humidity checking leading to high humidity which can cause the death of the worms.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is an agribusiness venture. |
| It is a source of manure and pesticide. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Compost and vermijuice can be sold to earn income. |
| Structures can be made from locally available material. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Not effective for large scale farming. | Establishment of many bigger structures. |
| The technology is not common among many farmers. | Need for increased awareness creation among farmers, especially on proper knowledge on composting. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Possible death of worms due to unfavourable temperature and humidity. | Ensure regular checking of temperature and humidity. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
One visit at one farm
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up on phone.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
30/01/2023
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Free download at https://kakamega.go.ke/public-participation-county-development-plans/
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Vermicompost Suppression of Pythium Aphanidermatum Seedling Disease: Practical Applications and an Exploration of The Mechanisms of Disease Suppression
URL:
https://ecommons.cornell.edu/bitstream/handle/1813/31195/alh54.pdf;sequence=1
7.4 General comments
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [เคนยา]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- ผู้รวบรวม: William Akwanyi
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล