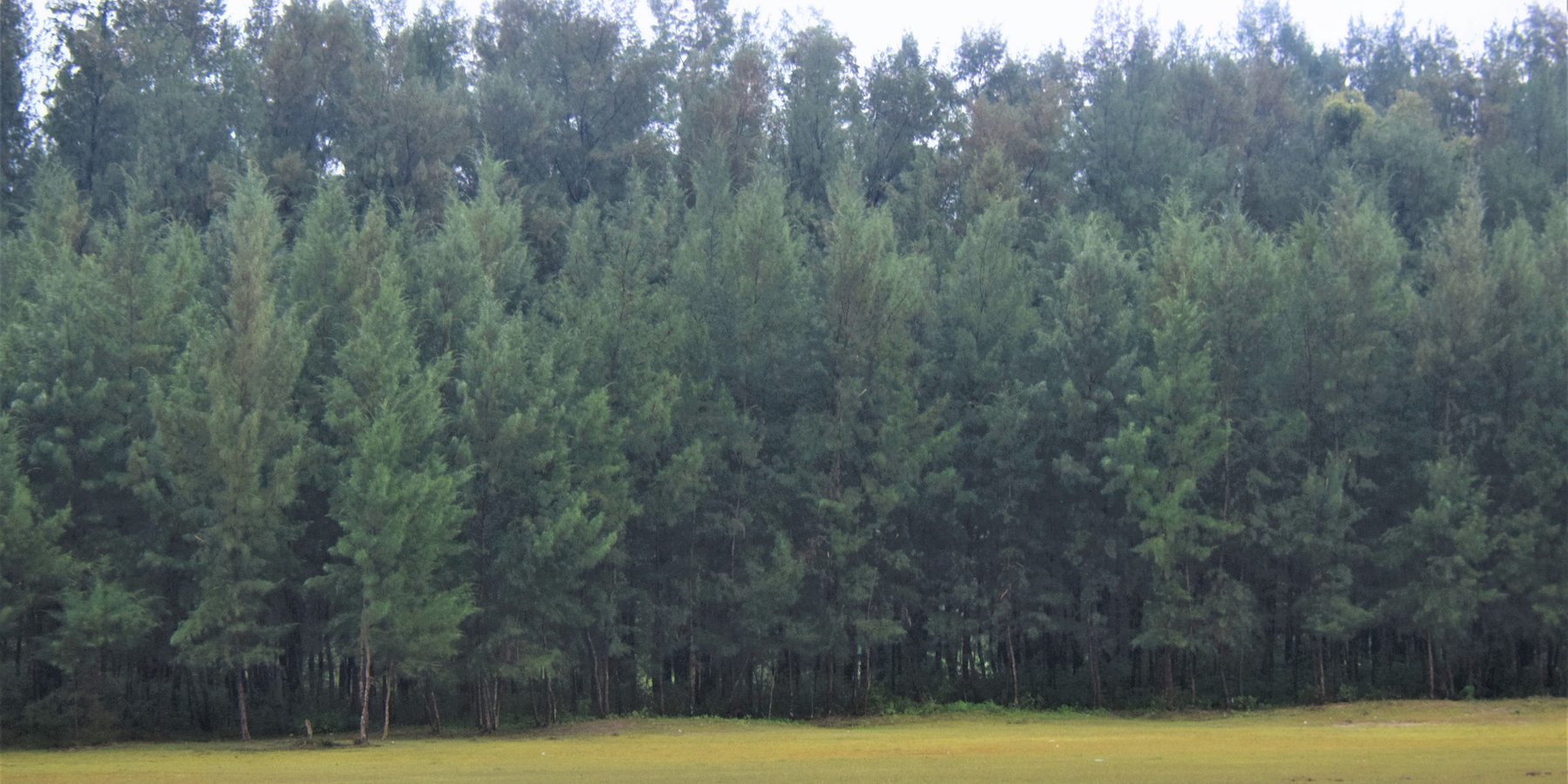
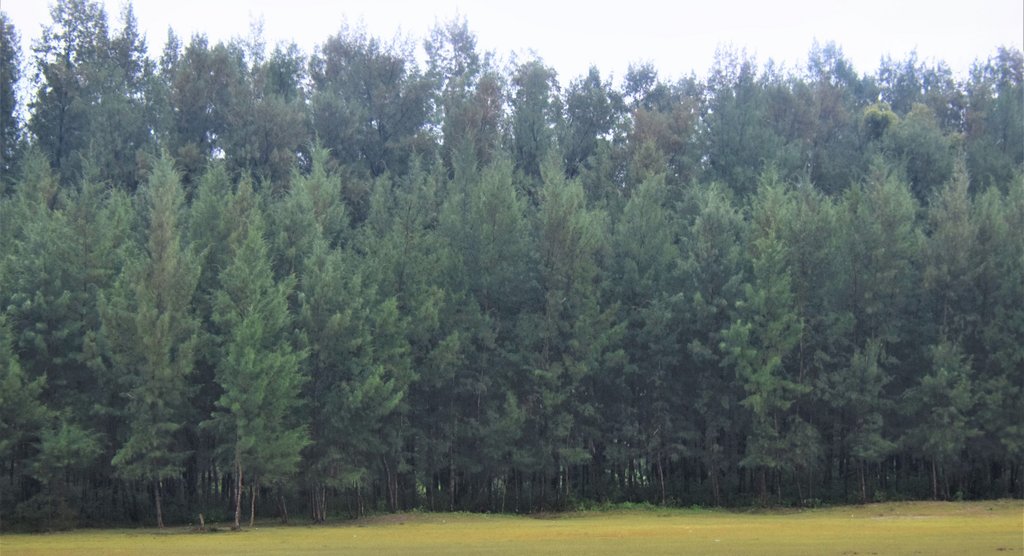
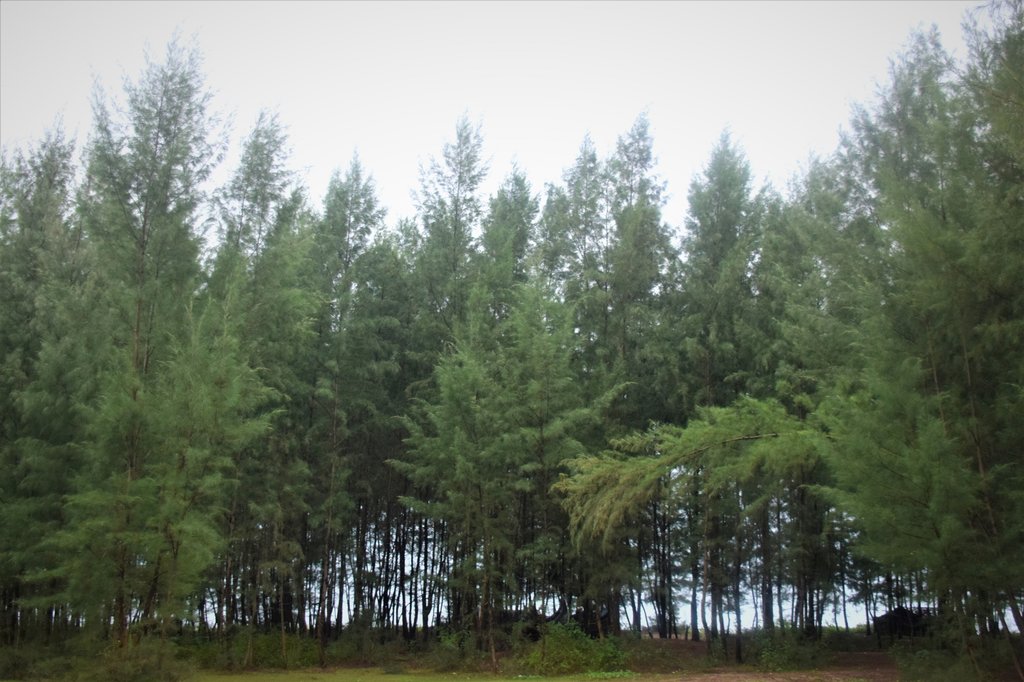
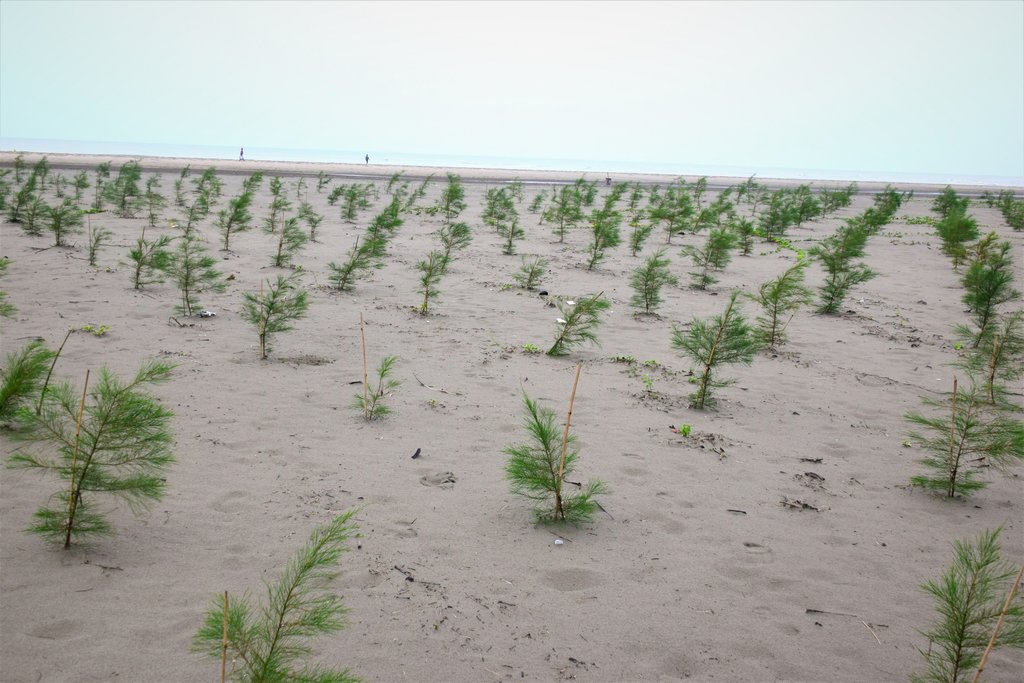
Creating green shelter-belt through Jhau (Casuarina equisetifolia) plantation in coastal area [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Fazlay Arafat
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Coastal Greenbelt
technologies_4333 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Morshed Hoq Mahabub
Bangladesh Forest Department
บังกลาเทศ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Mondol Dhiman
Bangladesh Forest Department
บังกลาเทศ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Ali Md. Sobur
Local community people
บังกลาเทศ
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - บังกลาเทศ1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Creation of green shelter-belt along the coast line through plantation of Jhau (Casuarina equisetifolia) to reduce vulnerabilities and hazards of extreme weather events like cyclones.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
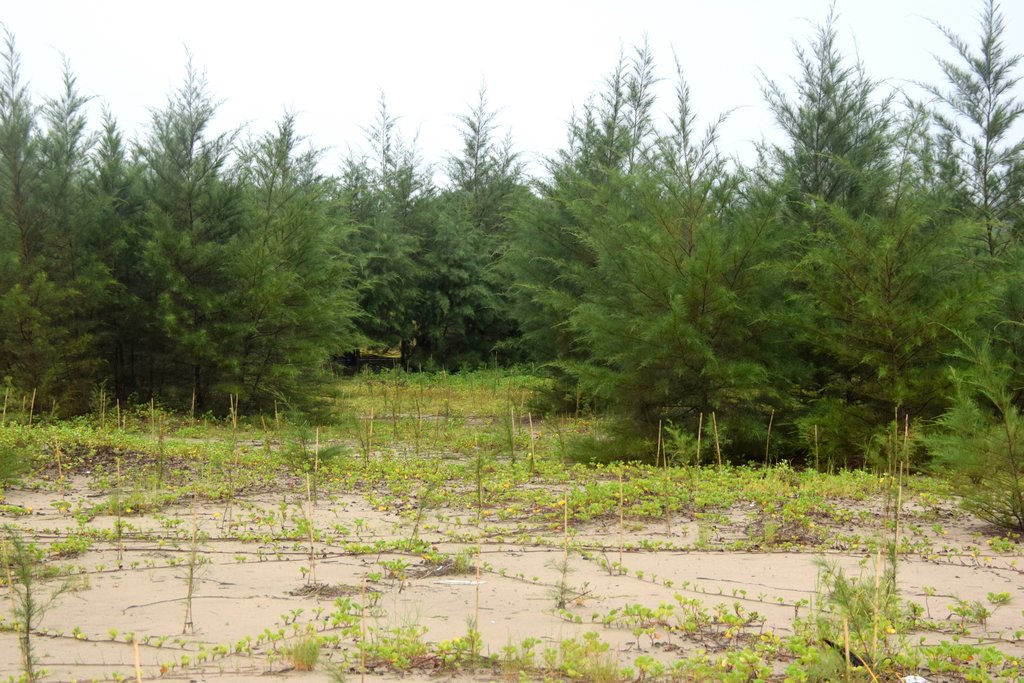
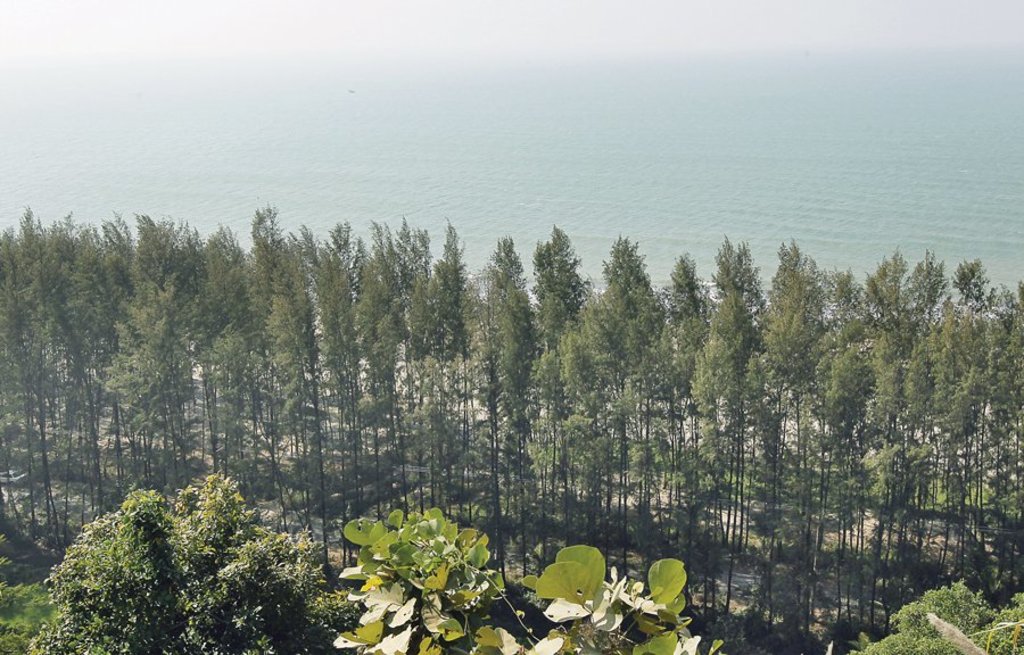
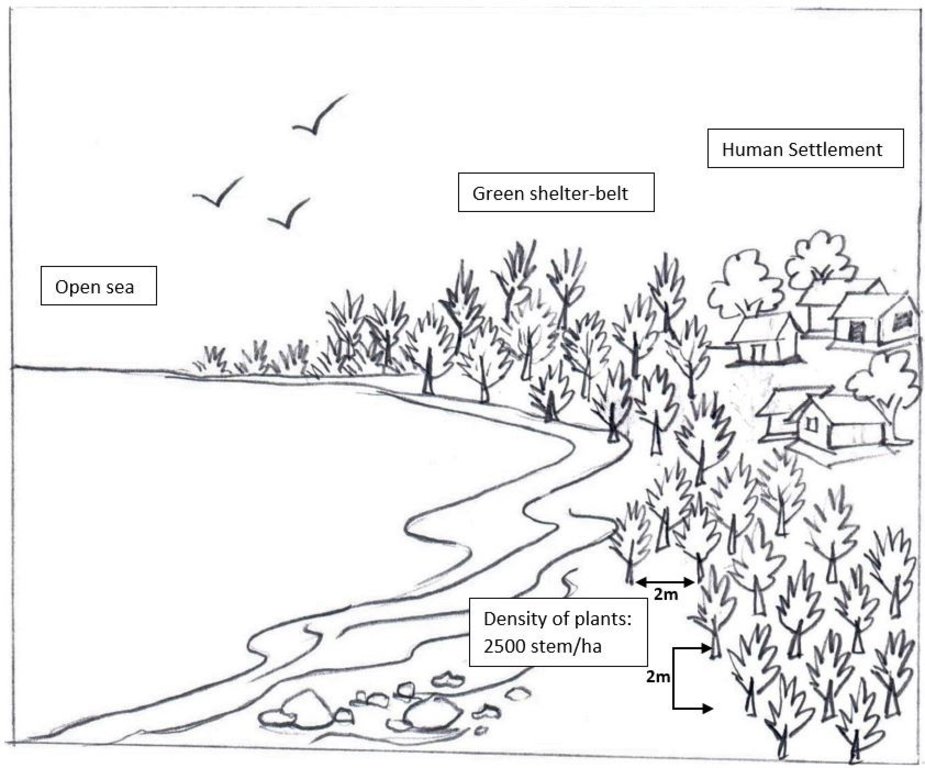
The coastal zone of Bangladesh is extremely vulnerable to the impact of climate change. The coastal populations are mostly poor and some of them are landless with livelihoods connected to agriculture, fishing, shrimp farming, salt farming etc. Past devastating cyclones have killed thousands of people and destroyed homes and infrastructure. Creation of green shelter-belts, including mangrove and non-mangrove plantations, reduces the vulnerabilities and hazards related to extreme weather events like cyclones and storm surges. Afforestation along coastal areas is usually cheaper and ecologically more beneficial than other measures and serves to conserve biodiversity and stabilize newly accreted land. As a general guideline, a shelter-belt protects an area over a distance up to its own height on the windward side and up to 10 times its height on the leeward side, depending on the strength of the wind.
The current sustainable land management practice takes particular account of the Jhau plantation along the coastline of Himchari National Park of Cox's Bazar. Jhau (Casuarina equisetifolia) is one of the most promising non-mangrove species for creating shelter-belts and the Bangladesh Forest Department has been planting them in raised coastal lands and embankments since the 1990s. Casuarina equisetifolia is an evergreen tree with a finely branched, feathery crown and usually growing around 35 meters tall. It is fast growing, salt tolerant, grows in sand and can also tolerate occasional inundation by sea water at extremely high tides. Many areas where the species naturally occurs are susceptible to tropical cyclones, and its general tolerance to strong winds has encouraged its use in protective planting. The most common uses of C. equisetifolia are for coastal sand dune stabilization, shelter-belts, land reclamation and erosion control. The wood is hard and used for house posts, rafters, electric poles, tool handles, etc. It has been called ‘the best firewood in the world’ and also produces high-quality charcoal.
Coastal plantation with Jhau is a soft adaptation measure that has significantly contributed to reduce the loss of lives and properties against tropical cyclones and storm surges in the coastal areas. This species can be planted in coastline, roadside, embankment and marginal lands for creating dense vegetation, which can function as windbreak and combat tidal surges. The spacing used in this shelter-belt plantation along the coastline of Himchari National Park is 2m x 2m and 2500 trees are planted per hectare area. The examined shelter-belt plantations are approximately 1.5km long and 150m wide. The major activities required to establish the plantation were: nursery development (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control), site preparation (prepare plantation site map with GPS, weeding, marking pit location with sticks, carrying of seedlings to the site) and tree planting (digging of planting holes, tying up of plants with stick for support, application of fertilizers and compost). Weeding and vacancy filling were the maintenance activities which required up to three years after plantation establishment. All those activities carried out by the forest department with the financial help from world bank project fund. The local communities were involved as paid labour for nursery development, plantation and maintenance activities. Local people can only collect fuel wood from the plantation as its soul purpose is to act as shelter-belt from cyclones and tidal surge.
As the plantation site is on the coastline and beside the Himchari National Park, it turns to a tourist spot now for its scenic beauty. Local people involved with various sorts of tourist oriented small-scale business here e.g. parasailing, boating, restaurant, cottage industries, shops, etc. Though the initial establishment of Jhau stand need intensive care, it is functioning as a good wind breaker and combating with tidal surge along with creating alternate livelihood opportunities for local people.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Cox's Bazar, Chittagong
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Hiimchari
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Under the Coastal Green Belt project and Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project of World Bank, Jhau have been planted along the coastline to function as wind break and combat tidal surges
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกพืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นชนิดเดียว
Type of tree plantation, afforestation:
- tropical rain forest plantation - Pinus spp.
Type of tree:
- Casuarina equisetifolia
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Accreted coastal land along the shore.
ข้อสังเกต:
The land remain barren and submerged in high tide.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Regularly inundated by tidal water
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wc (Coastal erosion): การกัดเซาะชายฝั่ง

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Plant spacing between the Jhau trees is 2mx2m.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 hectare
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
2.47 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
BDT
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
83.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
500
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery development (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | September-October |
| 2. | Site preparation (prepare plantation site map with GPS, weeding, marking pit location with sticks, carrying of seedlings to the site) | April-May |
| 3. | Tree planting (digging of planting holes, tying up of plants with stick for support, application of fertilizers and compost) | June-July |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Nursery preparation | person-days | 17.0 | 500.0 | 8500.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Site preparation | person-days | 7.0 | 500.0 | 3500.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Planting activities | person-days | 22.0 | 500.0 | 11000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Bucket | pieces | 10.0 | 150.0 | 1500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | pieces | 8.0 | 300.0 | 2400.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Scissor | pieces | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Knife | pieces | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Cow dung | cubic meter | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Urea | kg | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | MoP | kg | 6.0 | 30.0 | 180.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | TSP | kg | 6.0 | 40.0 | 240.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost | kg | 1250.0 | 4.0 | 5000.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Poly bag | pieces | 3000.0 | 0.8 | 2400.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Bamboo stick | pieces | 2600.0 | 2.0 | 5200.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Signboard | Lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 43030.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 518.43 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Cost are not borne by the forest department (land owner) but by the project of World Bank
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | weeding | 3 times in a year |
| 2. | vacancy filling | June-July |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | 1st year Weeding (6 labor/weeding/Ha.) 3 times | person-days | 18.0 | 500.0 | 9000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | 2nd year Weeding (5 labor/weeding/Ha.) 3 times | person-days | 15.0 | 500.0 | 7500.0 | |
| แรงงาน | 3rd year Weeding (5 labor/weeding/Ha.) 2 times ng and cleaning (5 labor/weeding/Ha.) 1 time | person-days | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Vacancy filling | person-days | 5.0 | 500.0 | 2500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Bamboo stick | pieces | 1000.0 | 2.0 | 2000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 26000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 313.25 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Cost are not borne by the forest department (land owner) but by the project of World Bank
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labor
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Due to regular tidal inundation the soil become saline and only support to grow few saline tolerant plant species
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตไม้
การผลิตของจากป่าทุกชนิดยกเว้นไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
leaves and fruits are used for ornamental purposes
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Jhau tree performs better than other trees for stabilization of coastal sand dune
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
the plantation site now become a picnic spot for its scenic beauty (tourism has been attracted because of the coastal plantation)
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The area attract more tourists now and local people involved in various type of small scale business here
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The workload reduced due to diversified income source of local community
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
New year celebration program now organized here every year
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
This area now become a tourist hotspot
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Learn about the stabilization of sand dunes
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การสะสมของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The green belt support home for native birds
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
protection of agricultural land on back side of shelter-belt
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ดี |
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Forest department adopted the green-belt plantation technique with Jhau from the projects and now replicating the practice in other coastline areas with government fund
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Function as wind break and combat tidal surges |
| Increases the soil fertility of the degraded land through nutrient cycle |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Biodiversity conservation through habitat improvement |
| Increase carbon sequestration |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Initial establishment of stand need intensive care and risk of failure is high | Increase technical capabilities of forest officials |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Jhau tree is not a natural vegetation for the sand dunes | Introduce other indigenous salinity tolerant plant species in the green shelter belt |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Number of informants: 04
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Number of informants: 03
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Number of informants: 01
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
17/12/2018
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Islam, S. A. & Rahman, M. M. (2015). Coastal afforestation in Bangladesh to combat climate change induced hazards. Journal of Science, Technology & Environment Informatics, 02(01), 13–25, 2015
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
2015, Journal BiNET. This is an open access article distributed under terms of the Creative Common Attribution 4.0 International License.
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire covered all the technical specifications of this SLM technology.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล