In-field rain water harvesting [เลโซโท]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Matoka Moshoeshoe
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Infiltration pits
technologies_4591 - เลโซโท
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Integrated Catchment Management Project (Integrated Catchment Management Project) - เลโซโท1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Its adoption is still at marginal scale since the Department has not yet introduced this technology in all ten(10) administrative districts in the country.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The infiltration pits are constructed on bare lands with the aim to enhance re-vegetation of plant species. The pits help to reduce soil erosion/land degradation as water is now able to infiltrate through the pits because they are constructed in succession. It also improves land productivity and cover as well as soil organic carbon.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
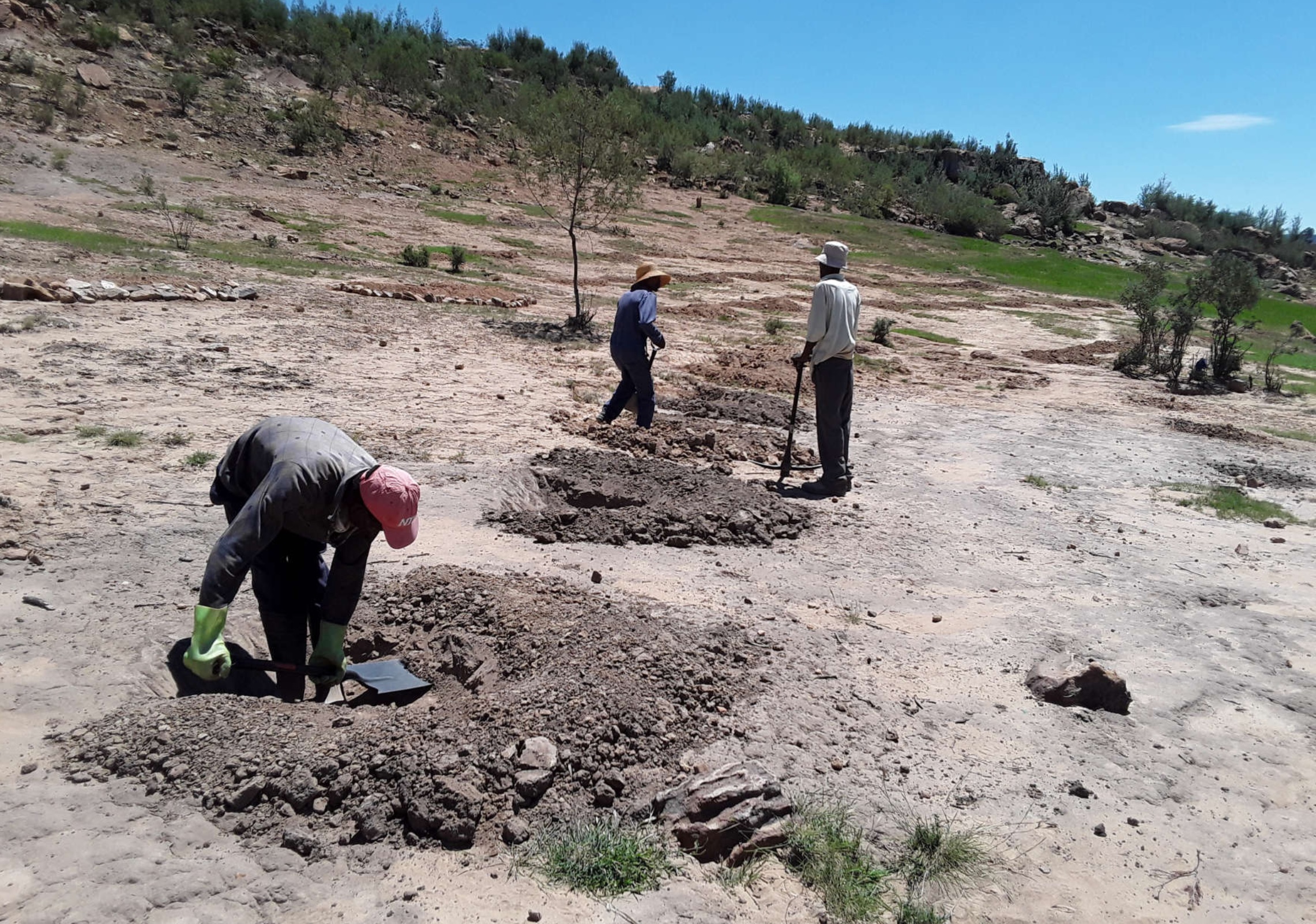
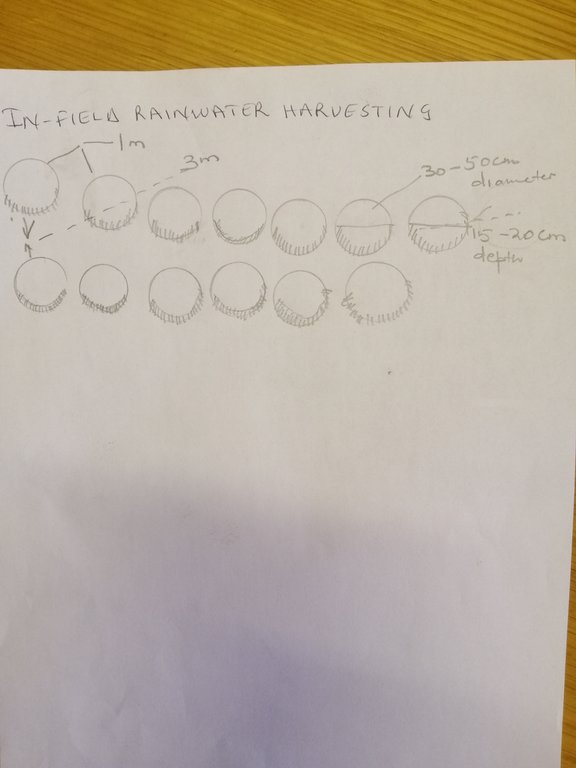
The technology is applied on natural marginal environment where the land is dry, they pits are mostly dug on the rangeland. The purpose is to harvest rain water/surface runoff consequently recharge soil moisture and support plant available water as highly as possible. After some time, there will be regeneration of vegetation. The dimensions of this structure may differ according to soil type, slope and rainfall intensity.
To construct this activity, the land should be bare or poor in plant biodiversity. Firstly, the extension workers hold public gatherings for a concerned community to make them aware of the land degradation in their area and possible solutions. In field rain water harvesting pits being one of them. The area is then surveyed using survey equipment (this is a technical survey not the one which uses questionnaires, this survey uses equipment such as theodolyte, auto cat etc). It is important to do the area survey because the technology follows the contour lines, otherwise it is likely to cause more harm on the land. The design of the technology is laid out by using the measuring tape, pick axe and spade. Construction starts from the top of field. Pits are dug in succession in a row following the contour with in row (intrarow) spacing of 1 m, pit depth of 20-30 cm and width of 1 m. Interrow spacing (between rows) is 3 m at 12% slope. After construction, kikuyu grass is sown around the pits to protect them from erosion. After the first storm, the area is then revisited for maintenance and repairs if need be. This technology is beneficial mostly in drylands where the water shortage is a major problem to improve land productivity. Although specififications are in this manner, this technology can be adapted differently in other areas depending on the amount of precipitation received by a certain area. For instance, some pits can be bigger or smaller than the given specifications.
The land users found it beneficial because the inputs needed to construct this technology are locally available such as spade, pick axe and grass for sodding. Furthermore, the rehabilitation benefits accrue within a short while. In addition, the technology is easy to construct. However, the land users found it tedious as they have to maintain it after every storm. The pits can be constructed on the rangeland and cropland which is no longer productive. in this era of climate change where this part of Southern Africa is becoming more dry everyday, this technology is even more applicable.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
N/A
วันที่:
26/03/2019
สถานที่:
N/A
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
N/A
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เลโซโท
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Leribe District
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Peri-Urban
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The activity is currently being scaled up/out in sub-catchments at sub-national level of which the areas are communally owned
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2019
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
DS-SLM project pilot stage facilitated the adoption of the innovation
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
- deferred grazing
Animal type:
- livestock - other small
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- transport/ draught
Species:
cattle - non-dairy beef
Count:
207
Species:
sheep
Count:
1307

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกพืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นชนิดเดียว
Type of tree plantation, afforestation:
- subtropical dry forest plantation
Type of tree:
- Acacia species
- Acacia dealbata
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- mixed deciduous/ evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
ข้อสังเกต:
settlement encroachment into range-lands
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Nearby waterways are natural and there are also seasonal streams full of fine sand which is currently mined. The mining of sand threatens stream banks thereby accelerating further erosion within the catchment boundaries. The sand mine is not directly where the SLM practices are practiced, but on the edge/boundaries and it will contribute to widening of gullies within this catchment in future.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area is very dry
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการป่าธรรมชาติและกึ่งธรรมชาติ
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A6: Residue management

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
- V4: การแทนที่หรือการนำพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น/ที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา ออกไปจากพื้นที่

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology is practised on the rangeland, where the land is bare or has little vegetative cover. The aim of this technology is to collect as much rainwater as possible, to facilitate regeneration of vegetation so that ultimately the bare land/rangeland will have cover.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)
- Pw (Waterlogging): ภาวะชุ่มน้ำ
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bf (Detrimenta leffects of fires): ผลเสียหายจากไฟ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology addresses several types of land degradation when implemented properly.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Lesotho's landscape is continuously becoming bare owing to the impacts of land degradation, desertification and drought. This technology has been used effectively to counter the impacts of land degradation.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical specifications:
Dimensions; height 20cm, depth 30cm, width 1m and length 1m
Spacing between structures; between rows 5m, between pits 3m
slope; 3-12%
construction material used; stones, soil, grass sodds , mulch and compost and grass seeds
6 litres is the water holding capacity of a pit
ผู้เขียน:
Matoka Moshoeshoe, Koetlisi Koetlisi and Mamofota Lekholoane
วันที่:
01/04/2015
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
0.2 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
N/A
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
4.6 US dollars
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | public awareness raising gathering | winter |
| 2. | survey of area/ terrain | winter |
| 3. | design and laying out of infiltration pits | winter |
| 4. | implementation/construction of pits | winter |
| 5. | sowing | winter and or summer |
| 6. | maintenance | when need arises |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to impacts of climate change, the activity logistics could be done any-time as long as meteorological predictions allow
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | one person | person-days | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | pick axe | piece | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | spade | piece | 1.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | measuring tape | piece | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | grass seed | kg | 2.0 | 13.0 | 26.0 | 25.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | stones | piece | 40.0 | 1.0 | 40.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 107.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 107.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Government
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There are no costs incurred by land users bacause the rate of erosion is massive and highly costly therefore, farmers cannot afford to protect their own land without government intervention. The landowner simply contributes in-kind not in cash by maintaining that piece of land after rehabilitation.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | public gathering | after storm |
| 2. | re-survey | after storm |
| 3. | implementation | after storm |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
all maintenance works done after storm
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | grass seed | kg | 1.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | |
| แรงงาน | one person | person day | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 18.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 18.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Government
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
maintenance is done by both community and government
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Government annual budget affects inputs and labour
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
735.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The Northern parts of the country receive good amount of rainfall generally. This is the place where generally soils are also good and agricultural production is satisfactory so far.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Hlotse
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
The climate in this region favours agricultural production more than anything else. The Leribe district was once referred to as the bread basket of the country simply because the climate and soils are good for both crop and animal production.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The slope is moderate to gentle as the area extends towards the stream bank where there is depression. Above the area where the technology is implemented, there is a plateau where the community lives. However, the whole area is within a valley.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil type was not classified, a detailed soil type map of Lesotho can be found at https://lesis.gov.ls
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
There are natural springs which have have been developed by village water supply for community to access safe drinking water. There are seasonal streams around the area which communities use for washing and animal drinking.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The area is mainly used as a range-land which is not given time to rest. Re-vegetation occurs very slowly due to mismanagement of the land.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The land is used mainly for crop and animal production although there are signs of settlement encroachment.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area was used as a demonstration site. The technology is yet to be up-scaled to other areas.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
According to the Land Act of 2010, land in Lesotho is vested in the Basotho nation and is held in trust by the King.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area is found in the peri-urban zone which is near the major town of Hlotse. There are access roads and they are closer to markets.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
vegetation cover was poor
หลังจาก SLM:
increased vegetation cover
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
quantity increased after SLM
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
fodder quality was also poor
หลังจาก SLM:
increased quality
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is now fodder available for animals
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
land was poorly managed
หลังจาก SLM:
community members agreed to protect the land
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The pits constructed have contributed positively to increase in land cover, land productivity and soil organic carbon
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
animals were too weak
หลังจาก SLM:
the quality of stock improved
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology has contributed positively towards availability of fodder hence good animal production
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
biodiversity was lost
หลังจาก SLM:
regeneration of biodiversity
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
both birds and wild animals are now occupying the habitat, communities use rehabilitated areas as parks or picnic area, and people pay to access that part of the land. The revenue collected will then be used for other purposes that might help community such as fixing a broken water tap etc.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
community members did not have knowledge of the technology
หลังจาก SLM:
community members can now construct the pits on their own in their own land
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
knowledge on land degradation now improved
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
water was not collected
หลังจาก SLM:
surface run-off was now collected
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
a lot of water is now collected through this technology and not lost like it used to be
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
surface runoff was not controlled
หลังจาก SLM:
surface run-off was partly collected
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
surface run-off now partly collected and soil erosion minimised
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
poor surface drainage
หลังจาก SLM:
infiltration improved drainage
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
surface drainage was controlled to enhance infiltration
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
prolonged dry-moist dry
หลังจาก SLM:
conditional moisture
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
the land was bare
หลังจาก SLM:
revegetation
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved vegetation abundance
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
sheet erosion
หลังจาก SLM:
sheet erosion disrupted
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
surface roughness improved
การสะสมของดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
much soil loss
หลังจาก SLM:
sedimentation improved
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
sediment is collected in ditches
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
bare ground
หลังจาก SLM:
above ground biomass improved
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved soil moisture supports biomass production
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
few species
หลังจาก SLM:
species variety
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
various species require availed prolonged soil moisture
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
general biodiversity improved
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
less carbon stored in the soil
หลังจาก SLM:
improved carbon sequestration
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
soil organic carbon improved
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
the activity is likely to be up-scaled
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology works very well when there is surface run-off as the main aim is to collect as much of run-off as possible for moisture retention.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
the technology can easily be maintained although maintenance plan does not exist
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
sixty
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
land users who own the land relative to those to those who have user rights only, saw the importance of the technology
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
the dimensions differ relative to the rainfall intensity, soil type and technician and land user preference
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| the technology is implemented by both men and women |
| Middle-aged and elderly group were impressed with the technology |
| the technology uses locally available inputs |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| it is environmentally friendly |
| it helps in achieving variuos LDN targets |
| it can be demonstrated to a large group of people at once |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| they could be easily destroyed by single hailstorm | trenches be constructed to lower velocity and discharge of surface run-off |
| they could conditionally be filled with sediment | sediments should be removed periodically |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| they could be easily destroyed by single hailstorm | trenches be constructed to lower velocity and discharge of surface run-off |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
sixty
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
18/02/2019
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A public gathering/focus group discussion was held on site, community members were sensitised by extension workers from the Ministry of Forestry and its Line Ministries (Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Water, Ministry of Local Government) on the importance of the technology. Demonstrations were held after the public was informed about the importance of the technology.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
In-field rainwater harvesting: Conservation of your natural resources through in-field rainwater harvesting, Jacobus Botha, [2012]
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Agricultureal Research Council, Institute for Soil, Climate and Water (ARC-SCW), South Africa
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Agricultural Research Council, South Africa
URL:
www.arc.agric.za
7.4 General comments
other information regarding this technology was deduced from the report from Larry C. Tennyson, 2012
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล