ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services via SMS [ตูนิเซีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_7002 - ตูนิเซีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Agricultural Economist:
Frija Aymen
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Agricultural and Resource Economist:
Dhebibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
PhD Candidate:
Oueghemmi H
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - เลบานอน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Lessons learned from the "Mind the Gap" project: … [ตูนิเซีย]
The “Mind the Gap” project researched the adoption gap between agricultural research and women and men farmers. Its objective was to determine most effective and cost-efficient technology transfer strategies and give recommendations to national extension institutes and development partners to adapt their scaling strategy
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
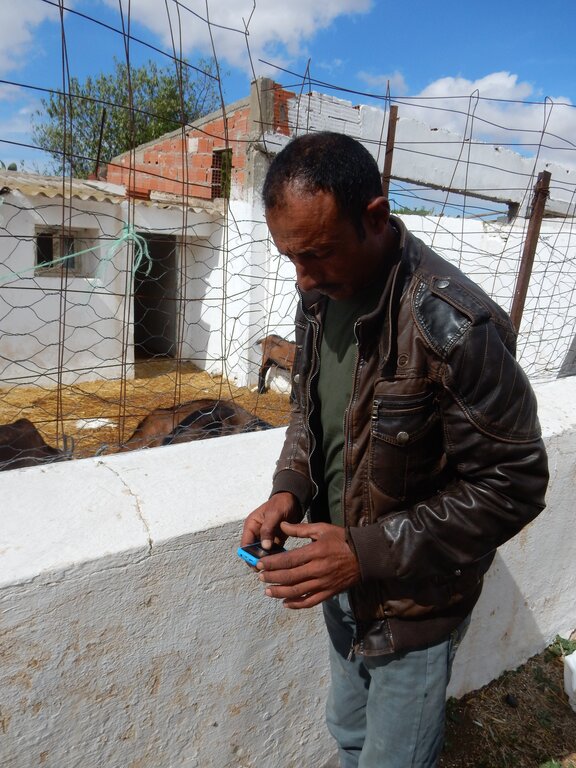
In Tunisia, smallholder farmers rely heavily on extension services for information regarding new and sustainable agricultural practices, improved varieties, and market prices. Unfortunately, these services often fall short, particularly in remote areas, due to inadequate financial, human, and logistical resources. Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) can play a crucial role in filling this void. This can strongly contribute to developing the agricultural sector and reducing or preventing land degradation.
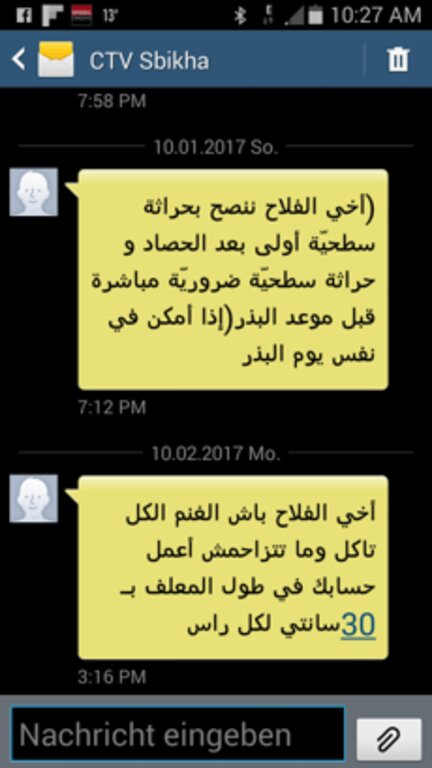
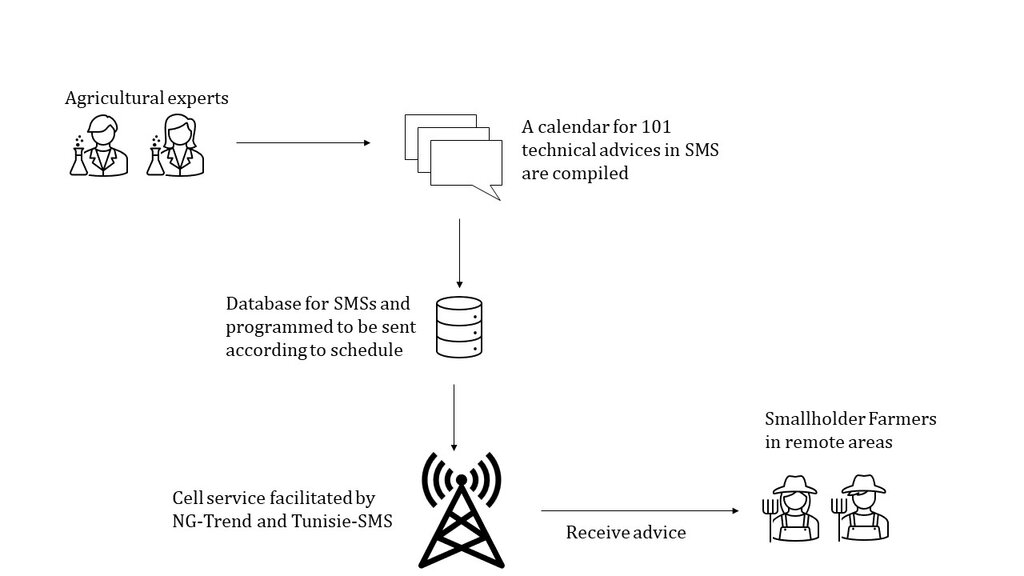
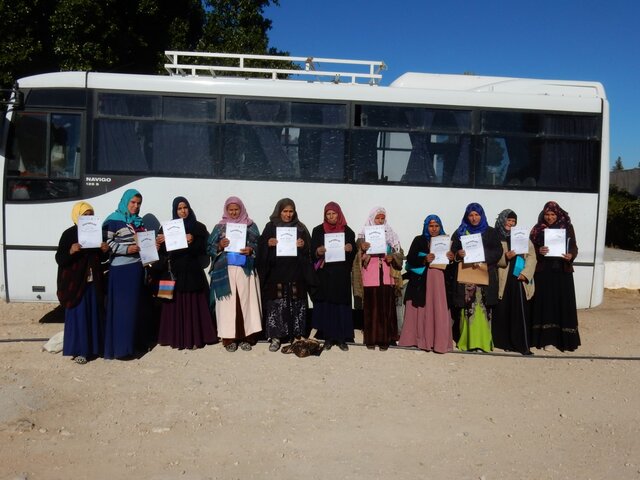
The ICT2Scale project aims to address these issues and reach these substantial group of farmers. The project was led by the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA). It was initiated in 2019 with a survey to identify the information needs of smallholder farmers. Tunisian farming experts crafted 101 technical SMS messages, disseminating them to approximately 1,000 smallholder farmers in Kairouan, Zaghouan, and Jendouba. These messages covered diverse commodities such as cereals, olives, citrus, honey, and livestock, simultaneously aiding farmers in sustainable land management and resource optimization.
A one-day workshop was organized to compile the advisory messages. Thirty specialists from various disciplines gathered, including different National Agricultural Research and Extension Services (NARES) centres. The workshop's estimated cost (including food and per diem) was around $1000 USD. Each SMS “unit” - of one message to one farmer - costs approximately $0.01 USD, totalling $1010 USD to make the 101 SMS available to 1000 farmers. Although the data services were provided free-of-charge by network companies, the overall project cost is still estimated at $3000 USD per year. Similar infrastructure with similar cost was implemented in the projects “Mind the Gap” and "Crop-Livestock and Conservation Agriculture (CLCA)".
A follow-up survey conducted by phone in May and June 2021 involved 421 SMS recipients, revealed that 60% found the messages useful, with 54% claiming to have learned something new. However, only 15% agreed that the messages arrived at the right time. Notably, 41% of farmers expressed a willingness to pay $0.01 USD per message after the project, indicating a potential avenue for the sustainability of this SMS technology. Farmers recommended using SMS for weather alerts and disease outbreaks; employing phone calls or Interactive Voice Responses (IVR); sending messages at the right time; and incorporating information on marketing, training, and livestock vaccination programmes.
Key advantages of an SMS service are:
-More cost-effective than in-person advice via public extension agents
-Particularly effective during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the lack of personal contact
-Immediate reach to thousands of farmers in case of emergencies or opportunities
-Flexible and adaptable for quick information updates
-Useful when extension resources, such as vehicles and funds, are limited or unavailable
-Effective in disseminating information about events like training and seed distribution
However, some weaknesses persist, including a lack of interaction (i.e. a top-down approach), less convincing than personal exchange, and ongoing funding challenges, with the Tunisian government hesitant to invest in the project without more dialogue and convincing arguments.
In summary, the ICT2Scale project has proved the viability and cost-effectiveness of employing SMS technology to reach smallholder farmers in remote areas. Consequently, this has the potential to enhance more sustainable and efficient use of land and natural resources, leading to an improvement in rural livelihoods. However, securing sustainable funding remains challenging in order to scale up and maximize impact.
Acknowledgement:
ICARDA’s work on Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) for agricultural development is supported by the German Agency for International Development (GIZ) in Collaboration with National Public Partners (AVFA, OEP, INRAT,ONAGRI, and CRDA) and Private Partners (NG Trend, Tunisie SMS) in Tunisia.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
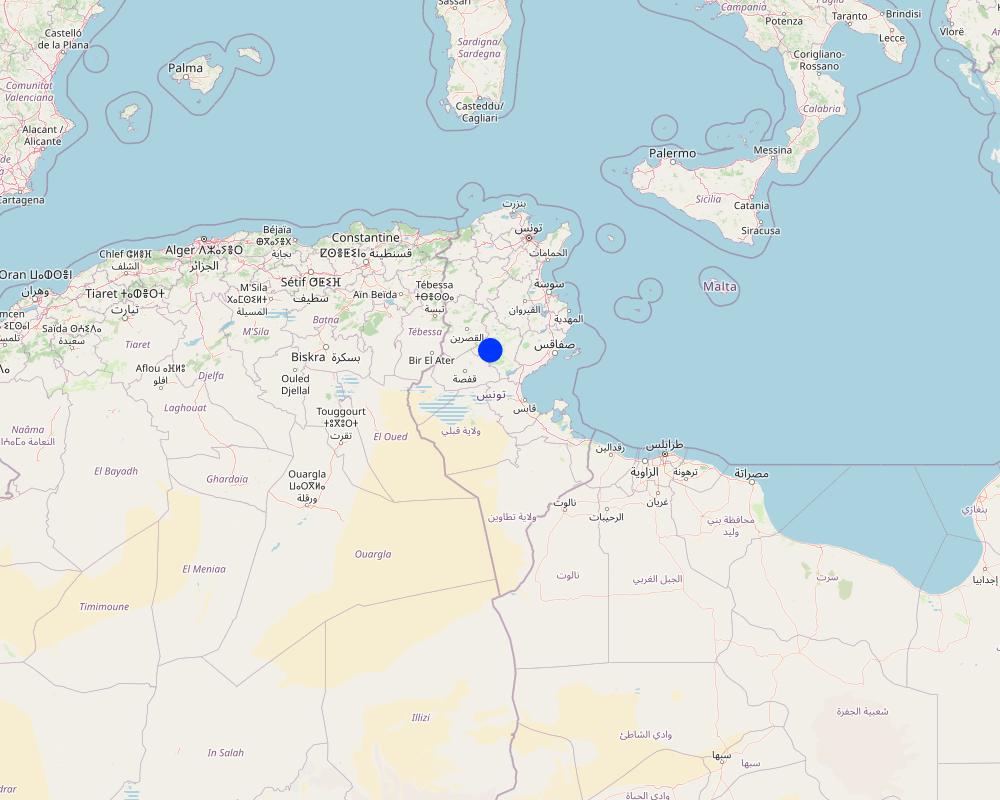
ตูนิเซีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kairouan, Zaghouan, and Jendouba
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2019
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
Animal type:
- goats
- sheep
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The SMS messages were directed to different land use and land management such as barley cultivation, livestock herding, and olive production.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- Digital agriculture
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
Digital
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most SMS messages were about agronomic and management measures.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
By informing farmers with technical advice, farmers can manage their land more sustainably.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Agricultural experts from different National Agricultural Research and Extension Services (NARES), lead farmers and ICARDA scientists formulated 101 technical advises in SMS following an elaborated "agricultural" calendar. This way farmers receive technical advice when needed. This is facilitated by NG-Trend and Tunisie-SMS
ผู้เขียน:
Joren Verbist & Udo Rudiger
วันที่:
2024
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Whole project / infrastructure
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Workshop to compile technical advice | |
| 2. | Setting up network |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Workshop to compile 101 SMS advice messages | workshop | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | SMS unit (101 SMSs to 1000 farmers) | unit | 101000.0 | 0.01 | 1010.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Remaining | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | ||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3010.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 3010.0 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
...
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
- แห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the production increases.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the quality of production increases.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the production increases.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers with technical advise and current prices, so they can lower their expenses.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers with technical advise and current prices, it is expected they can increase their selling prices.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By informing farmers when the best moment is to plough the field, soil loss through erosion is reduced.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Informing farmers about management operations and their timing, drought impact decrease
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers can receive various advice that allows them to cope with a wide range of climate-change induced issues and disasters.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
Around 1000 smallholder farmers
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The system in SMS-based which does require a smartphone, making it more accessible. |
| The technical advises allow to improve production practices. |
| The technical advice gives good reference for current practices |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| More cost-effective than in-person advice via public extension agents |
| Particularly effective during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the lack of personal contact |
| Immediate reach to thousands of farmers in case of emergencies or opportunities |
| Flexible and adaptable for quick information updates |
| Useful when extension resources, such as vehicles and funds, are limited or unavailable |
| Effective in disseminating information about upcoming events like training and seed distribution |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| SMS is often received at wrong timing. | |
| SMS messages did not include advice on animal vaccination programs. | Include this in the technical advice |
| SMS messages did not include early warnings for (weather) hazards. | Include this as well in the infrastructure and adding underpinning (weather) forecast models for this. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| SMS is not useful for illiterate farmers | Education in the rural areas should be improved in general. |
| Lack of dialogue (a top-down approach) | Include farmers when writing the advice and consider their needs beforehand, which was also done during the project. |
| Less convincing than personal exchanges | |
| Challenging to have ongoing investment | By showing to donors and national government that using SMS services is a viable and cost-effective way to improve rural livelihoods and make better use of the land and natural resources. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Udo Rudiger. (20/9/2021). Lesson learned from the study on "Impact of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) on Agricultural Development in Tunisia". Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/66236
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Aymen Frija, Hassen Ouerghemmi, Barbara Rischkowsky, Udo Rudiger. (26/10/2023). A contextual ICT model to explain adoption of mobile applications in developing countries: A case study of Tunisia. PLoS ONE, 18 (10).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68779
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
List of SMS messages to be send to farmers.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10637
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Udo Rudiger, Boubaker Dhehibi. (5/11/2021). General project "ICT2Scale" presentation.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/66426
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Lessons learned from the "Mind the Gap" project: … [ตูนิเซีย]
The “Mind the Gap” project researched the adoption gap between agricultural research and women and men farmers. Its objective was to determine most effective and cost-efficient technology transfer strategies and give recommendations to national extension institutes and development partners to adapt their scaling strategy
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล