Gully Rehabilitation [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kithinji Mutunga
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1488 - เคนยา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kiio Jacqueline
MOARD
เคนยา
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Kirimi Patrick
MOARD
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Gitau Mary
MOARD
เคนยา
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Erosion control by use of physical barriers and vegetative materials
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
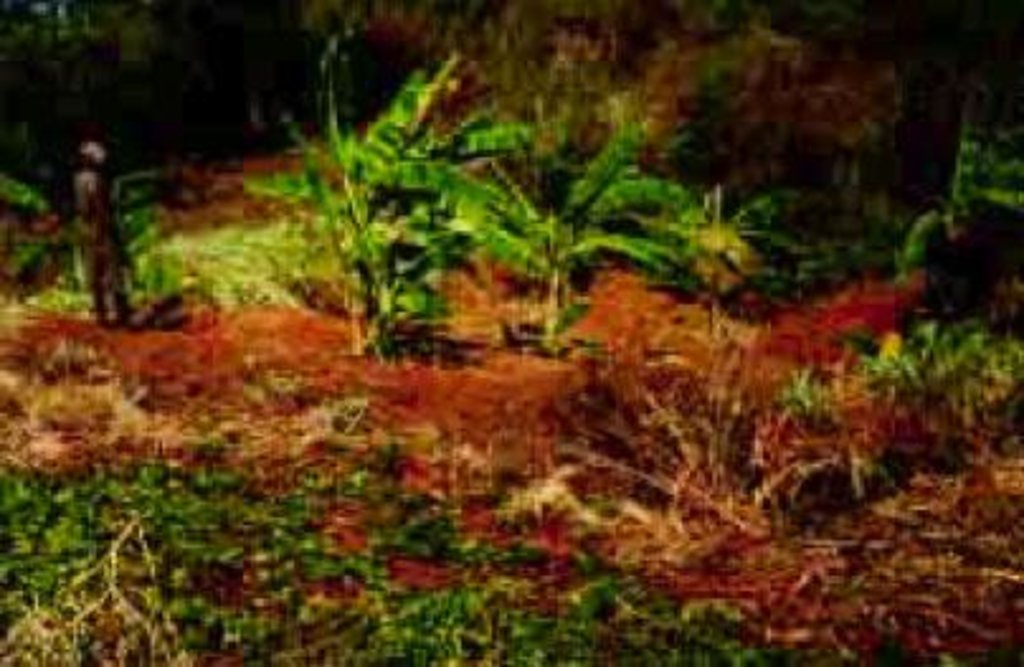
The innovation comprises control of gully erosion by use of constructed barriers (check dams) combined with vegetative materials. The end result is a stabilized gully that is prevented from advancing further. The system also involves fruit trees/banana establishment and fodder grass planting for structure stabilization. Establishment of the technology involves excavation of pits, planting fruit trees/bananas and grass cuttings.
Purpose of the Technology: This is a structural measure that is vegetated for stabilization. Its purpose is to rehabilitate a gully bed, through control of concentrated runoff by reduction of slope length and both trapping of runoff and sediment harvesting. The productive use of the innovation is mainly for perennial crops (fruit trees and
bananas) and for fodder production.
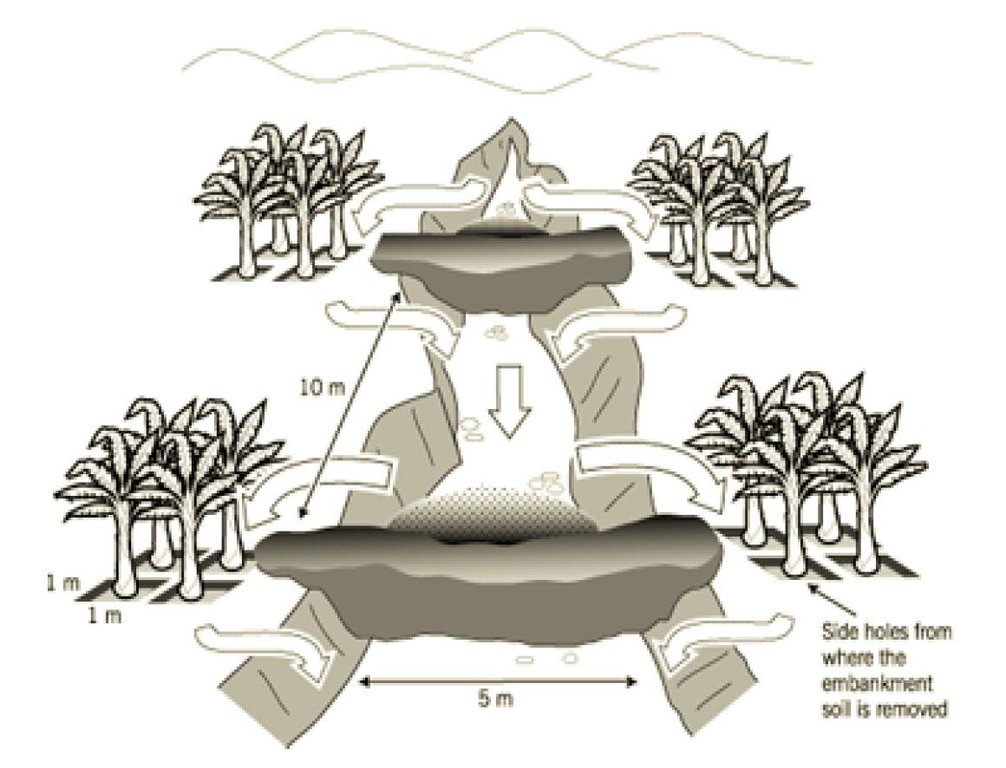
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Earth check dams are constructed in the gully, using borrow spoil from square pits in the walls of the gully (see diagram). The earth embankment of the dams are then stabilized with grass. Pawpaws are planted on the original gully floor. Initially the innovator left the pits empty: now she plants bananas in them.The 5 check dams, each 1 m or more in height, are spaced at about 10 m apart in the gully. The excavated pits are about 1 m x 1 m wide and 1 m deep. Four pits are dug separately on each side of each check dam. Makarikari grass (Panicum coloratum var. makarikariensis) is used for stabilization, while bananas and pawpaws are planted within the rehabilitated area. When it rains, runoff generated from the neighbouring plots upstream flows down and is slowed by the check dams. The runoff passes around both wings of each embankment, filling and flowing through the pits. Sediment is trapped in the pits. Excess runoff flows on to the second embankment, then through the second set of pits and so on. Only during heavy rains does water pass through and out of the system, though its velocity is reduced. Thus the gully heals slowly with time and vegetation becomes established. Regular maintenance work is required, involving repair of broken sections from time to time, using manual labour with a panga, shovel and jembe. Also of importance is manure application every season to the planted areas before the rains to sustain fertility and thus productivity.
Natural / human environment: Kalekye Mutua is a single household head in her mid thirties. Although she has no partner to help support her three children, she manages quite well through farming her 6 hectares of land - where she grows various crops and keeps a few local cattle. She had a small trading venture but has recently abandoned
this. Kalekye is not amongst the poorest in Mwingi, but represents a number of female-headed households who prosper through hard work and enterprise. In fact she even employs labourers part-time to help with the farming activities.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Eastern Province
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
a very small portion of the individual farm is covered by the technology
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
farmers own intiative
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 75 Second longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pawpaws (Asimina triloba)
Perennial crops species: bananas
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, overgrazing, declining soil fertility
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): low yields
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Gully under reclamation: note flow of runoff
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pawpaws
Perennial crops species: bananas
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Construction material (earth): Local soil excavated from pits on the side of the gully
Construction material (other): Grass for stabilization Makarikari grass prefeered
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
kenya shillings
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
70.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.14
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging banana holes | dry season |
| 2. | acquisition of grass cuttings | dry season |
| 3. | acquisition of banana cuttings | before |
| 4. | planting of grass and bananas | onset of rain |
| 5. | manure application | before the rains |
| 6. | Excavation | Dry season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | repair of broken structures | after rains /seasonally |
| 2. | weeding | during rains /twice /season |
| 3. | banana prunning | after rains /biannually |
| 4. | manure application | dry season /annually |
| 5. | Repair of broken sections | during /after rains/seasonally |
| 6. | Stabilization with grass | during rains/when required |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
1100 banana/ fruit trees holes/ha
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
slope, soil type, timeliness of operation
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
4% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: the are few members of the household who are in formal employment
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sale of bananas
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60
หลังจาก SLM:
10
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
610
หลังจาก SLM:
1
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
1 household
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Kalekye only started the innovation two years ago, and while there has been a policy of taking women’s groups to visit Kalekye, this is a relatively recent occurrence (starting approximately a year ago). Despite the visitors obviously being inspired, there have been no reports as yet of direct adoption of the technology.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Reclamation of land for production of fodder and bananas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Possible improvements would include planting improved fruit trees that are rapidly maturing and yield more: grafted mangoes for example |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High labour requirements |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Farm Management handbook of Kenya Vol II
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Ministry of Agiculture, Nairobi
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล