Sub-Surface Dams (SSD) [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Guyo Roba
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Brigitte Zimmermann, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter, Hanspeter Liniger, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_3340 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 22 มิถุนายน 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 7 พฤษภาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 17 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 15 สิงหาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Surface Dams (SSD): 5 ธันวาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 3 กันยายน 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Surface Dams (SSD): 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
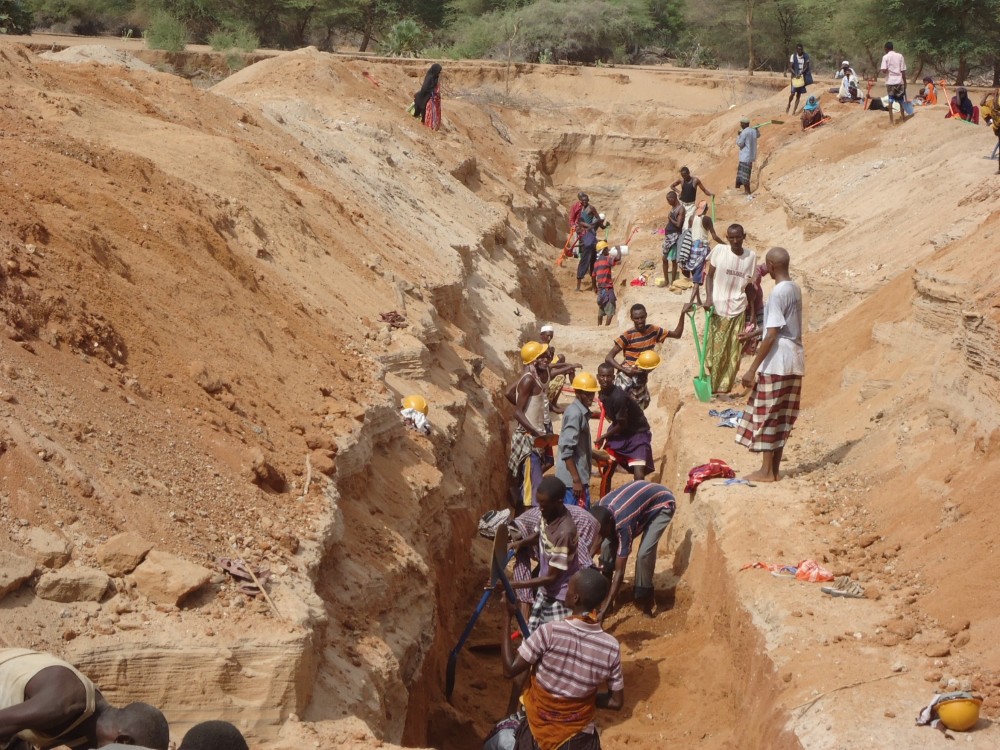
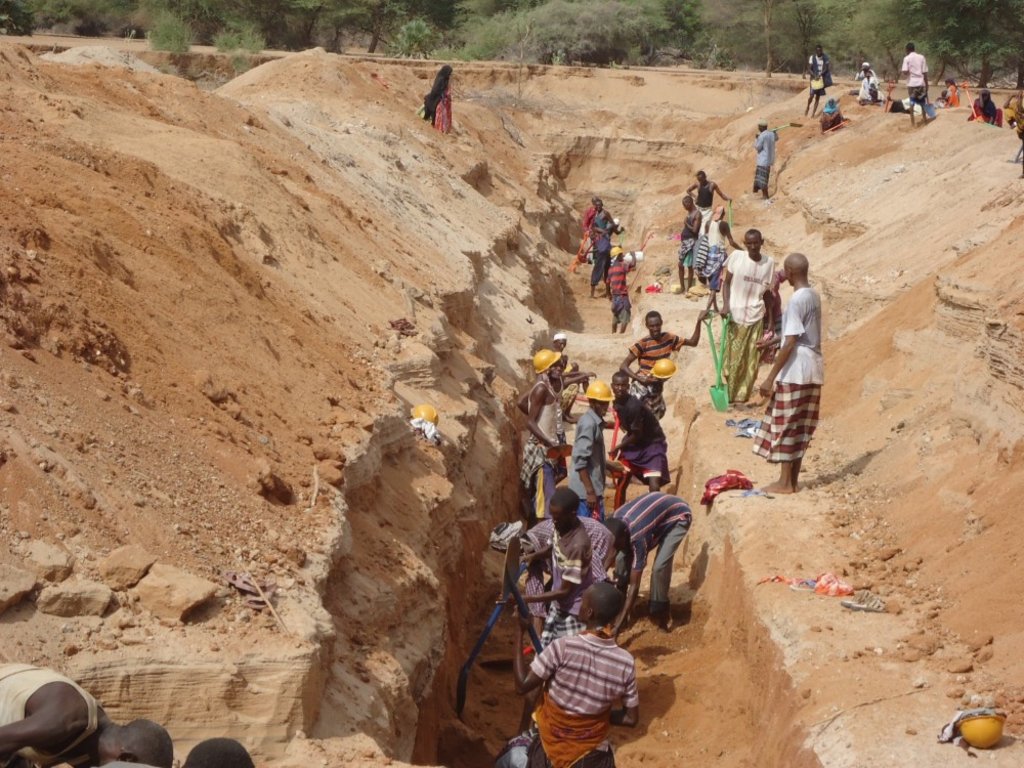
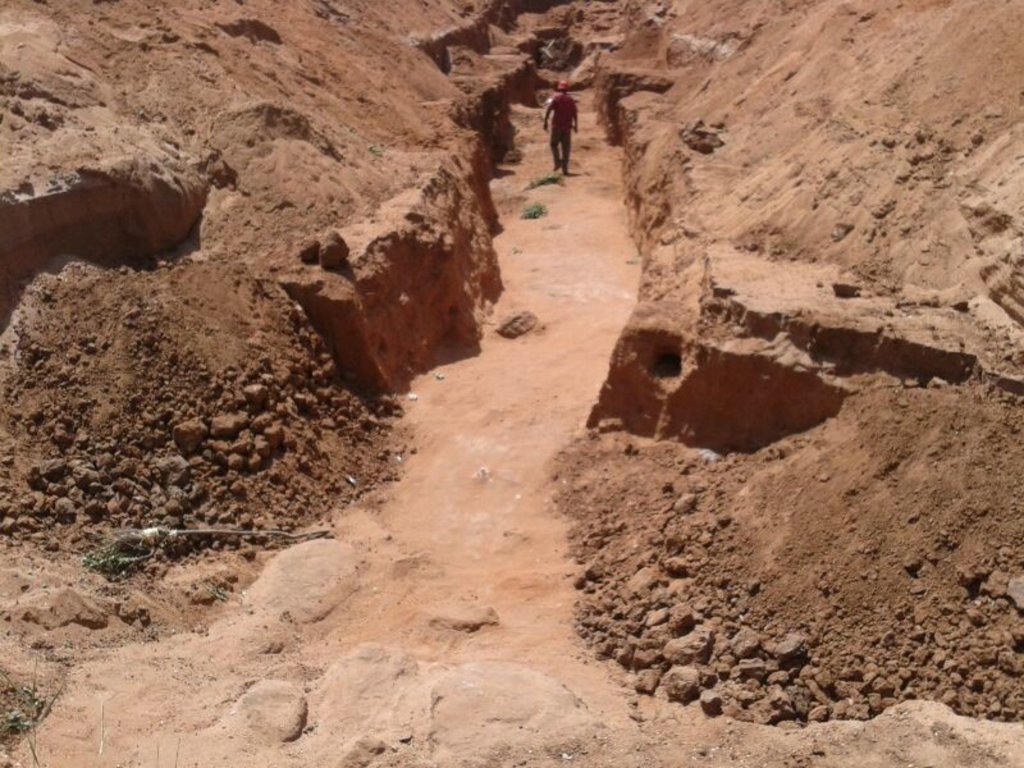
These are constructions stretching across the sand filled dry riverbed, down towards the impermeable floor of the riverbed. They are totally submerged into the ground. For example by fully covering after construction by sand. This are done along dry rivers with huge sand deposits, which has high yield potential and where water can be easily extracted. The aim is to raise groundwater tables and increase the storage capacity for water withdrawals.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
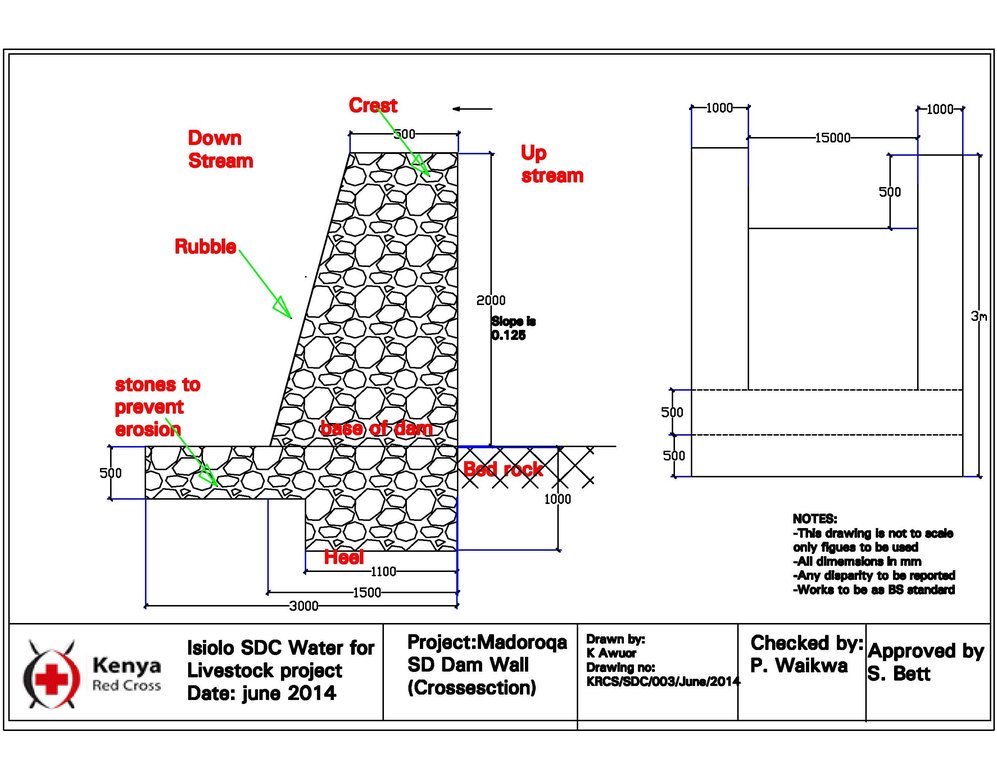
The technology is applied in northern rangeland of Isiolo County which is managed under communal management systems. The aim of technology to reduce pasture and water availability imbalances. The dimensions of sub-surface dam include: a length of water spread (103m),width of the dam (15m), width of water spread (18m), effective dam height (2m), volume of retained sand (103 x 0.5(15 +18) x0.5 x2.0 = 5098.50m3) and the volume of water that can be abstracted from the sand bed (25/100x 5098.50m3 = 1274.6.36m3).
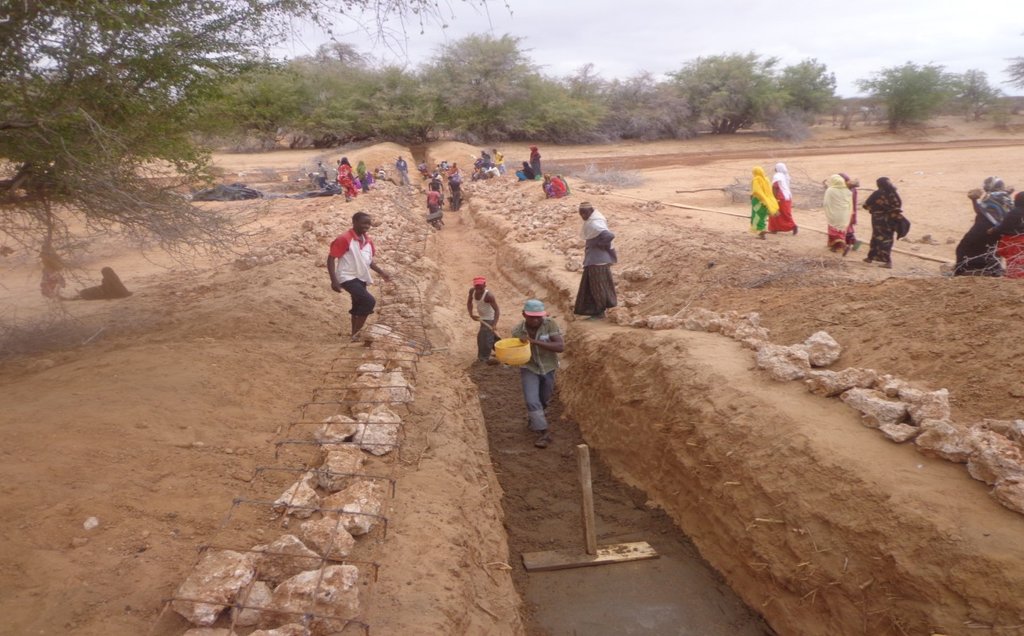
The technology functions as underground water storage infrastructure and the typical activities include, excavation of top porous soil, excavation of sample pits within the excavated area, checking filtration rates of soil, compaction of soil on which dam liners are laid, smoothing the sharp liners along which the dam liners are laid, making grooves to anchor the dam liner, laying the dam liner, anchoring the dam liner with a mixture of cement, water proof and sand with water (motor) and finally drying of the motor and filling back of sand.
The development of Sub-Surface Dams (SSDs) was done through Cash for Work program where local labours comprising of 40-50 persons are engaged in excavation, compactions and developing the liners. Farm tools like jembe, panga, spades and human labour are required to develop the SSD. The technology improves water supply/availability, thereby extending the period of livestock grazing in areas where typically water is depleted before the pasture hence improves water access for livestock in ways that support wider management and utilization of the rangeland and as such strength the resilience of pastoralists to droughts. This effectively gives pastoral groups, an extra grazing time (typically 2 extra months), a period usually not too long to encourage land degradation through over-grazing but long enough to enable pastoralist utilize the remaining pasture in wet season grazing areas. In so doing, the technology enable balanced use of vast communal lands without livestock retreating to dry season grazing areas.
In the process of the landscape level participatory planning with the communities: i) they identified different challenges, including need for decommissioning certain water points that they consider are contributing to over grazing and also attracting other communities, hence drive frequent conflicts, secondly, ii) they mapped areas in the rangeland where there is mismatch between water and pasture availability, most of these areas are in wet season grazing areas. So the next discussion was on what strategic water infrastructures that will enable herders to graze for 2 -3 extra months to enable them utilize the grass before they migrate to the traditional dry season grazing areas. So by design, the technology should only yield water that can allow settling for those extra months, not longer to the detriment of the rangeland
The technology was instrumental in fostering both balanced utilization of land and strengthening sustainable use of the vast rangeland by ensuring that herders utilize available pastures in the wet seasons grazing areas before moving to dry seasons grazing areas. The water stored through the technology stays longer, in this case study, the water lasted for 5 months after the end of the rainy season .
The area receives bimodal rainfall, long rain in March-May and short rain in November-December. With changing seasons/climate, the dry seasons can last up to 1 year in case of rainfall failure. Typically, dry seasons are 6-7 months (May- November).
Normally, the water is depleted within 2 months after the rainy period. The technology is also cheap and easy to understand and construct (especially in areas with clay as the underlying impermeable material) with a possibility of the communities to be taught how to identify suitable site and the entire process of construction. However, in areas without clay soil, the excavation of clay and transportation can be labour intensive and expensive.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Northern Kenya
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Garba Tula, Isiolo County
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Map
×2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Communal grazing area that is shared by 2 and more pastoral groups
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Mismatch of pasture and water resources - there are areas where pastures are plenty but surface rain water is depleted earlier than pasture.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The SSD technology increase water availability is period immediately after the rain, hence ensuring better pasture utilization and more sustainable use of land.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
chamber
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.5 USD per day
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removing sand over dyke and man-days for excavating and transporting soil to dam site | 21 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 2. | Building and compaction soil in dam wall | 3 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 3. | Supplying water for compaction | 0.5 day for 45 casual labourers |
| 4. | Back-filling sand on dam | 1 day for 45 casual labourers |
| 5. | Supplying water for compacting clay in dam wall | 2 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 6. | Compacting soil and placing liners | 12 days for 45 casual labourers |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The construction of SSD was done through “Cash for work” which is participatory process that involves community mobilization, identification of beneficiaries and formation of “Cash for work” committees, registrations and verification of beneficiaries and implementation/supervision of the work.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | tools - jembe, spade etc. | pieces | 80.0 | 5.33 | 426.4 | |
| แรงงาน | Removing sand over dyke and Man-days for excavating and transporting soil to dam site | per day | 945.0 | 4.0 | 3780.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Building and compaction soil in dam wall | per day | 135.0 | 4.0 | 540.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Supplying water for compaction | per day | 22.5 | 4.0 | 90.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Back-filling sand on dam | per day | 45.0 | 4.0 | 180.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Supplying water for compacting soil in dam wall | per day | 90.0 | 4.0 | 360.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Compacting soil and placing liners | per day | 540.0 | 4.0 | 2160.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 7536.4 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As stated, the cash for work approach means that people get paid 4 USD per day for working on SSD until completion. There are phases where people participated in preliminary phases in meetings and consultation without payments but the actual work was done on cash for work basis.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of communities to manage and maintain the structures | yearly |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour for site protection and maintenance of hygiene | per site | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1000.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water User Associations on the sites are trained on the management of the structures on behalf of the community e.g. on the protection of structure and hygiene maintenance.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Distance of the sub-surface dam from villages, extent of destruction by floods and human activities
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
because of the climate change, the rainfall is becoming more erratic.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Isiolo
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
การจัดการที่ดิน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology copes very well with floods as the construction is embedded in the sand and thus very well protected.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology has limited running and maintenance costs once its done fairly well.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology created opportunity to graze in wet season grazing areas for an averge extra 2 months period after rainy seasons. The technology has provided additional water that gave herders extra days to graze in wet season areas and utilize the pasture that would have been unutilized due to water constrains. In so doing, the land users utilized the pasture without retreating to traditional dry season grazing areas. |
| The extra grazing months has reduced overall livestock mortality during droughts and also improved resilience of pastoral community. |
| The distance travelled and effort required to access water was reduced. Community members reported reduced distances covered and time spent in search of water for livestock. In some instances the distance reduced from 12-15 Km to 3 Km. Community members also mentioned reduction in conflict incidences over water resources in some areas due to adequate supply of water as a result of construction of water infrastructure. |
| The balanced utilization of the grazing area through SSD water provision, enables herd to graze in wet season grazing for slightly longer period and utilize pasture optimally, this however, does not mean that during that garzing period, there will be overgrazing. The volume of water available restricts the number of animals sustained by the grazing area. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology has created an opportunity to optimally use the grazing area and overall reduced land degradation. The technology Improves access to water for livestock in ways which promote more sustainable management of rangeland resources and as such strengthening the resilience of local communities. |
| The validation process prior to construction of the SSD is draws critical lessons of identifying and agreeing on where to construct the SSD in a way that fit within broader sustainable rangeland management in a manner that ensured sustainable and efficient utilization of pasture and browse resources in targeted areas. The increase in water supply allowed livestock to graze additional 2-3 months in target areas before shifting to dry grazing areas where previously they migrated before exhausting the pasture and browse resources due to water scarcity. The dry season grazing area is towards Merti, in Kom and Sabarwawa where there are deep boreholes, under, lock and key and only opened during dry seasons. In typical year, the dry season period is about 7 months. But when one rain season fail it goes to about 11 months. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| When the construction season for SSD is not well planned, there is likelihood/risks of the dams being washed away by flash floods. | Better planning and timing of the development of SDD, just slightly before the onset of rainfall. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
11/01/2018
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Promoting resilience by influencing water infrastructure development in community managed rangelands of Kenya
URL:
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2014-088.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Balancing water infrastructure in community-managed rangelands in the arid and semi-arid lands of Kenya
URL:
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2014-089.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล