Afforestation with mangrove plants to protect land degradation [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Fazlay Arafat
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Mutasim Billah, Md. Arfanuzzaman
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Upokuliyio Bonayon
technologies_4300 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Hossain Md. Kamal
Bangladesh Forest Department
บังกลาเทศ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Hussain Md. Jobair
Bangladesh Forest Department
บังกลาเทศ
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - บังกลาเทศชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - บังกลาเทศ1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
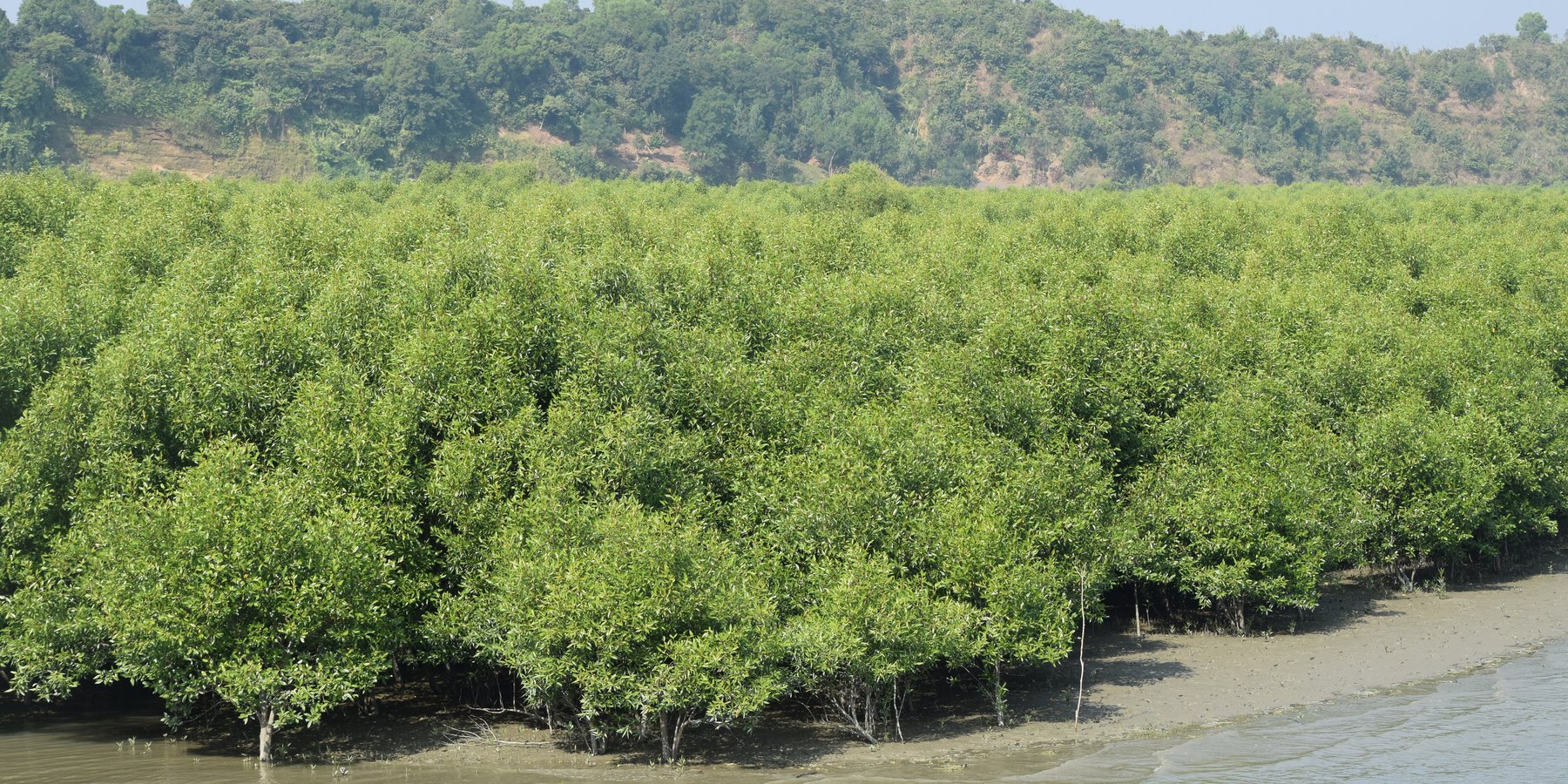
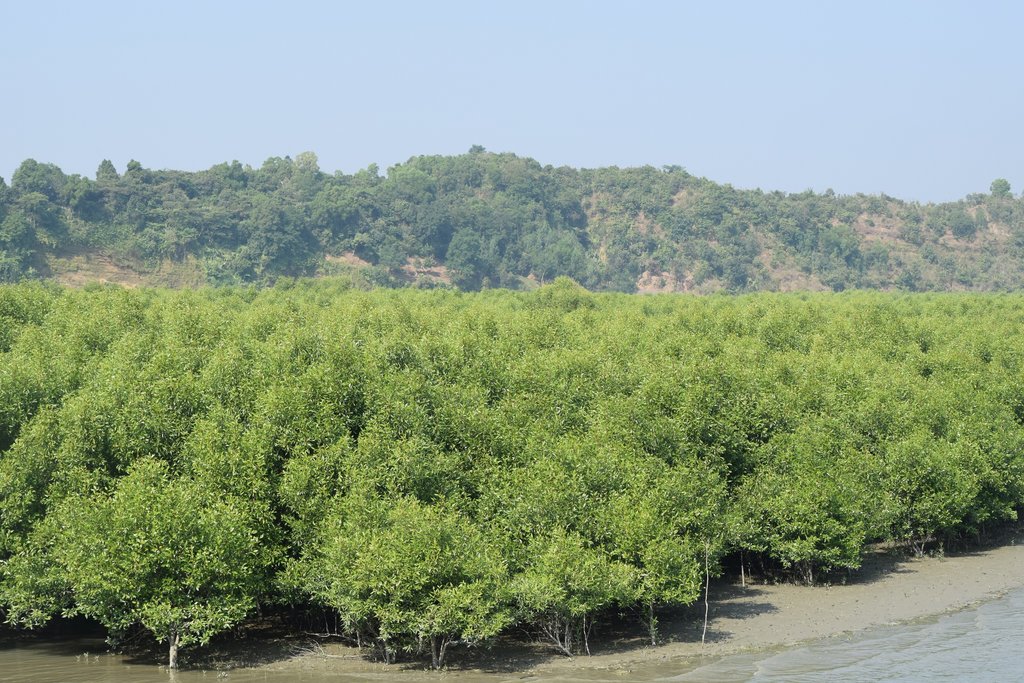
Mangrove afforestation in newly accreted land along cooastal regions accelerates the process of land stabilization, creates new forest resources, and enriches biodiversity.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
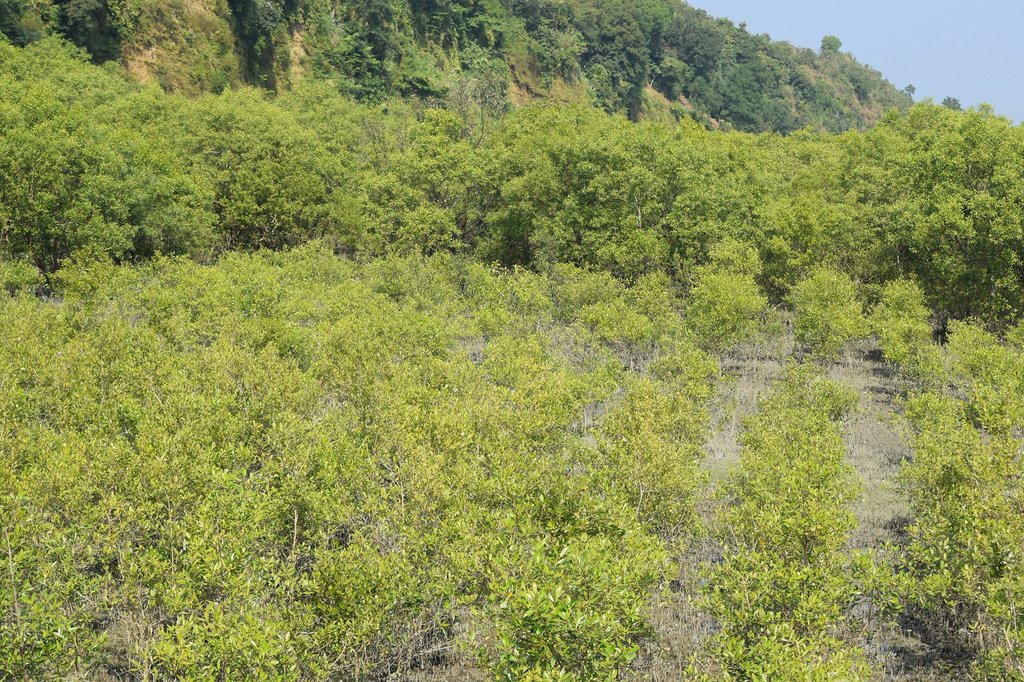
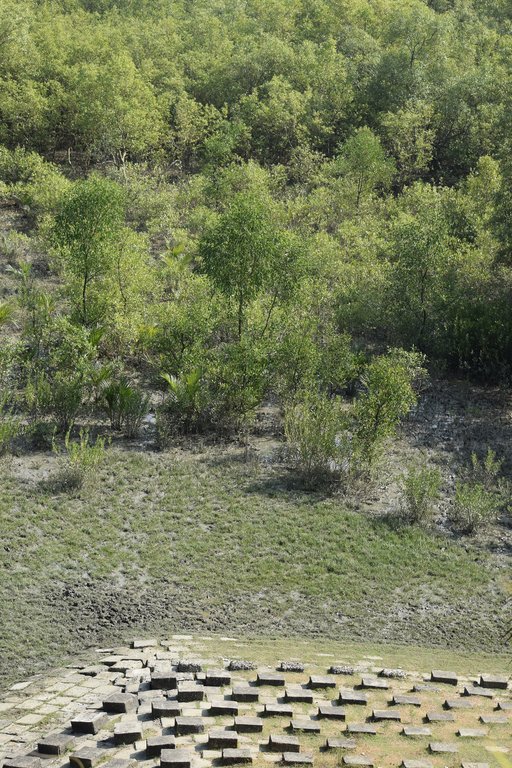
Maheshkhali is the only hilly island of Bangladesh and situated in northwest of Cox’s Bazar. This island has become a tourist destination for its mangrove plantation and ancient Adinath Temple situated at the hilltop. Historically the island had suffered from coastal erosion and structural measures like building blocks along the coast were implemented in some places to protect the Adinath hill from erosion. The Maheshkhali channel have deposited sediments in the near-shore zone and formed mud banks along the coast. This newly accreted land and other lands were used for mangrove plantations, which stabilized the land and provided protection against coastal erosion, storm damage, flooding, and siltation of adjacent seagrass beds. Mangrove plantations can provide a long-term and cost-effective solution to coastal erosion while at the same time improving the landscape aesthetically and increasing ecological habitats. Before the mangroves were planted, the existing shrub and tree vegetation along the coastline of Maheshkhali was scattered. The barren and exposed coastline is now converted to a green shelter-belt and protecting the soil. Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the mangrove plantation was carried out with the support from World Bank through "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)" project in 1997. Later, some new plantation also carried out in 2016 on newly accreted land through "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP).
The mangrove plant species Baen (Avicennia officinalis) was used to create the plantation. Salinity in coastal regions increased as consequence of global warming and Avicennia officinalis is among the most salt tolerant species that prefer clay soil. The young tree forms a low, dense bushy crown. When it matures, it forms a columnar tree up to 15 m and may grow up to 30 m. The spreading root system of the plant also provides stability in shifting substrates. When planting mangroves, site selection and proper nursery management is crucial. Geo-morphological changes in coastal areas can be rapid and unpredictable, making it difficult to identify suitable sites correctly. Accreted land with grasses and crab burrows indicating a stable site, ideal for planting. The experience of field staff is a key factor in identifying suitable sites. Nursery management is carried out by forest department. Seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation and weed control are the major activities of nursery management. Proper care of seedlings needs to be ensured while transporting from nursery to plantation site thorough boat. Gunny bags can be used to carry the seedlings while transporting. The spacing between each plant was 1.5m x 1.5m and 4444 seedlings/ha were planted in the visited site. Compost fertilizer was used both in nursery and while planting in pit. After planting, each seedling was tied up with a bamboo stick for support and to prevent from washing away in tides. The plantation activities were carried out by the staff of forest department. As mangrove afforestation is carried out in unstable environments, there is always a risk of losing some plantation during the time it takes for trees to reach maturity.
Coastal afforestation accelerates the process of land stabilization, and by creating new forest land it enriches biodiversity and natural resources. It also protects the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna. It produces timber for fuelwood and industrial uses. However, the local community people can only collect fuelwood and other non-timber forest products like honey, crabs and fishes from this plantation site. The mangrove plantation increased the aesthetic beauty of the area and also create employment opportunities for remote rural communities through eco-tourism.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Chittagong division
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Moheskhali, Cox's Bazar
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Plantation was carried out from the support of World Bank project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP) project in 1997" and "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP) in 2016"
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกพืชพันธุ์ท้องถิ่นชนิดเดียว
- Mangrove plantation
- Avicennia officinalis
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to the establishment of mangrove plantation, the degraded land is now covered with vegetation and protected from land degradation
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- fellow accreted land
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Fish and crabs
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The areas were inundated regularly by the tide and physical barriers were imposed to protect the land from degradation
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Plantation of mangrove species in newly accreted land to stabilize the soil to protect from land degradation
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wc (Coastal erosion): การกัดเซาะชายฝั่ง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
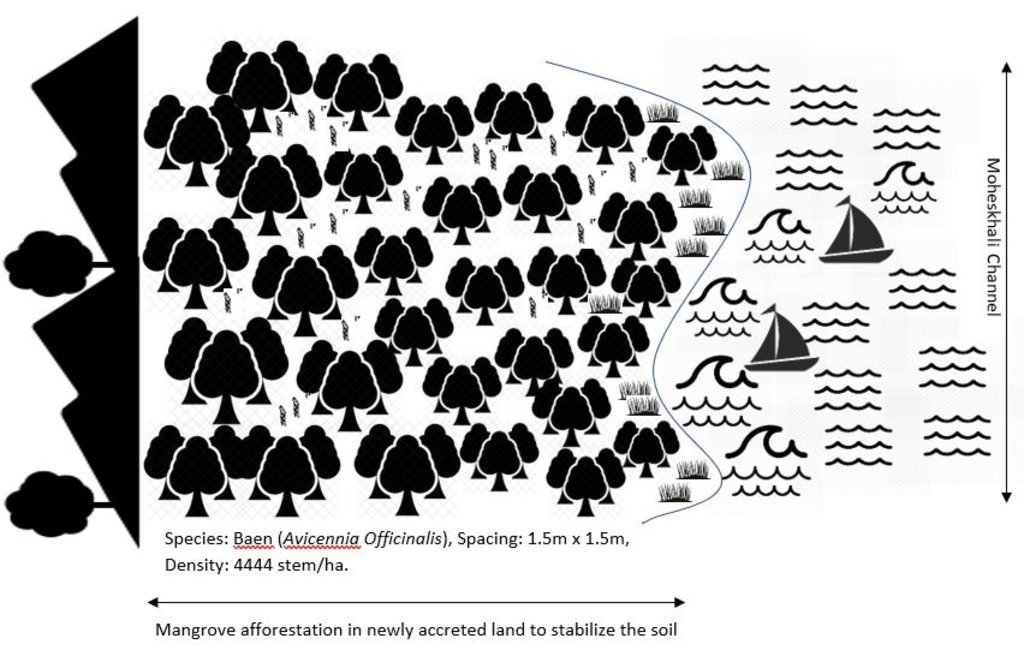
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Planted species: Baen (Avicennia officinalis)
Soil condition: Accreted land with grasses indicated a stable site and suitable for planting Baen plant.
Spacing: 1.5m X 1.5m
Density: 4444 stem/ha.
Vacancy filling: 3 consecutive years after plantation
ผู้เขียน:
Md. Fazlay Arafat
วันที่:
21/04/2019
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
2.47 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
BDT
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
84.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
BDT 500
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | March-April |
| 2. | Survey plantation site and prepare site map | August |
| 3. | Transportation of seedlings | September-October |
| 4. | Plantation | September-October |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | person-days | 20.0 | 500.0 | 10000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Plantation site survey | person-days | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Transportation of seedlings | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Plantation | person-days | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | lump-sum | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Poly bags | pieces | 4500.0 | 1.0 | 4500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Rope for tying up seedlings with bamboo stick | lump-sum | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Gunny bags (to carry seedlings to the plantation pit) | lump-sum | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Bamboo sticks to support seedlings | pieces | 4500.0 | 2.0 | 9000.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost fertilizer (to apply in pit) | kg | 50.0 | 10.0 | 500.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 35900.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 427.38 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the costs was borne from the project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)"
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 year old plantation replanting nursery 40% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 2. | 2 year old plantation replanting nursery 30% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 3. | 3 year old plantation- replanting nursery 20% (1 bed/Ha.) | March-April |
| 4. | 1 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 40% (1777 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 5. | 2 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 30% (1333 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 6. | 3 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 20% (888 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Nursery work | person-day | 18.0 | 500.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Replanting work | person-day | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | Lump-sum | 1.0 | 6000.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost fertilizer | kg | 25.0 | 10.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 20250.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 241.07 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and borne the maintenance cost of the technology
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labor cost
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
3700.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Cox's Bazar
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Mean annual temperature is 25.6 °C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Due to regular tidal inundation the soil become saline and only support to grow mangrove plant species
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
ระบุ:
Land use rights based on forest management type
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตไม้
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
การผลิตของจากป่าทุกชนิดยกเว้นไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Honey, fish and crab production increased
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The mangrove plantation support production of timber, fuel wood, crabs, fruits for wildlife, honey, etc.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Promote alternate income through ecotourism
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The mangrove plantation saved one ancient temple (Adinath Mondir) of Hindu religion from destruction by land degradation.
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The mangrove forest now become a tourist place
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Forest department now replicating the practice in other degraded areas
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
surface runoff decreased due to canopy coverage and accretion of sediments in plantation site
ดิน
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
soil accumulation increased as the plantation promote soil accretion during tides
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
the plantation site support habitats for birds and crabs
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Honey bee and various birds living here and add benefits in pollination and pest control
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife and fish
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The plantation protect the debris flows of Adinath hill from washed away in water. The Adinath hill is on the edge of coast and now protected from bank erosion.
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The plantation act as a buffer to reduce the saline water flow of high tide towards terrestrial land
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไปอื่น ๆ | water salinity in coastal areas due to global warming | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Forest Department is the land user here
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Protect the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. |
| Conserve and stabilize newly accreted lands and protect from land degradation |
| Produce fuel wood for local people |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Develop ecotourism facility for local communities |
| Develop suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Vulnerable to natural calamities specially in initial stage | Proper management and vacancy filling |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Risk of low production due to unstable environment for plantation | Proper monitoring and management of plantation |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
number of field visits: 02
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
number of informants: 04
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
number of informants:02
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
16/01/2019
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Macintosh, D.J., Mahindapala, R., Markopoulos, M. (eds) (2012). Sharing Lessons on Mangrove Restoration. Bangkok, Thailand: Mangroves for the Future and Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. ISBN: 978-2-8317-1558-2
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Mangroves for the Future
URL:
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.4 General comments
The WOCAT questionnaire covers all the aspect of this technology
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล