Irrigated Oasis gardens [ไนเจอร์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Julie Zähringer
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_947 - ไนเจอร์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Oasis gardens in Niger for crop, vegetable and fruit production are supplied with irrigation water from traditional wells.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
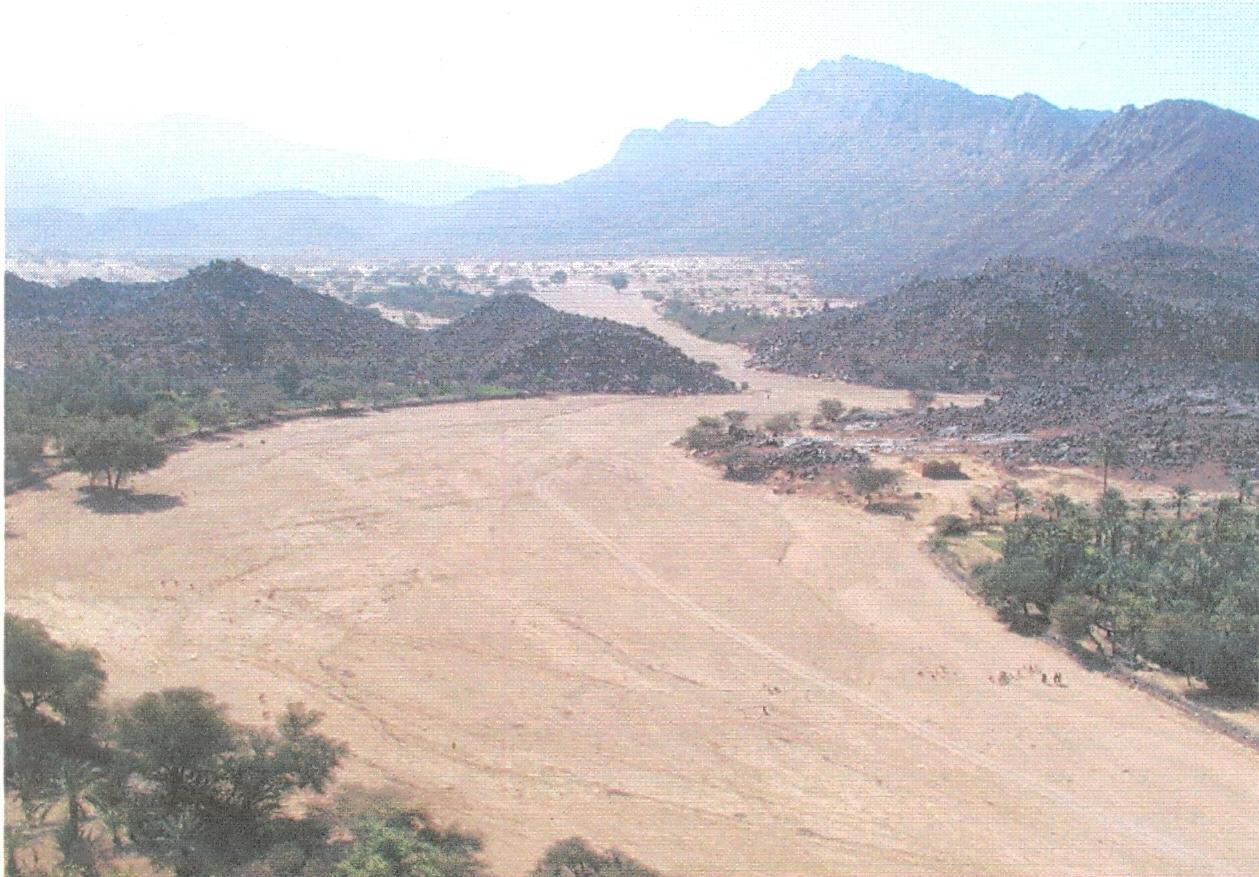
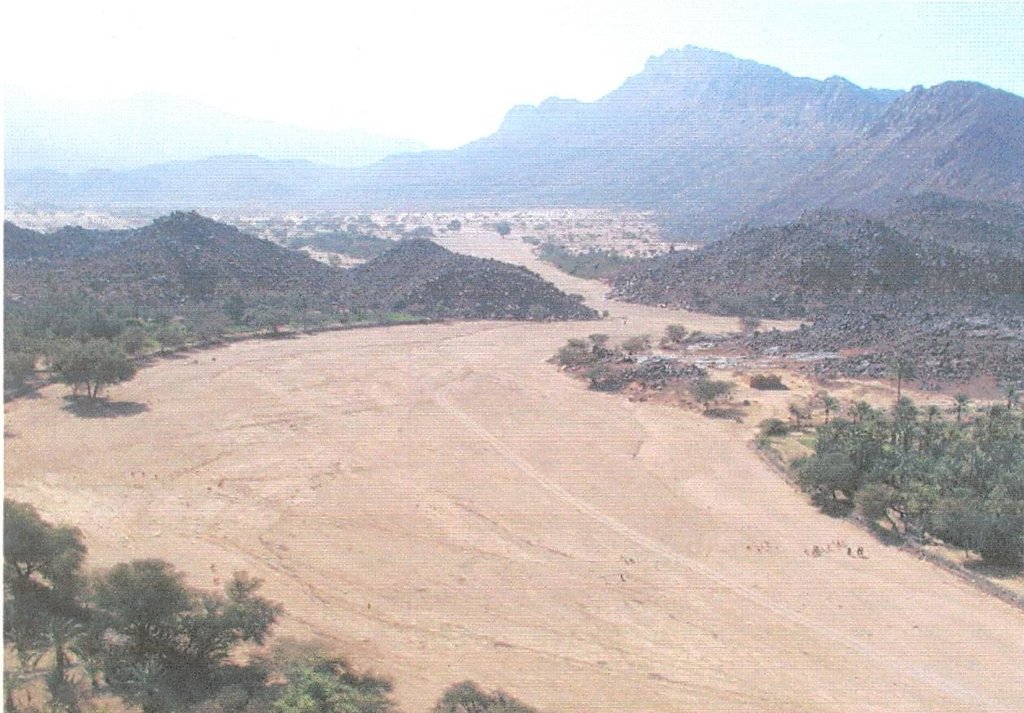
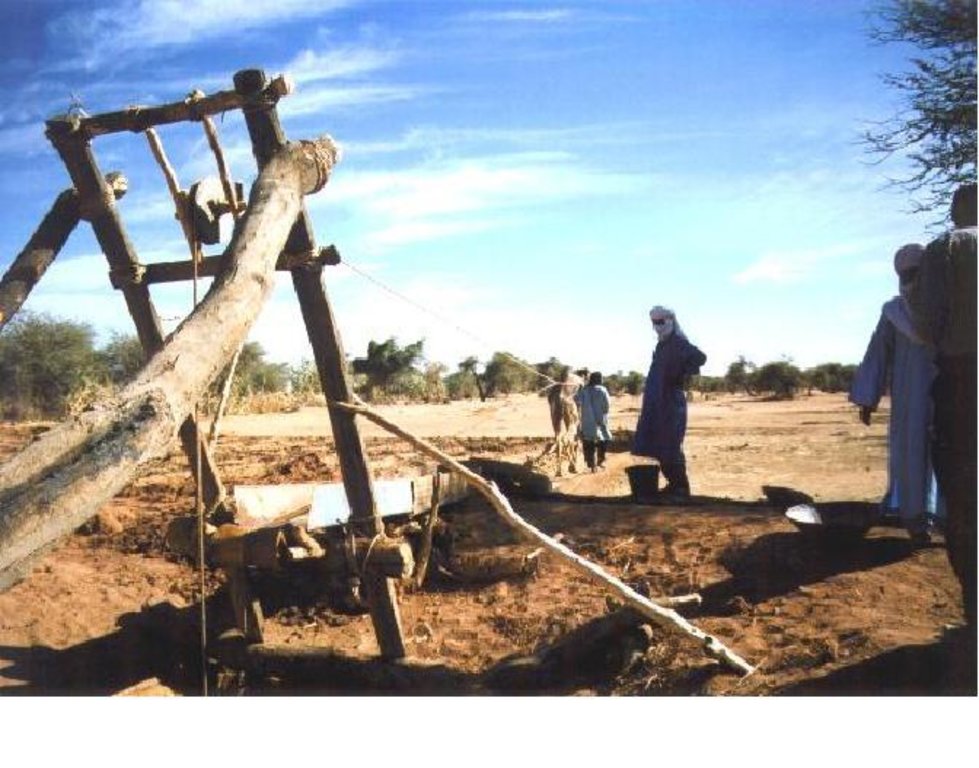
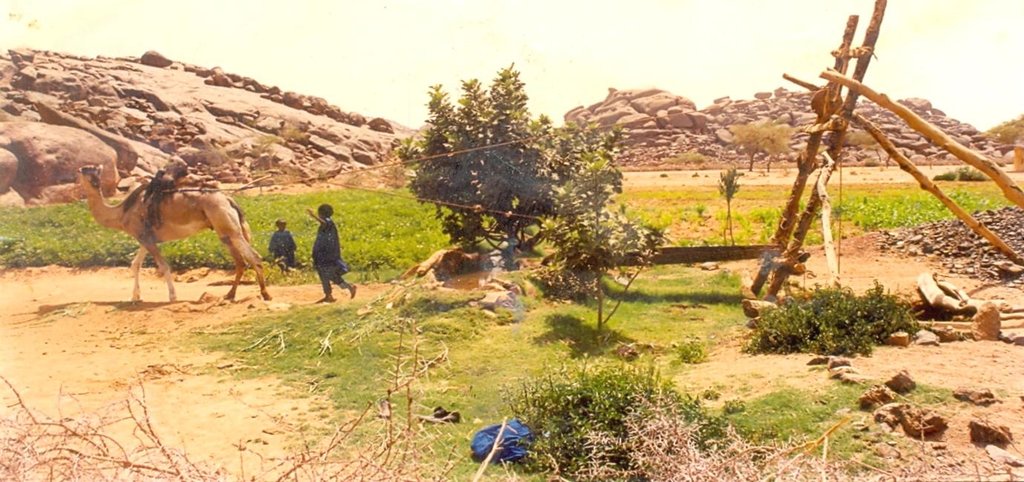
In Timia Oasis in Aïr, small irrigated gardens (< 0.3 ha) have been used for over a century, producing dates and tree crops (figs, citrus, cherries, etc.) for sale and cereals for consumption (wheat, maize and pearl millet). With the onion boom in the 1990s, the establishment of new gardens grew dramatically. The new gardens cover a bigger area (0.5 - 1 ha) and focus on cash crops - mainly onions, but also potatoes and garlic. Gardens are fenced using branches from acacia trees. The water supply system in most cases is based on traditional wells with an animal-drawn scoop. The wells are less than 20 meters deep and generally built without a casing. Local experts were trained by GTZ project staff in well construction and maintenance. Modern motor pumps have recently become common and are used in new gardens. Water is conveyed to the plots through a hand-dug network of distribution channels. The channels are lined with clay and stones to minimize water loss through infiltration, evaporation, or breaching. Irrigating a whole garden takes about two hours. There are two cropping seasons per year: the rainy season (June-Sept) with staple crops such as maize and millet; and the dry/cold season (Oct.-Feb.) with wheat-barley associations and cash crops such as onions, garlic, tomatoes and vegetables. Fruit trees covering up to a fifth of the gardens; one section of the garden is reserved for keeping small ruminants. Agricultural residues are used as fodder and manure produced by livestock ensures fertility of gardens in combination with inorganic fertilizers. Traditional techniques (local plants, ash, etc) are used for pest management. Seed production and selection is done strictly locally.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main establishment activities for this technology are: 1. Identify and demarcate of a free area to be converted into a garden. Fence area with acacia branches and living hedge. 2. Establish a traditional or cement well, max. 2 m wide and 15-20 m deep (contract with local well builder) in the middle of the field. 3. Installation of traditional water conveyance system (Tekarkat): wooden poles hold a pulley which conducts a rope with a scoop for extraction of water from the well. The system is powered by a dromedary. A 5-meter-chute (palm stem or iron sheet) conducts the water to a small reservoir.
4. Mark and dig irrigation canal system and basins for crop cultivation (8 m2): Main canal and secondary canals (perpendicular to main canal) are reinforced with clay or stones. 5. Purchase inputs (local market): seed, seedlings, fertilizer, tools. 6. Plant fruit trees.
Maintenance activities are the following: 1. Maintenance of fence: replace missing branches; plant new tree seedlings to reinforce the living hedge (biannually). 2. Irrigation (daily). 3. Maintenance of Tekarkat and canal system: control (and replace) poles; periodic weeding, cleaning, repair leaks and improve lining with clay/stones (biannually, after harvest). 4. Field preparation and application of organic manure (beginning of each cropping season). 5. Maintenance of well: cleaning (hot season), reinforce walls with cement (if needed).
6. Feeding draught animal using natural grassland and crop residues.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไนเจอร์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Aïr
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Timia oasis
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Ces jardins traditionnels ont tendance à être adoptés spontanément. La technologie a été une réponse aux sécheresses successives des années 1970 et 80 qui ont causé d’importantes pertes de bétail dans la région. Les éleveurs nomades ont adopté la technologie pour diversifier leurs moyens de subsistance et diminuer les risques. Depuis les années 1990, 700 nouveaux jardins ont été créés à Timia (comparé aux 100 qui existaient précédemment)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Desertification, soil erosion by wind and water, chemical and biological degradation of soil
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct-Feb
Second longest growing period in days: 90
Second longest growing period from month to month: June-Sept
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: droughts
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (indigenous knowledge, extension from farmer to farmer))
Main technical functions: water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: fig, citrus, cherries
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant fruit trees | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | Identify and demarcate of a free area to be converted into a garden. Fence area with acacia branches and living hedge | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Establish a traditional or cement well, max. 2 m wide and 15-20 m deep (contract with local well builder) in the middle of the field | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 4. | Establish a traditional or cement well, max. 2 m wide and 15-20 m deep (contract with local well builder) in the middle of the field | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 5. | Installation of traditional water conveyance system (Tekarkat) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 6. | Mark and dig irrigation canal system and basins for crop cultivation (8 m2): Main canal and secondary canals (perpendicular to main canal) are reinforced with clay or stones | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 7. | 5. Purchase inputs (local market): seeds, seedlings, fertilizer, tools | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field preparation and application of organic manure (beginning of each cropping season) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | beginning of each cropping season |
| 2. | Maintenance of fence: replace missing branches; plant new tree seedlings to reinforce the living hedge (biannually) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Irrigation | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | daily |
| 4. | Maintenance of Tekarkat and canal system: control (and replace) poles; periodic weeding, cleaning, repair leaks and improve lining with clay/stones | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | biannually, after harvest |
| 5. | Field preparation and application of organic manure | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | beginning of each cropping season |
| 6. | Field preparation and application of organic manure | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 7. | Maintenance of well: cleaning (hot season), reinforce walls with cement (if needed) | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cost calculation is based on local land prices and traditional irrigation systems. Maintenance costs include also fodder (for draught animal) and organic manure. Establishment as well as maintenance costs were calculated for a garden size of 0.5 ha.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
- communal unorganised
- communal unorganised
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user can be (1) the owner of the garden; (2) a family member managing the family-owned garden; (3) a paid labourer; (4) a usufructuary
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
สถาบันของชุมชน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology serves a double purpose: food security and income generation
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Since the 1990ies, 700 new irrigated gardens were established in Timia (as compared to 100 gardens)
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High implementation costs | establish national financial support systems for acquisition of garden area by very poor people |
| High maintenance costs | promote efficient irrigation technologies that reduce maintenance costs (such as drip irrigation) |
| Uncontrolled spread of the technology resulting in an overexploitation of groundwater and over-production (e.g. onions) | increase water use efficiency; regulate market and promote agro-industrial food processing |
| High dependency on climatic factors influencing the recharge of the groundwater level | exploitation of deep water resources through artesian wells and introduction of adapted drip irrigation technologies |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Suchantke, J. and A. S. Soumaila. 2001. Etude cadre pour le programme NIGETIP IV, KfW, Niamey, Niger
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Soumaila, A. S., 2005. Rapport du symposium international sur le développement des filières agropastorales en Afrique organisé par GREAD.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
PPEAP. 2006. Rapport final d’évaluation du projet de promotion des exportations agropastorales
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ministère du développement agricole. 2008, 2009. Données statistiques sur la production maraichère
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล