Drought-resistant crops [สวิตเซอร์แลนด์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Seraina Lerf
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Tatenda Lemann, Maria Eliza Turek, Joana Eichenberger
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6272 - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Brunner Stefan
Brunner Eichhof
สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The technology described covers one such response in Switzerland.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The key is the improved adaptation of the crops to heat and drought. These adaptations are based on plant physiological and morphological characteristics that confer increased drought tolerance, as well as phenology, which can also affect the plants' water requirements. The goal is to reduce production losses and promote a regional, plant-based food system in Switzerland. To introduce and maintain drought-resistant crops requires specific activities and inputs, such as selecting suitable seeds and ensuring long-term profitable cultivation. This technology is applied to cropland in Switzerland, especially in the Swiss Plateau, where climate change is causing increasingly warmer and drier summers, as well as more intense precipitation in the winter months. These climatic changes favour the cultivation of crops that can better cope with drought periods, allowing for the replacement of crops that require irrigation in the same growing areas.
The main purpose is to adapt agricultural production to the effects of climate change while simultaneously reducing the emissions caused by farming. By cultivating drought-resistant crops, the risk of production losses during drought periods can be minimized, and a transformation towards more diverse, plant-based, and regional food production systems can be promoted. A major advantage of this technology lies in the adaptability of the selected crops to climate change. Since they are better adapted to tolerating drought periods, no additional irrigation is needed: this saves labour and other resources. Moreover, growing drought tolerant crops enables the production of regional, plant-based, and protein-rich foods (especially legumes) that are appreciated by certain consumer groups and can be better marketed.
However, there are also challenges and disadvantages that are not yet appreciated by land users. The lack of knowledge about non-traditional crops in Switzerland is a significant problem. Both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in cultivation are lacking, leading to high risk for farmers who must experiment with cultivation. Additionally, despite climate scenarios predicting drier summers, there is still the risk of cool and wet summers with increased precipitation. Besides the biophysical challenges, there are also socio-economic obstacles, as the demand from wholesalers is often focused on traditional crops, and niche crops like millet are commonly not popular.
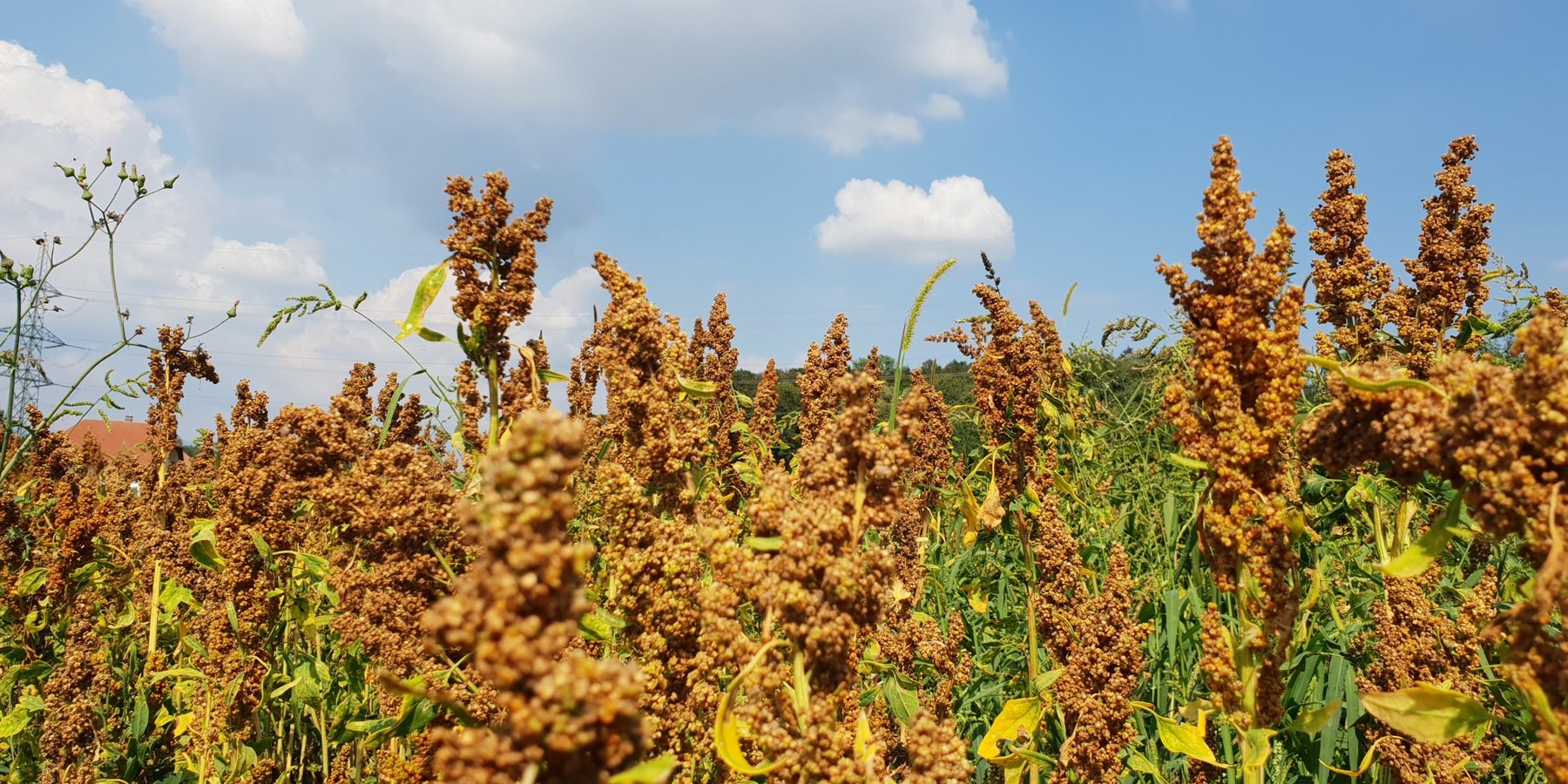
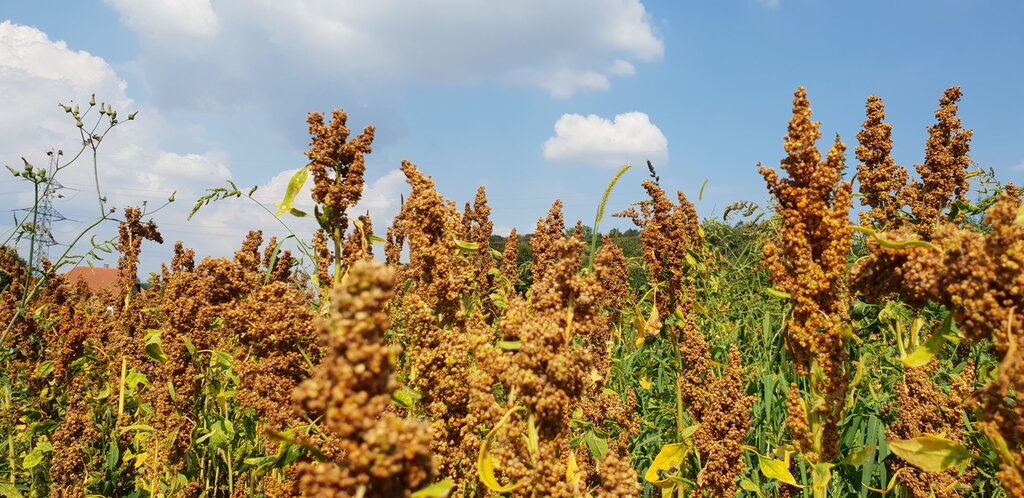
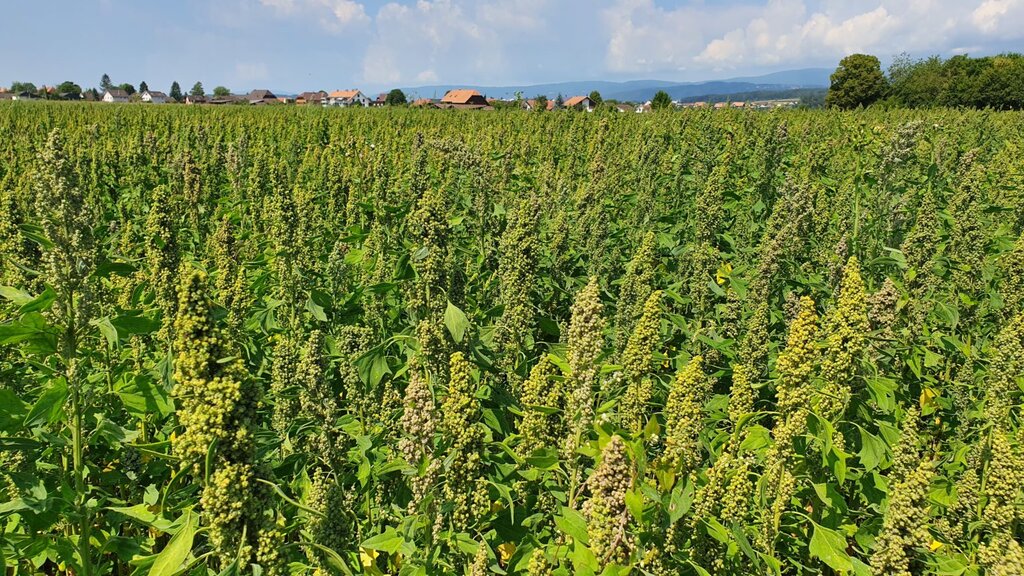
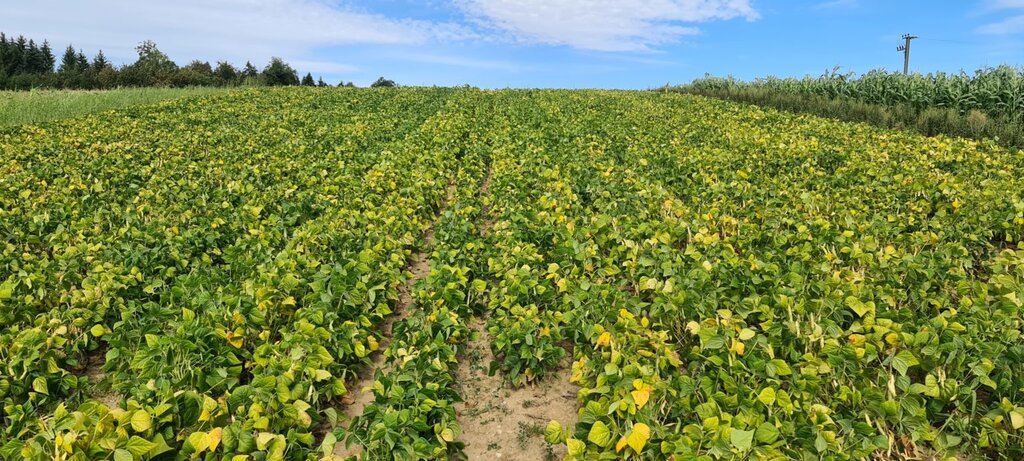
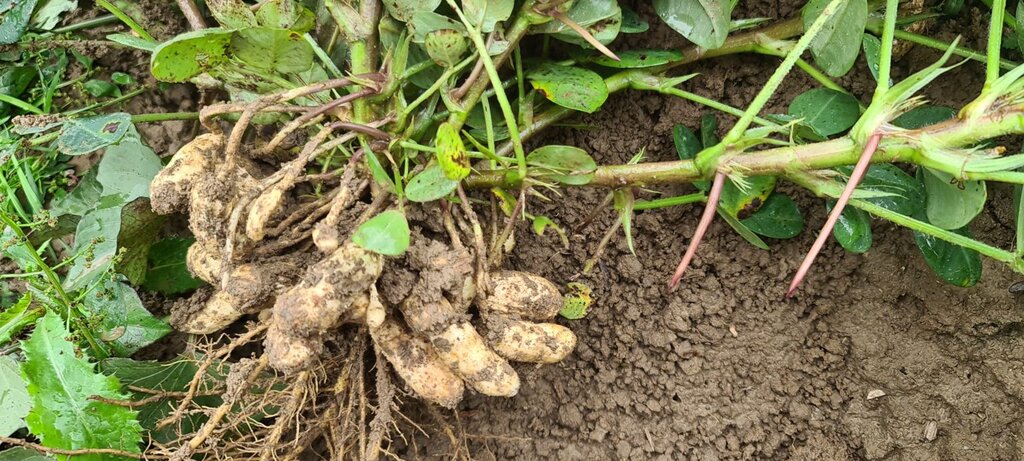
This documentation focuses on an example of an innovative farmer in Spins, Switzerland. Stefan Brunner has been testing a wide variety of drought-resistant legumes such as lentils, lupins and black runner beans on his Eichhof farm since 2017. In addition to the large-scale cultivation of these drought-resistant crops, he also cultivates quinoa, peanuts, chia, sorghum, millet and rice in a demonstration plot. Stefan Brunner simultaneously attaches great importance to sustainable cultivation methods which include surface tillage and mulching.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
All pictures were taken on the agricultural land of Stefan Brunner in Spins near Aarberg. The pictures of the quinoa field, the bean cultivation and the peanut harvest were taken from the website of the Brunner family's Eichhof farm:
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
western midlands of switzerland
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
western midlands of switzerland (Broye catchment area), example farm in the canton of berne in Spins (near Aarberg)
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The regions in which the technology is used are located in the agricultural zone of Switzerland
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - quinoa or amaranth
- cereals - sorghum
- cereals - wheat (winter)
- fodder crops - grasses
- legumes and pulses - lentils
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
The number of growing seasons depends on the crops grown. With a crop rotation of 6 years, winter cereals, winter lentils/winter legumes and lupins are grown overlapping after three years of permanent grassland (grass production). Brunner also uses green manure between the different crops and therefore has around 2 growing seasons per year
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
6 years crop rotation:
3 years grass
Winter cereals
Winter lentil (winter legumes)
Lupin

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Stefan Brunner is able to irrigate all his fields in Spins near Aarberg. He owes this to the nearby location of the "Alte Aare" river, which gives him the privilege of having sufficient water available even during the summer.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A5: การจัดการเมล็ดพันธุ์ การปรับปรุงพันธุ์
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Brunner sees soil degradation as an unavoidable consequence of all agricultural tillage. However, this can vary greatly depending on the type of tillage. Brunner does not see a direct improvement in soil degradation through the cultivation of drought-resistant plants. However, in combination with soil-conserving forms of cultivation. Brunner attaches particular importance to shallow tillage (maximum depth of 5 cm). Accordingly, crops that can be sown at this depth are suitable. Brunner strives for permanent rooting of the soil and prefers crops that can be sown in the fall so that the soil is rooted over the winter or can handle green manure. These measures (shallow cultivation and root penetration) keep the soil looser. The roots form flow paths, which increases the water storage capacity of the soil. The shallow tillage with small machines, which Brunner uses for his drought resistent crops, also reduces the physical pressure on the soil compaction.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
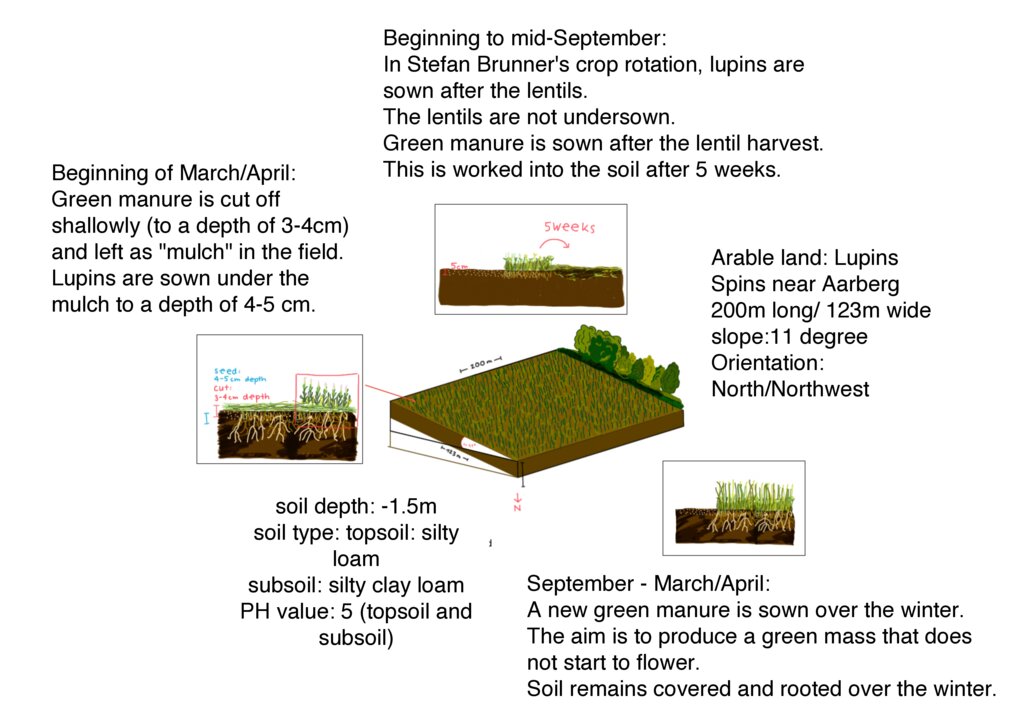
The depicted technical drawing shows the farmland of Stefan Brunner, where lupins were sown in the spring of 2024. This field is representative of all the arable land, totaling 14 hectares of crop rotation areas managed by Brunner. The cultivation areas are situated at an altitude of 487 meters above sea level on flat or slightly sloping terrain on a hill range in the Bernese Mittelland. The depicted field is 200 meters long and 100 meters wide, with a slope of approximately 11° and an orientation towards the north/northwest. The soil is classified as silty loam based on the finger roll test, with the subsoil containing more clay compared to the topsoil. The pH value is 5, which is in the slightly acidic range.
The fields in Spins are located near the river "Alte Aare." Due to the proximity to the water, the farmer has the privilege of having irrigation available for all his fields. Since the implementation of large-scale cultivation of drought-resistant crops in 2017, Brunner has been growing a variety of crops on his land. According to Brunner, the following crops that he cultivates can cope well with drought: lentils, lupins, sorghum, corn, peanuts, millet, and cabbage. In combination with the method of surface rotting and mulching, the soil is protected against drying out and erosion and can retain moisture for longer. The cultivation of various crops can be combined with this farming method, leading to better drought resistance.The graphic illustrates the cultivation of lupins using a green manure cultivation method.
ผู้เขียน:
Seraina Lerf
วันที่:
21/06/2024
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
18 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage: and sowing | (once per cultivation period) |
| 2. | maintenance: weeding (recurring work step, but less labor-intensive than tillage) | (Recurring work throughout the year) |
| 3. | harvesting: threshing | (once a year for grain legumes) |
| 4. | Threshing the previous crop. Before the lupins, lentils were grown in Stefan Brunner's crop rotation. | summer (july-september) |
| 5. | If there is no undersowing (as with the lentils), the soil must be tilled. This is very shallow, i.e. no more than 5 cm deep. | summer (july-september) |
| 6. | A varied green manure is sown in the cultivated soil. The aim of this is to keep the soil rooted and to incorporate nutrients into the soil | summer (july-september) |
| 7. | After 6-7 weeks, the green manure is worked back into the soil. When the plants are still young, they have the highest nutrient input before they extract the nutrients from the soil again if they continue to grow. As a result, the nutrients are mineral-bound in the soil, i.e. stored so that they are available to the plants. | autumn (early/mid-September) |
| 8. | Another green manure is sown, which produces a lot of mass but freezes off in winter before it starts to flower. The aim is to keep the soil covered and rooted throughout the winter. | autumn |
| 9. | In spring, the soil is again worked shallowly. This means a maximum depth of 3-4 cm. The winter green manure is "planed". This means cutting it to a depth of 3-4 cm and leaving the plant material on the ground. | spring |
| 10. | The lupins are sown under the plant material to a depth of 4-5 cm, so that the soil remains moist and the plant material protects the soil from drying out. | spring (beginning of March/April) |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The first three information does not refer to a specific crop, but describes general maintenance activities that Brunner takes into account when cultivating his crops.
Stefan Brunner's crop rotation also includes 3 years of grassland. This cultivation reduces the workload, as no maintenance work has to be taken into account in addition to the harvest.
The activities 4-10 described relate to the cultivation of lupins. This crop was cultivated at the time of documentation in spring 2024.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
22575.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs of cultivating drought-resistant plants cannot be precisely quantified. Based on the interview results, it is therefore not possible to make any general statements about the costs of cultivation.
Nevertheless, in order to be able to make a rough estimate of the input costs required to implement the technology (Example based on the cultivation of lupins), information from REFLEX 2024 (AGRIDEA's business database) and FiBL (Research Institute of Organic Agriculture) was used. According to REFLEX 2024, the target price for lupins in 2023 and 2024 is 144Fr./dt. A FiBL leaflet also states a requirement of 130-170kg seed/ha (blue lupins).
According to the results collected, the documented farm uses a disk coulter seed drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm, sows approx. 3-4 cm deep and requires 200 kg/ha of seed.
With a field size of the documented farm of approx. 2 ha, the costs for the required lupin seed amount to CHF 576 according to the data from REFLEX 2024.
Then there are the labor costs and the machines. Depending on which machines are required and whether the required machines are already available or whether a new investment or rental would be necessary.
The estimate only refers to the seed required. Additional recurring costs include maintenance/ rental costs for machinery and labour. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more precise information on this. It depends on the machines and labor costs used.
However, according to the interview results with a farmer who grows drought-resistant crops, there are no significant additional costs if the drought-resistant crops can be grown with the same machinery as for conventional crops.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The greatest difficulty in terms of costs lies in the lack of knowledge in the cultivation of these crops. The fact that very little scientific and practical knowledge and experience is available means that farmers take a greater risk in cultivating these crops. If cultivation is not carried out correctly and the farmer suffers production losses as a result, he bears the consequences. This is why they have to look for inventive solutions.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
865.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Payerne
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Production losses during periods of drought can be minimised
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Product diversity can be increased by growing alternative drought-resistant crops
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By improving the soil's ability to cope with weather extremes (drought/heavy rainfall), land management in cultivation is simplified through greater flexibility.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Gentle tillage without the use of pesticides in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops (good groundwater quality)
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Drought-resistant crops require less irrigation. In addition, the tillage method (surface rotting) also prevents the soil from drying out.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Gentle soil cultivation with minimal use of machinery (and application of surface rotting) requires more labour, even if the cultivation of drought-resistant crops does not mean additional work compared to conventional crops
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less water required for irrigation
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Avoiding the use of pesticides leads to improved water and soil quality
Harvesting/collection of water
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods) can lead to improved groundwater recharge
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Surface runoff can be minimised by improving the water absorption capacity of the soil (permanent root penetration).
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods), less excess water is formed
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil can lead to improved groundwater recharge
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Permanent ground cover can reduce soil drying out
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The permanent ground cover reduces drying out and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This can improve the soil water balance.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The ground should be permanently covered. The permanent ground cover reduces drying out.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The permanent covering and rooting of the soil prevents surface run-off. This can prevent soil loss.
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Green manuring can ensure an improved hummus structure.
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The permanent ground cover reduces dehydration and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This prevents soil sealing.
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The soil should remain permanently rooted and covered and be worked with as few and light machines as possible. This minimises soil compaction.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By applying green manure, the soil can be enriched with nutrients (nutrient cycle of the soil).
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
greater plant diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the improved ability of plants to cope with drought. to deal with drought. In combination with good water storage capacity of the soil, the effects of drought on the harvest can be minimised.
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
Information in this chapter on practical experience in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops is based on interview results from Stefan Brunner. He cultivates drought-resistant crops in combination with surface cultivation and mulching. As a result the effects of the two technologies cannot be considered entirely separately.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The use of herbicides and fungicides was avoided in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, thus preventing contamination
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved water absorption capacity (through soil cultivation methods) of the soil
Stability of production
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the improved adaptability to climatic conditions, production remains more stable
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. Annelie Holzkämper
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| คลื่นความหนาว | ไม่ทราบ |
| สภาพอากาศฤดูหนาวที่รุนแรง | ไม่ทราบ |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. rer. nat. Annelie Holzkämper
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The more equipment has to be used in cultivation, the more expensive the maintenance costs become. As Brunner is able to cultivate drought-resistant crops such as lupins and lentils with the existing equipment, he did not incur any additional costs. Even if a new machine for gentle soil cultivation in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, such as a “planer”, had to be purchased, a plow could be sold in return. As long as the same mechanization can be used as Brunner was already using for conventional crops, the costs remain the same. As a result, Brunner's cost-benefit ratio was assessed as positive, even in the short term.
In the long term (over a period of 10 years), Brunner also sees an increased positive cost/benefit ratio. Consistently good soil cultivation regenerates the soil so well that it is able to absorb much more water. The amount of work required to implement this form of cultivation increases in the short term. However, the improved soil conditions in connection with the cultivation of drought-resistant crops have a positive effect on the workload and yield in the long term, as the crops on healthy soil are more flexible in the face of extreme weather conditions such as increasingly frequent droughts. Brunner also emphasizes that, from his perspective, it is worth incurring higher start-up costs for careful cultivation in order to generate long-term benefits.
The start-up costs are often relatively high, but the long-term benefits are all the more valuable. Start-up capital is therefore essential to be able to generate long-term benefits.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Information based on the experience of Stefan Brunner (Spins)
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
breeding
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Continuous adaptation in the context of breeding
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| No Irrigation Needed: These crops do not require irrigation, thus saving water and reducing labor. |
| Promotion of Soil Health: The cultivation of these crops is beneficial for the soil, as as the tillage is shallow and legumes do not require additional nutrient inputs through fertilization. |
| Benefits in Direct Marketing: These crops are niche products produced in limited quantities in Switzerland. Conscious consumers who value regional food products appreciate these items and understand the higher costs due to the high labor requirements. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Reduced Irrigation Needs: If the crops can tolerate more drought, less irrigation is needed. |
| Minimized Economic Risk: Drought tolerance reduces the risk of crop failure during dry periods. |
| Crop Rotation Benefits: Better adaptation through diverse crop cultivation. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High Labour Requirements: initial labour requirements are significantly higher due to limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation, but with time this reduces - as less and less work is required on healthy and nutrient rich soils. | More practical knowledge should be gathered by encouraging more farmers to cultivate these crops and facilitating knowledge exchange. |
| Lack of Mechanization: Available market machines are not suited for the desired cultivation methods. | Alternative machines are needed, which are smaller and lighter and only minimally till the soil. New approaches and inventions in machinery are required. |
| The wholesale market is not particularly interested in domestically produced alternative foods. Wholesalers are profit-oriented and primarily offer what is consumed in Switzerland. | A reorientation of dietary habits is necessary. Millet, for example, is ideally suited to the climatic conditions in the Seeland region. Increased consumption could lead to more extensive cultivation. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge: limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation | More research should be carried out in this area and practical experience in cultivation should be gained through practical implementation. Inovative farmers are in demand. |
| Weather Variability: There is no guarantee that heavy rains won't occur, potentially ruining the harvest. | The extent to which crops are affected by severe weather events depends on when they occur. Severe weather events have an impact on every crop, but of course you don't know when they will occur. A useful strategy is therefore to build a highly diverse production system at farm and landscape level. |
| Practical and Socioeconomic Challenges: Market preferences and practical issues, such as livestock not favoring sorghum feed, can be obstacles. | No answer given. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
On June 10, 2024, an interview was conducted with farmer Stefan Brunner on his farm in Spins near Aarberg. Additionally, the cultivated area was inspected
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
On June 20, 2024, an interview was conducted with PD Dr. Annelie Holzkämper.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
10/06/2024
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Inspection of the cultivation aera
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Heinz, Malve et al. (2023): How to find alternative crops for climate-resilient regional food production, in: Agricultural Systems, Bd. 213, S. 103793, doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103793.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Wuyts, Nathalie et al. (2023): Klimaresilienter Ackerbau 2035, Agrarforschung Schweiz, doi:10.34776/afs13-135.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Heinz, Malve. (2021): Prospects of cultivating alternative crops in a changing climate in Switzerland, Master’s Thesis, University of Bern.
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Internet platform of the Eichhof of the Brunner family from Spins near Aarberg
URL:
https://www.brunnereichhof.ch
7.4 General comments
The information used to complete this documentation is mainly based on the experience reports of Stefan Brunner from an interview on June 10, 2024
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล