Non-inversion shallow cultivation [เบลเยียม]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
Oppervlakkige niet-kerende bodembewerking
technologies_966 - เบลเยียม
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Gillijns Katleen
Catholic University of Leuven
เบลเยียม
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Govers Gerard
Catholic University of Leuven
เบลเยียม
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Catholic University of Leuven (KU Leuven) - เบลเยียม1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
08/11/2010
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [เบลเยียม]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
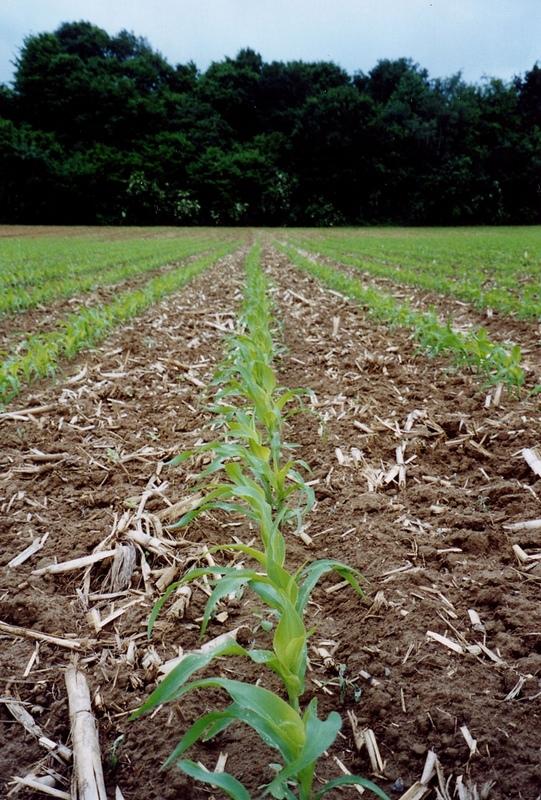
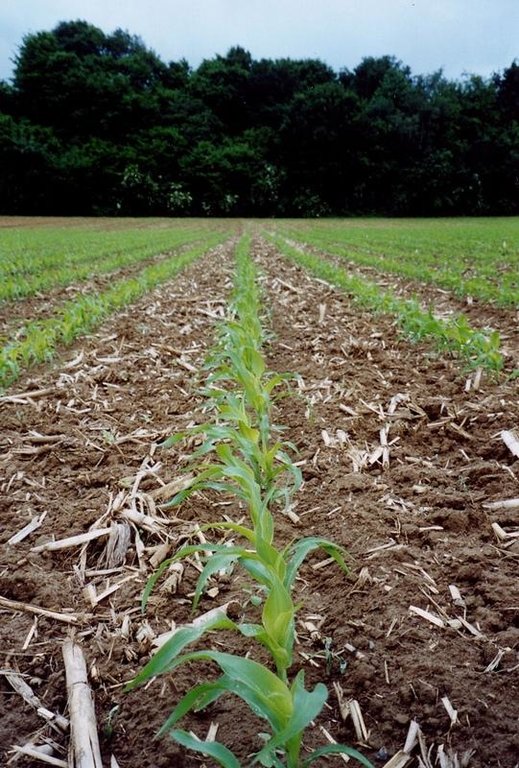
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The technology consists of the use of cover crops and of a non-inversion seedbed preparation
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
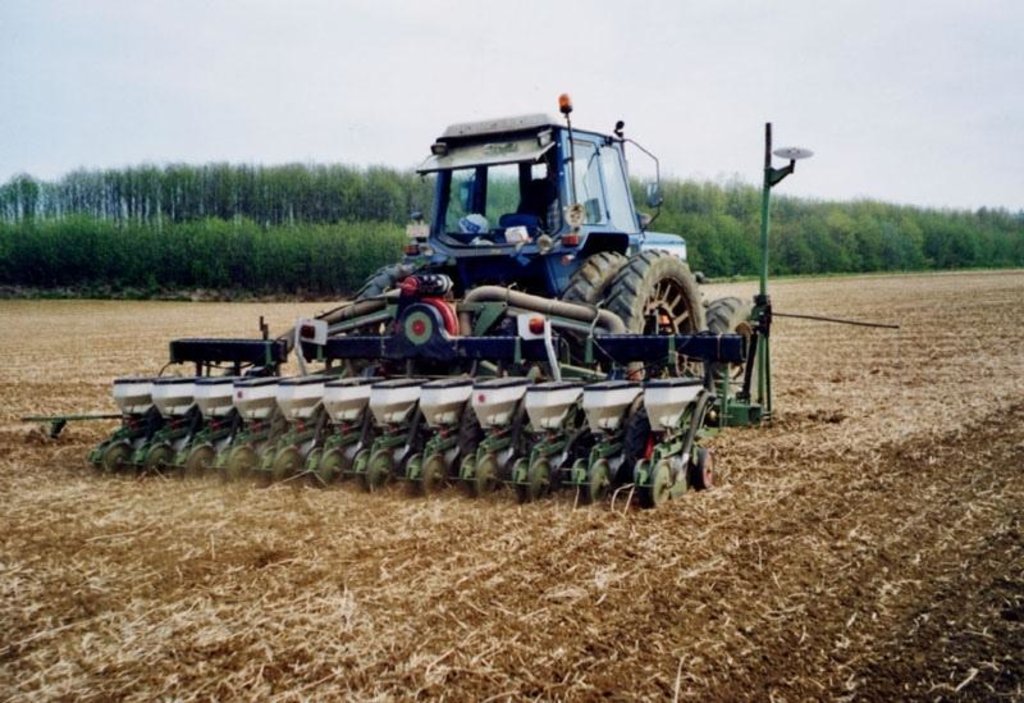
The technology consists of agronomic measures. The most important thing is that the farmers are not allowed to invert the soil by ploughing. Farmers may only cultivate their fields as minimum and as shallow as possible. Farmers also have to use a cover crop, if possible. In this way the soil is always covered with residues of a previous crop or with residues of the cover crop. The improvement of the ground cover protects the soil against different kinds of water erosion. In the long term period, the soil structure will improve (more organic matter in top soil) and more earthworm activity will be determined. The infiltration of water will increase.
Purpose of the Technology: Protecting the soil against erosion and increasing infiltration.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer may never plough.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on cropland with annual crops.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เบลเยียม
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Flanders
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Vlaams-Brabant
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In the Walloon part of Belgium and in the surrounding countries (France, Germany), farmers are already applying this technology for a long time. In Flanders, the technology was introduced in the '1970 by a professor De Ploey of our Faculty. Farmers didn't see the benefits of the technology and decided not to implement the technology. Now time has changed: farmers know that they have to do something ageist the erosion problem.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop: Sugar beet
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Soil loss by water erosion. 2. soil erosion related environmental problems (muddy floods, retention pond sedimentation, declining water quality due to sediment and sediment - fixed contaminants)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Strong nitrogen regulations and EU rules are hindering the farmer.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat- potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat - sugar beet.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period from month to month: Mar-Oct; Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0046 km2.
It's a fiedl trial with 3 treatments: every treatment is 4620 m² (see map). The treatments are: non-inversion shallow cultivation, non-inversion deep cultivation and conventional ploughing. In the region of this field, other farmers are also experimenting with new technologies on their own fields.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soil erosion), lack of knowledge
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes: hevay machinery)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter
Better crop cover
Material/ species: winter barley 2003
Quantity/ density: 200 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover (every year)
Remarks: by not ploughing
Agronomic measure: better crop cover2004
Material/ species: maize 2004
Quantity/ density: 178600
Remarks: seeds/ha
Agronomic measure: better crop cover 2004
Material/ species: winter wheat 2004
Quantity/ density: 165 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: better crop cover 2005
Material/ species: oats 2005
Quantity/ density: 110 kg/ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: slury injection 2004
Quantity/ density: 40000l/ha
Remarks: before sowing
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2004
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: 26%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 175 kg/ha
Remarks: 39%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 45 kg/ha
Remarks: 27%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Haspargit
Quantity/ density: 800 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 120 kg/ha
Remarks: 38%
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: every year
Remarks: the field is cultivated as minimal as possible
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | sowing maize, inorganic nitrogen | จัดการพืช | apr 2004 / |
| 2. | sowing winter barley | จัดการพืช | oct 2003 / |
| 3. | injection of slurry, herbicide paraquat | จัดการพืช | mar 2004 / |
| 4. | spraying herbicides | จัดการพืช | may 2004 / |
| 5. | harvesting, sowing winter wheat | จัดการพืช | nov 2004 / |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comparing to ordinary field operations, there are normally no additional costs if applying the new technique. The farmer will not plough anymore, this is an economic benefit. In some cases and for some crops the farmer will use another machine, for example: the farmer will need a direct drilling machine for sowing sugar beets in stead of a normal sowing machine. In Flanders, always agricultural contractors are sowing beets (not farmers). The agricultural contractor will ask the same price for normal sowing machine as for the direct drilling machine. Although farmers have no additional costs, they get subsidies (80€/ha.year for shallow cultivation, 200€/ha.year for no tillage) from the Flemish Government for practicing the new technique - subsidies are mainly given to encourage the farmers.
Additional info: inorganic nitrogen - mar 2005 spraying herbicides - apr 2005 inorganic nitrogen - apr 2005 spraying herbicides - apr 2005 spraying herbicides - may 2005 spraying herbicides - jun 2005 inorganic nitrogen - jun 2005 harvesting winter wheat - aug 2005 injection of farm yard manure - sep 2005 sowing oats - sep 2005 broadcasting Haspargit - sep 2005
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
780.10
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: 10 %
Landforms: The main topography is a plateau (100 m above sea level) in which rivers are incised. The technology is applied at fields situated on the slopes between the plateau and the valley
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: The loess deposits which vary in thickness between a few dm to several m cover Tertiary sands
Soil texture (topsoil): 60% loam, 30% sand and 10% clay
Topsoil organic matter: 1,2%
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is only working with his own farm.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Because of reduced working time and lower fuel consumption.
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
special equipement
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
farmers opinion of a non-ploughed field
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
34
หลังจาก SLM:
16
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Also 21 before and 16 after
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More residues
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
4.47
หลังจาก SLM:
1
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Significant reduction in soil loss
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
biodiversity
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
more earthworms
use of herbicides
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Because of less runoff
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays about 49% of the farmers in the region are practising conservation tillage, whereas only 33% was doing it in 2001. At the beginning of the project 63% of the farmers intend to cultivate their fields in a conservative way into 3 years. (based on e
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| less soil erosion |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology clearly reduces the erosion risk while maintaining profitability. |
| The new technology also has other benefits on soil structure and biodiversity. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| high investment costs for buying new agricultural machinery | |
| more attention to crop damages caused by slugs and mice should be given | |
| Practicing the new technology requires a relative dry soil |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Practicing the new technology requires a greater skill of the farmers. | education, training |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SOWAP - Project. 2003-2006.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
www. Sowap.org
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [เบลเยียม]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล