Pond development in wetland areas [ลาว]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: kang phanvongsa
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Bounthanom Bouahom, Pasalath Khounsy
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Nicole Harari, Oulaytham Lasasimma, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2905 - ลาว
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Inphet Amthae
ลาว
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
keosonghueang tulan
ลาว
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - ลาว1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
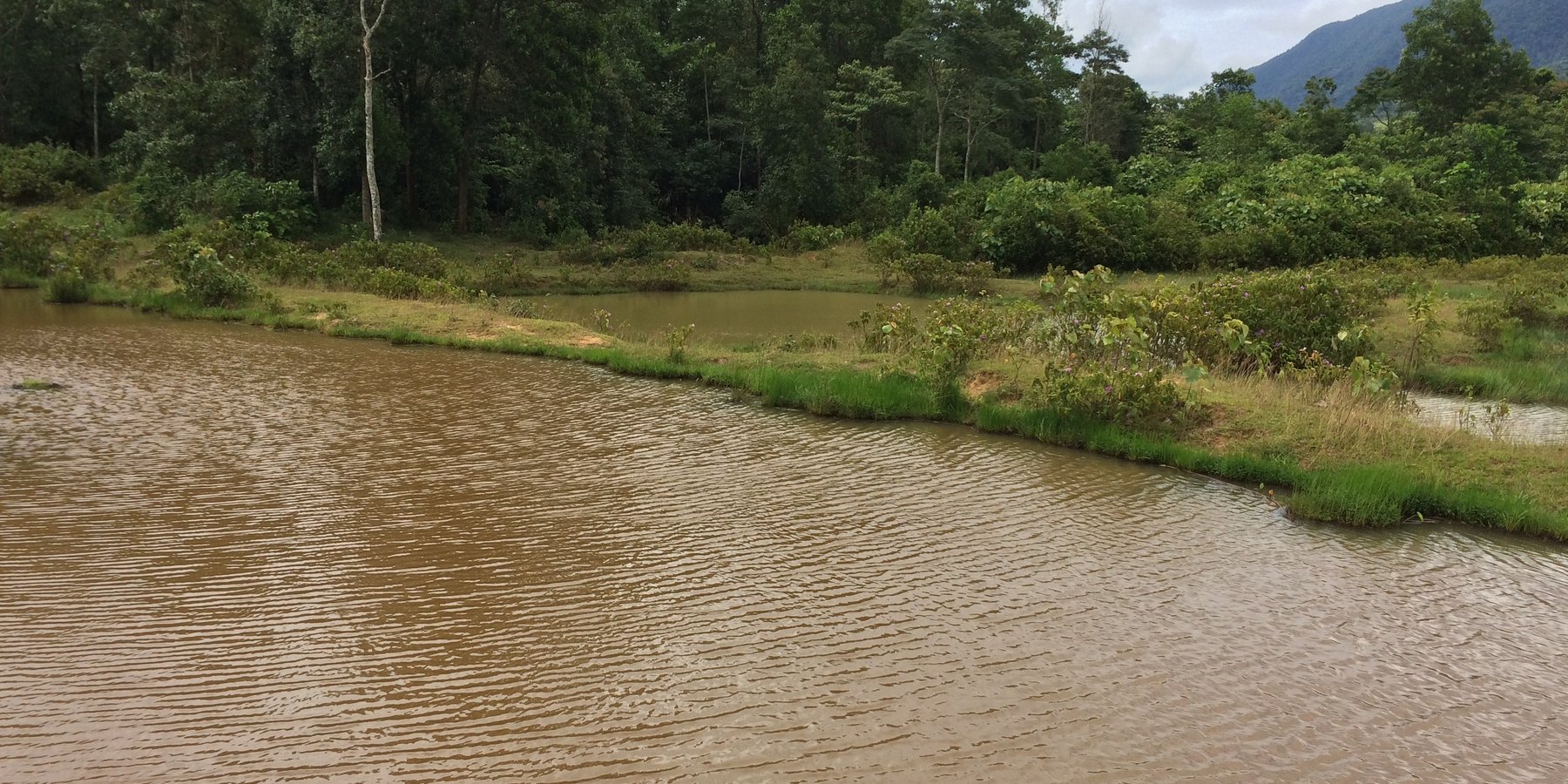
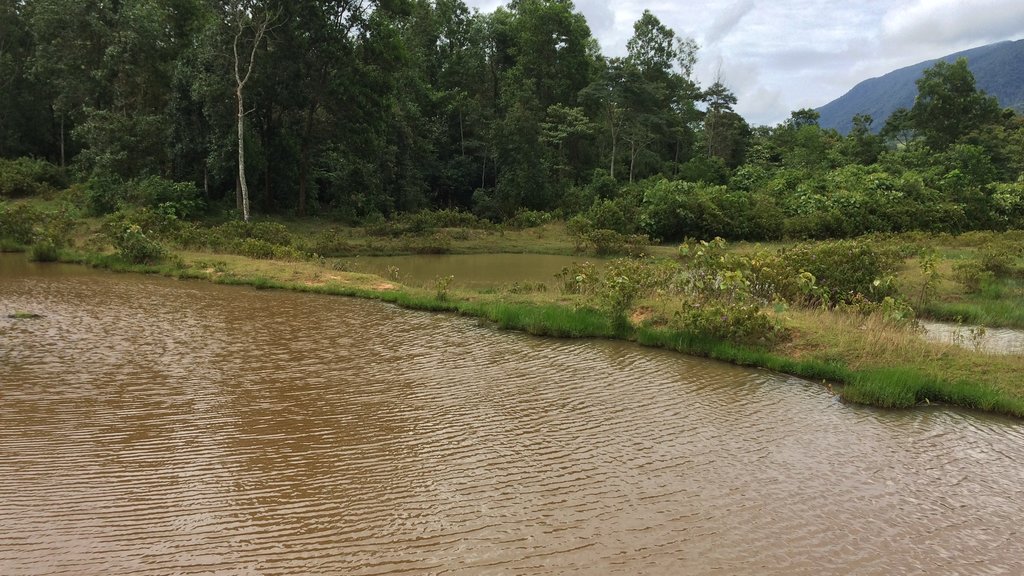
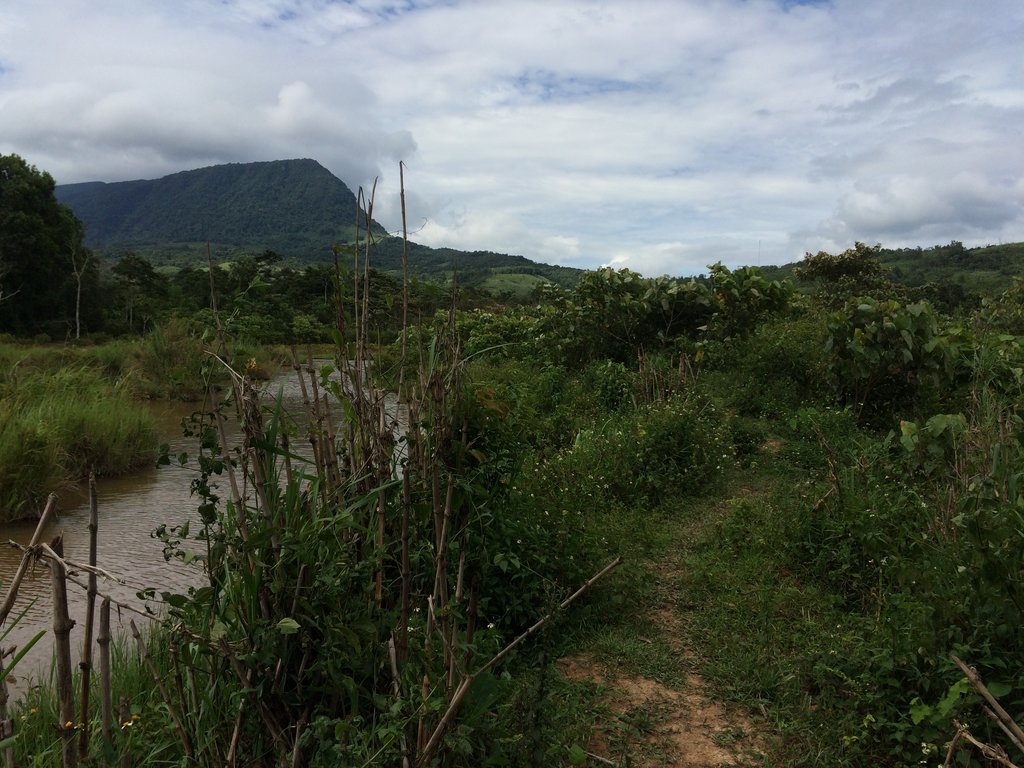
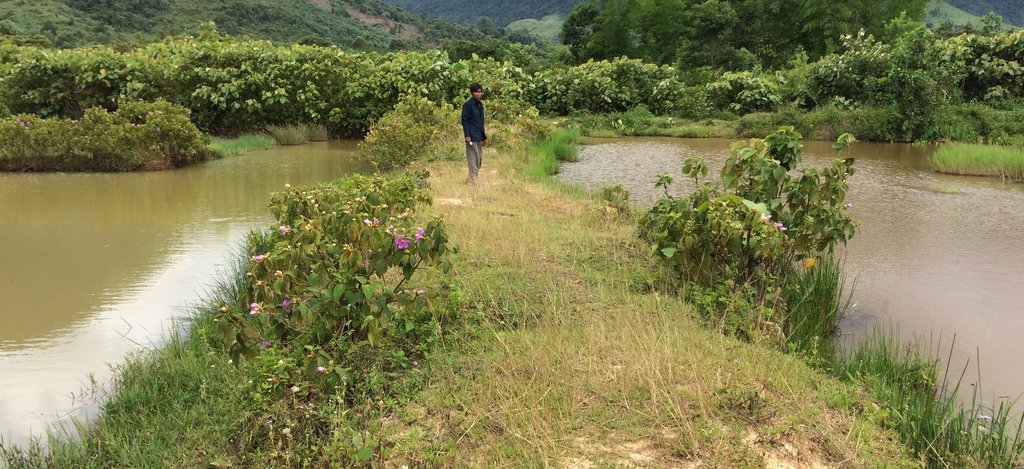
Conversion of wetland plots into fishpond.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
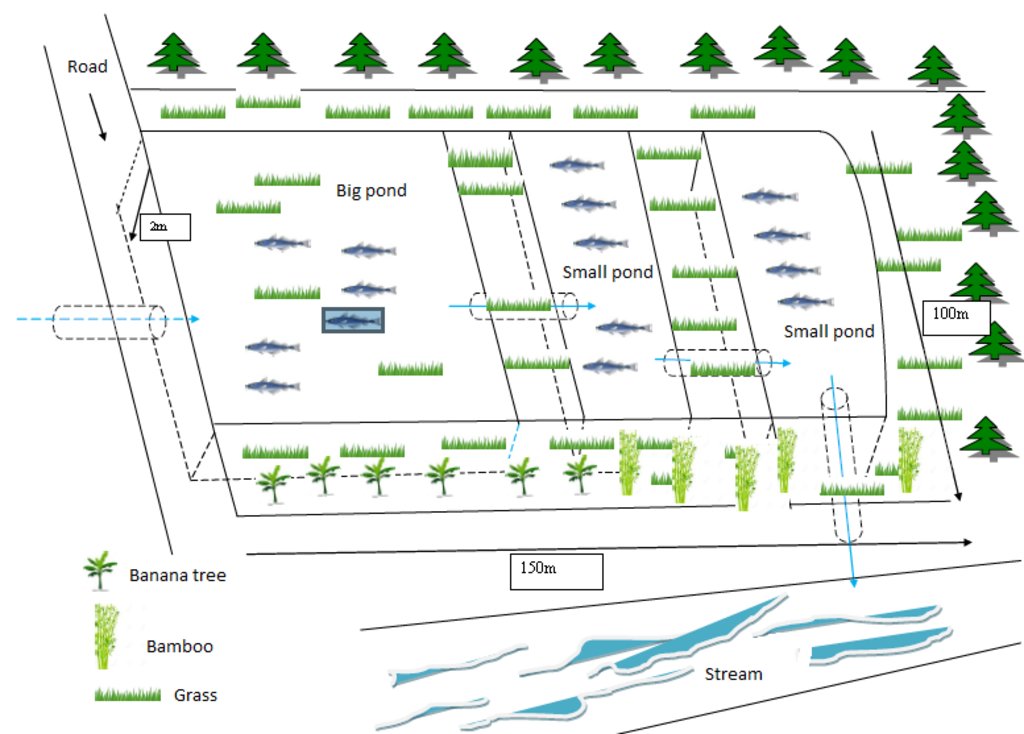
At Asoy village and its neighboring villages in the Salavan Province of Lao PDR some rice fields were regularly flood prone during rainy season (August ̶ October) because of a newly constructed road containing culverts leading first through the rice fields and then into natural water ways. Therefore, in 2005 one of the village's land users spread the idea to convert this regularly damaged and increasingly unproductive rice land into fish ponds. The soil texture in this area is mostly clayey and therefore also generally not very suitable for agriculture, but certainly appropriate for water holding throughout the year. Thus, the main objective of these pond constructions was the raising of fishes for income generation and for getting water for household purposes during dry season; e.g. for gardening, fodder production, and for banana and bamboo cultivation along the edges of the pond dikes. The fishpond should also provide water for livestock such as cattle, buffalo, and poultry farming. The construction of the ponds in the case documented here started by shutting off the culvert at the inlets by using sawn wood and clay to close the concrete pipe (Ø80 cm) crossing the road. After, vegetation clearance was required by using a bulldozer. A backhoe then was applied to excavate an area of 1.5 ha to create a first big pond (150 m long and 100 m wide). The excavated soil was used directly for the dike construction. The dikes were around 2.5 m high and 2 m wide. For the first big pond only two dikes had to be shaped because the other two sides were road and fallow. At completion of the big pond, two smaller ponds have been constructed also by backhoe directly next to it. The first of them encompasses an area of 2,000 square meters (20 m x 100 m) and the second 3,000 square meters (30 m x 100 m). After this, four new Ø40 cm drainage pipes were installed; a first one throughout the road leading into the first pond, two of them connecting the ponds and the last pipe is needed to lead the water finally into the natural water way. The pipes have to be installed at a height of 50 cm from the edges. To stabilize the ponds Napier grass, banana, and bamboo can be cultivated on the top of the dikes. Maintenance of the pond requires regular cutting of the Napier grass, which is done by hand. Also regular weeding of the dike’s edges is required, as well as the stabilization of the embankments by using timber and soil. Where repair is required, the timber can be placed vertically, and then filled out with soil. The ponds are hold and maintained individually by the land owner and the benefit of them is considerable. The annual fish production is approximately 1 ton , equivalent to 15 million Kip . The ponds also store water for utilization during dry season especially for the animals (cattle, buffalos, and poultries). The grass growing on the edges can serve as fodder for animals. Banana and bamboo shoots can be consumed and sold for income generation. Material from branches of bamboo trees is used for handicrafts such as baskets and bamboo sheets for house walls, etc. The fishpond improves the aquatic ecosystem habitats in the area. The pond provides spawning areas for a large variety of fish, shrimp, crab, and frog species. However, with changing climate and rainfall patterns it happened that the ponds dried up and the soil became hard with rapidly growing weed around the ponds. Plants such as Napier and banana that are cultivated on the edge of the dikes can die. On the other hand in particular years, there flash floods occur that can affect the dikes due to rapid water runoff; in consequence also fish and other aquatic species can be lost and crops can be damaged. Nonetheless, the land owners at Asoy village prefer this technology and want to expand and improve it, when they have capability or when support from external institutions can be expected (e.g. training in fish breeding and required equipment such as hapa fish net for fish nursery, air pump, dip nets and harvesting net). Finally, the fishponds have been expanded to neighboring villages as well.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ลาว
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Samoaui district, Salavan province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Asoy village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2005
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- บ่อน้ำ เขื่อน
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Fishs
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density : 5 buffalo, 7 goats, 30 pigs, 7 cows
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

อื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
Wetland
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Before implementation of the Technology this land was a wetland that is unsuitable for agricultural activities
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การเลี้ยงผึ้ง การเพาะเลี้ยงสัตว์น้ำ สัตว์ปีก ฟาร์มกระต่าย ฟาร์มหนอนไหม
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
- The dykes height is approximately 2.5m, and the water level from the bottom to the drainage pipe is 2 meters, and the canal width is 3 meters.
- The total size is 100m x150m
- Slope 3-5 %
- Water storage capacity 30,000m3
- Water storage area 1.5 ha
- Development inputs include land, concrete pipes, and sawn woods
- Fish species include: tilapia, grass fish, and crab
ผู้เขียน:
Phonesyli phanvongsa
วันที่:
05/07/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
1.5 ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
kip
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8500.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
50,000
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Close up the stream | before on set of rain |
| 2. | Exaction works at the bog wetland or seasonal flood prone area | |
| 3. | Build dykes (use backhoe) |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | person-day | 50.0 | 50000.0 | 2500000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | excavator | machine | 1.0 | 3000000.0 | 3000000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | hoe | piece | 20.0 | 50000.0 | 1000000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | shovel | piece | 20.0 | 30000.0 | 600000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | knife | piece | 5.0 | 20000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | fodder | bunch | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Fry | Fry | 2400.0 | 1000.0 | 2400000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 9660000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1136.47 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs for the driver is included in the hiring costs the excavator of the pond.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Canal maintenance | yearly |
| 2. | Canal reparation | yearly |
| 3. | Canal reparation | yearly |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | person | 6.0 | 50000.0 | 300000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | hoe | piece | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | shovel | piece | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | knife | piece | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | trolley | piece | 2.0 | 250000.0 | 500000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 930000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 109.41 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Cost for labour and backhoe service is the most important input.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
2000.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainy season from May to November, highest rainfall between July to October. dry season from December to March April (rainfall)
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Samoui Agriculture Office
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After ponds construction various crops can be planted on the dike of the ponds.
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Very rare
หลังจาก SLM:
1 ton of fish
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before, only small amount of fish was captured because the fish came only from natural water bodies. The farmer also increased the poultry due to the fish ponds.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before, only small amount of fish was captured because the fish came only from natural water bodies. The farmer also increased the poultry due to the fish ponds.
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
No management (bog wetland)
หลังจาก SLM:
fish farm management
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
water harvesting and fish production
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before they was only a not very suitable natural bog area that accumulated peat from dead plant material and contained only shallow water. After the pond construction the water was deep enough for fish production, drinking water for livestock and also for crop irrigation.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After completion of the pond the farmer has to buy costly fish breed every year from Vietnam (1000 kip/fry)
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before the pond construction the farmer produced only for reaching self sufficiency without any income from the agricultural production. After implementation of the technology the farmer got income from fish, crop and fruit at around 15 million kip/year.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Previously there is not any income from agriculture produce, after pond have been complete, they have many kind of produce for sell such as banana, vegetation, fish
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Previously the farmer relied on natural wetland without substantial maintenance work. Then after completing the ponds the farmer has to spend quite a lot of work time to maintain them properly.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After pond construction the family was able to increase food sedcurity and self-sufficiency as they got supplmentary fish, fruits and other crops for self-consumption. Futher, they were able to sale the products and by this getting money when required.
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The pond serves now as recreational site for fishing and swimming.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before, the water streamed though the land without beeing harvested. Since the creation of the ponds - which were surrounded by dykes - the water were collected and stored easily for different already mentioned purposes.
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil surface runoff and accumulate in down stream. the ponds can control and reduced runoff by by overflow, the sediment are accumulated on pond bottom
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are many kind of animals in the area including prey ( rats, fish, frogs...) and predators ( snakes, snake fish, bird...), all acting as a small food chain elements.
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The increase in animal types and animal species in the area indicates the increase of the habitat diversity.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูแล้ง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ปานกลาง |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ขยายออกไป | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Increased aquatic resources with a variety of species including crabs, shrimps, fishes, snails |
| Suitable to carry out agricultural activities all year-round including crops and animal raising |
| Increased food security and cash crop production |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Having sufficient food for the whole year from agriculture production such as crops and animals |
| Able to produce fry for individual ponds and distribute to others |
| Able to store water for agricultural activities (cultivation and animal feeding) during dry season |
| Able to generate income for households from integrated fishing practices |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of fund to maintain the ponds | Producing fry by themselves for sale. By this, creating fund for solid maintenance work. |
| Occasional floods cause repair work of the pond dykes | |
| Some times, occurring droughts run the ponds dry. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of expertise in fish raising and breeding | provide fish breeding training activities for local people |
| Lack of fund for fish raising and fish breeding (purchase of juvenile fish is needed) | provide equipment or fish breeds |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
1 place
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
2 persons
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
04/07/2017
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล