Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Kakawate as live trellis "balag"
technologies_1930 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Urriza Girlie
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Dela Pena Calixto
Local Government of Nagcarlan, Laguna
ฟิลิปปินส์
Soil Specialist / GIS Specialist:
Pine Baldwin
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
ฟิลิปปินส์
Engineer:
Raquid Jemar
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
ฟิลิปปินส์
Engineer:
Torino Mharicar
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
ฟิลิปปินส์
Engineer:
Tayao Aries
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
ฟิลิปปินส์
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - ฟิลิปปินส์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
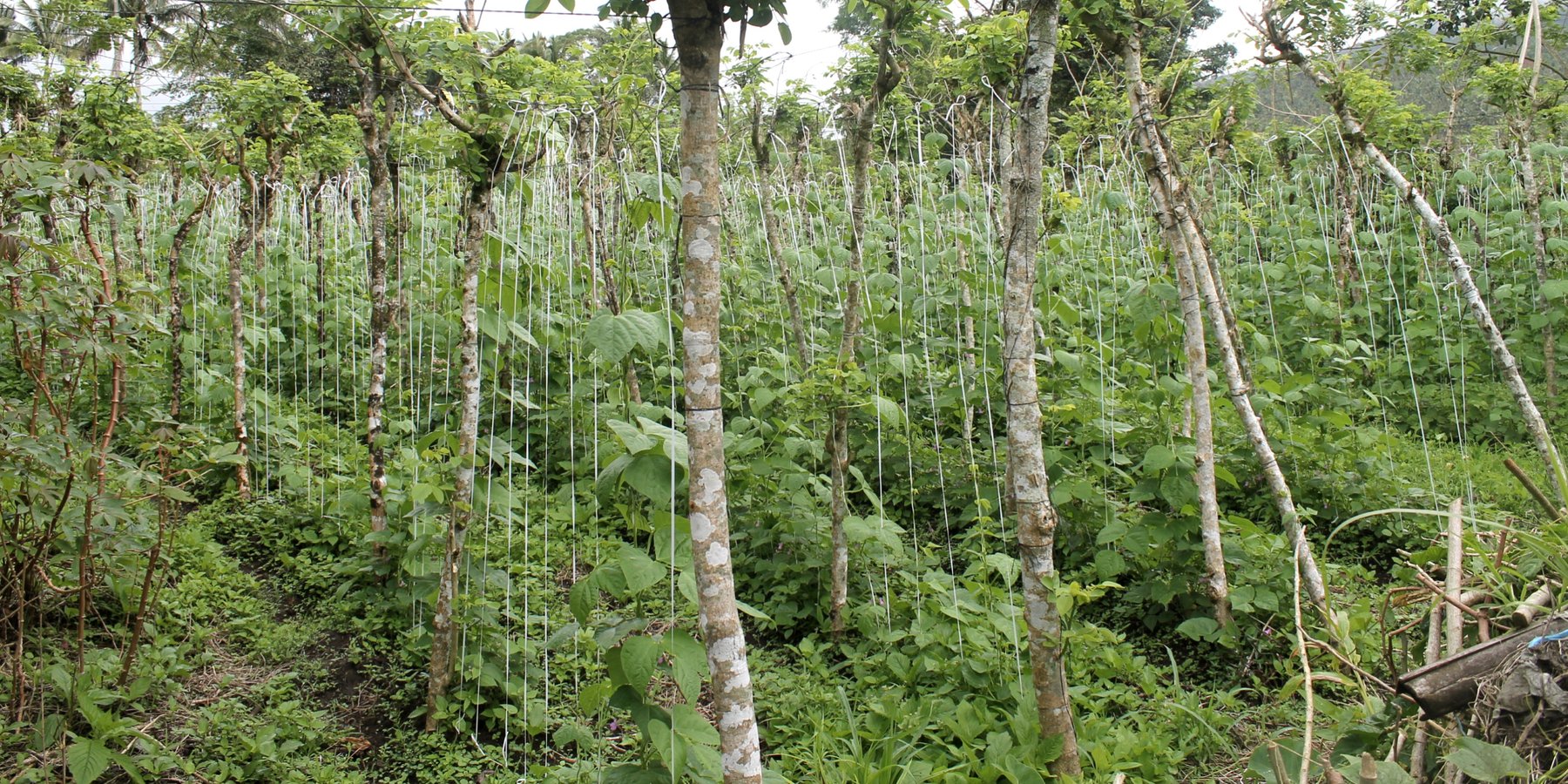
Gliricidia sepium locally known as "kakawate" served as live trellis / or anchorage for annual crops (mostly creeping-type vegetables) and erosion control measure. The technology is well-adopted in the community providing immediate food for the farmers and increased income due to diversified farming.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
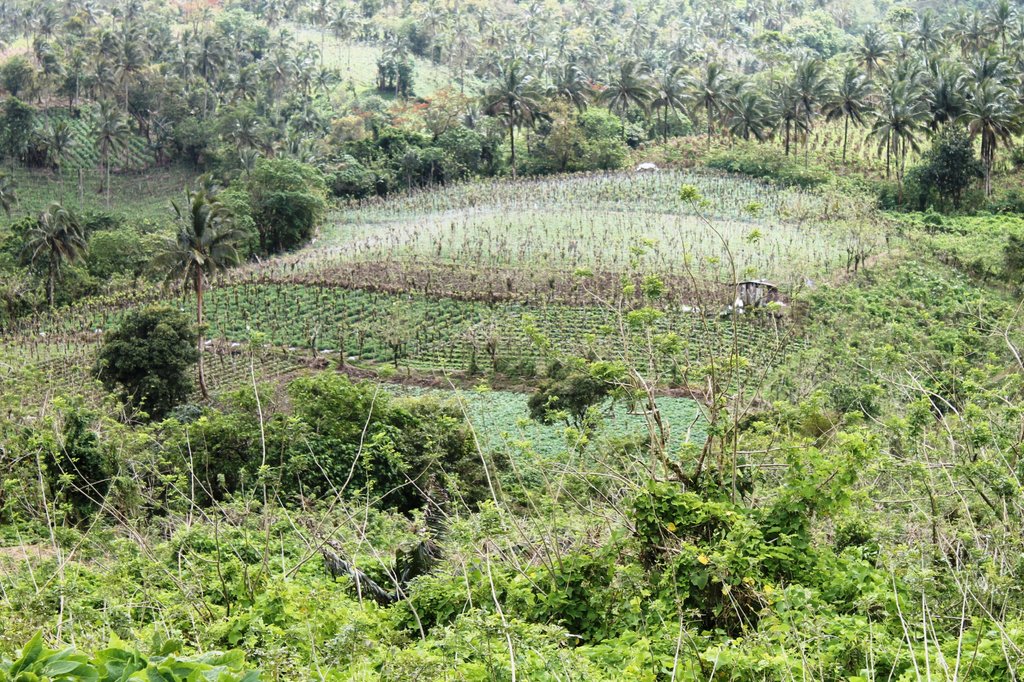
The Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System is a traditional or local farmers' initiative technology widely practiced in Brgy. Bukal, Nagcarlan, Laguna situated in the area of Mt. Banahaw. The area with rolling to hilly terrain is receiving an annual rainfall of 1000-2000 mm. Each of the farmers who practiced the technology has 0.5 to 1.0 ha production area. Moreover, the community is accessible to infrastructures such as schools and market. Soils in the area is relatively good for agriculture cultivation.
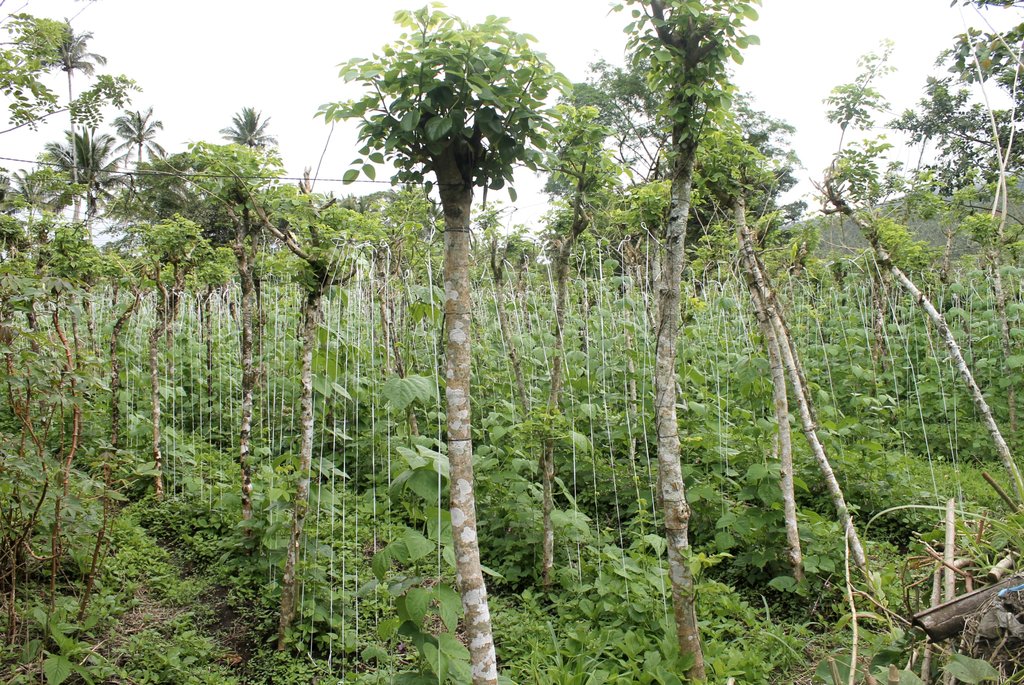
Kakawate, a small to medium-sized, thornless tree which usually attains a height of 10-12 m is being used as live trellis or "balag" to various annual crops such as tomato, cucumber, chayote, beans, and ampalaya in the community. The cropping system is highly diversified since crop rotation is being practiced throughout the year. Aside from being an anchorage for annual crops, kakawate also stabilizes sloping lands and reduces soil erosion due to its strong roots which can grow 3-5 meters laterally, thereby holding the soil firmly. They are planted in a row of approximately 2-3 meters making it more effective in preventing soil erosion. Furthermore, kakawate is being trimmed and maintained every 3-6 months or as needs arise to a approximate 3 meters high as live trellis, the trimmed leaves are very rich in nitrogen and will eventually serve as compost or crop cover. These will help in improving soil quality and moisture in the soil. In addition, kakawate has multiple uses and benefits; they can serve as hardwood or firewood when matured, as materials in making furniture and anchorage for flowering plants like orchids.
In establishing the live trellis system, kakawate trunks/or cuttings "quick sticks" with at least 2-meter height are planted in a row. An estimate of 0.5 to 1 meter planting distance within a row and also between rows is used. When the kakawate trunks are already set up and planted, they are interconnected using a metallic wires. Along these wires, plastic straws are tied in a vertical position whereby crops can utilize this straws for creeping/ climbing . Finally, the desired crop will be planted according to their cropping pattern. Maintenance of the technology includes: weeding and trimming. During infestation, application of pesticide is done but in minimal.
The technology requires manual works resulting to elimination of machines that contributes to soil compaction.
The technology has been a practice in the community for a long time, and land users continue to adopt the technology because of it's easiness and inexpensiveness to establish, and low cost in terms of maintenance activity. Adding up to this is the variety of plants to be grown, making their market more profitable.
Gliricidia normally grows in tropical countries like the Philippines and is being utilized as hedgerows for erosion control measures. Over the years, its effectiveness as erosion control is known, and an increasingly used forage crop in cut-and-carry systems.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Laguna
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Brgy. Bukal, Nagcarlan
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most of the farmers in the community adopt the technology
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
1950
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- legumes and pulses - beans
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- tomatoes
- Sayote (cf. Cucurbitaceae family), Kakawate (cf. Gliricidia sepium)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 3
ระบุ:
Cabbages and lettuce can be harvested three times a year.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Sayote, beans, tomato, cabbage, lettuce, Kakawate
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
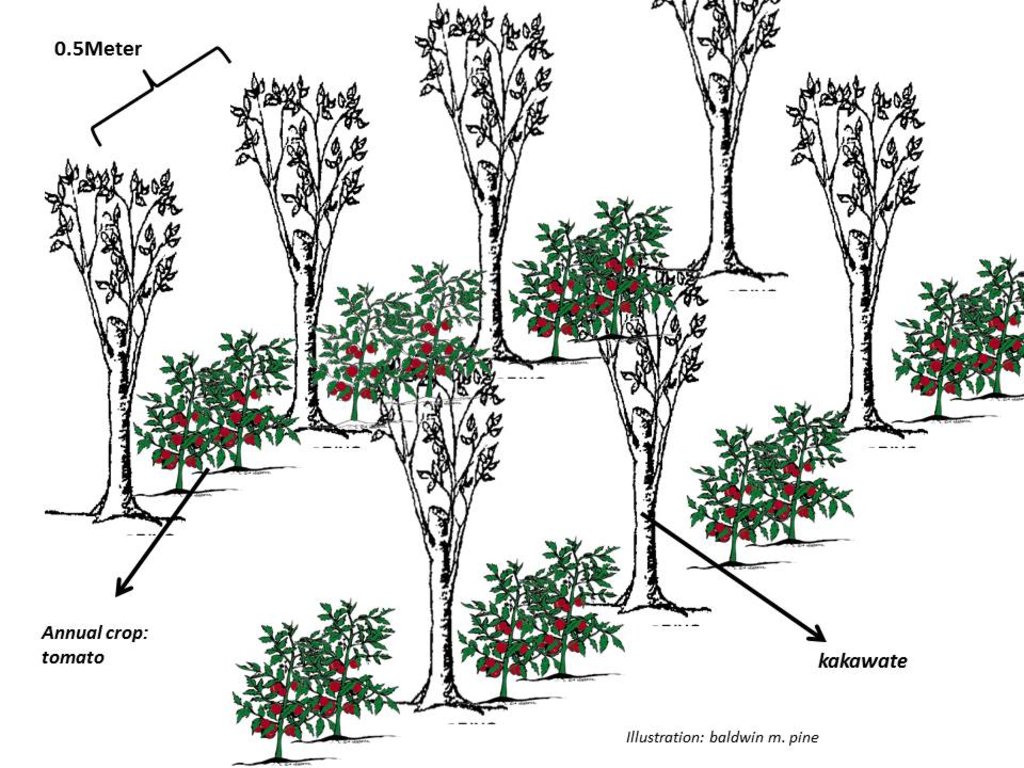
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Kakawate cuttings are planted with an estimated planting distance of 0.5 m to 1 m. They are trimmed and maintained at around 3 meters high for every 3-6 months or as needs arise. In between the kakawate are annual crops like tomato, chayote, beans,cucumber, lettuce and cabbages which are planted in rotation depending on the season.
ผู้เขียน:
Baldwin M. Pine
วันที่:
03/03/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
0.5 hectare
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Philippine Peso (Php)
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
50.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
300
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of the area | As needs arise or before planting of kakawate and annual crops |
| 2. | Planting of kakawate cuttings | |
| 3. | Installation of metal wire and plastic straws | |
| 4. | Planting of annual crop: tomato | First cropping usually from December to March |
| 5. | Planting of annual crop: cucumber or beans | After harvest of the 1st crop (tomato) usually from April to June |
| 6. | Planting of annual crop: chayote | After harvest of the second crop ( cucumber or beans) usually from July to December |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Manual labour: Weeding | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Manual labour: Planting | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Manual labour: Fertilizer Application | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Manual labour: Harvesting and Hauling | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Kakawate cuttings (cuttings are abundant in the area and not for sale) | 100.0 | ||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Tomato @ 100grams per can | can | 1.0 | 1950.0 | 1950.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Cucumber @ 100grams per can | can | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Chayote (seeds are abundant in the area) | 100.0 | ||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Inorganic fertilizer: Urea | bag | 5.0 | 1500.0 | 7500.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Organic fertilizer: chicken dung | bag | 5.0 | 450.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Pesticide | bottle | 1.0 | 280.0 | 280.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Metal wire ( can be used for a long time, up to 10 years life span | roll | 6.0 | 480.0 | 2880.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Straw | roll | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 20060.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 401.2 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | As needs arise but normally twice per cropping per crop |
| 2. | Trimming of kakawate | As needs arise |
| 3. | Application of organic fertilizer | Once per cropping |
| 4. | Application of inorganic fertilizer | Twice per cropping |
| 5. | Spraying of pesticide | As needs arise |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Weeding | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Trimming of kakawate | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Application of organic fertilizer | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Application of inorganic fertilizer | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spraying of pesticide | person-days | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4500.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 90.0 | |||||
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1500.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
pH is 6.59
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
An increase in production due to crop diversification
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Organic farming is a common practice in the community, and with this, it aids in the development of crop quality.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Kakawate are being utilized as forage crop for ruminants in the area.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Kakawate is rich in Nitrogen.
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Kakawate when matured can be utilized as firewood and materials for making furnitures.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop rotation makes the technology diverse.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The area is maximized for cultivation at a minimum soil disturbance.
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The application of inorganic fertilizer is minimal due to organic farming.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers' income is increased due to crop diversicification
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers' income is increased due to crop diversicification.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The continued adoption of the technology testifies that SLM and/land degradation knowledge is improved in the community.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Kakawate when left on the ground aids in the improvement of soil moisture.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop rotation practice improves soil cover.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Over the years, kakawate is proven to be an effective erosion control measure in the sloping areas.
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Manual cultivation aids in minimal disturbance of the soil, thereby does not contribute to soil compaction in the area.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Organic farming is a practice in the community.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop rotation helps in the decreased of pest population.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology requires manual cultivation with least or no machine intervention, organic farming is a must with minimum usage of inorganic fertilizer, and biodiversity is also encourage. With that, the technology is believed to be effective to address carbon emission and greenhouse gases.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
Almost all of local farmers practice the technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
(1) Increase farm income (2) Diverse farm produce (3) Easiness to establish, no need for technical knowledge to establish (4) Inexpensive (4) Organic farming |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
(1) Low production cost (2) Easiness to maintain (3) Effective erosion control measure (4) Increase farm yield and income (5) Diverse farm produce (6) Easiness to transfer |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| (1) Pest infestation | (1) Pesticide application |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| (1) The technology is very good in terms of erosion control and improving lives of farmers in the community, but then the technology is not well-known for the whole country. | (1). The WOCAT database as an excellent information tool /or medium in the dissemination of this kind of technology, not only within Philippines but all over the world. These would highlight initiatives of the local farmers situated in remote areas in terms of managing the land productively and sustainably. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Two infomants: Local Government Unit (LGU) technical staff and the land owner
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Two infomants: LGU technical staff and the land owner
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
One LGU technical staff
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
03/03/2017
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล