Oyster Mushroom [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sabita Aryal
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Parale Chyau
technologies_1194 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Dahal Dikshya
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Karki Nabina
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Budhathoki Karuna
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ghimire Kishor
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Singh Yubraj
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
เนปาล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Neupane Shankar
Management Post Institution Lalitpur, Hattiban
เนปาล
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kathmandu University (KU) - เนปาลชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
District Agriculture Development Office, Sindhuli (DADO) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
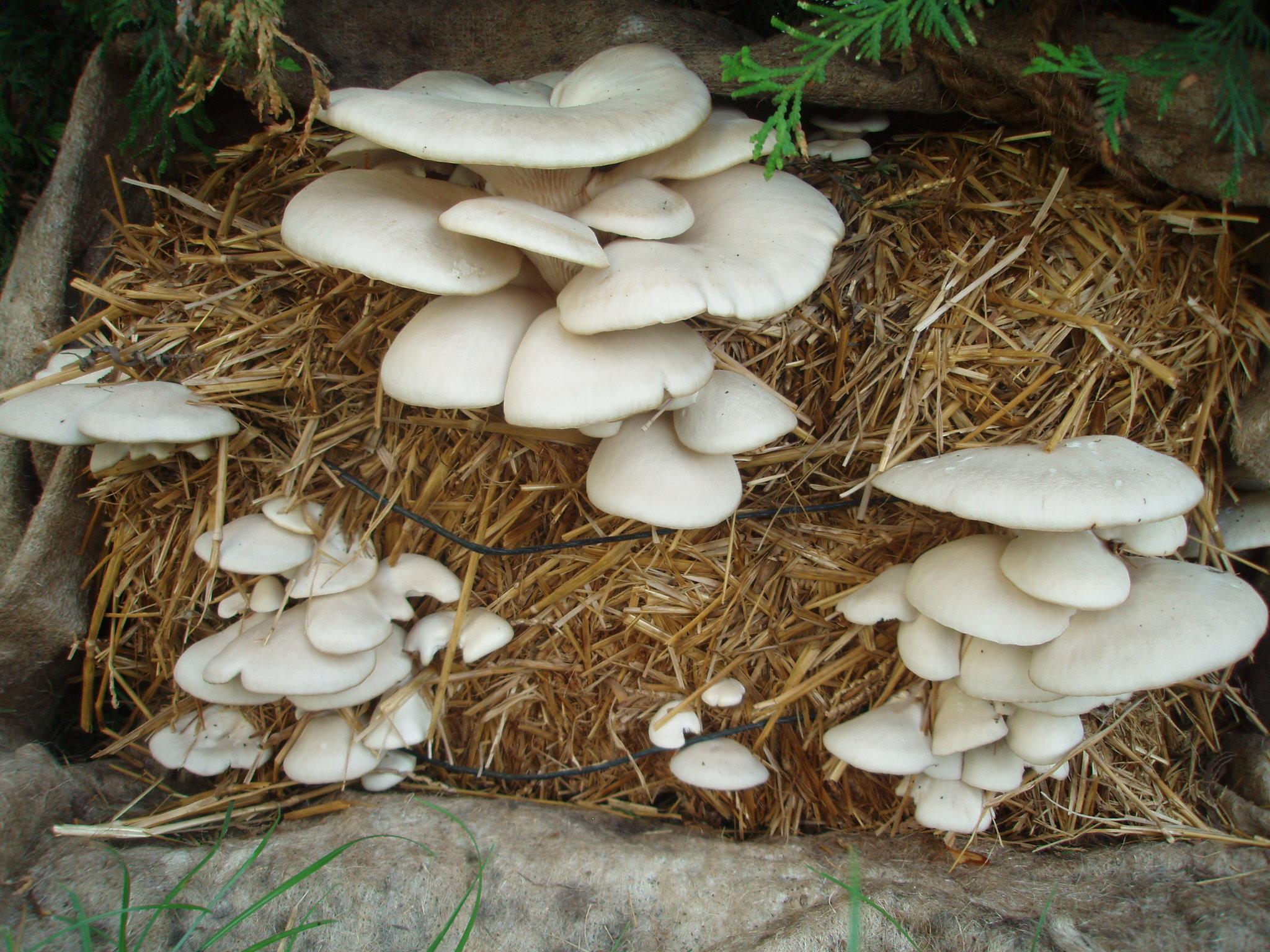
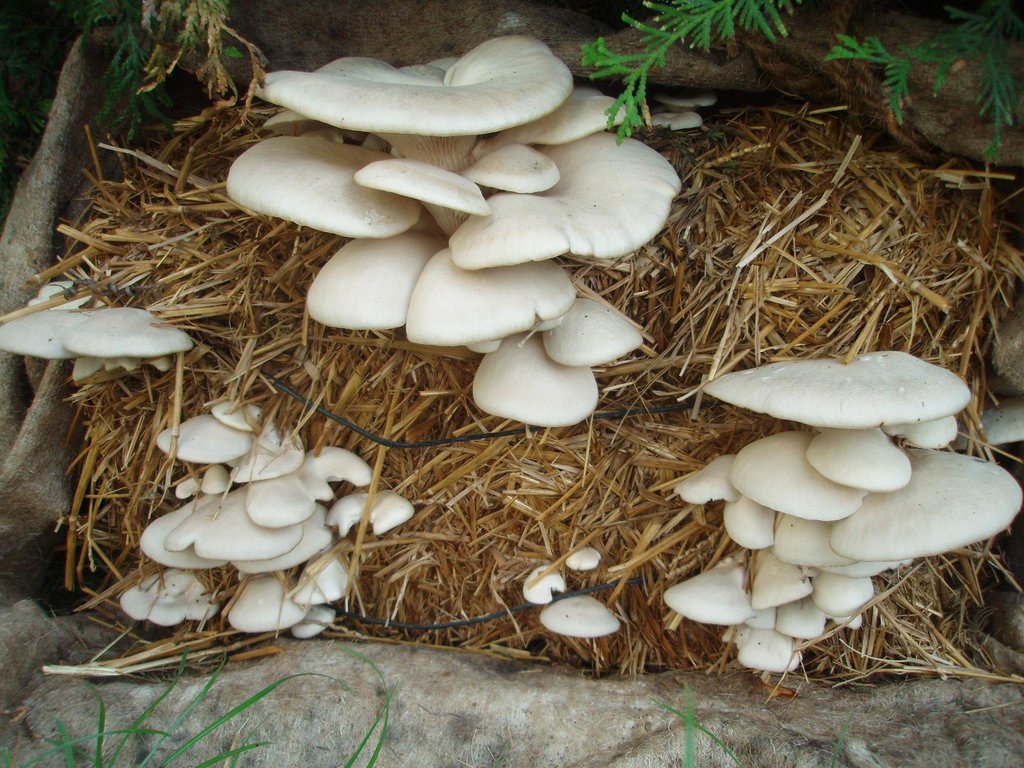
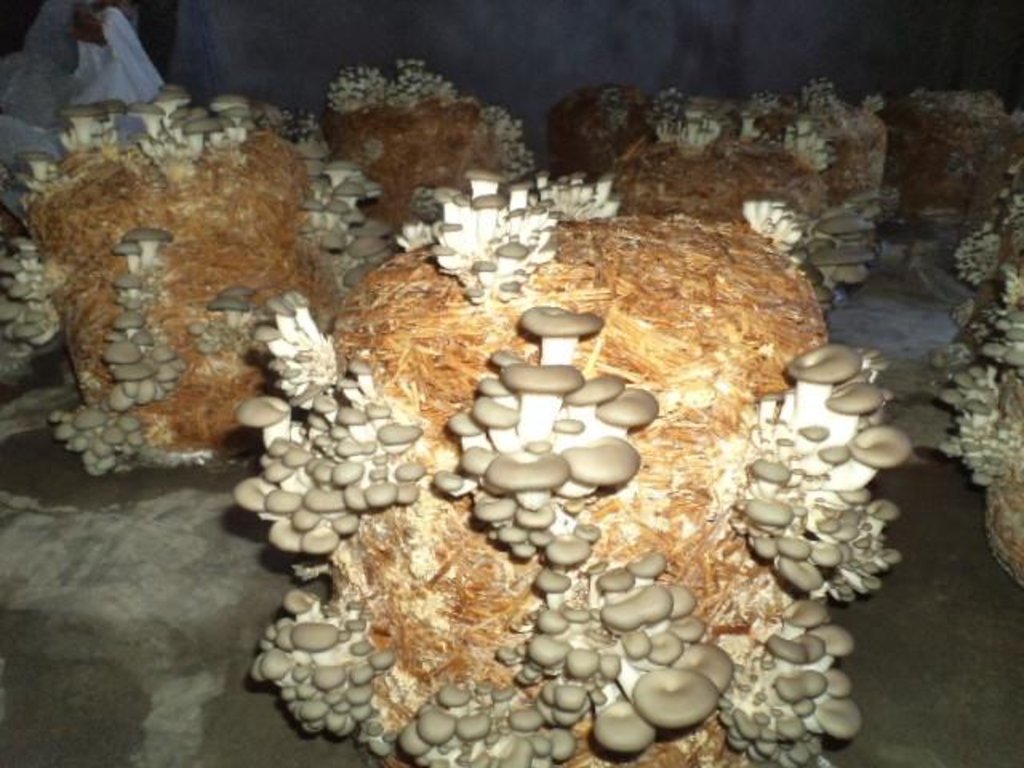
Oyster Mushroom Farming Technology is the cultivation of oyster mushrooms as a food source, economic source, and as primary compost, to increase the quality of soil and help upgrade living standards of local farmers.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
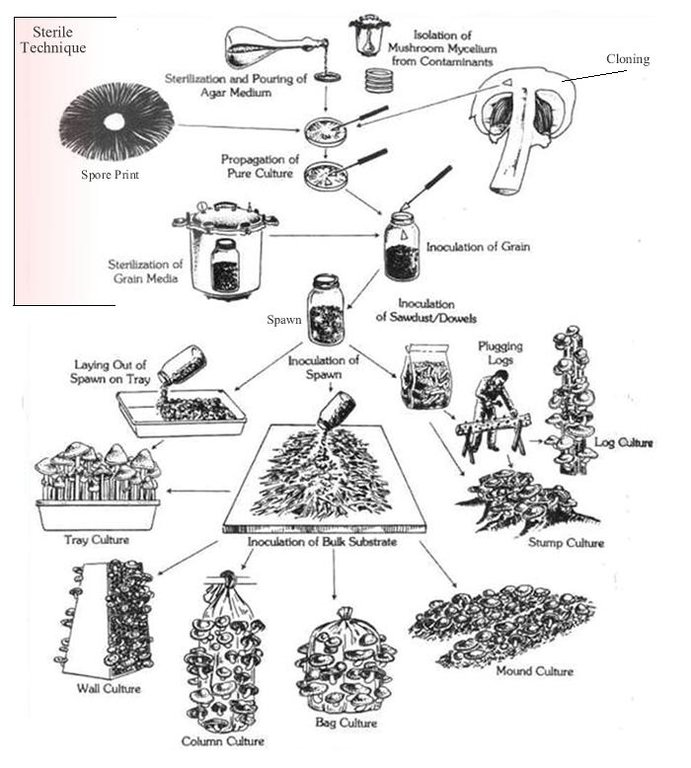
คำอธิบาย:
The technology is carried out in Kamalamai Municipality, Sindhuli District, Janakpur, Nepal. The Pennsylvania Department Of Environmental Protection (DEP), other regulator agencies and the community are at charge. Oyster were identified as being both economically viable and suited for local cultivation. Nepal Agriculture Research Council (NARC) and a few private organizations are the major resources centers for supplying the quality spawn to the farmer/growers.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this document is to provide uniform instructions and operating procedures for the use or disposal of mushroom compost (as soil amendment or conditioner). Another basic purpose is use of mushroom as food and income source for local farmers.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm
Community (1997) was developed as a result of realization among authorities of Pennsylvania DEP, to help people to understand that farms are operating according to the highest environmental standards, and will help improve coexistence with nearby residents, through environmental regulation. This implemented a mushroom farm development for specific operations with the natural resource conservation. The member co-ordination, knowledge, and experiences are critical in establishing the practices as workable and rational means to meet the goal of environmental protection and agricultural operation.
Natural / human environment: Mushroom Farm Environmental Management Plan (MFEMP) is designed to prevent pollution or danger of ground or surface water on common health, by helping in maintaining/improving the condition of soil, and prevent the pollution of surface water, groundwater and air, as well, at little or no cost. This technology helps local farmers to increase soil fertility and act as a good income source in small scale.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Janakpur
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Sindhuli
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12*18 inch.
The straw and spawn (mushroom) should be packed in plastic bags. Two or three inches of straw are packed into the plastic bag and the spawn is lightly sprinkled on top. This should be repeated until the bag is almost filled, the top of the plastic should be closed and holes should be poked in the bag.
Map
×2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
This practice was performed by American mushroom institutions in 1997 and earlier 1984.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low productivity of land, soil erosion, water scarcity, cultivation of land slopes, tillage resulting in soil loss.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Infertility of land, having to use fertilizers and pesticides, scarcity of water for irrigation, having to plow farm seasonally and repeatedly.
Constraints of recreation: Dark and moist environment is necessary.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 75; Longest growing period from month to month: January-March
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (soil erosion, low productivity of land, tillage), overgrazing (Fodder for domestic animals such as cow, buffalo, goat etc.), change in temperature (Uneven rainfall, long dry or cold seasons)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (terrace farming problems), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Use of timber for burning), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Only required vegetation was used), poverty / wealth (Medium to large scale production costly for local farmers)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
It is kept in a room with temperature 22-28 degree.
Location: Room. Sindhuli
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge on preparing substrate, incubation period and harvesting of mushroom and proper use of mushroom compost.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Since land usage is very less.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mulching
Material/ species: straw and spawn
Quantity/ density: 2:1
Construction material (earth): mud in cement
Construction material (stone): stone
Construction material (wood): wood plants
ผู้เขียน:
Nabina Karki, Karuna Budhathoki
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Rupees
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
90.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.00
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Straw | unit | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Container | unit | 1.0 | 990.0 | 990.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Fuel | unit | 1.0 | 125.0 | 125.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stove | unit | 1.0 | 770.0 | 770.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Plastic | unit | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Cutting Machine | unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2210.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 24.56 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Method of cutting straw | dry season |
| 2. | Warming the straw | dry season |
| 3. | Harvesting the mushroom | dry season |
| 4. | Maintainance of mushroom | dry season |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Method of cutting straw | persons/day | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 150.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1.67 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: plastic bag,water storage tank.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour should be managed properly.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
DADO Sindhuli, 2010
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Flat surface is needed.
5.3 ดิน
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil water storage capacity is medium: Mushroom need water daily two times.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: May face scarcity of drinking water in dry seasons.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Found mostly in eastern region, and almost in the western parts as well.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is no difference in involvement of men and women in this technology, both can be involved.
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is found that this technique is used even by people with little amount of land.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mushroom Compost usage
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Leftover straw
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Richer in nutrients than dry hay
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Little to no cost required
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mushrooms sold widely as food source
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Recreational method, provides options for farmers
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
1 or 2 individuals are enough.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cheap and easy way for earning money
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mushroom compost used instead of chemical fertilizers
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good way to utilize time, gain profits
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It has helped to increase knowledge
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Provide nutrients to plants
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Composting
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Composting
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mushroom: edible fungi
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Alternative mushroom composts
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology could be made more tolerant by keeping the room dark and warm (22-28 degrees), and carry out cultivation in almost all seasons (except winter).
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Yes, this technology can give both short-term returns and long-term returns.Positive result because it is the best type of production for the environment and economic resources.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
3 households covering 32 percent of stated area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
By government point of view almost all members of a village and city, both can cultivate this technology. 1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support. Comments on spontaneous adoption: Without external support also this technology can be carried out.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm Community
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is used as vegetable. |
| Waste water management |
| It is used as manure |
| Good income source |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Erosion and sedimentation control |
| Surface water and stormwater management |
| Economic purpose |
| Nutrient management for substrate utilization |
| Integrated pest management |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Place for growing | All locals do not have spare rooms or sheds for mushroom cultivation. This proves to be a huge disadvantage as they require dark room and moist conditions. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Less theoritical knowledge | Locals should be made aware about growing technologies that can help increase their quality of life. |
| Place for growing | Rooms or shed may not always be available. Providing darkness during can be a problem. |
| Seasonal problem | Room temperature required is 20-30 degree Celsius. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล