Cut stump [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: John Mbwambo
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Albrecht Ehrensperger, Beatrice Otieno
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Christian Hergarten, Albrecht Ehrensperger
Kukata visiki
technologies_6207 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
R4D Woody Weedsชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Tanzania Forestry Research Institute (TAFORI) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CABI Switzerland (CABI Switzerland) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is an SLM technology and is being tested for out-scaling in areas invaded by Prosopis juliflora
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
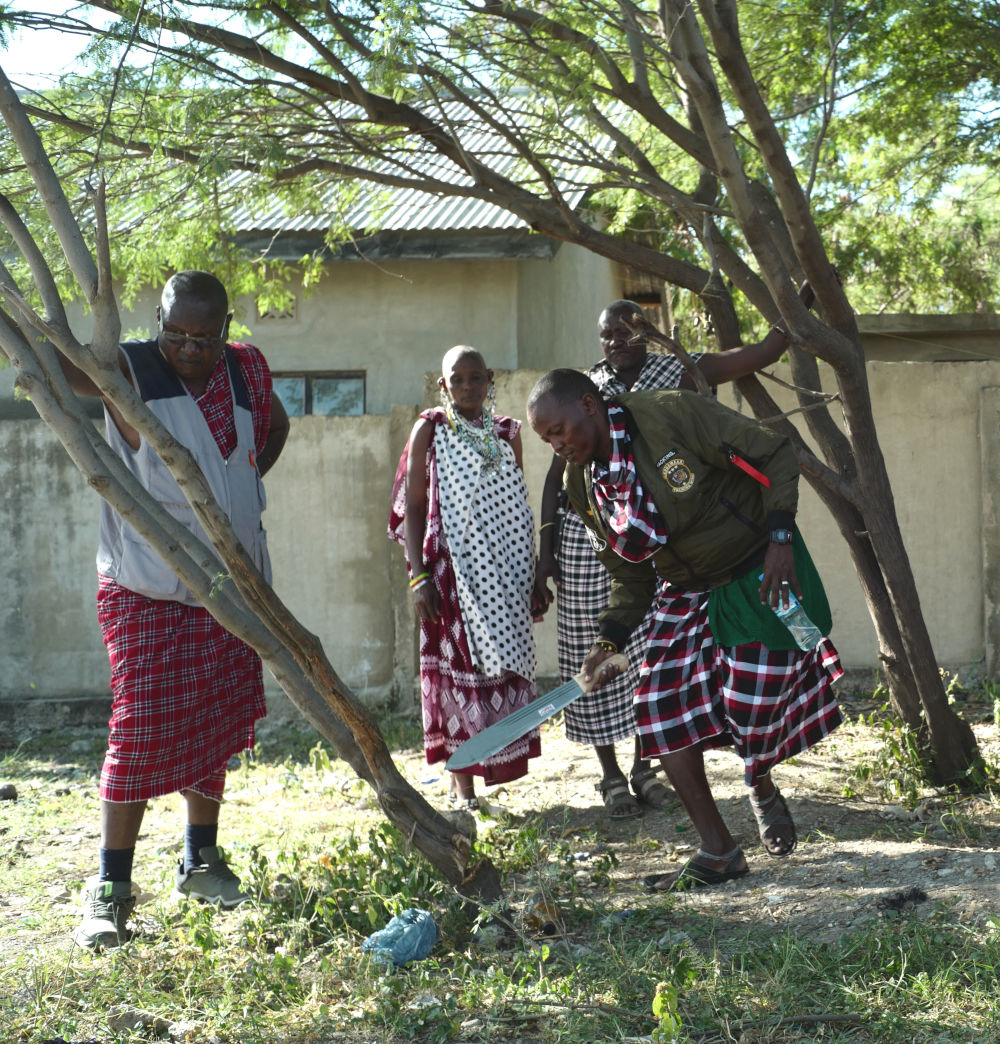
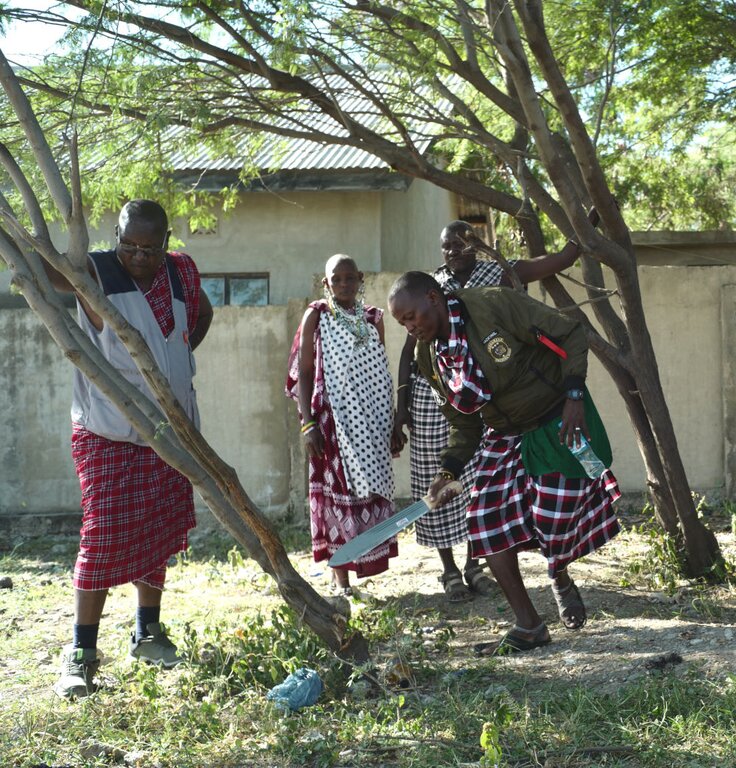
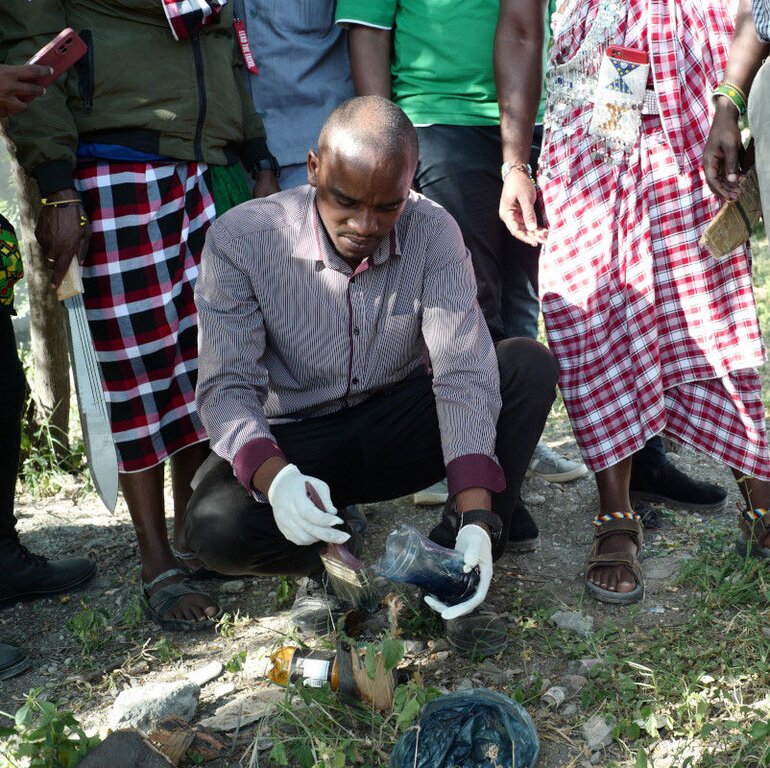
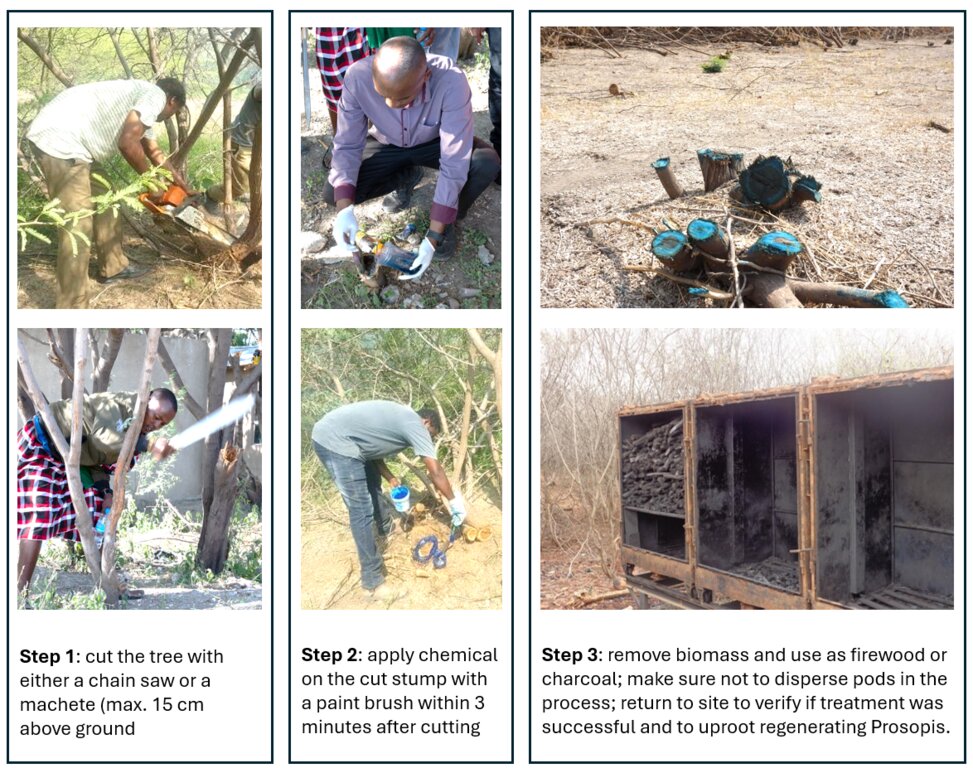
The cut stump technology is probably the most effective means of killing mature Prosopis trees using the herbicide Triclon with active ingredients Triclopyr 480g/l . Stems are cut with a chainsaw as close to the ground as possible and the herbicide is applied to the stump within three minutes of cutting using a paintbrush. The young plants with less than 2 cm root collar diameter should be uprooted by hand. The treatment is repeated after three months on resprouting stumps.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The technology is highly relevant and effective for controlling the invasion of Prosopis spp. in both agricultural and grassland areas where the species is considered problematic. It is particularly suitable for dry regions prone to Prosopis invasions, especially those experiencing drought periods of more than four months, which allow the herbicide to take significant effect. To avoid chemical contamination, the technology should only be applied in areas located more than 200 meters away from water sources.
This method requires simple tools to cut trees efficiently, with a chainsaw being recommended for the task. However, in areas where infestations cover less than 20 percent of the land, simpler tools such as machetes can be used. Trees should be cut as close to the ground as possible (no more than 15 cm stump height), and herbicide should be applied to the stump within three minutes of cutting. The treatment should be carried out during the dry season, ensuring no rainfall is expected within a month to allow for complete absorption of the herbicide.
A minimum of two people equipped with proper protective clothing is required for this operation: one to cut the trees and another to apply the herbicide and clear the cut branches. The herbicide, typically Triclopyr, is often mixed with diesel at a 1:50 ratio. A follow-up application is crucial to target any trees that were not completely killed during the initial treatment.
Herbicides can be ordered from Arysta Co. Ltd in Tanzania at a cost of TZS 1,000,000 (USD 430) per 20 liters. The advantages of using this technology include its effectiveness in killing the trees and the ability to utilize the cut branches as fuelwood or for making Prosopis charcoal. However, the major drawbacks include limited information leading to scepticism among land users regarding the health risks and potential long-term effects on soil quality, as well as the limited availability of the herbicide in local agro-stores.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
The photograph has been added later than the documentation has taken place.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kilimanjaro
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kahe
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology was introduced through experimentation during the implementation of the Woody Weeds Project. For more details visit www.woodyweeds.org
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- vegetables - other
Annual cropping system:
Continuous vegetables
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Maize and tomato, Maize and black nightshade
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Maize with tomato, black nightshade with bell peppers

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- Transhumant pastoralism
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Livestock are released to graze around fenced farmlands or graze/feed on stalks left after harvests.
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
Species:
cattle - non-dairy beef
Count:
10
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Crop cultivation and grazing are rotated to avoid crop damage and sometimes cropland is fenced with thorny branches of Prosopis juliflora to deter livestock from accessing the crop fields.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping system:
Continuous vegetables
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Maize and tomato, Maize and black nightshade
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Maize with tomato, black nightshade with bell peppers

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- Transhumant pastoralism
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Crop cultivation and grazing are rotated to avoid crop damage and sometimes cropland is fenced with thorny branches of Prosopis juliflora to deter livestock from accessing the crop fields.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cultivation of vegetables relies fully on irrigation. Water is obtained from shallow bore holes and pumped out to irrigate the fields.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- Weed control and management
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cut stump technology is considered a control of species composition because the intention is to remove or reduce the abundance of the invasive species and improve performance of desired native plant species.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology controls and reduces the density of an invasive tree Prosopis juliflora on grazing land and cultivated fields.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land degradation is due to change of vegetation cover as a result of increasing abundance of an invasive tree.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Stems of Prosopis should be cut very close to the ground (ca. 15 cm from the ground)
ผู้เขียน:
Albrecht Ehrensperger (based on photos from different authors)
วันที่:
03/07/2024
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
0.01 Hectares
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tanzanian Shilling
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
2400.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
20,000
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Acquisition of Chemical (Triclon) | anytime of the year |
| 2. | Hiring a Chain Saw | anytime of the year |
| 3. | Cutting of stems | During dry season (normally January - March) |
| 4. | Chemical application using paint brush | Within five minutes after cutting the stems |
| 5. | Separating intertwined branches | Immediately after cutting the stems |
| 6. | Cleaning the area from thorns and small branches | Immediately after cutting the stems |
| 7. | 2nd treatments of stumps | Two months after chemical treatments and during dry season |
| 8. | 3rd treatment of stumps | After 6-8 months after 1st treatment and should be during dry season (normally September - October) |
| 9. | Removing regenerating Prosopis | Every three months after 1st treatment for 15 months |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It is important to find out which chemical is registered for use in your area. Triclopyr was easy to use and very effective to kill trees with stem diameter > 5cm.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cutting of stems | Mandays | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Chemical application using paint brush | Mandays | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Separating intertwined branches | Mandays | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Removing small branches and debris | Mandays | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hiring a Chain saw | Hours | 8.0 | 4000.0 | 32000.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Triclon (480g/l Triclopyr) | Litres | 1.2 | 50000.0 | 60000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 212000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 88.33 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
R4D Woody Weeds Project
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The estimated costs is for an area covered with > 80 Prosopis juliflora. The technology has not yet been out-scaled. The main challenge with its adoption is the availability of the chemical Triclon.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Uprooting regenerating Prosopis | after every three months |
| 2. | Chemical application | Every dry season up to 15 months |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
To ensure effective control it is important to uproot all regenerating Prosopis after every three months.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | uprooting regenerating Prosopis | Mandays | 5.0 | 20000.0 | 100000.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Triclon (triclopyr 480g/L) | Litres | 0.6 | 50000.0 | 30000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 130000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 54.17 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
R4D Woody Weeds
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After every three months, uprooting of all regenerating Prosopis should be done before they develop deep roots and start competing with desired plants.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
(i) Availability of labor during farming seasons
(ii) Distance from and availability of agro-chemical stores
(iii) Size of Prosopis trees
(iv) Length of dry and wet seasons (long wet season makes many seed of Prosopis to germinate and long dry season makes it difficult to work out under the sun)
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
400.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Extended dry seasons from September to mid-March. Bi-annual rainfall, with most rain falling from April to Mid and short rains from Mid November to December.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
TPC Sugar Manufacturing Company
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
The area is very dry and agriculture is only possible through irrigation. Temperatures are very high during the day, at about 30 degrees Celcius. However, domestic animals such as cattle, goats, and sheep thrive fairly well in the area and there is very good hay during rainy seasons.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Extensive flat terrain interrupted by seasonal rivers flowing southeast of the Kilimanjaro Mountains. There are big acacia (mainly Vachelia xanthophloea) and fig trees along the seasonal rivers and anthills far away from rivers where floods are unlikely.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
See attached soil information that was taken before implementation of the Cut Stump at Kahe, Kilimanjaro Tanzania
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Continuous irrigation from underground waters increases salinity and makes farms unproductive thus necessitate rotational cropping and woody trees
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
The underground water recharges quickly after rain seasons but due to limited vegetation cover, the rate of evapotranspiration is high thus the water remaining in the ground is very little.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Typical diversity of continuous cultivated areas
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1 t/ha of maize
หลังจาก SLM:
1.5 t/ha of Maize
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
A significant increase was seen in maize production but also the production of tomatoes increased by about 25%.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
4 loads@ 10kg
หลังจาก SLM:
15 loads@ 10kg
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
A significant increase in fodder production due to reduced competition with Prosopis and increased production area.
การผลิตไม้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
30 bags @ 20kg
หลังจาก SLM:
0 bags
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Absence of wood products was due to the removal of Prosopis. Wood from Prosopis was harvested after every 4 years, but with continuous application of the technology, no harvest is expected.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
USD 260 per season
หลังจาก SLM:
USD 470 per season
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income from harvests per season (about 4 months)
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only income from selling charcoal but after the application of the technology income is obtained from selling cereals and vegetables.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
more than 10 injuries
หลังจาก SLM:
0 injuries
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology has reduced incidences of injuries to both animals and humans from Prosopis thorns.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
lesser than 10%
หลังจาก SLM:
greater than 80%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased cover of preferred grass for pasture.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
SLM/Land degradation knowledge
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
less than 5% of the village population
หลังจาก SLM:
about 10% of the village population
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
10% of the village population (about 450 households) is now aware of SLM technologies to manage invasive plant species.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Frequent floods may limit the application of the technology because it requires long dry periods for it to be effective and for the chemical to degrade.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It might be difficult to assess after 4 years of implementation of the technology but quick assessment of land users'perception indicate high initial costs that requires time to offset.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
4 households farming a total of 5 hactares
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Very few have adopted the technology spontaneously.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Efficient and fast method with minimal impact as the chemical is applied directly on the cut stump. |
| Allows to use the tree's biomass e.g. charcoal production |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Even though the method is relatively fast, very large invaded areas would still be difficult to clear with this method. | For such large invasions the only feasible approach would be biological control. |
| One must be very careful not to disperse seeds during the treatment, for example when transporting the cut biomass, as this could worsen the situation. | Implement when trees have no fruits. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
About 10 visits were done to monitor the progress of the technology.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
About 10 informants were contacted to provide information about the tested technology.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Experimental prosopis management practices and grassland restoration in three Eastern African countries, Eschen et al., 2023
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43170-023-00163-5
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Cut stump treatment to manage Prosopis juliflora
URL:
www.woodyweeds.org
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is very good and well designed to collect information that will be very useful to others that wish to practice the technologies.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล