Freezing winter cover crops [เยอรมนี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Michael Strauch
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Felix Witing, Mona Pauer
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Abfrierende Zwischenfrüchte
technologies_5929 - เยอรมนี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
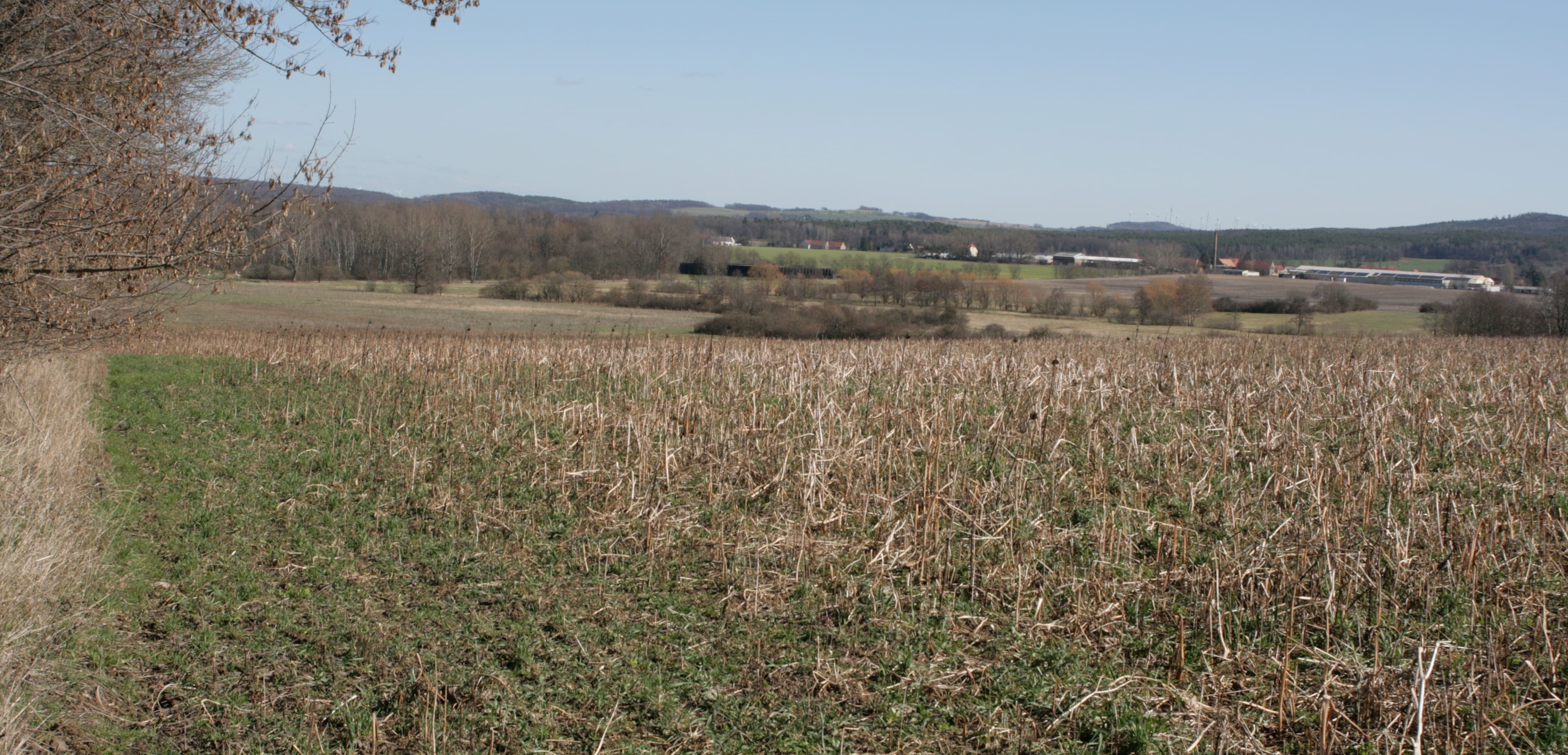
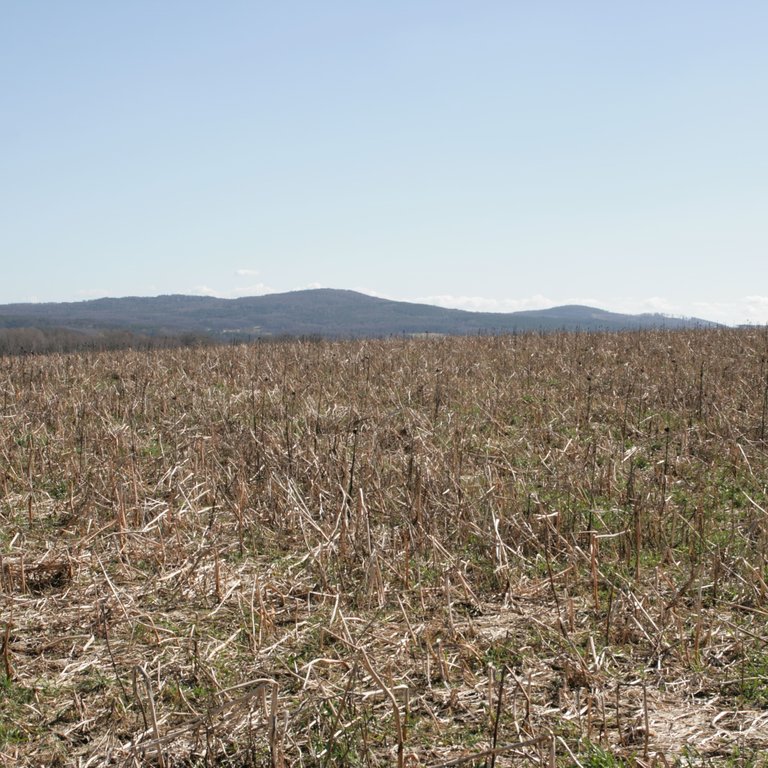
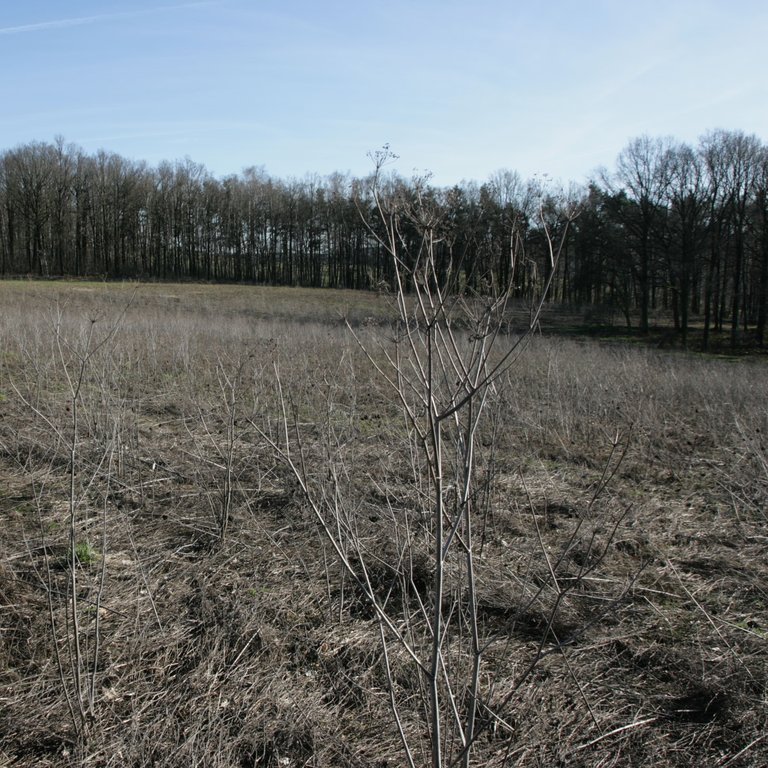
Freezing winter cover crops are planted to cover the soil rather than for the purpose of being harvested. They improve soil structure, diversify cropping systems, suppress weeds and pests, and prevent nutrient loss.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
In general, cover crops are divided into summer and winter cover crops. They can be used as fodder or as a biogas substrate. However, when left in the field, cover crops support the formation of humus and serve as a source of nutrients for the following crop. Winter cover crops can be divided into winter-hardy and freeze-killed (freezing) cover crops. Choosing the appropriate cover crop depends on its purpose and its position in the crop rotation. Cover crops from the brassica/cruciferous family should be avoided in rotations with oilseed rape (because of increased risk of pests such as clubroot, Sclerotinia or Verticillium), while buckwheat and phacelia are difficult to control in crop rotations with sugar beet. Crops that are used as main crops in a given crop rotation should not be used as cover crops.
Compared to pure stands, mixed stands have the advantage of higher biomass production, rooting density, biodiversity, weed suppression and nutrient availability for the following main crop. Mixed seeds should include at least five types of plant species, including shallow- and deep-rooted species, varieties of freezing and hardy crops that will last over the winter, mycorrhizal species (e.g. phacelia, sunflower) and ruderal species (e.g. legumes, brassica), as well as high growing and soil shading species. Alternatively, monocrops of yellow mustard or oil radish can be grown. However, in this case, ecological benefits are not as high as with mixed stands (LfULG, 2010).
Where appropriate, winter cover crops should be established through direct sowing or mulch sowing. They should be sown immediately after the main crop is harvested (to make maximum use of the remaining growing season and soil moisture). However, delayed sowing (10-14 days) after harvest and stubble cultivation can be beneficial to permit the suppression of weeds and volunteer grain seedlings. Seeding density should be high enough to ensure weed suppression and sufficient biomass development, but not too high, as seed is the main cost of this technology.
To maximize benefits of cover crops, seedbed preparation for the following main crop should be done as late as possible, to avoid mineralization and leaching of nutrients - ideally in combination with the first tillage, for example with the application and incorporation of farm manure at the end of February.
In this documentation we focus on freezing winter cover crops (a mixture of phacelia, buckwheat and sunflower) sown in August/September before the following spring crop (maize). The cover crop is left in the field as ground cover for the winter. It freezes during this period. In spring, the remaining crop residues are worked into the soil by deep tillage. The farmer in our example doesn’t apply this management practice for short-term economic reasons or to fulfill cross-compliance requirements - but rather for the beneficial impact on soil structure, such as reduced bulk density.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เยอรมนี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Saxony
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kodersdorf
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The farmer decided to apply cover crops to improve soil structure (e.g. reduced bulk density) and diverse its crop rotation.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rye
- cereals - wheat (winter)
- fodder crops - grasses
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Crop rotation: arable grass, (winter cover crop) silage maize, winter wheat,(winter cover crop) silage maize, winter rye, winter wheat, winter barley
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Freezing cover crops are planted in autumn and before the main crop silage maize (spring).
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A6: Residue management
A6: Specify residue management:
A 6.4: retained
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Ps (Subsidence of organic soils): การยุบตัวของดินอินทรีย์ การทรุดตัวของดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เขียน:
Verband der Landwirtschaftskammern 2012 (translated from German into English by Michael Strauch)
วันที่:
18/03/2022
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
€
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.91
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
18.70€ per hour
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
there are no establishment activities needed
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage | autumn, after harvest of preceding crop |
| 2. | sowing | autumn, right after/ a few days after tillage |
| 3. | mulching/seedbed preparation for the main crop | spring, before main crop of the year is planted |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 65.4 | 65.4 | |
| อื่น ๆ | sowing costs (incl. labour, machinery, diesel) | ha | 1.0 | 68.4 | 68.4 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 133.8 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 147.03 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
78€/ha were covered by the state of Saxony as a subsidy, AL_4 planting of cover crops (SMUL Sachsen, 2015)
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Seeds are the most relevant cost of this technology.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
775.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
https://whh-kliwes.de/mapview
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
LGP: 209 (https://www.umwelt.sachsen.de/dauer-der-vegetationsperiode-30631.html)
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
cambisol (Braunerde)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
GWS: -2m
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
คุณภาพพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reffering to soils in winter
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
wildlife observed by farmer
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
natural pest disease-> increased diversity in crop rotation
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
The assessment of on-site impacts is based on the response of the interviewed farmer and not based on on-site measurements.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to reduced surface runoff.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to improved soil cover.
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
There are no off-site impacts reported by the farmer as they are difficult to assess for him. However, based on expert knowledge of the compiling team, the most relevant off-site impacts that can be expected have been given.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไปอื่น ๆ | changing weather conditions | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ดี |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No implementation costs, only maintenance costs.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
72.7 ha
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In the past, there have been several subsidy programmes for cover crops. However, these programmes were not continuous and the farmer did thus not adopt the technology because of the payments, but because of the expected benefits of the cover crops.
https://www.landwirtschaft.sachsen.de/anbau-von-zwischenfruechten-und-untersaaten-37212.html
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Improvement of the soil structure. |
| Diversification of the cropping system. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Reduction of wind and water erosion. |
| Mitigate the loss of soluble nutrients. |
| Suppress weeds and pests. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Potential lack of soil moisture in spring because of water use of the cover crops in autumn/winter. | |
| Lack of nutrients because of nutrient uptake by plants in winter. | This weakness only applies to cover crops that are harvested and not to those that are left on the field and incorporated into soil. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
2
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
1
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
4
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
16/03/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Verband der Landwirtschaftskammern 2012: Zwischenfrüchte für Futternutzung und Gründüngung
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.landwirtschaftskammer.de/riswick/pdf/fb-zwischenfruechte-2012.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
LfULG 2010: Zwischenfrüchte
URL:
https://publikationen.sachsen.de/bdb/artikel/11856/documents/12569
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Gläser (2021): Boden und Gewässerschutz durch Zwischenfruchtanbau
URL:
https://www.landwirtschaft.sachsen.de/download/Merkblatt_Zwischenfruchtanbau.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Romdhane S, Spor A, Busset H, Falchetto L, Martin J, Bizouard F, Bru D, Breuil M-C, Philippot L and Cordeau S (2019) Cover Crop Management Practices Rather Than Composition of Cover Crop Mixtures Affect Bacterial Communities in No-Till Agroecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 10:1618.
URL:
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01618
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Messerschmidt (2022): Die Zwischenfrucht muss weg.
URL:
https://www.digitalmagazin.de/marken/agrarheute/magazin/agrarheute-magazin-2022-2/pflanze-technik/118_die-zwischenfrucht-muss-weg
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
SMUL Sachsen (2015): Förderperiode 2014-2020-Art. 28 der Verordnung (EU) Nr. 1305/2013 - Richtlinie Agrarumwelt- und Klimamaßnahmen (RL AUK/2015)- Sächsisches Agrarumwelt- und Naturschutzprogramm (AUNaP)
URL:
https://www.smul.sachsen.de/lfulg/download/AUK-Massnahmen-Ueberblick.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล