INTEGRATED AGRICULTURE-BASED LAND USE IN AREAS WITH SALINE SOIL [ไทย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Laksamee Mettpranee
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7276 - ไทย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Siangsunthia Mana
ไทย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
co-compiler:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - ไทย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Regarding soil amendment for planting vegetables in the Northeast, the method to increase and keep the fertility level throughout the harvesting season, including off-season production of chili spur pepper is to increase organic matter and plant nutrients, and to adjust pH values to be suitable
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
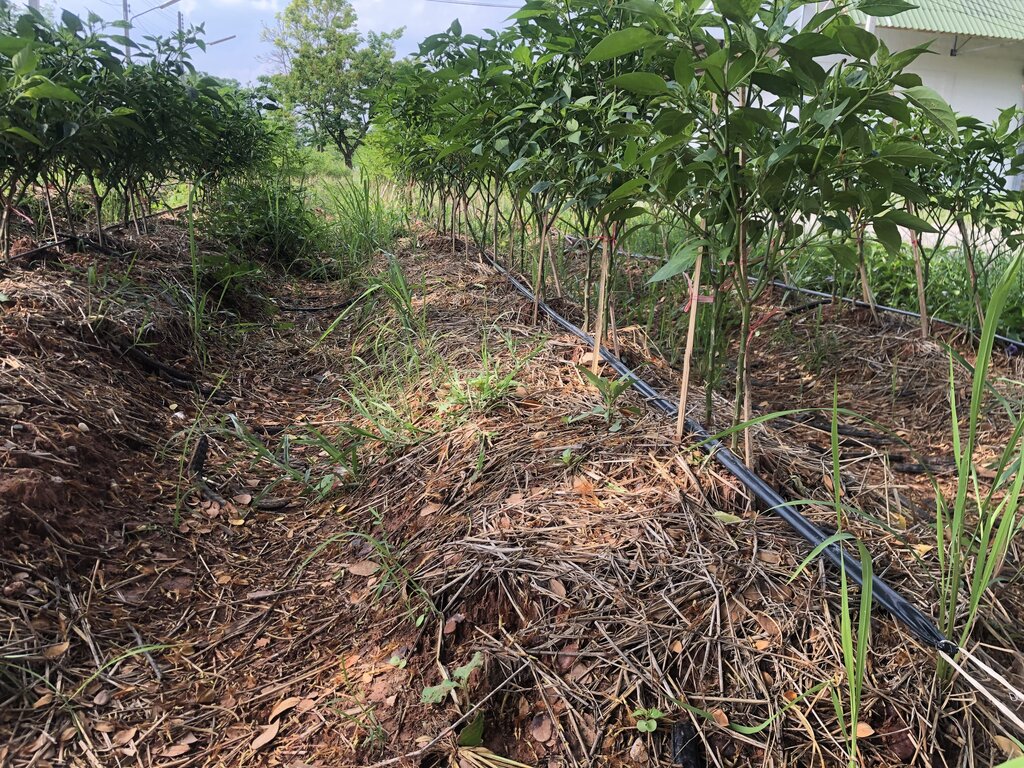
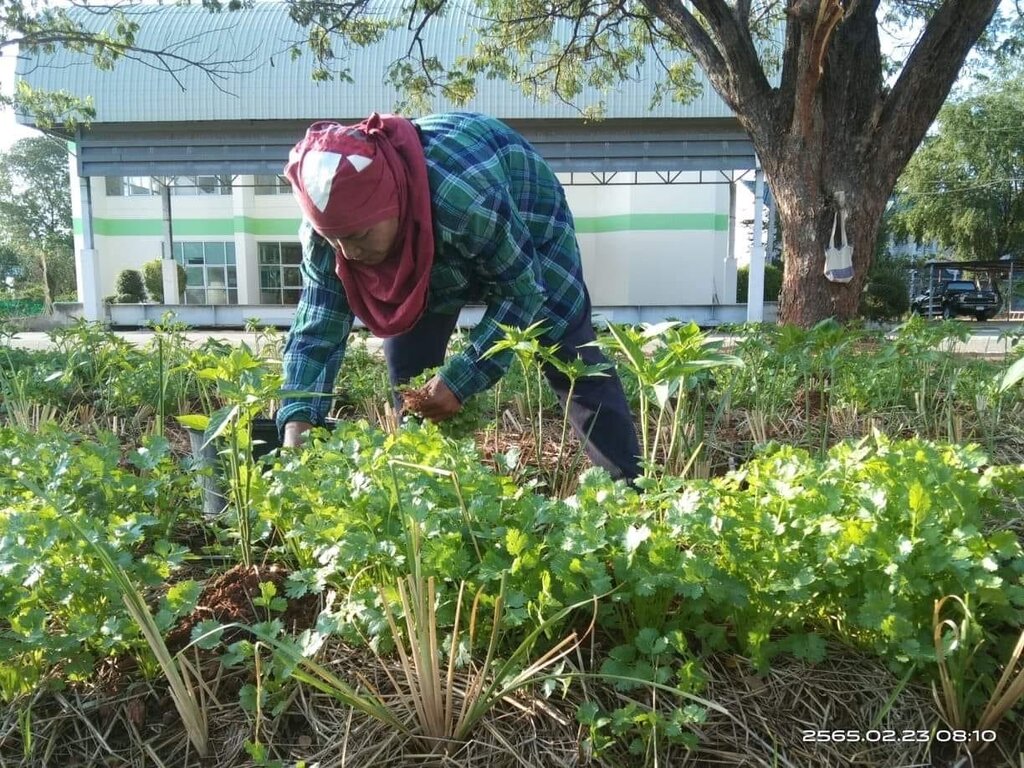
Mr. Mana Siangsunthia is a farmer who has implemented the knowledge obtained from being a soil doctor stationed at Non Thai district, Nakhon Ratchasima province to build opportunities for himself and farmers in the area. The problem of soil degradation in areas with saline soil originates from chemical and physical degradation and low fertility which are main limitations for land use, including shortage of water in the dry season and spell of rain in the cropping season. This has been brought an association of farmers ready to learn about increasing soil management potentials to increase plant yields and solve problems in their own occupation areas. The group is supported in terms of factor of production, namely LDD microbial activators producing organic fertilizers and bio-fertilizers, vetiver of Songkhla 3 variety and dolomite. Moreover, the guideline obtained from learning, observance, trial and errors has been implemented and developed in the 0.04 ha planting vegetables. Previously, the mentioned area was characterized by soil with soil fertility deficiencies and giving low yields due to the problem of soil degradation. The soil texture was sandy clay loam consisting of saline soil a little bit. Moisture in the soil was very low in the dry season. Moreover, the area was outside the irrigation zone. Therefore, an idea came up with developing occupations for farmers in the community located at Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district to implement knowledge regarding integrated utilization of areas with saline soil in the organic agriculture system whereby agencies from Land Development Department provide knowledge in analyzing soil and improving soil prior to cultivation area preparation. The wisdom of farmers themselves is used together with the technology of Land Development Department, namely dolomite application for pH value adjustment and killing germs affecting growth of chili peppers together with applying manure to increase organic matter to the soil. Fermented bio-extracts have microbes which help stimulate the root system. Regarding moisture storage in the plot where chilies are planted, the drip irrigation technology system has been installed. The soil is covered with straw and vetiver is used to restore soil conditions. The objective is to do this as a prototype in building incomes for the community further.
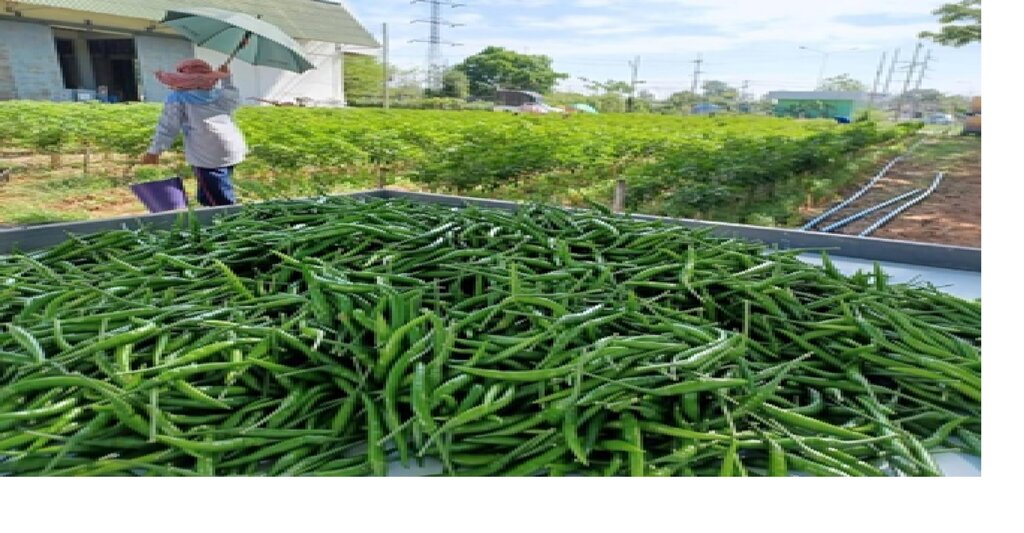
After soil amendment, the soil has a better structure and has become friable and suitable for planting chili peppers by selecting the Amphawa Gold according to the demand of the market. Moreover, regarding intercropping, parsley is also inserted to be planted between plots, resulting in using water efficiently and worthily. Average yields of chili spur peppers account for 400 kilograms per 400 square meters throughout the age at 180 days. The harvesting price is 2.47 USD per kg and yields of parsley account for 108 kilograms per 400 m2 (byproducts from watering chili pepper trees) based on harvesting yields for 1 generation per round of chili pepper production
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไทย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Nakhonratchasima
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2022
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Farmer groups in Non Thai Subdistrict and nearby areas transfer knowledge through the volunteer soil doctor network.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- vegetables - other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area is outside the full irrigation zone and has a local or community small size water sources.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A5: การจัดการเมล็ดพันธุ์ การปรับปรุงพันธุ์
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Cultivation plot preparation
1. Plough and blast soil, followed by plowing in regular furrows for the second time by using a 65 HP tractor and a small Kubota tractor to disintegrate soil to become smaller and finer
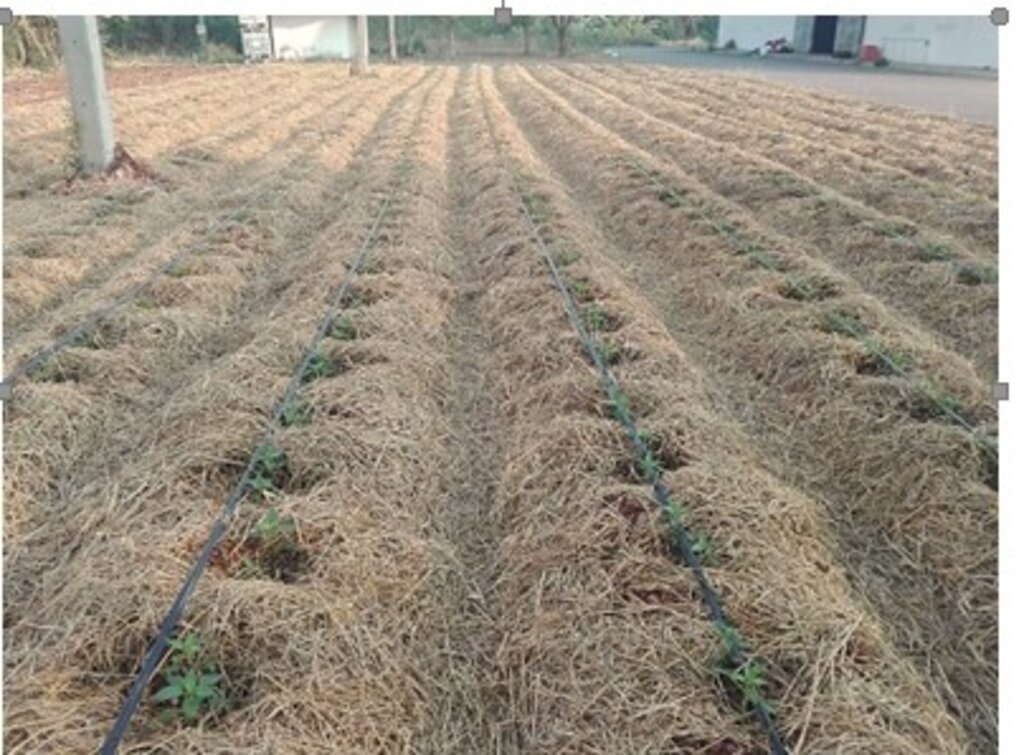
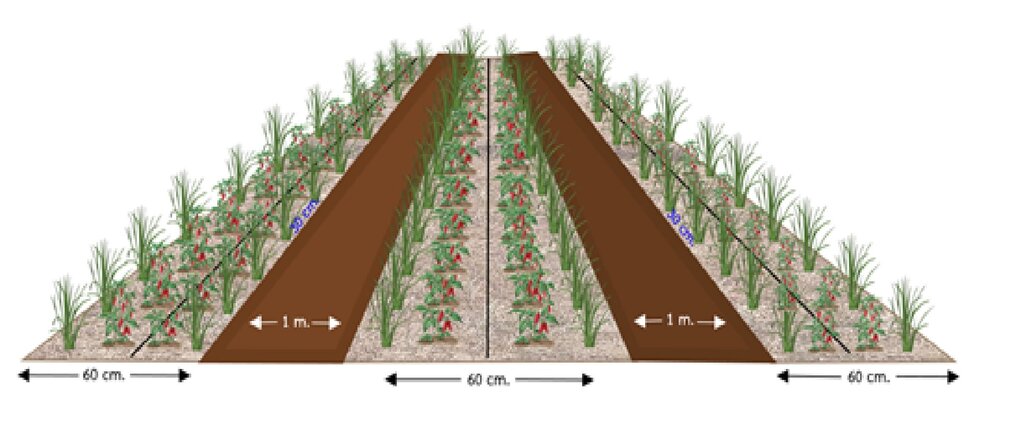
2. Elevate the furrow for the dimension of 30 centimeters high and 60 centimeters wide. The spacing between plots is 1 meter. Burn a pile of plant residues with the height of about 30 centimeters in the cultivation plot until it becomes charcoal with red spark to kill bacteria and disease-causing fungi. After that, follow by watering it to extinguish the blaze.
3. Spread dolomite thinly for soil amendment with the rate of 25 kilometers per rai. This is followed by using dung which is waste from pigs going through the process of gas fermentation at the rate of 100 kilograms per rai. Incorporate together and use the bio-extract with the rate of 2 spoons per 20-liter water to help improve the soil and stimulate the growth of plant roots.
4. Mix the cultivation soil with the ratio of 3 handfuls of soil: 1 handful of dung.
5. Dry the soil for 7-14 days. Before planting, place a cut banana stem with the length of 10 centimeters at the bottom of the hole to mix with the soil in the planting hole.
Planting and maintenance
1. Plant the chili pepper young plant of the Amphawa Gold variety at the age of 35 days together with sprinkling parsley around the planting plot. Cover it with rice straw and grow vetiver around the planting plot.
2. Watering in the morning and watering mixed with the Indian Laburnum pod fermented extract at the rate of 2 spoons per 20-liter water in the evening. Spray wood vinegar to prevent fungi once a week.
3. When the chili pepper buds, spray with the LDD 2 in the evening for every 5 days.
4. Put in place the drip system to be used in case of labor shortage of morning watering in order to keep moisture
5. In case of the anthracnose epidemic, destroy the chili pepper stricken with the disease. During the outbreak of aphis, spray with plain milk at the point of the outbreak. Leave it for 20 minutes and then wipe it off.
6. Withdraw old leaves of the chili peppers when they are at the age of 45-50 days in order to make the trunk expose to the sun. This helps chili peppers grow well and increase their yields.
Harvesting yields
1. When the chili pepper tree is at the age of 65 days, harvest the yield of the first generation and harvest yields the next time for every 5 days for the period of 6 months.
ผู้เขียน:
Ms. Nisa Sahoh
วันที่:
01/04/2025
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1.12ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
6.25rai
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
8.82
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cultivation plot preparation | Before mulching/ cropping (March) |
| 2. | Planting and maintenance | |
| 3. | Harvesting yields |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Plough to prepare plots | Labor | 4.6 | 1.76 | 8.1 | |
| แรงงาน | Soil preparation | metre | 10.0 | 0.59 | 5.9 | |
| แรงงาน | Cultivation, watering, plot maintenance | Labor | 1.0 | 67.65 | 67.65 | |
| แรงงาน | Yield harvesting | Labor | ||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Chili pepper tree | tree | ||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Parsley seeds | gram | ||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Rice straw | kilogram | ||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fermented bio-extracts | Liter | ||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Dolomite | kilogram | ||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Dung | bag | ||||
| อื่น ๆ | Drip line | meter | ||||
| อื่น ๆ | PVC tubes | meter | ||||
| อื่น ๆ | 1,000 liter bucket | bucket | ||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 81.65 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 81.65 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | In case of the anthracnose epidemic, destroy the chili pepper stricken with the disease. During the outbreak of aphis, spray with plain milk at the point of the outbreak. Leave it for 20 minutes and then wipe it off. | |
| 2. | Withdraw old leaves of the chili peppers when they are at the age of 45-50 days in order to make the trunk expose to the sun. This helps chili peppers grow well and increase their yields. | |
| 3. | Harvesting yields | |
| 4. | In case of an anthracnose epidemic, destroy the chili pepper stricken with the disease. During an outbreak of aphids, spray with plain milk at the point of the outbreak. Leave it for 20 minutes and then wipe it off. | |
| 5. | Remove leaves of the chili peppers when they are 45-50 days in order to make the trunk expose to the sun. This helps chili peppers grow well and increase their yields. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Ploughing to prepare plot | Person days | 1.0 | 8.08 | 8.08 | |
| แรงงาน | Soil preparation | Person days | 1.0 | 4.41 | 4.41 | |
| แรงงาน | Cultivation, watering, plot maintenance | Person days | 1.0 | 24.25 | 24.25 | |
| แรงงาน | Harvesting | Person days | 1.0 | 137.64 | 137.64 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor/ cultivator maintenance | Fuel etc | 1.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Chili peper plant | plant | 1200.0 | 0.029 | 34.8 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Parsley seeds | gram | 600.0 | 0.01 | 6.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Rice straw | kilogram | 180.0 | 0.1 | 18.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fermented bio-extracts | liter | 120.0 | 0.29 | 34.8 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Dolomite | kilogram | 13.6 | 0.73 | 9.93 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Dung | bag | 35.0 | 2.5 | 87.5 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Drip line | meter | 4.6 | 1.76 | 8.1 | |
| อื่น ๆ | PVC tube | meter | 10.0 | 0.59 | 5.9 | |
| อื่น ๆ | 1,000 liter bucket | bucket | 1.0 | 67.65 | 67.65 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 522.06 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 522.06 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Drip irrigation systems have no maintenance costs but they are replaced after 2 to 3 years.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
1. Labor costs
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
The mentioned area has the average amount of rainwater between 1,001 - 1,500 milliliters. It is situated in the zone of semi-arid climate. The area is flat. The altitude level is 200 meters from the sea level. The soil is sandy clay loam. The level of organic matter is low. The ground water cannot be used. The water at the soil surface is at a good level. Regarding water quality, the water can be used for agriculture only.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Being areas with degraded soil, filled soil with lack of fertility
หลังจาก SLM:
Going through soil amendment making the soil have better properties
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
คุณภาพพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Plants could not grow.
หลังจาก SLM:
Plant thrive and give yields continuously.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Plants cannot be planted.
หลังจาก SLM:
Integrated cultivation, namely chili peppers, parsley and vetiver for soil amendment
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
There was no cultivation.
หลังจาก SLM:
The quantity of products can be sold and exported.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
--
หลังจาก SLM:
Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Studied how to solve problems by themselves
หลังจาก SLM:
Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
There was no knowledge propagation
หลังจาก SLM:
Farmers in the area accept the technology and gather together to learn methods of soil management so that they can grow plants and implement them in their own areas.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Being earthfill areas
หลังจาก SLM:
There is soil amendment by using plant debris, rice straw and growing plants.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Information from a questionnaire
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
--
หลังจาก SLM:
Nutrients increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etcnts increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Using a questionaire
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
--
หลังจาก SLM:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Using a questionaire
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
--
หลังจาก SLM:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Using a questionaire
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
Information from a questionnaire
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
Information from a questionnaire
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Rainfall has decreased due to climate change, a result of global warming.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land users are responsible for covering the cost themselves. Supported by agricutural production factors from LDD.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Yes. Use the drip system for morning watering with organic fertilizer.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Farmers manage soil and water and use integrated farming methods, leading to additional income opportunities. |
| Farmers in the area are committed to overcoming challenges and limitations related to soil, water, and environmental conditions. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Support for forming farmer groups in the area to exchange knowledge on soil management for increasing crop yields and addressing local farming issues, as well as developing professions for community farmers. This includes promoting the production of safe, non-toxic crops and creating value for products, leading to increased household income for farmers. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Farmers who use the technology must learn to follow procedures carefully. | Training and experience |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technology used is precision farming. Farmers who use the technology must pay attention to every step. | Training |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
10
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
10
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
https://lddmordin.ldd.go.th/web/data/Tank_Soilmanagement/Soil_58.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
URL:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล